Method for detecting content of impurity elements in electrolyte of vanadium cell
A technology of impurity elements and electrolytes, applied in the direction of material excitation analysis, thermal excitation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as detection and analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
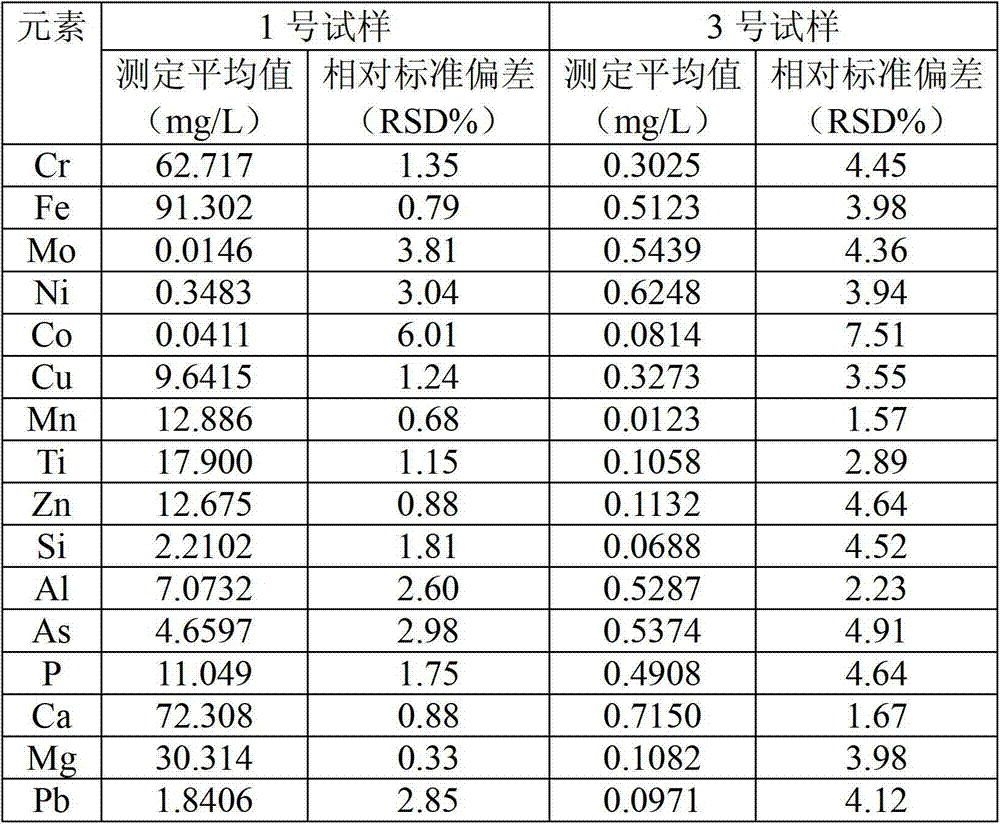
[0036] Prepare the sample solution for the detection and analysis of the electrolyte sample of the No. 1 vanadium battery
[0037] In this example, the ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometer) used for elemental determination uses two types of spectrometers, iCAP6300 and IRIS / HR from Thermo Fisher Corporation of the United States.
[0038] Firstly, a sample solution for detection and analysis of the vanadium battery electrolyte is prepared. Dilute the electrolyte according to the relationship of 6.25 times, accurately measure 8.0mL vanadium battery electrolyte mother liquor into a 50mL volumetric flask with a pipette, dilute directly to the scale with water, and mix well.
[0039] Then, prepare the calibration curve standard solution. Take by weighing 16g high-purity vanadium pentoxide (V 2 o 5 ≥99.99%) in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask or other container, first wash the container wall with 120mL (2+1) dilute hydrochloric acid and shake to disperse vanadi...
example 2
[0047] Except following difference, all the other adopt the No. 2 vanadium battery electrolyte sample of example 2 in the same method as example 1:
[0048] Dilute the electrolyte solution according to the 5-fold relationship, accurately measure 10.0mL vanadium battery electrolyte mother solution in a 50mL volumetric flask with a pipette, add water to directly dilute to the scale, and mix well.
[0049] Weigh 16g of high-purity vanadium pentoxide, rinse the container wall with 120mL (2+1) dilute hydrochloric acid and shake to disperse vanadium pentoxide, add (2+1) dilute sulfuric acid 53g, and digest at 160°C for 2 hours; Add 30mL of water, heat up to 250°C and react for 1 hour; add 40mL of water, heat up to 320°C and react until the sample is completely digested, heat up to 400°C and evaporate for 30min, add (2+1) dilute sulfuric acid 30g, cool to room temperature Then transfer it to a 500mL volumetric flask; add the standard solution of impurity elements to be tested.
[00...
example 3
[0053] Except following difference, all the other adopt the method identical with example 1 to measure the No. 3 vanadium battery electrolyte sample of example 3:
[0054] Dilute the electrolyte solution by 10 times, measure 5.0mL electrolyte solution in a 50mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to volume, and mix well.
[0055] Weigh 16g of high-purity vanadium pentoxide, wash the container wall with 120mL (2+1) dilute hydrochloric acid and shake to disperse vanadium pentoxide, add (2+1) dilute sulfuric acid 53g, digest and react at 200°C for 2 hours, replenish Add 40mL of water, heat up to 280°C and react for 2 hours; then add 50mL of water, heat up to 350°C and react until the sample is completely digested, heat up to 450°C and evaporate for 30min; finally add (2+1) dilute sulfuric acid 30g, cool to room temperature Then transfer to a 500mL volumetric flask; add the standard solution of impurity elements to be tested.
[0056] Set the working parameters of the inductive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com