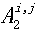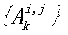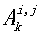Gray-code-based distributed data layout method and query method
A distributed data and Gray coding technology, applied in the database field, can solve the problems of unbalanced computer development, over-distributed physical storage of multi-attribute continuous data, complex query and analysis tasks, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the sequential access rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Overview
[0049] data sheet ???? Projected into a set of projections according to requirements ?????? , where each projection consists of a set of attributes, namely . Without loss of generality, we look at the projection in detail ?????? , and assume that the projection consists of the attribute group form, where 0 .
[0050] In order to adapt to the current popular distributed file system architecture (such as HDFS, etc.), our data layout also adopts a master-slave architecture, such as figure 1 shown. The host (Namenode) stores a content-aware index (content-aware index) indicated by gray coding, so that the query request can be directly located to a specific data block according to the index, thereby realizing efficient query. Slaves (i.e. Datanodes) store each split data table fragment in index order in a distributed manner. Each slice has a slice header / The load data has two parts. For the slice header, the statistical information of t...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Content-Aware Bitmap Indexing
[0052] The content-aware bitmap index proposed in this invention has a dual role: first, it is used to indicate the content of multidimensional data records (i.e., the role of bitmap index); second, it is used to indicate the Location. Basically, the index is created based on the content of the records. The following describes how to create an index based on record content.
[0053] Encoding of numeric attribute values:
[0054] The system supports various numeric attributes, including continuous numeric attributes with known ranges, segmented numeric attributes with known ranges, and numeric attributes with unknown ranges.
[0055] For continuous numeric attributes with a known value range, the value range of the attribute is evenly divided into several segments, and the number of segments after division is a power of 2, and its size is determined by the system (will be introduced when introducing the multi-attribute data c...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: Index Construction
[0067] This embodiment illustrates the effective storage of data in the present invention, that is, the implementation of content-aware indexing with minimal additional storage overhead.
[0068] Currently popular and commonly used distributed file systems (such as HDFS, GFS, etc.) all have a master / slave architecture, because this architecture can effectively simplify the design of distributed file systems. On the host side, metadata is stored (ie, file name, file storage location, file size, backup, etc.), while on the slave side, payload data (ie, the data that actually needs to be stored) is stored. Based on the master / slave architecture of the above-mentioned distributed file system, this system proposes the deployment of a two-layer index, one of which is for the projection content index, called the projection hierarchical index; and the other layer is for the fragmented content index, called Shard hierarchical index.
[0069] As ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com