Cytomegalovirus-based immunogenic preparations
A technology of cytomegalovirus and human cytomegalovirus, applied in the direction of antiviral agents, viruses, viruses/phages, etc., can solve the problems of restricting the use of CMV tumor vaccines and becoming immunodeficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0195] Example 1: Antitumor efficacy of CMV-loaded antigen-primed CTLs
[0196] A major challenge in developing effective anti-tumor vaccines is overcoming the inability of the immune system to distinguish tumors from self-proteins. More recently, attempts to develop a heritable immuno-sterility control for wild mice have shown that normal self-proteins expressed in recombinant CMV vectors have the potential to become antigenic (Lloyd et al., Biol. Reprod. 68:2024-2032, 2003 and Redwood et al., J. Virol. 79:2998-3008, 2005). In this study, the native sequence of murine zona pellucida 3 (ZP3), a normal mouse protein, was introduced into MCMV behind the immediate early 2 (IE2) promoter. Strikingly, a single inoculation of the virus rendered female mice completely sterile for the length of time as observed (>230 days).
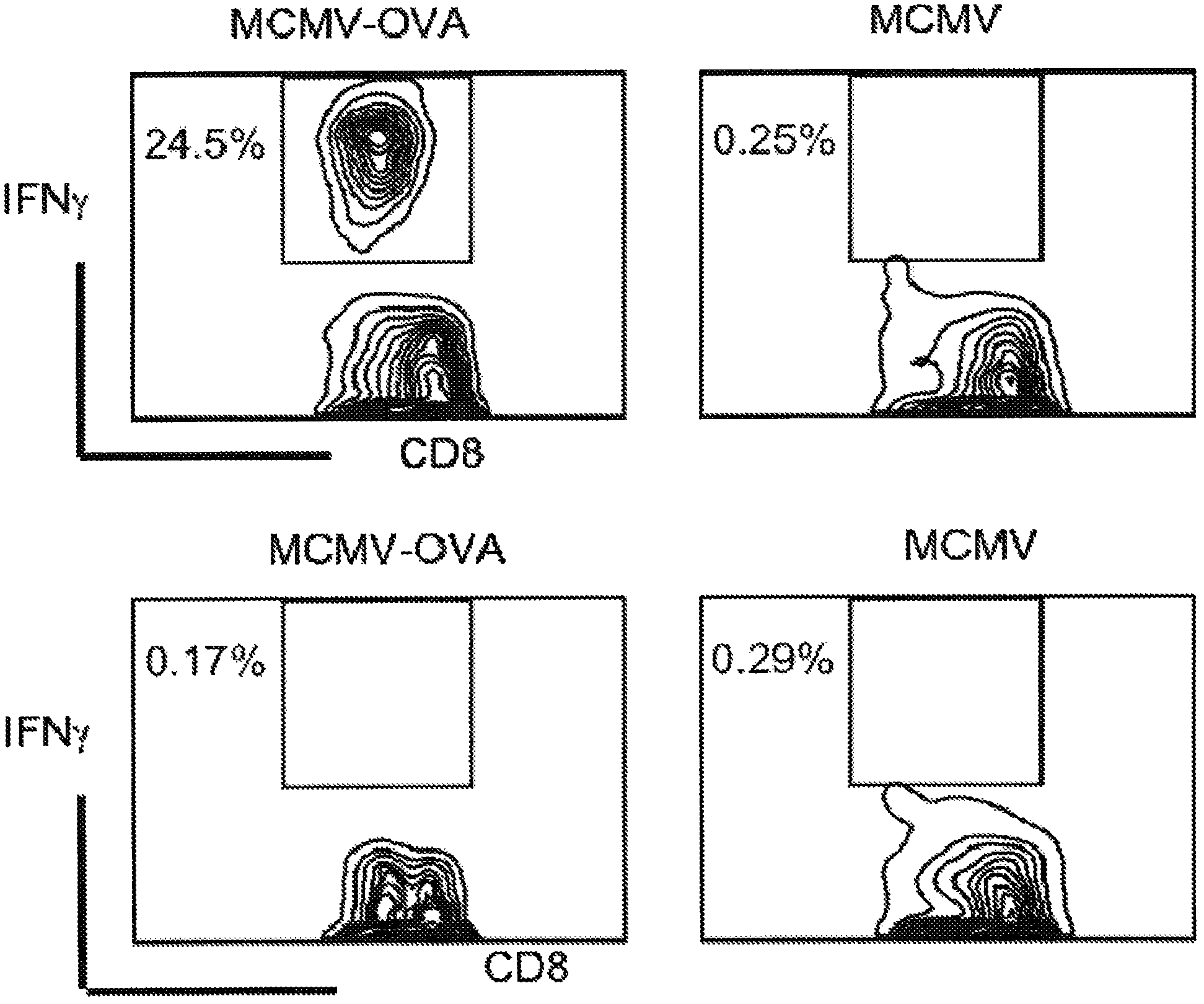
[0197]This example demonstrates that tumor-expressed self-antigens also become immunogenic when expressed in the context of CMV. The therapeutic capacity of t...
Embodiment 2
[0206] Example 2: Infection with replication-deficient ΔgL MCMV elicits durable immunogenic priming and expansion of T cell memory
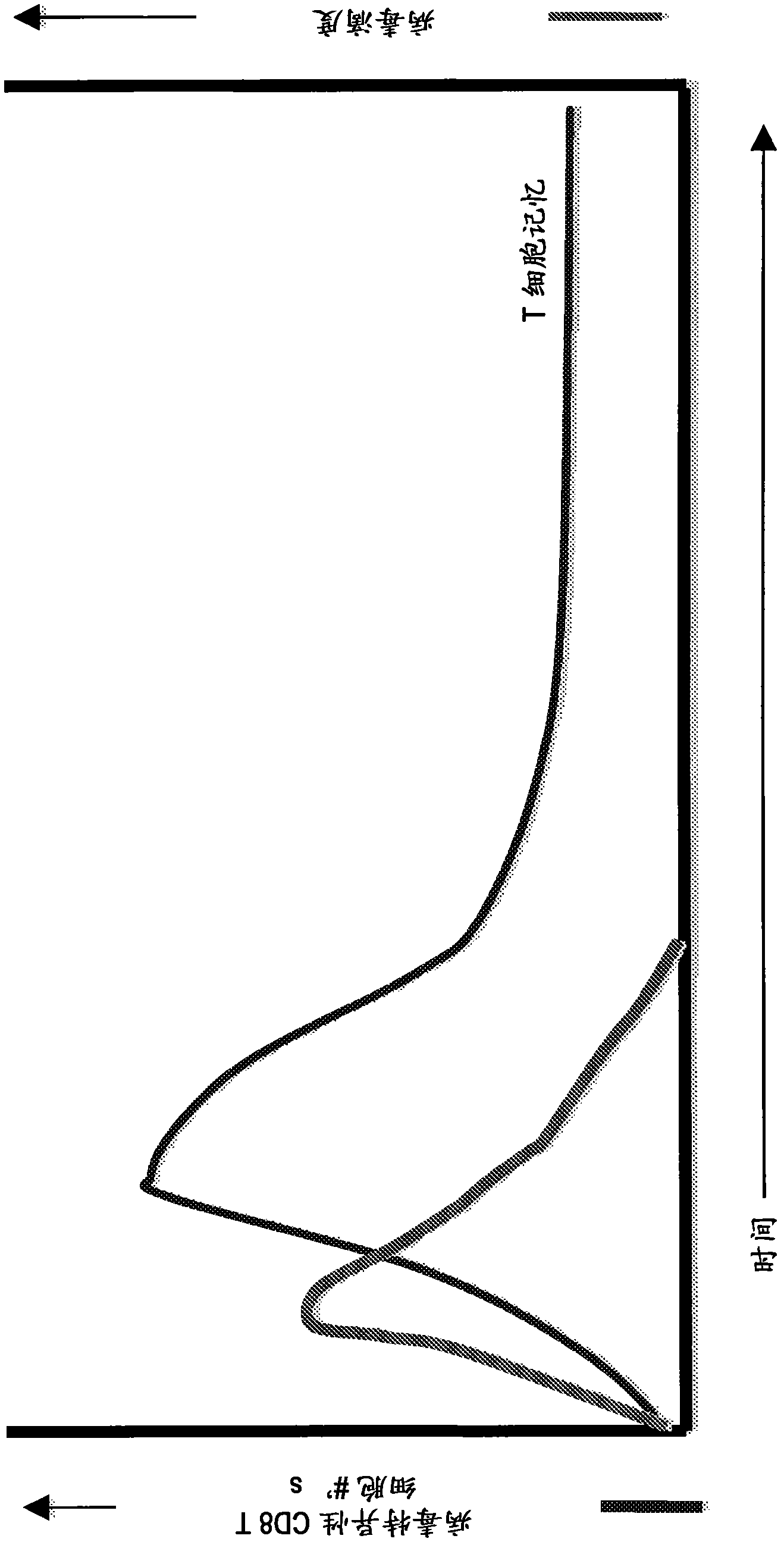
[0207] On average, humans contribute their memory CD8 to CMV + 10% of the T cell compartment. Research in recent years has revealed that this extraordinary immune response to CMV infection involves several stages. In initial CD8 + Following the T cell response, the T cell response to MCMV begins to decline to the characteristic "memory" level (Munks et al., J. Immunol. 176:3760-3766, 2006). However, it then begins a remarkable process called "memory expansion" (Karrer et al., J. Immunol. 170:2022-2029, 2003 and Munks et al., J. Immunol. 177:450-458, 2006). For a period of several months, CD8 T cell responses to specific epitopes increased in number, eventually plateauing at higher levels such that the total CMV-specific response contained between 10% and 30% CD8 + T cells.
[0208] This example demonstrates that replication-defective MCMVs i...
Embodiment 3
[0221] Example 3: Lack of expansion of T cell memory in response to subcutaneous ΔgL MCMV infection
[0222] As shown in Example 2, CD8 + T cell memory expansion is driven by intraperitoneal infection of mice with wild-type and ΔgLMCMV. It is believed that the ability of ΔgL MCMV to elicit long-lasting self-excited T cell memory is a consequence of establishing CMV latency in HSCs. Thus, any administration of CMV that exposes the virus to HSCs (eg, intravenous administration) will similarly trigger the characteristic expansion of T cell memory. This example shows that subcutaneous administration of replication deficient MCMV failed to detect expansion of T cell memory.
[0223] method
[0224] Mice were infected as in Example 1 and Example 2. However, in this example, mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and infected with either wild-type or ΔgL MCMV by a single injection into the left hind footpad. T cell responses to wild-type and ΔgL MCMV in peripheral blood were det...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com