Method for recovering ferric oxide from red mud by leaching-photocatalysis by oxalic acid
An iron oxide and red mud technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, cement production, etc., can solve the problems of red mud stacking pollution and alkalinity reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Take 10g of air-dried red mud and add it to 100ml of 1mol / L oxalic acid solution, carry out stirring and leaching at 60°C for 2h, and then filter. The chemical analysis of red mud and filter residue was carried out respectively, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0024] Table 1 Chemical analysis results before and after treatment of red mud with oxalic acid solution
[0025]
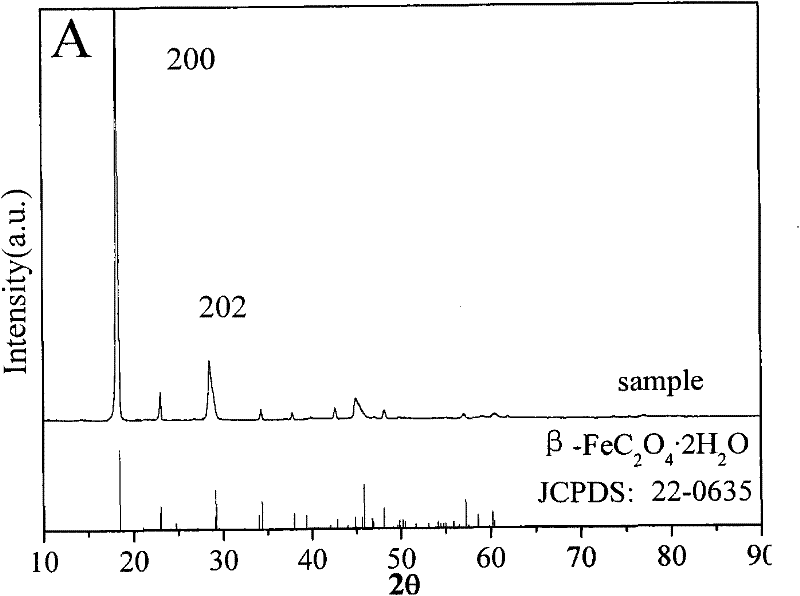
[0026] The iron oxide content in the treated red mud is only 0.6%, which is suitable for use as raw materials for refractory bricks and cement. The oxalate concentration in the leach solution is 0.95mol / L, and the iron content is 9.8g / L (as Fe 2 o 3 count). Put the leaching solution under ultraviolet light irradiation, and stir it properly, a large amount of light yellow precipitate will appear in 0.5h, and the amount of precipitation will not continue to increase after 2h. Stop the irradiation. In the filtrate after separating ferrous oxalate precipitation, oxalate content is 0.65mol / ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Take 15g of dry red mud and add it to 180ml of 0.8mol / L oxalic acid solution, carry out stirring and leaching at 70°C for 1h, and conduct chemical analysis on red mud and filter residue respectively, the results are shown in Table 2.
[0029] Table 2 Chemical analysis results before and after red mud treatment with oxalic acid solution
[0030]
[0031] The content of iron oxide in the treated red mud is 0.56%, which is suitable for use as raw materials for refractory bricks, cement and the like. The oxalate concentration in the leach solution is 0.72mol / L, and the iron content is 7.7g / L (as Fe 2 o 3 count). Put the leaching solution under ultraviolet light irradiation, and stir it properly, a large amount of light yellow precipitate will appear in 0.5h, and the amount of precipitation will not continue to increase after 3h. Stop the irradiation. Separating the oxalate content in the filtrate after ferrous oxalate precipitation is 0.46mol / L, and iron content is 0....
Embodiment 3
[0033] Take 10g of dry red mud and add it to 200ml of 0.5mol / L oxalic acid solution, carry out stirring and leaching at 80°C for 2h, and then filter. The chemical analysis of red mud and filter residue was carried out respectively, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0034] Table 3 Chemical analysis results before and after red mud treatment with oxalic acid solution
[0035]
[0036] The iron oxide content in the treated red mud is 0.71%, which is suitable for use as raw materials for refractory bricks and cement. The oxalate concentration in the leach solution is 0.47mol / L, and the iron content is 4.3g / L (as Fe 2 o 3count). At 12:00 noon, put the leach solution under sunlight and stir it properly. A large amount of light yellow precipitates appeared in 0.5 hours, and the amount of precipitates did not continue to increase after 2 hours. Separating the oxalate content in the filtrate after ferrous oxalate precipitation is 0.3mol / L, and iron content is 0.34g / L (as F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com