Method for producing iron oxide red by using ferrous sulfate as titanium dioxide byproduct
A technology of ferrous sulfate and red iron oxide, applied in the directions of iron oxide, iron oxide/iron hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of increased solution viscosity, difficult filtration, serious hydrolysis of ferrous ions, etc., and achieves high recovery rate and purity. , the effect of reducing production costs and simplifying the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
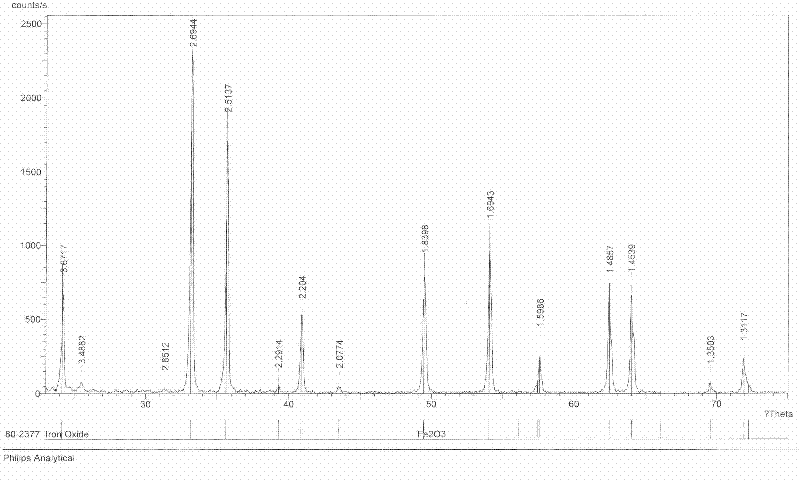
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
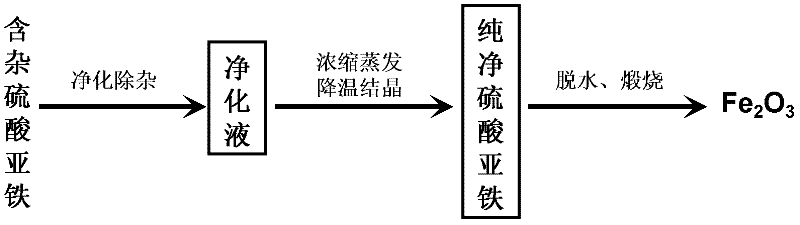
[0027] In this embodiment, the process flow of producing iron oxide red with titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate is shown in figure 1 ,Proceed as follows:
[0028] (1) Purification and removal of impurities by titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate
[0029] In the reaction vessel that is equipped with stirring paddle, load raw material: titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate and tap water, the mass ratio of described ferrous sulfate and tap water is 2: 1, the raw material in the reaction vessel is heated to 70 ℃ and in Stir at this temperature until the ferrous sulfate dissolves, add ammonia water to adjust the pH of the aqueous solution to 3.97, and then add NH 4 F, react at normal pressure and 70°C for 30 minutes under stirring, after the reaction time expires, centrifuge to separate the precipitate to obtain a purified solution, the NH 4 The addition of F is 6% of the mass of ferrous sulfate by-product of raw material titanium dioxide;
[0030] (2) Conc...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In this embodiment, the process flow of producing iron oxide red with titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate is shown in figure 1 ,Proceed as follows:
[0039] (1) Purification and removal of impurities by titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate
[0040] In the reaction vessel that is equipped with stirring paddle, load raw material: titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate and tap water, the mass ratio of described ferrous sulfate and tap water is 1: 1, the raw material in the reaction vessel is heated to 50 ℃ and in Stir at this temperature until ferrous sulfate dissolves, add ammonia water to adjust the pH of the aqueous solution to 2.23, then add NaF to the aqueous solution, and react at normal pressure and 50°C for 60 minutes under stirring. After the reaction time expires, centrifuge to separate Precipitate, obtain purification liquid, the add-on of described NaF is 0.3% of the mass of ferrous sulfate of raw material titanium dioxide by-product;
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0047] In this embodiment, the process flow of producing iron oxide red with titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate is shown in figure 1 ,Proceed as follows:
[0048] (1) Purification and removal of impurities by titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate
[0049] In the reaction vessel that is equipped with stirring paddle, load raw material: titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate and tap water, the mass ratio of described ferrous sulfate and tap water is 1.5: 1, the raw material in the reaction vessel is heated to 60 ℃ and in Stir at this temperature until ferrous sulfate dissolves, add ammonia water to adjust the pH of the aqueous solution to 2.95, then add KF to the aqueous solution, and react at normal pressure and 60°C for 40 minutes under stirring. After the reaction time expires, centrifuge to separate Precipitate, obtain purification liquid, the add-on of described KF is 1.6% of the mass of ferrous sulfate of raw material titanium dioxide by-product;
[0...
PUM
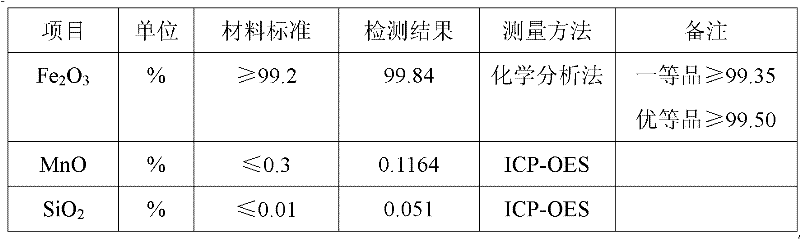
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com