Screening method of strain capable of producing acetoin and acetoin production method based on strain fermenting method
A screening method and acetoin technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high cost, restricted raw materials by petroleum, heavy pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
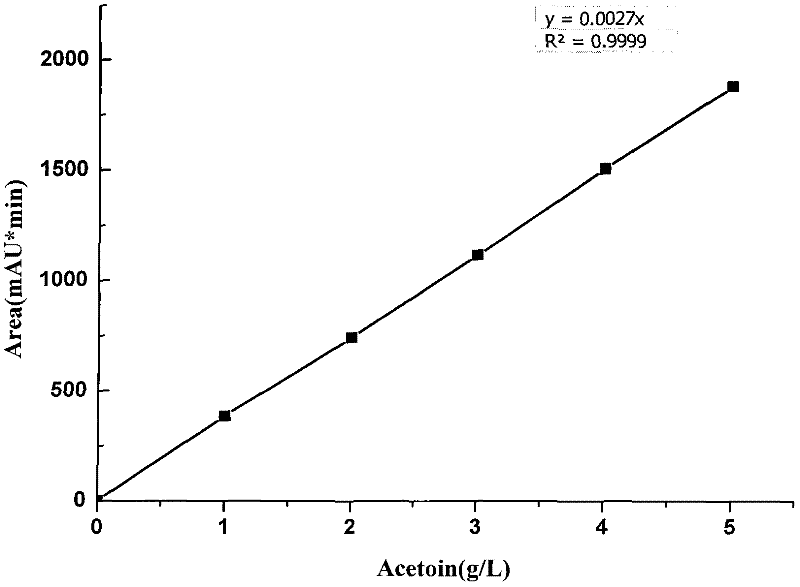
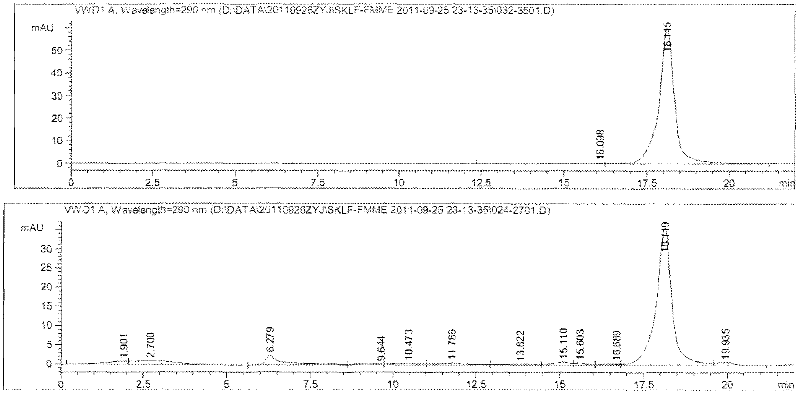
[0038] Take a soil sample from the surface near the winemaking workshop, weigh about 5.0g, bake in an oven at 80°C for 48h, and add it to 200mL of sterile water to make a suspension. This bacterial suspension was diluted to 10 as a stock solution -6 , take 10 -4 -10 -6 Spread the diluted bacterial solution on the enrichment medium, culture it upside down at 37°C for 24 hours, pick single colonies with different colony forms for V-P experiment investigation, transfer the V-P positive strains to the fermentation medium one by one, and store them by number; after the culture is over Take 2 mL each, centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for 10 min, detect the acetoin content in the supernatant by HPLC, and screen out more than a dozen acetoin-producing strains, among which strain FMME044 has the strongest acetoin-producing ability.
Embodiment 2
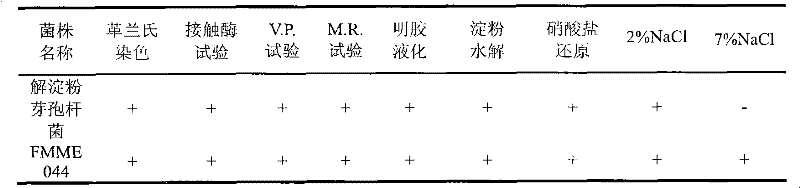
[0040] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of the screened FMME044 strain were identified according to "Microbial Taxonomy" (see Table 1), and the genomic DNA was extracted according to the extraction method of the bacterial genome extraction kit, with P1 and P2 as forward and reverse primers:
[0041] P1: 5'-CAGATGGGAGCTTGCTCCCTG-3',
[0042] P2: 5'-CGACTTCACCCCAATCATCTG-3'.
[0043] The 16S rDNA gene was amplified by PCR, and the BGI Research Center was entrusted to perform 16S rDNA sequencing. After obtaining the partial 16S rDNA sequence of this strain, the BLAST search tool was used for homology comparison analysis on the NCBI website. Based on 16SrDNA sequence analysis and identification of physiological and biochemical characteristics, combined with the study of the growth and fermentation characteristics of the bacteria, it was considered to be Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and named Bacillus amyloliquifaciens FMME044.
[0044] Partial 16S rDNA sequence of ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Step 1: Media Preparation
[0074] Seed medium (g / L): glucose 10, beef extract 5, peptone 5, NaCl 5, initial pH 7.0;
[0075] Fermentation medium (g / L): glucose 120, peptone 10, yeast powder 10, NaCl 5, K 2 HPO 4 3. MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.4, initial pH 7.0;
[0076] Step 2: Seed Preparation
[0077] The seed medium in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask was 50mL, and sterilized at 121°C for 15min. The strains were preserved in glycerol tubes with a final concentration of 15%, and 200 μL of the preserved bacteria liquid was taken into 50 ml of seed medium for seed culture, and cultured at 37° C. and 200 rpm for 12 hours.
[0078] Step 3: Shake flask fermentation culture
[0079] The seed medium was inserted into 50mL fermentation medium with 10% inoculum size to carry out fermentation culture. Ferment for 60-72 hours at 37° C. and 200 rpm, take the fermented liquid and centrifuge, collect the supernatant and measure the content of acetoin in the fermented liquid by HPLC. Yield ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com