Method for extracting and separating element palladium from high-level waste
A technology of high-level radioactive waste and elements, which is applied in the field of post-processing of high-level radioactive waste in the nuclear industry, can solve problems such as large-scale promotion, and achieve the effects of high selectivity, good separation effect, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] (1) The high-level radioactive waste is made into a nitrate solution according to the process of the U.S. invention patent with the document number US6843921B2 and the secondary actinides are separated to obtain a nitrate solution containing metal elements such as Cs, Sr, Rh, Ru, Pd, etc. The total concentration of metal ions in the high-level waste nitrate solution is 10×10 -3 mol / L, adjust the concentration of nitric acid in the nitrate solution to 3mol / L with concentrated nitric acid;
[0044] (2) Mix 2,6-bis(5,6-dinonyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)pyridine, octanol and dodecane to obtain solution B, 2,6-bis(5 ,6-Dinonyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)pyridine concentration is 4×10 -2 mol / L, based on the total volume of octanol and dodecane, the volume fraction of octanol is 30%, and the volume fraction of dodecane is 70%;
[0045] (3) Mix the nitrate solution of high-level radioactive waste with a nitric acid concentration of 3mol / L and solution B in equal volumes, shake at 25°C for 90 minut...
Embodiment 2~7
[0050] Examples 2-7 are the same as the experimental conditions in Example 1, except that in step (1), the concentration of nitric acid in the nitrate solution is adjusted to 0.42mol / L, 1mol / L, 1.5mol with concentrated nitric acid. / L, 2.5mol / L, 4mol / L, 5.11mol / L.
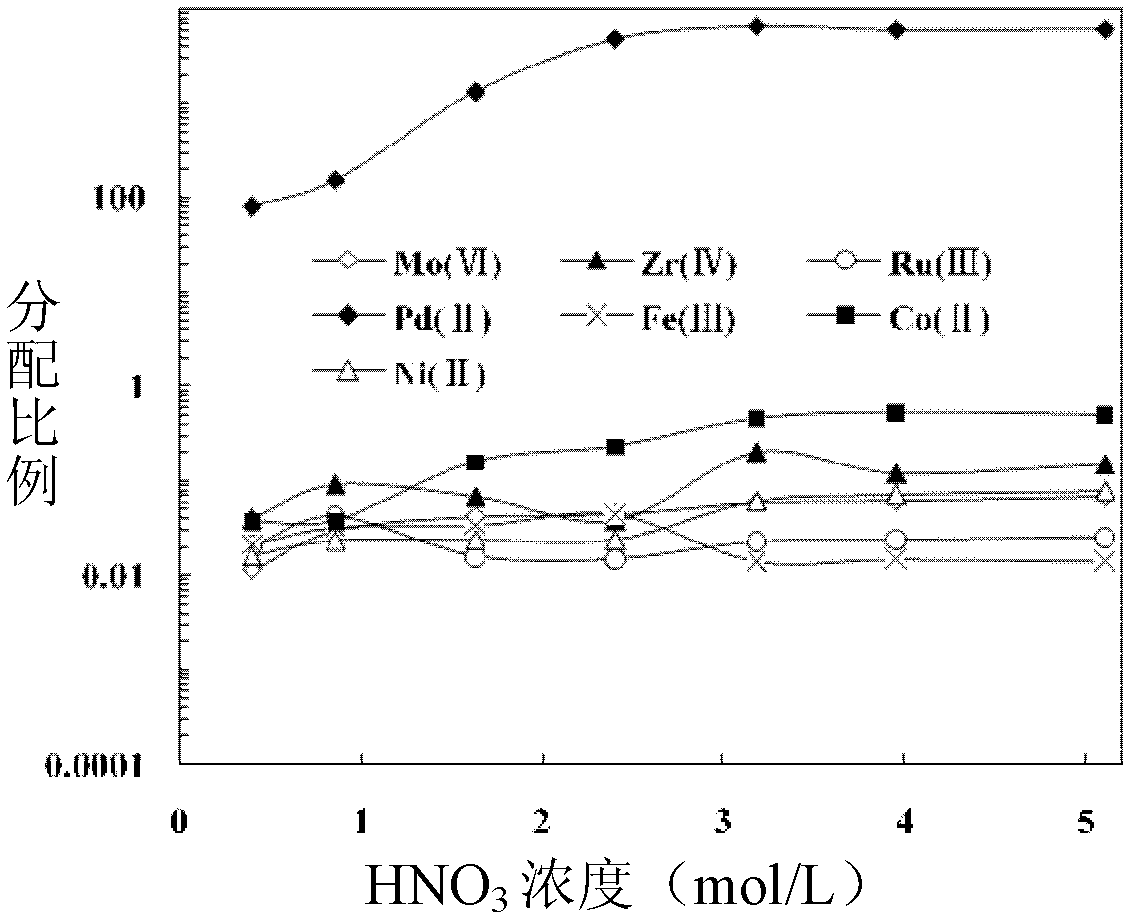
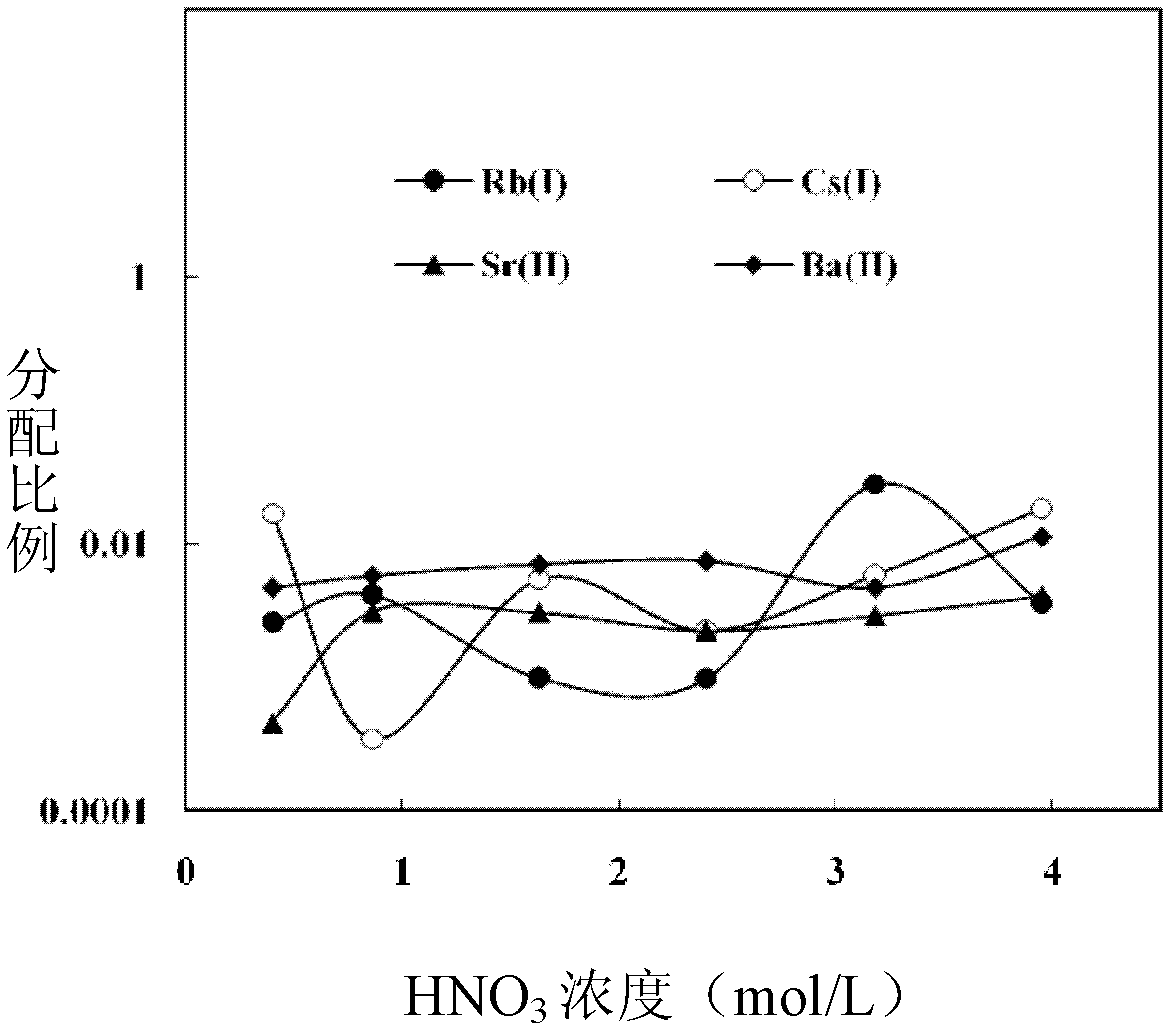
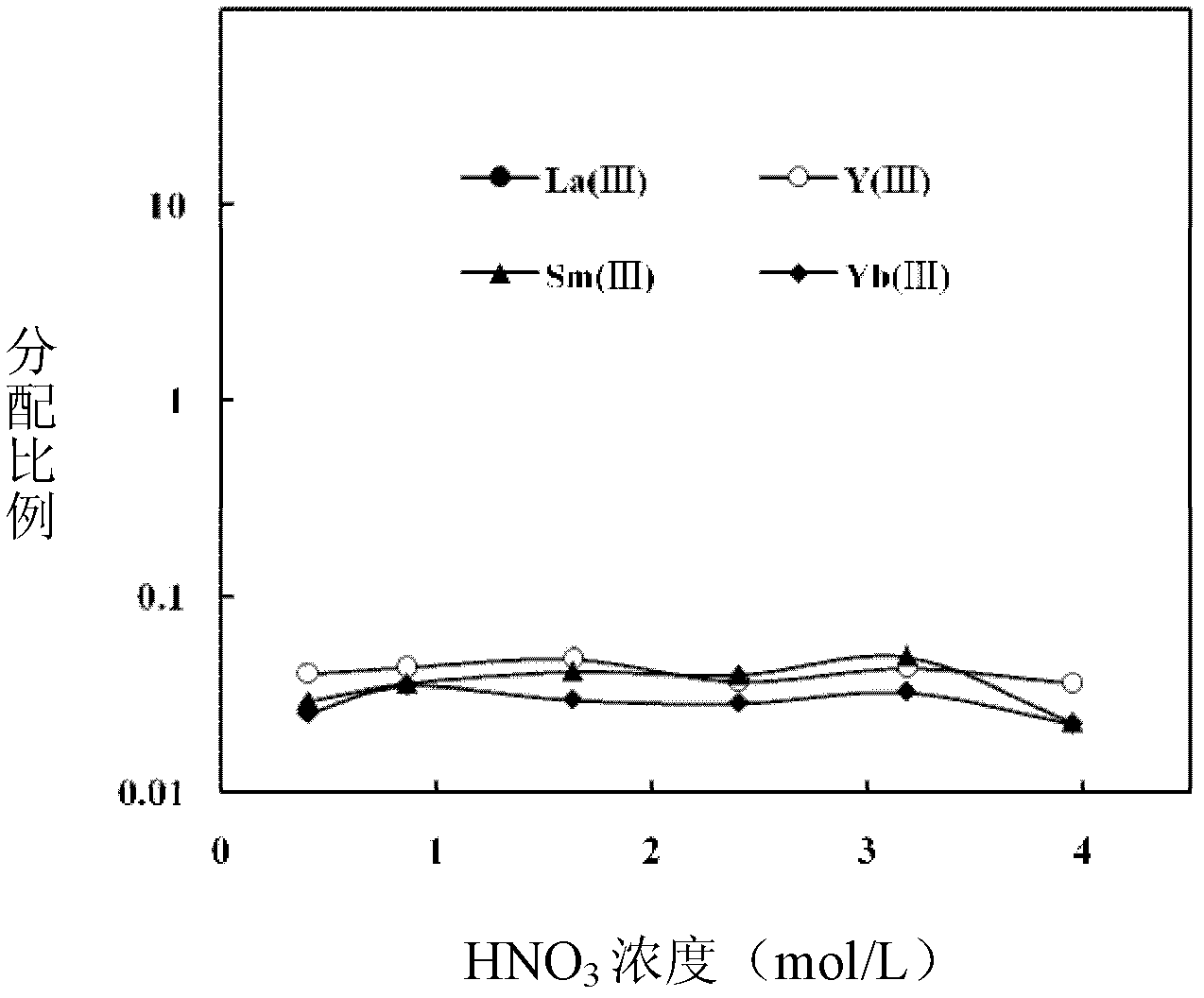
[0051] See the attachment for the separation results figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 .
[0052] Attached figure 1 , 2 , 3 It can be seen that with the difference of nitric acid concentration, the distribution ratio of metal ions (distribution ratio = equilibrium concentration of metal ions in the organic phase / equilibrium concentration of metal ions in the water phase) is also different, and the concentration of nitric acid is adjusted to At 3mol / L, the distribution ratio of Pd(II) reaches the maximum, continue to increase the concentration of nitric acid, and the distribution ratio of Pd(II) is a constant value.
Embodiment 8
[0054] (1) The high-level radioactive waste is made into a nitrate solution according to the process of the U.S. invention patent with the document number US6843921B2 and the secondary actinides are separated to obtain a nitrate solution containing metal elements such as Cs, Sr, Rh, Ru, Pd, etc. The total concentration of metal ions in the high-level waste nitrate solution is 10×10 -3 mol / L, adjust the concentration of nitric acid in the nitrate solution to 3mol / L with concentrated nitric acid;
[0055] (2) Mix 2,6-bis(5,6-dinonyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)pyridine, hexanol and dodecane to obtain solution B, 2,6-bis(5 ,6-Dinonyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)pyridine concentration is 4×10 -2 mol / L, based on the total volume of hexanol and dodecane, the volume fraction of hexanol is 30%, and the volume fraction of dodecane is 70%;
[0056] (3) Mix the nitrate solution of high-level radioactive waste with a nitric acid concentration of 3mol / L and solution B in equal volumes, shake at 25°C for 90 minut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com