Mycoplasma bovis enolase and new applications of coding gene thereof
A kind of technology of enolase and Mycoplasma bovis, applied in the field of biomedicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Cloning and expression of embodiment 1 Mycoplasma bovis enolase gene (P18)
[0036] 1. Materials
[0037] 1.1 Mycoplasma culture
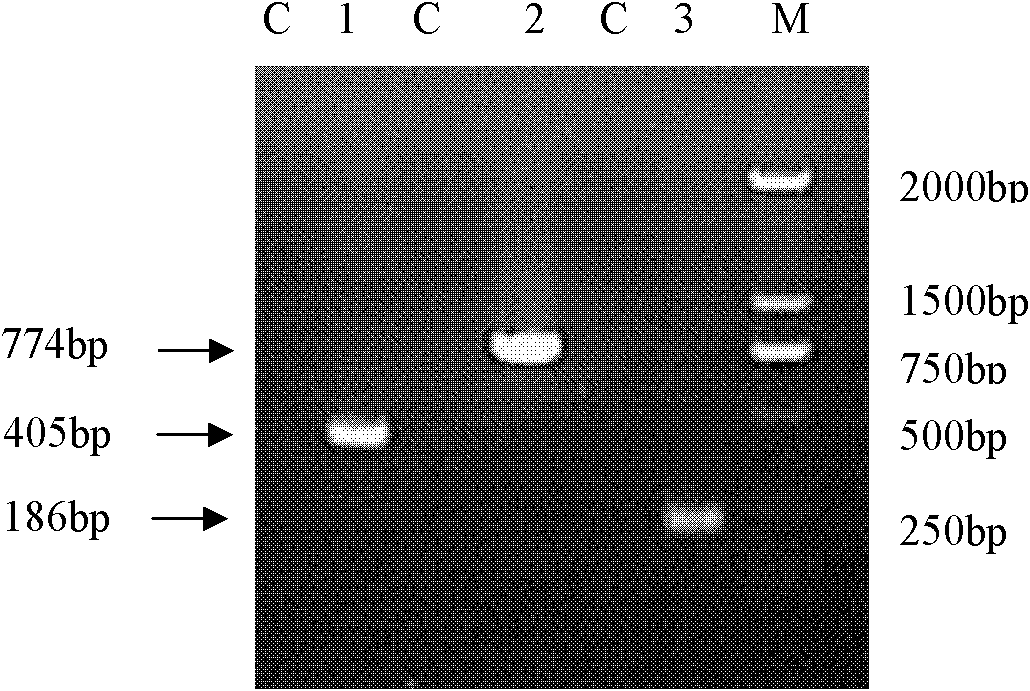
[0038] Mycoplasma bovis Hubei isolate (HB) was isolated and identified by our laboratory (Vassalli J D, Sappino A P, and Belin D. The plasminogen activator / plasmin system [J]. J Clin. Invest. 1991.88 (4): 1067-1072). According to the literature (Radaelli E, Luini M. Bacteriological, serological, pathological and immunohistochemical studies of Mycoplasma bovis respiratory infection in veal calves and adult cattle at slaughter [J], Research in Veterinary Science 2008.85 (2): 282-290.) described Methods: Expand the strains in PPLO medium containing 20% horse serum, 10% yeast extract, thallium acetate (0.125mg / ml) and penicillin (200IU / ml). After culturing at 37.0°C for 3-5 days, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 13,000 r / min for 30 minutes at 4°C, and the cells were washed with PBS for 3 times. Bacteria are stored in -70°C refrig...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 The binding activity of recombinant Mycoplasma bovis enolase and plasminogen
[0058] The purified recombinant Mycoplasma bovis enolase sample obtained in Example 1 was subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and then transferred to a cellulose acetate membrane. Block overnight at 4°C with PBS containing 5% fish gelatin, wash the membrane three times with PBST, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour with PBS containing 1 unit / ml human plasminogen (containing 1% BSA and 25MmEDTA). Wash the membrane with PBST to wash away unbound plasminogen, and incubate overnight at 4°C with PBS containing 25ug / ml goat anti-human plasminogen antibody. After washing with PBST, the HRP-labeled rabbit anti-goat secondary antibody diluted 1:10000 (v / v) was incubated with cellulose acetate membrane at 37°C for 1 hour. DAB chromogenic detection.
[0059] The ability of Mycoplasma bovis enolase to bind plasminogen was detected by ligand experiment, and the results showed that the purif...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Western blot detection of protein immunogenicity
[0061] The purified recombinant Mycoplasma bovis enolase sample was subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and then transferred to a cellulose acetate membrane. After blocking overnight at 4°C in PBS containing 5% fish gelatin, the bovine anti-Mycoplasma bovis hyperimmune serum (1:160) prepared and preserved in our laboratory was used as the primary antibody, and the HRP-labeled goat anti-bovine secondary antibody (1:8000). DAB chromogenic detection.
[0062] The immunogenicity of Mycoplasma bovis enolase was detected by Western blot experiment, and the experimental results showed that the purified Mycoplasma bovis enolase had immunogenicity and could react with Mycoplasma bovis positive serum ( Figure 5 ).
[0063] In this experiment, Mycoplasma bovis enolase was obtained through prokaryotic expression, and the protein was successfully soluble expressed by adjusting the induction conditions, and finall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com