High-work-hardening magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
A work hardening, magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve problems such as poor plasticity, and achieve the effects of improving plasticity, reducing magnesium stacking fault energy, and high strength and toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
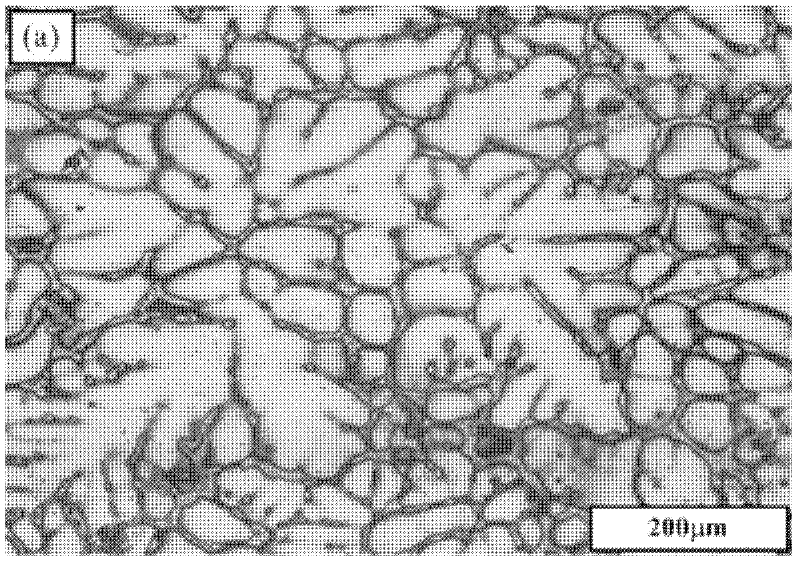
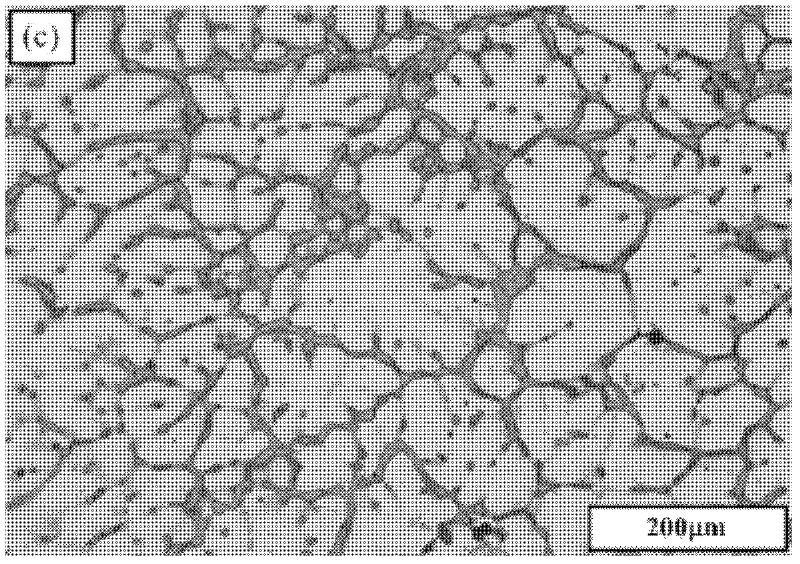
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Prepare materials according to the composition content of magnesium alloy: 2.9% tin, 1.1% zinc, and the rest are magnesium and unavoidable impurities;
[0028] (2) Prepare materials according to the above-mentioned magnesium alloy composition content; use No. 2 solvent for protection, melt the pure magnesium ingot, and then add pure tin and pure zinc preheated at 80-120°C;
[0029] (3) Gas blowing, stirring, refining, slag removal, and after standing still, the melt is directly cast into ingots, and then the ingots are hot-extruded into pipes, profiles or plates; among them, casting Mg-2.9Sn-1.1Zn Tensile strength σ b ≥165MPa, elongation δ≥19%, work hardening ability Hc≥3.69, work hardening index n≥0.574.
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Prepare materials according to the composition content of magnesium alloy: tin 4.0%, zinc 3.5%, added elements: silicon 0.5%, antimony 1.0%, tellurium 1.0%, strontium 0.03%, manganese 0.5%, the rest is magnesium and unavoidable impurities ;
[0032] (2) Prepare materials according to the above-mentioned magnesium alloy composition content; use No. 2 solvent for protection, melt the pure magnesium ingot, and then add pure tin and pure zinc preheated at 75-135°C;
[0033] (3) Adding additional elements: first add silicon, antimony and tellurium elements, stir well and then add strontium and manganese; among them, silicon, antimony and tellurium elements are introduced in the form of pure silicon, pure antimony and pure tellurium, while strontium and manganese are introduced in the form of commercial The standard magnesium master alloy is introduced, and the mass percentage content of the elements in the commercial standard magnesium master alloy is 10-15;
[0034] (4...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Prepare materials according to the composition content of magnesium alloy: tin 3.5%, zinc 2.5%, added elements: silicon 0.1%, antimony 0.5%, tellurium 0.5%, strontium 0.15%, manganese 0.2%, the rest is magnesium and unavoidable impurities ;
[0037] (2) Prepare materials according to the above-mentioned magnesium alloy composition content; use No. 2 solvent for protection, melt the pure magnesium ingot, and then add pure tin and pure zinc preheated at 140-170°C;
[0038] (3) Adding additional elements: first add silicon, antimony and tellurium elements, stir well and then add strontium and manganese; among them, silicon, antimony and tellurium elements are introduced in the form of pure silicon, pure antimony and pure tellurium, while strontium and manganese are introduced in the form of commercial The standard magnesium master alloy is introduced, and the mass percentage content of the elements in the commercial standard magnesium master alloy is 10-15;
[0039] (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com