Method for preparing ceramic particle reinforced steel-based mesh material
A technology of ceramic particles and composite materials, applied in the field of metal matrix composite materials, can solve the problems of easy formation of slag inclusion, poor process controllability, unsuitable for large-scale industrial production, etc., and achieves shortened crystallization process, wide adaptability and wear resistance. The effect of organic unity of sex and resilience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
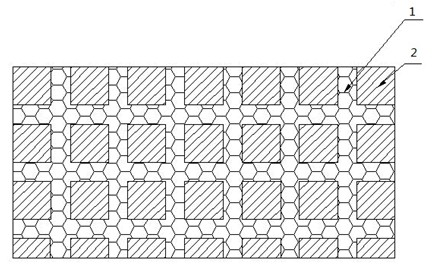
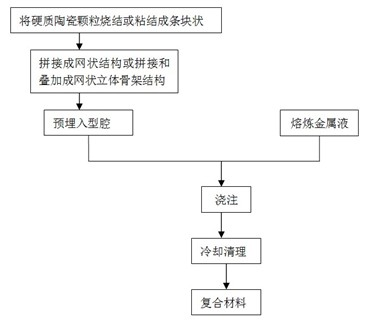
[0027] (1) Use powder sintering to sinter alumina particles with a particle size of -20 to +30 mesh into strips;
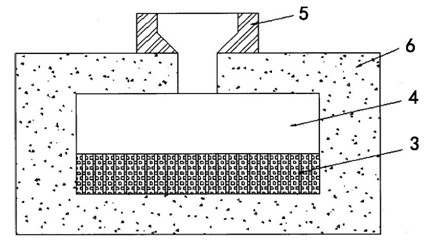
[0028] (2) The strip blocks in step (1) are spliced into corresponding network structures according to the shape of the working surface of the workpiece (in the case of local compounding), accounting for 50% of the volume fraction of the wear-resistant layer of the workpiece, using conventional sand casting, such as figure 2 After the high manganese steel is smelted to the pouring temperature, it is poured into the cavity 4 embedded with the network structure 3 through the pouring riser 5 in the middle of the sand mold 6, and cooled and solidified at room temperature. The ceramic particle reinforced steel-based mesh composite material composed of the wear-resistant layer 1 and the metal layer 2 of the high-manganese steel base material.
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Use powder sintering to sinter the mixture of ferromolybdenum powder and silicon carbide and tungsten carbide particles with a particle size of 60 meshes into a strip block; wherein, the alloy powder accounts for 20% of the volume of the strip block;
[0031] (2) After splicing and superimposing the strips in step (1), a net-like three-dimensional skeleton structure (in the case of overall composite) is formed. The spacing between each layer of strips is 3mm; conventional sand casting is used to melt gray cast iron HT300 After the material reaches a pouring temperature of 1530°C, it is poured into a cavity with a pre-embedded mesh three-dimensional skeleton structure, cooled and solidified at room temperature, and sand-cleaned to obtain a ceramic particle-reinforced steel-based mesh composite material.
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Use a binder to bond the mixture of tungsten iron powder and silicon nitride and titanium nitride particles with a particle size of 10 meshes into a strip block; wherein, the alloy powder accounts for 60% of the volume of the strip block;
[0034](2) The strip blocks in step (1) are spliced into corresponding network structures according to the shape of the working surface of the workpiece (in the case of local compounding), accounting for 20% of the volume fraction of the wear-resistant layer of the workpiece, using conventional lost foam casting, melting After the gray cast iron reaches the pouring temperature, it is poured into a cavity with a pre-embedded network structure, cooled and solidified at room temperature, and cleaned of sand to obtain a ceramic particle reinforced steel-based network composite material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com