Preparation method for pea aspartic acid protease inhibitor
A technology of protease inhibitors and aspartic acid, which is applied in the direction of protease inhibitors, peptide sources, animal/human peptides, etc., can solve the problems of environmental pollution, waste of protein resources, etc., achieve wide application, easy material acquisition, and prevent waste of resources Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
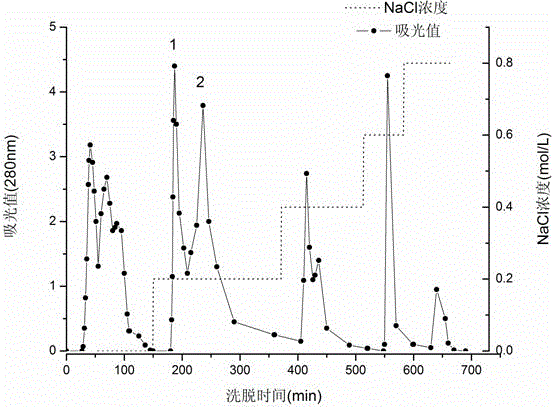
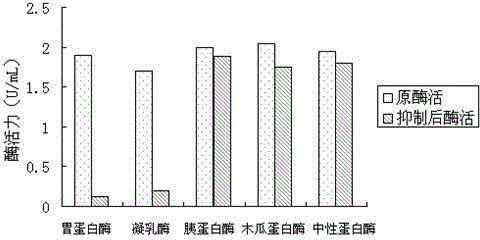
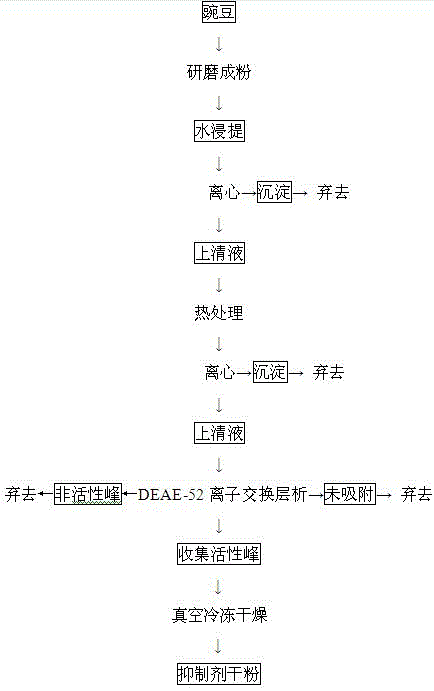
[0029] Wash 50 g of peas and bake them immediately, grind them into powder, add 200 mL of ultrapure water at a ratio of 1:4 (w / v), put them in the refrigerator, and carry out leaching at 4 °C for 2 h. Stir every hour. After the extraction, the extract was centrifuged at 8000 r / min and 4°C for 30 min to obtain 175 mL of supernatant. The supernatant was water bathed at 60°C for 20 min, cooled to room temperature, 8000 r / min , Centrifuge at 4°C for 30 min to obtain 160 mL of supernatant, the concentration ratio of protein to sugar was measured to be about 0.98, the pepsin inhibitory unit was about 0.97 IU / mL, and the recovery rate was 87.6%; the supernatant was subjected to ionization For exchange chromatography, 20 mL of crude inhibitor was taken each time for DEAE-52 ion exchange chromatography, 30 cm × 2.2 cm, and the equilibration buffer was 10 mmol / L sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Elution mode: After 2 column volumes of equilibration buffer were eluted, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, an...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Wash 50 g of peas and bake them immediately, grind them into powder, add 200 mL of ultrapure water at a ratio of 1:4 (w / v), put them in the refrigerator, and carry out leaching at 4 °C for 2 h. Stir every hour. After the extraction, the extract was centrifuged at 8000 r / min and 4°C for 30 min to obtain 175 mL of supernatant. The supernatant was water bathed at 60°C for 20 min, cooled to room temperature, 8000 r / min , Centrifuge at 4°C for 30 min to obtain 160 mL of supernatant, the concentration ratio of protein to sugar was measured to be about 1.05, the pepsin inhibitory unit was about 0.99 IU / mL, and the recovery rate was 88.4%; the supernatant was subjected to ionization For exchange chromatography, 20 mL of crude inhibitor was taken each time for DEAE-52 ion exchange chromatography, 30 cm × 2.2 cm, and the equilibration buffer was 10 mmol / L sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Elution mode: After 2 column volumes of equilibration buffer were eluted, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Wash 50g of peas and bake them immediately, grind them into powder, add 200 mL of ultrapure water at a ratio of 1:4 (w / v), put them in the refrigerator, and carry out leaching at 4°C for 2 hours, every half an hour. Stir once. After the extraction, the extract was centrifuged at 8000 r / min and 4°C for 30 min to obtain 175 mL of supernatant. The supernatant was water bathed at 60°C for 20 min, cooled to room temperature, 8000 r / min , Centrifuge at 4 °C for 30 min to obtain 160 mL of supernatant, the concentration ratio of protein to sugar was measured to be about 1.06, the pepsin inhibitory unit was about 0.98 IU / mL, and the recovery rate was 87.4%; the supernatant was subjected to ionization For exchange chromatography, 20 mL of crude inhibitor was taken each time for DEAE-52 ion exchange chromatography, 30 cm × 2.2 cm, and the equilibration buffer was 10 mmol / L sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Elution mode: After 2 column volumes of equilibration buffer were eluted, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com