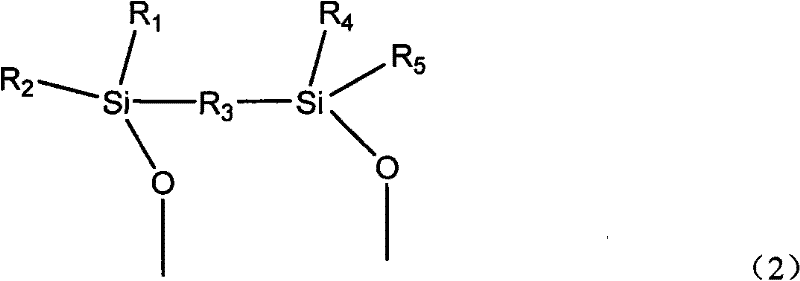
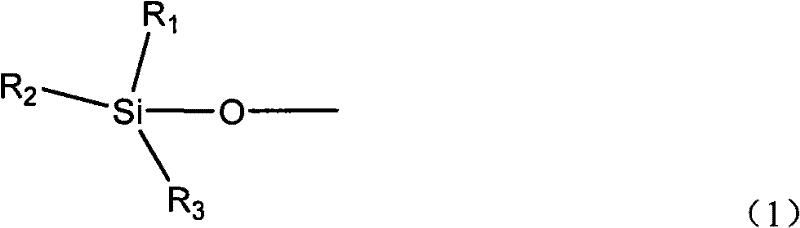Method for removing phenylacetylene in presence of styrene
A technology of phenylacetylene and styrene, which is applied in the field of removing phenylacetylene, can solve the problems of reduced lifespan, decreased reaction activity, carbon deposition of catalysts, etc., and achieves the effect of long service life and small amount of production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] This example illustrates the preparation of the hydrogenation catalyst used in the process of the invention.
[0051] 1) Weigh 100.0 g of the alumina carrier, impregnate with 75 ml of aqueous solution containing 1.80 g of potassium nitrate isometric impregnation for 0.5 h, dry at 120 °C for 4 h, and roast at 550 °C for 6 h;
[0052] 2) Then impregnate with an aqueous solution containing 100.3g of nickel nitrate in two steps using an equal-volume impregnation method, dry at 120°C for 4h, roast at 450°C for 6h, and reduce in a hydrogen atmosphere at 400°C for 20h;
[0053] 3) Silylation treatment with methyltriethoxysilane at 120° C. for 1.5 h to obtain catalyst A-1. See Table 1 for the catalyst composition.
Embodiment 2
[0055] This example illustrates the preparation of the hydrogenation catalyst used in the process of the invention.
[0056] 1) Weigh 100.0 g of the alumina carrier, impregnate with 75 ml of aqueous solution containing 4.86 g of magnesium nitrate for 0.5 h, dry at 120 °C for 4 h, and roast at 550 °C for 6 h;
[0057] 2) Then impregnate with an aqueous solution containing 120.4g of nickel nitrate in two steps using an equal-volume impregnation method for 0.5h, dry at 120°C for 4h, roast at 450°C for 6h, and reduce in a hydrogen atmosphere at 400°C for 20h;
[0058] 3) Silylation treatment with methyltriethoxysilane at 120° C. for 1.5 h to obtain catalyst A-2. See Table 1 for the catalyst composition.
Embodiment 3
[0060] This example illustrates the preparation of the hydrogenation catalyst used in the process of the invention.
[0061] 1) Weigh 100.0g of alumina carrier, impregnate with 75ml aqueous solution containing 3.73g of cerium nitrate for 0.5h by equal volume impregnation method, dry at 120°C for 4h, and roast at 550°C for 6h;
[0062] 2) Then impregnate with an aqueous solution containing 100.3g of nickel nitrate in two steps using an equal-volume impregnation method for 0.5h, dry at 120°C for 4h, roast at 450°C for 6h, and reduce in a hydrogen atmosphere at 400°C for 20h;
[0063] 3) Silylation treatment with methyltriethoxysilane at 120° C. for 1.5 h to obtain catalyst A-3. See Table 1 for the catalyst composition.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com