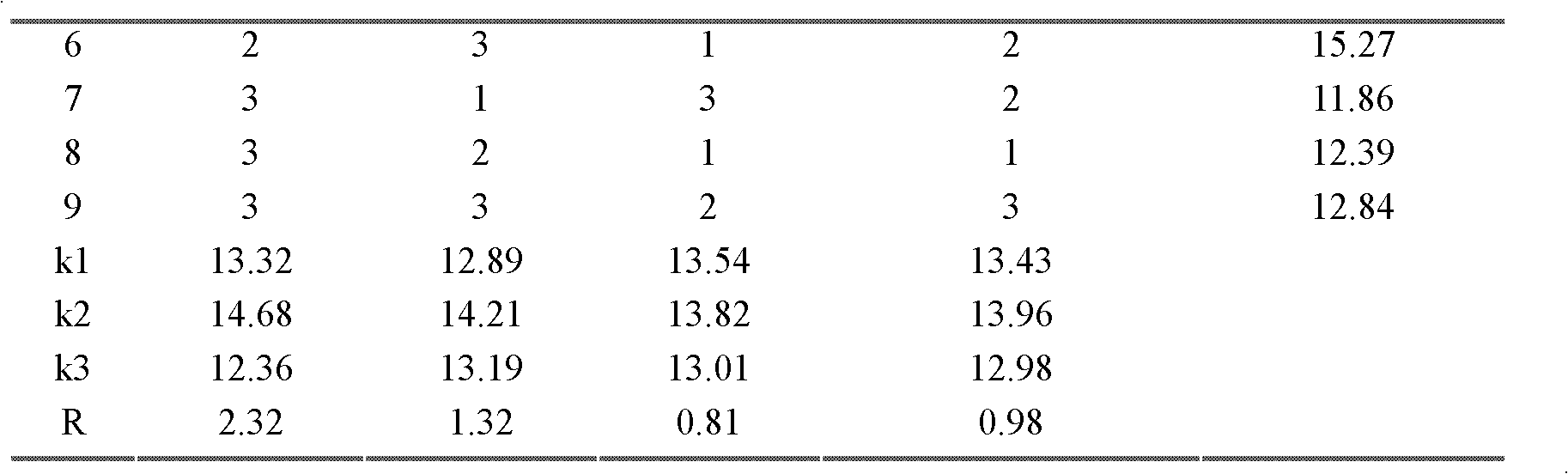Method for extracting tea polysaccharide
An extraction method and technology of tea polysaccharides, which are applied in the field of tea polysaccharide extraction, can solve the problems of reducing bioavailability, inactivation of tea polysaccharides, and easy destruction of polysaccharide structures, so as to ensure effective wall breaking at low temperature, small activity damage, and improved resistance. The effect of oxidation activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
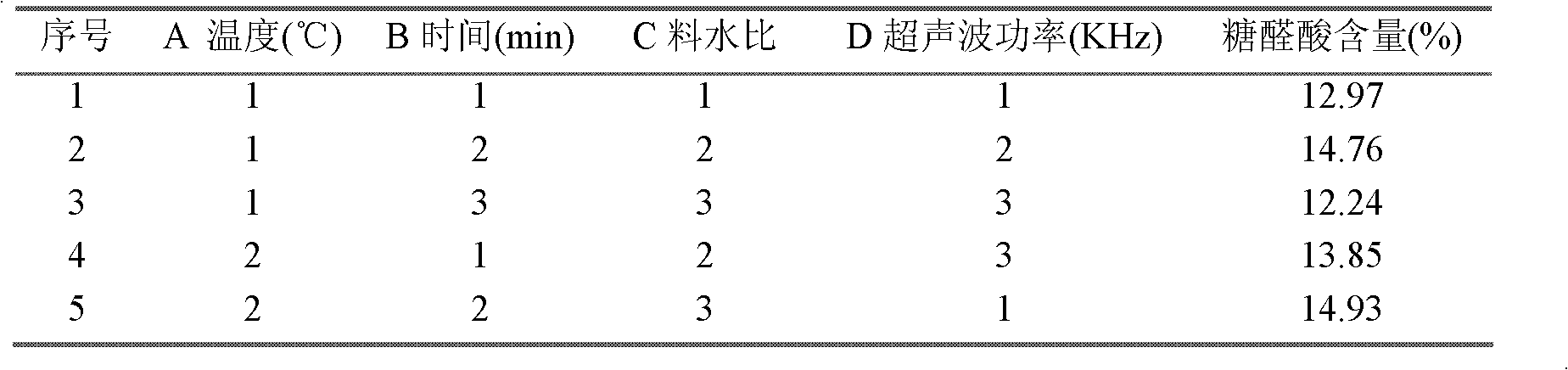
[0035] 1 Materials and reagents
[0036] Fresh thick old tea leaves (West Lake Longjing, provided by Hangzhou Longguan Industrial Co., Ltd.); For analytical purity.
[0037] 2 experimental equipment
[0038] UV-2000 ultraviolet spectrophotometer; DFY-400 pulverizer; SANYO ultra-low temperature refrigerator; RE-52A rotary evaporator; WVD-01 microwave vacuum drying oven.
[0039] 3 Experimental methods
[0040] 1) Pretreatment of coarse and old tea leaves
[0041] Take 1000g of fresh coarse old tea leaves and freeze at -80°C for 18 hours, freeze and pulverize them, pass through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain tea powder, reflux with absolute ethanol for 3 hours to remove the fat surrounded by extracellular lipids in the tea leaves, and then use 80% ethanol by volume fraction Soak at room temperature for 24 hours, filter to remove small molecular impurities, monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, glycosides, alkaloids, tea polyphenols, amino acids and alcohol-soluble pro...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The experimental operation is the same as that in Example 1, except that the thick and old tea leaves are frozen at -80°C for 12 hours at an ultra-low temperature. Other operations and conditions are the same as in Example 1, and 1.36 g of tea polysaccharides are obtained, the polysaccharide content is 56.84%, and the dissolution rate of tea polysaccharides is 4.53. %, the antioxidant capacity is 81.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0084] The experimental operation is the same as in Example 1, except that the thick and old tea leaves are frozen at -80°C for 24 hours at an ultra-low temperature, and other operations and conditions are the same as in Example 1 to obtain 1.73g of tea polysaccharide, with a polysaccharide content of 57.36%, and a tea polysaccharide dissolution rate of 5.76%. %, the antioxidant capacity is 84.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com