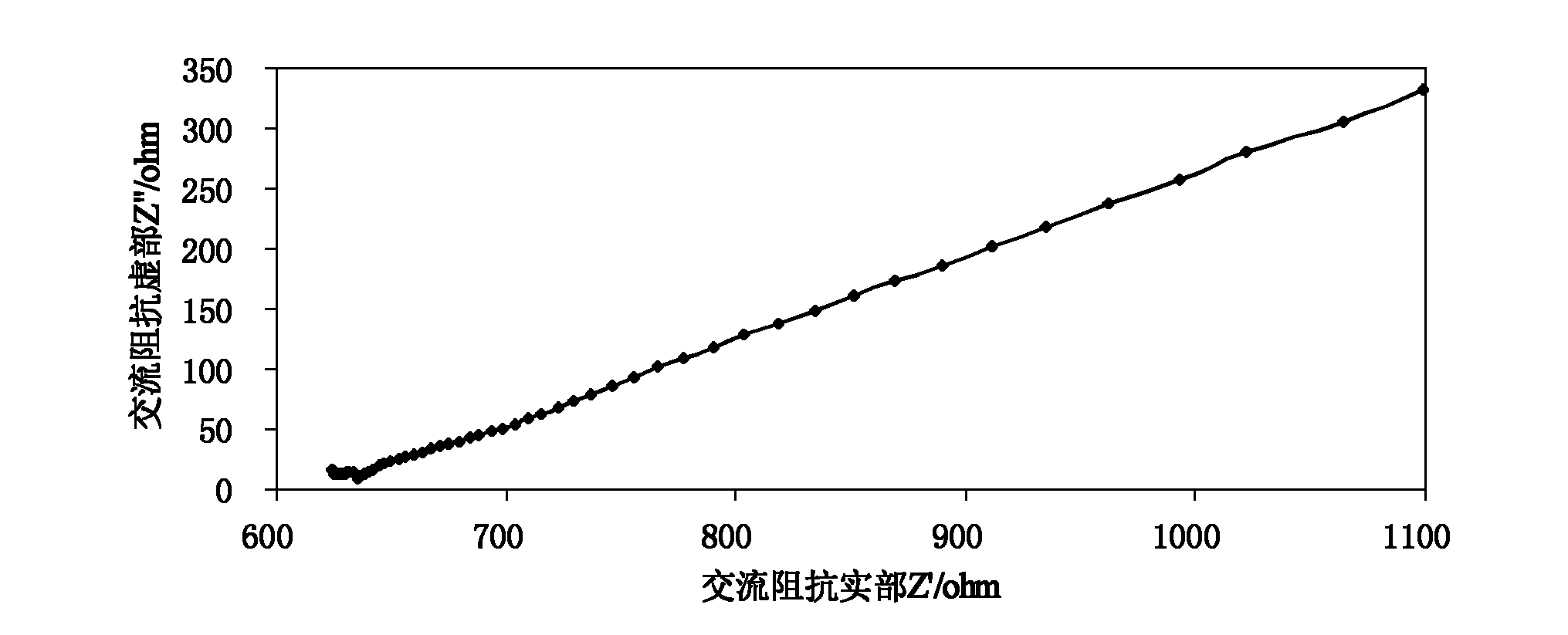
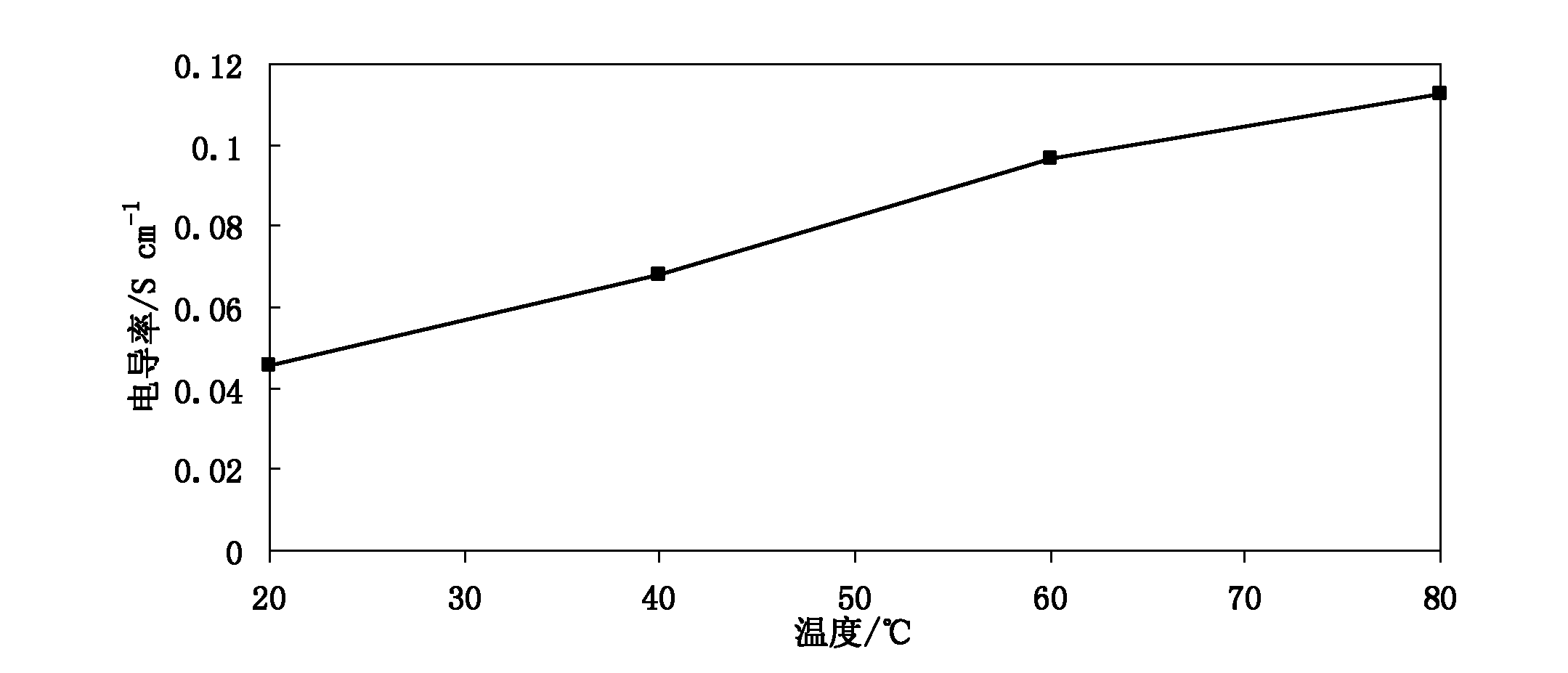
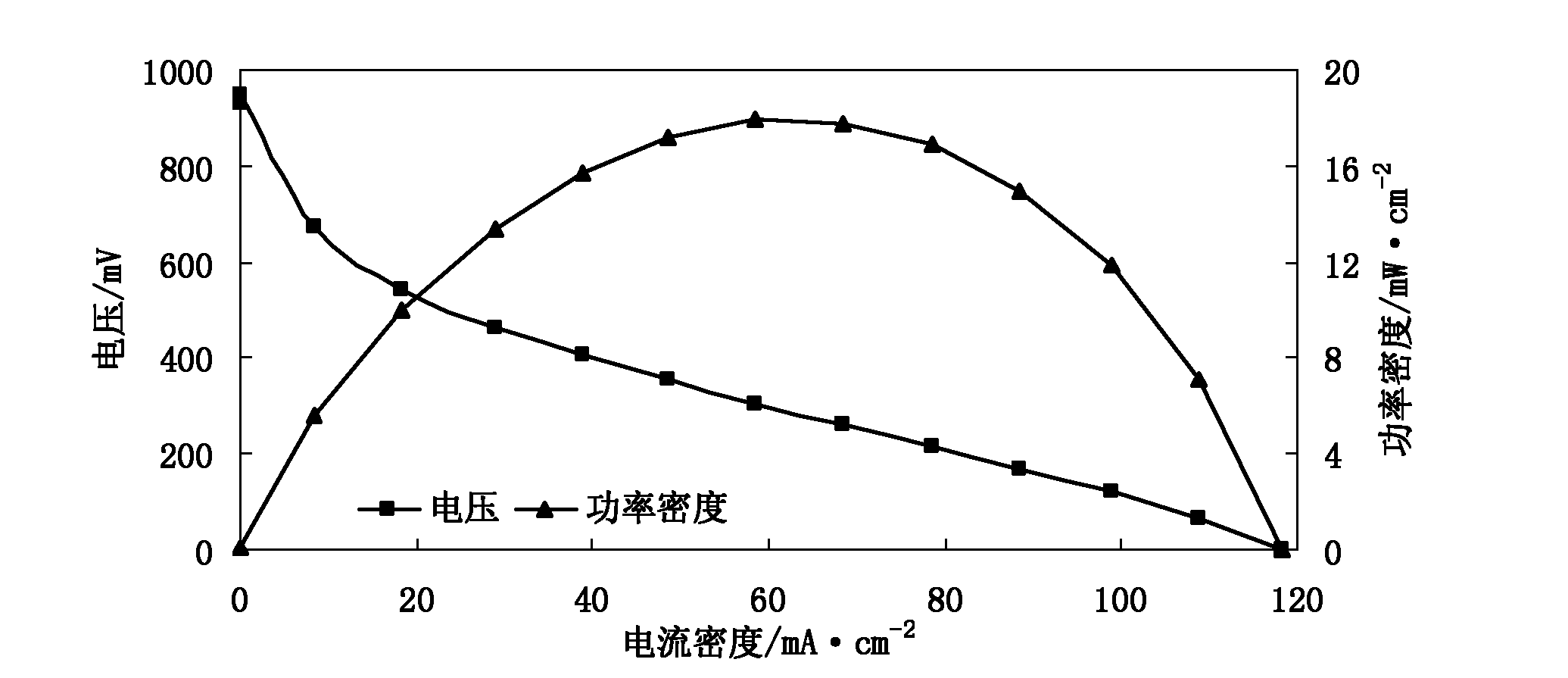
Method for preparing proton exchange membranes from modified bacterial cellulose membranes and application thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose membrane and proton exchange membrane, which is applied in the field of preparation and application of proton exchange membrane, can solve problems such as low proton conductivity, and achieve the effects of simple and easy preparation process, avoiding secondary pollution and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Rinse the bacterial cellulose membrane with deionized water several times to remove impurities such as residual medium, and then place it in a 1% by mass sodium hydroxide solution at 90°C for 1 hour in a water bath until the BC wet membrane becomes white and translucent ; Wash several times with deionized water, and boil the membrane in deionized water for 0.5h, then take it out and rinse with deionized water until the surface pH of the bacterial cellulose membrane is neutral, and then place the bacterial cellulose membrane on a flat surface Dry on a glass plate in an oven at 50°C. Take out the bacterial cellulose dry film, cut it into 1×1.5cm film, and save it for future use.
[0027] (2) The excess molar concentration is 8.4mol L -1 Phosphoric acid solution soaked the bacterial cellulose dry film for 72 hours, took out the bacterial cellulose film and blotted the residual phosphoric acid on the surface with absorbent paper, and dried it naturally in the air to pr...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Rinse the bacterial cellulose membrane with deionized water several times to remove impurities such as residual culture medium, and then place it in a 1% by mass potassium hydroxide solution at 80°C for 1 hour until the BC wet membrane becomes white and translucent ; wash several times with deionized water, and boil the membrane in deionized water for 1 hour, then take it out and rinse it with deionized water until the surface pH of the bacterial cellulose membrane is neutral, and then place the bacterial cellulose membrane on a flat surface Let the glass plate dry naturally, take out the dry film of bacterial cellulose, cut it into 1×1.5cm film, and save it for future use.
[0039] (2) The bacterial cellulose dry film was modified by doping with phosphoric acid. The excess molar concentration is 6mol L -1Phosphoric acid solution soaked the bacterial cellulose dry film for 72 hours, took out the bacterial cellulose film and blotted the residual acid on the surface ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Rinse the bacterial cellulose membrane with deionized water several times to remove impurities such as residual culture medium, and then place it in a 5% by mass sodium carbonate solution for 2 hours in a water bath at 80°C until the BC wet membrane becomes white and translucent; Wash several times with deionized water, and boil the membrane in deionized water for 1 hour, then take it out and rinse with deionized water until the surface pH of the bacterial cellulose membrane is neutral, then place the bacterial cellulose membrane on a flat glass On the board, dry it in an oven at 50°C, and cut it into membranes of different shapes according to the size of the single cell, such as 3×3cm, and save it for future use.
[0043] (2) The bacterial cellulose dry film was modified by doping with phosphoric acid. The excess molar concentration is 8.4mol L -1 Soak the bacterial cellulose dry film in a phosphoric acid solution for 72 hours, take out the bacterial cellulose fil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| impedance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com