Methods for purification of single domain antigen-binding molecules
A combination and molecular technology, applied in the preparation method of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, etc., can solve ligand leakage, cumbersome size exclusion chromatography, and contamination of eluted products, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0110] Preparation of SDAB molecules
[0111] The SDAB molecule may comprise one or more recombinant, CDR-grafted, humanized, camelized, deimmunized and / or in vitro generated (e.g., selected by phage display) single domain molecules ( For example, Nanobody molecules). Techniques for generating antibodies and SDAB molecules and modifying them recombinantly are known in the art and are described in detail below.
[0112] Various methods known to those skilled in the art can be used to obtain antibodies. For example, monoclonal antibodies can be produced by generating hybridomas according to known methods. Then using standard methods such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and surface plasmon resonance (BIACORE TM ) assay to screen the hybridomas formed in this manner to identify one or more hybridomas that produce a Nanobody that specifically binds to a given antigen. Any form of a given antigen can be used as an immunogen, for example, recombinant antigens, natura...
Embodiment 1
[0187] Example 1: Description of the ATN-103 coding sequence
[0188] ATN-103 is a trivalent nanobody molecule targeting TNFα and HSA. Nanobodies were isolated from a phage library derived from llama by selection for TNFα or HSA as described in WO 06 / 122786. The specific activity of the Nanobodies was tested and TNF1 was selected as a Nanobody inhibitor of human TNFα and ALB1 as a human anti-HSA Nanobody for half-life extension. TNF1 and ALB1 were humanized by CDR grafting onto the closest human framework (DP51 / DP53). During the humanization of TNF1, 2 camelid residues (P84 and R103) were retained and this version was named TNF30. During the humanization of ALB1, seven camelid residues (N16, N73, T76, P84, T93, I94 and S103) were retained and this version was named ALB8. Each of the two TNF30 Nanobodies was linked by a 9 amino acid glycine-serine linker (Gly 4 SerGly 3 Ser (SEQ ID NO:9)) was linked to the central ALB8 Nanobody resulting in a trivalent molecule referred to...
Embodiment 2
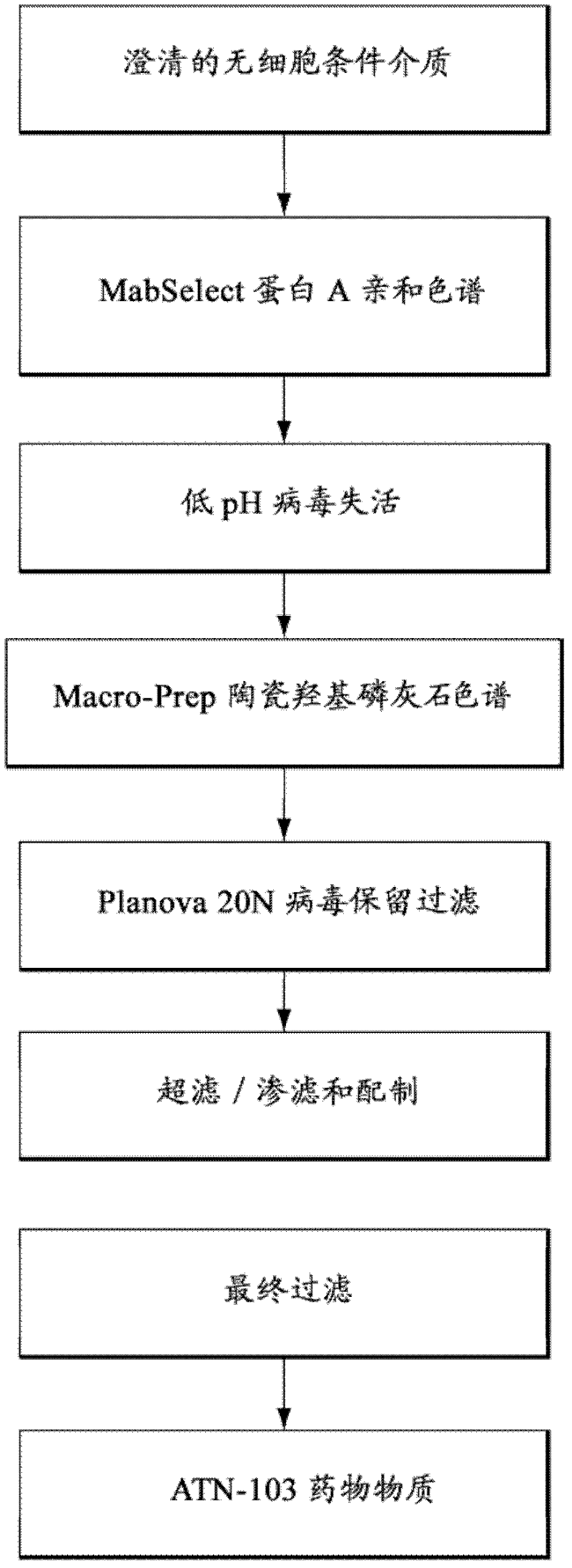
[0189] Embodiment 2: ATN-103 purification process
[0190] The ATN-103 purification process consists of two chromatography steps and three membrane filtration steps (see image 3 ). All steps were performed at room temperature unless otherwise indicated.
[0191] The rationale, purpose and description of each purification step are provided below.
[0192] MabSelect Protein A affinity chromatography and low pH virus inactivation
[0193] MabSelect TM The main purpose of the protein A chromatography step included product capture from the clarified cell-free conditioned media and separation of ATN-103 from process-derived impurities (e.g., host cell DNA and proteins, media components and adventitious agents).
[0194] MabSelect Protein A is an affinity resin composed of a highly cross-linked agarose matrix covalently derivatized by thioether linkage with recombinant Protein A produced from E. coli fermentation.
[0195] MabSelect Protein A columns were equilibrated with Tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com