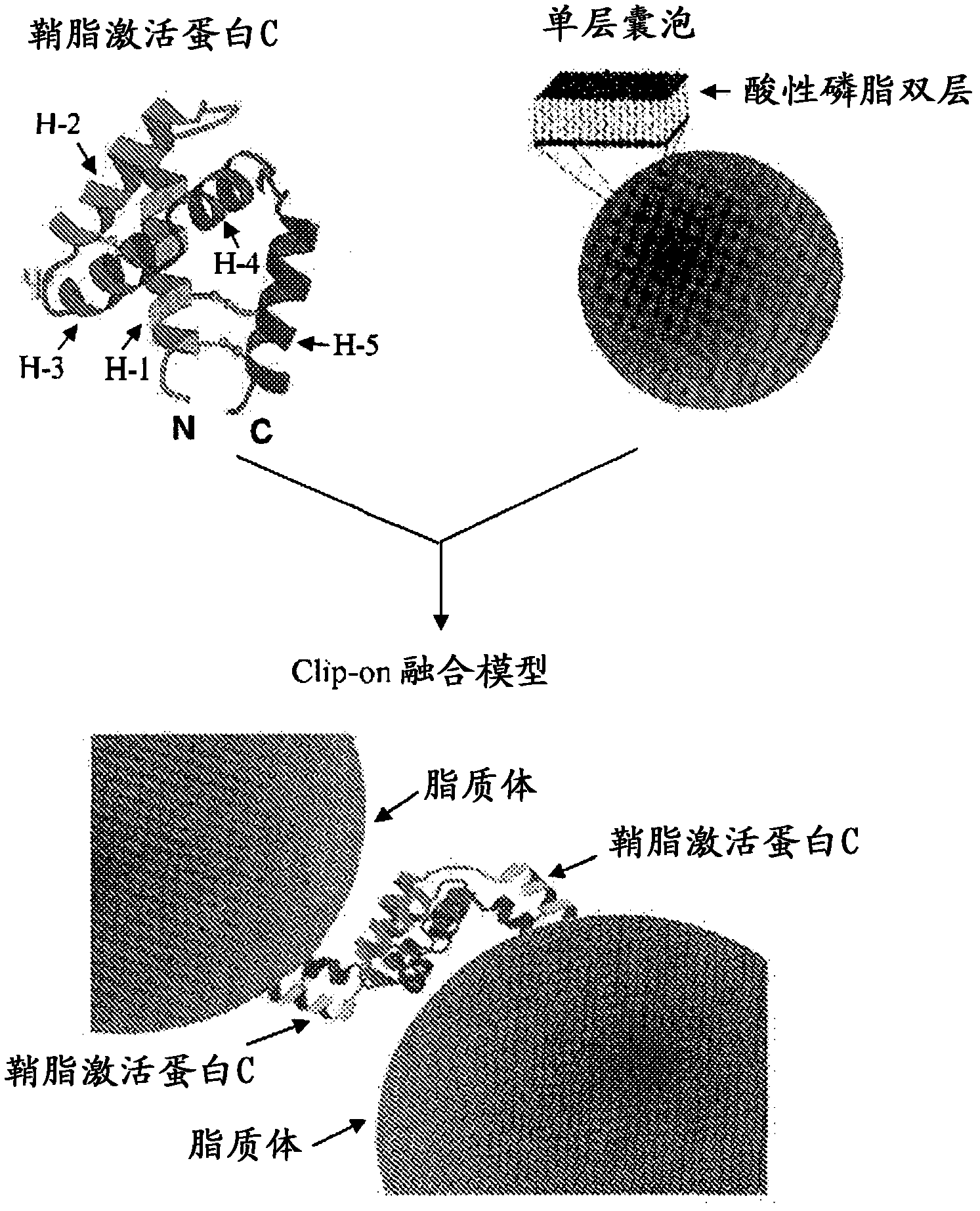
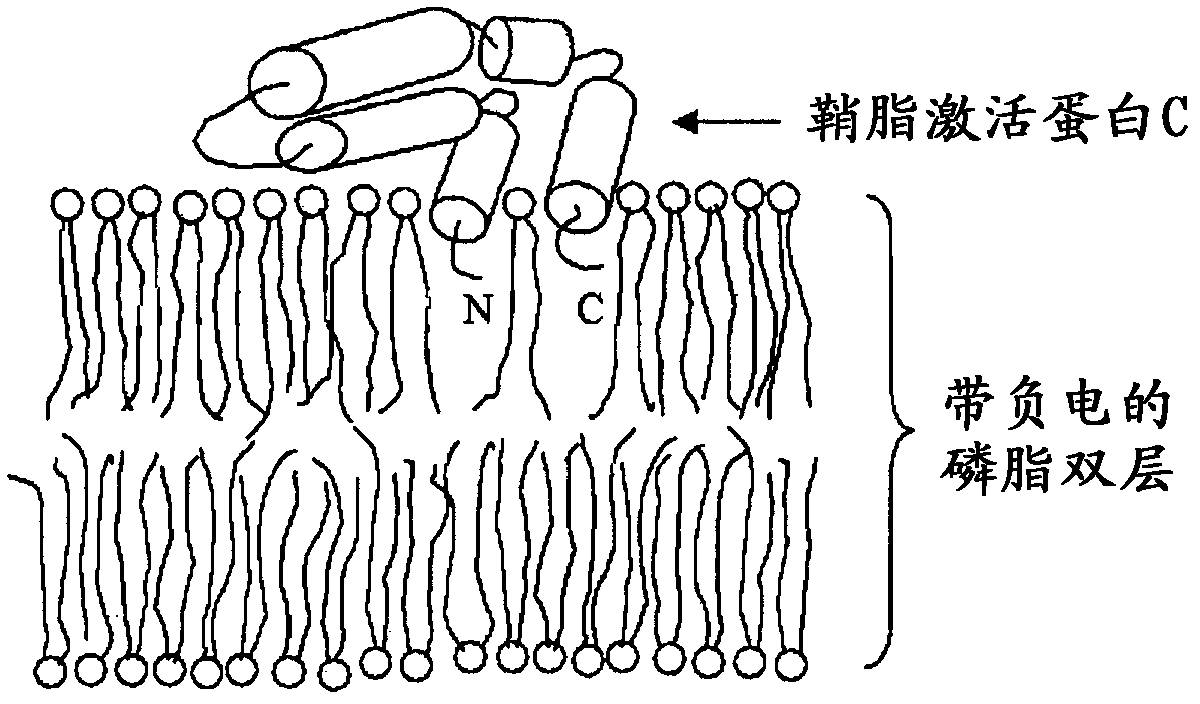
Fusogenic properties of saposin c and related proteins and peptides for transmembrane drug delivery systems
A lipid and phospholipid technology, applied in animal/human protein, drug combination, drug delivery, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0126] A number of methods are available in connection with the preparation of liposome compositions. Thus, liposomes can be prepared using any of a number of conventional liposome preparation techniques, which will be apparent to those skilled in the art. Such techniques include, for example, solvent dialysis, French press, extrusion (with or without freeze-thaw), reverse phase evaporation, simple freeze-thaw, sonication, chelate dialysis, Homogenization, solvent infusion, microemulsions, spontaneous formation, solvent evaporation, solvent dialysis, French pressure cell techniques, controlled detergent dialysis, etc., each involving in different ways Prepare vesicles. See, eg, Madden et al., Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 1990 53, 37-46, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. Suitable freeze-thaw techniques are described, for example, in International Application Serial No. PCT / US89 / 05040, filed November 8, 1989, the disclosure of whi...
Embodiment 1
[0529] Example 1: Saposin C and liposome formulations and in vitro and in vivo delivery
[0530] Materials - The following materials were obtained from commercial sources: mouse laminin, P / S, fetal bovine serum, and DMEM (Gibco BRL, Gaithersborg, MD); Neurobasal medium with B27 supplement (Life Technologies, ); Dicer (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA); pET21a(+) DNA vector, Escherichia coli (E.Coli) host strain [BL21(DE3)] and His Bind resin (Novagen, Medison, WI); conjugated with Monoclonal anti-His antibody to Alexa Fluor488 (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA); goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to fluorescein and sheep anti-mouse antibody conjugated to rhodamine (ICN / CAPPEL, Aurora, OH); anti-fading Reagents (Ventana Medical Systems, Tucson, AZ); C 4 Reverse-phase HPLC column (Alltech Association Inc., Deerfield, IL); DOPS and 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine-N-(7-nitro-2-1,3 -benzoxadiazol-4-yl) (NBD-DOPS) (as stock solution in chloroform) (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster,...
Embodiment 2
[0541] Example 2: Synthesis of Liposomes Using Acidic Long-Chain Lipids, Neutral Long-Chain Lipids and Neutral Short-Chain Lipids
[0542] Materials and methods
[0543] All phospholipids DOPS, DPPC and DHPC were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids in powder form and used without further purification. For dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements, the molar ratio of DOPS to DPPC in the mixture was from about 10 to about 1, for all samples ([DPPC]+[DOPS]) / DHPC=about 4. The lipid mixture was dissolved in filtered ultrapure HO at a total lipid concentration of 10 wt.% using a combination of vortexing and temperature cycling (between 50 and 4 °C). 2 O (Millipore EASYpure UV). then filtered with H 2 O The homogenized 10 wt.% solution was diluted progressively to 5, 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.1 wt.%.
[0544] Lipid sample stocks were diluted 5, 50, and 200-fold with N4 prior to DLS + Particle size analyzer (Coulter, Miami, FL) for analysis. It was determined that the dilution system had...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com