Orally rapidly disintegrating tablet, and process for producing same
An oral fast disintegrating tablet, oral technology, applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations with inactive ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of bad tongue, deterioration of preparation properties, and high hygroscopicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
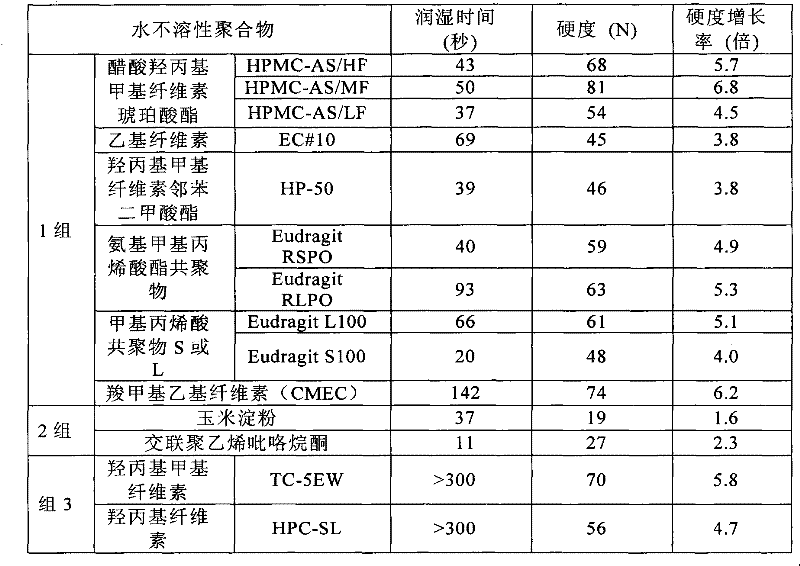
[0083]Excipients (97 parts by weight (or 90 parts by weight)) and water-insoluble A mixture (300 mg) of polymer (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate, HPMC-AS, grade: HF) (3 parts by weight (or 10 parts by weight)) was compression-molded to obtain tablets. The water wettability (wetting time) and hardness of each tablet were measured according to the following evaluation procedure, and based on the measurement results (see Table 1 below), the excipients were divided into the following 2 groups.
[0084] Group A: Excipients with good water wettability and compressibility when the tablet contains water-insoluble polymers, which exhibit tablet wetting times within 300 seconds, and tablet hardness exceeding that of excipients alone. 3 times that of the formulation.
[0085] Group B: Excipients with poor water wettability or compressible formability when the tablet contains a water insoluble polymer, which exhibit a tablet wetting time greater than 300 seconds, and a tab...
experiment example 2
[0094] To a mixture of D-mannitol (97 parts by weight) and various water-insoluble polymers (3 parts by weight) was added 80% (W / W) aqueous ethanol (5 parts by weight). The mixture was kneaded in a stainless steel container, then granulated with a No. 22 mesh sieve described in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, and the resulting granules were dried in a ventilated box type drier at 50° C. for 2 hours to obtain granulated granules. The granulated granules (300 mg) were compression-molded (flat punch: 10 mm in diameter, tableting pressure: 1000 kg / punch) using a tableting analyzer (manufactured by Kikusui Seisakusho Co., Ltd.) to obtain tablets. The water wettability (wetting time) and hardness of each tablet were measured in accordance with the evaluation procedure in Experimental Example 1. Based on the measurement results (Table 2 below), the water-insoluble polymers are divided into the following 3 groups:
[0095] Group 1: Water-insoluble polymers that do not cause a decrease in...
experiment example 3
[0101] According to Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 2, tablets were prepared using various excipients in Experimental Example 1 and a water-insoluble polymer (HPMC-AS / HF). Tablet hardness was measured according to the evaluation procedure in Experimental Example 1. The disintegration time of the tablet in the oral cavity was measured by the following method.
[0102] Disintegration time of the tablet in the mouth:
[0103] Put one tablet in each mouth of three healthy adult males, and measure the time when the tablet is completely disintegrated with saliva when gently put in the mouth (ie, do not chew or vigorously move the tongue, etc.) to calculate the average value.
[0104] result)
[0105] The hardness of each tablet and the disintegration time of each tablet in the oral cavity are shown in Table 3 below. As can be seen from Table 3, the hardness of each tablet (i.e. the tablets of Examples 1 to 3) made by using the excipients of Group A is greater than 4...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com