Cellulose base adsorption material used for removing arsenic ions and fluoric ions in water and preparation method thereof
A cellulose-based, adsorption material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of difficult treatment, high material cost, and many reaction by-products, etc., and achieve a wide working pH. The effect of large range, large specific surface area and high adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Use rice straw as raw material to prepare cellulose (cellulose) obtained after pulverization of paper plates, prepare cellulose (cellulose)-g-PDMAEMA (sample 1), and test the adsorption performance of sample 1
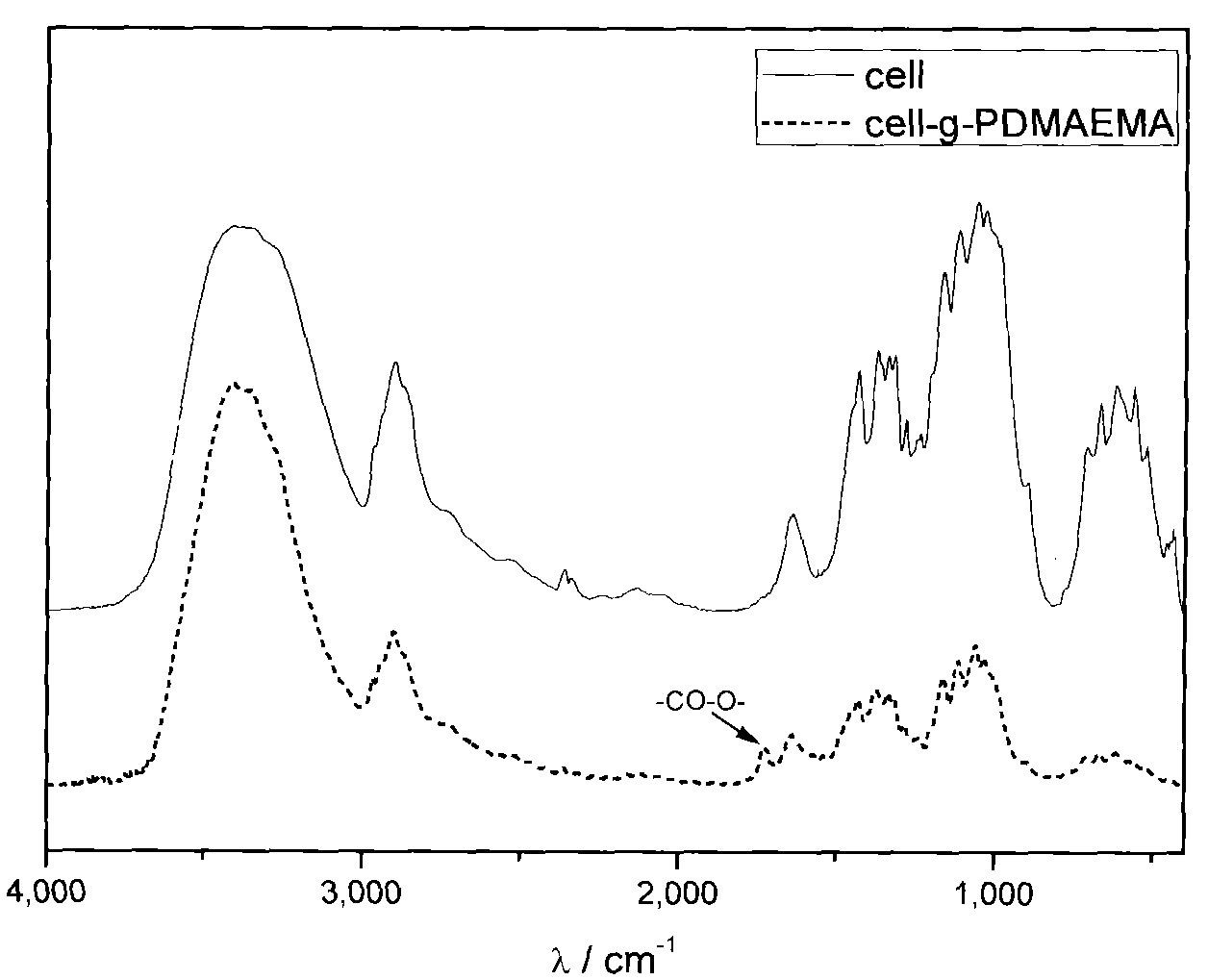
[0033] In a 100ml single-mouth bottle, add 40ml ultrapure water, 1.5g (NH 4 ) 2 Ce(NO 3 ) 6 And 1mL of nitric acid with a mass concentration of 65%-68%, fully dissolve it, then add 0.5g of cellulose fibers with a diameter of 1μm-100μm processed by a pulverizer, fully stir and disperse, bubble with nitrogen for 30 minutes, add 3mL monomer DMAEMA, continue to purge nitrogen for 10 minutes. After sealing, place it in an oil bath at 100°C for 1 hour, and pass Ce in an acidic water system 4+ Initiation of free radical polymerization, graft polymerization of DMAEMA at -OH of cellulose, to obtain amine-containing DMAEMA monomer grafted on the surface of cellulose, and control the grafting of about 18wt% of amine-containing PDMAEMA. Air is introduced to terminate the react...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The cellulose (cellulose) obtained after pulverization of the paper plate prepared with wood chips as raw materials was used to prepare cellulose-g-PDMAEMA (sample 2), and the adsorption performance of sample 2 was tested
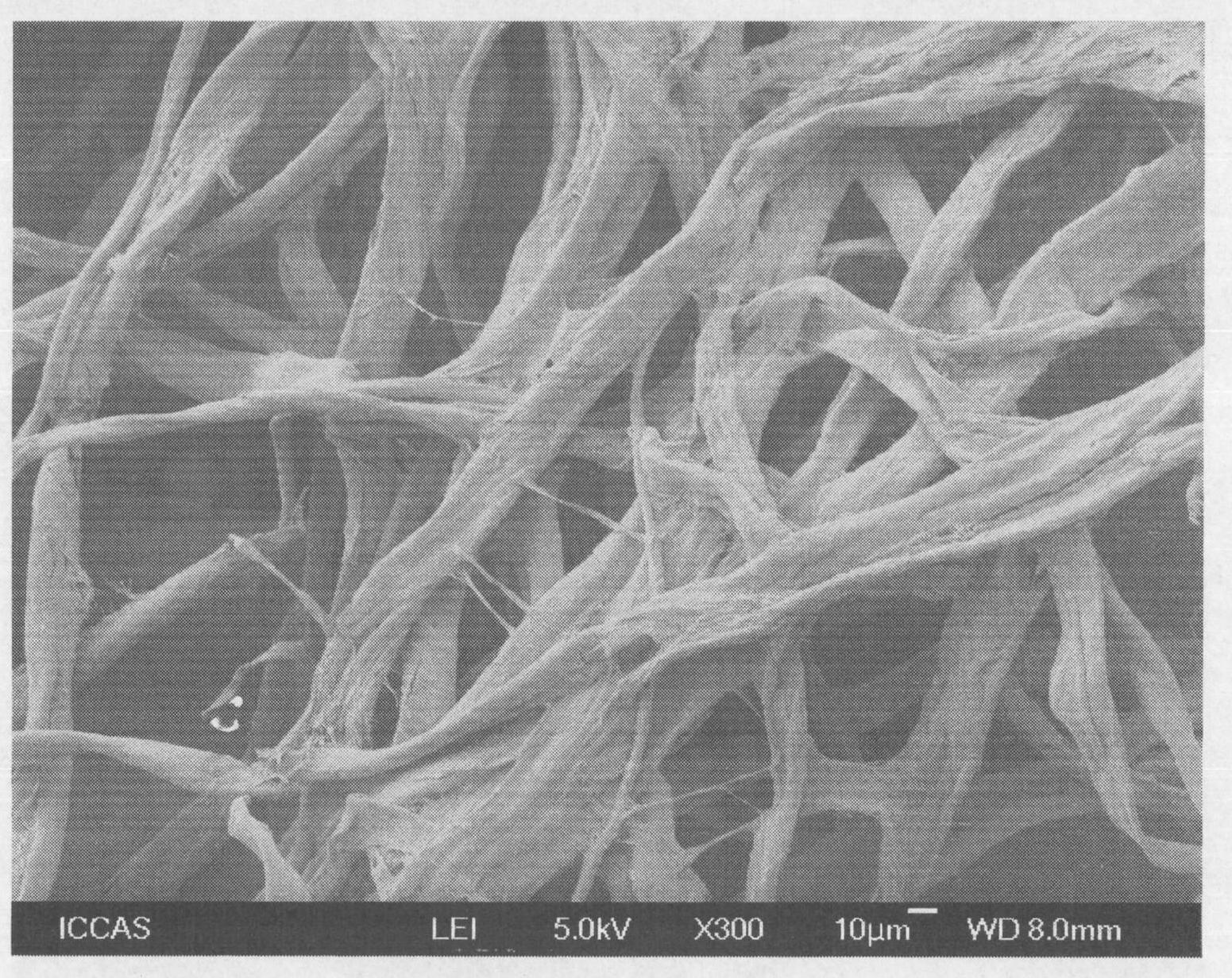
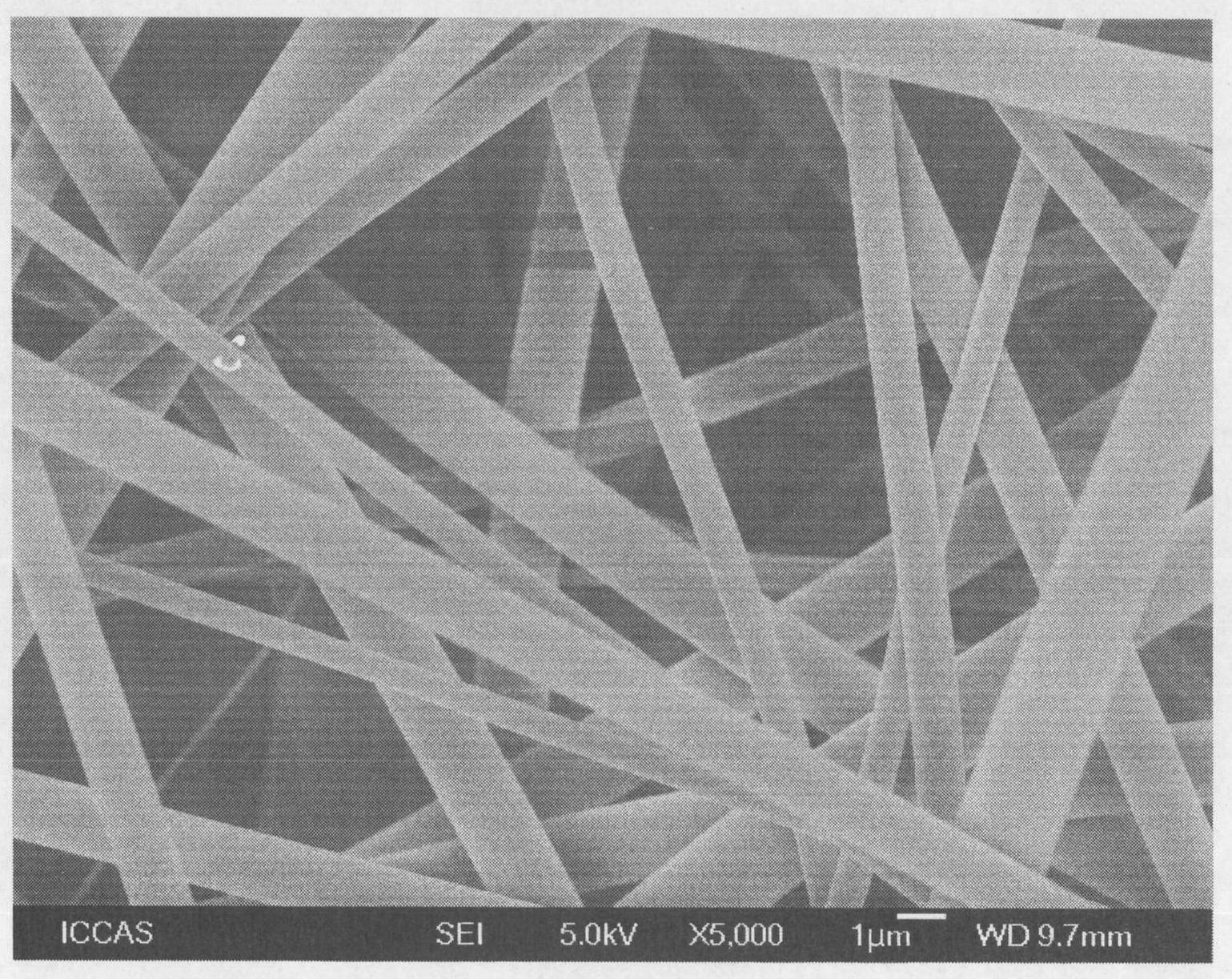
[0037] In a 100ml single-mouth bottle, add 40ml ultrapure water, 1.0g (NH 4 ) 2 Ce(NO 3 ) 6 And 2mL of nitric acid with a mass concentration of 65%-68%, fully dissolve it, and then add 0.5g of cellulose fibers with a diameter of 1μm-100μm processed by a crusher (scanning electron microscope (SEM) photos of cellulose fibers are shown figure 1 ), fully stir and disperse, bubbling with nitrogen for 30 minutes, add 3 mL of monomer DMAEMA, and continue to bubbling with nitrogen for 10 minutes. After sealing, place it in a 40℃ water bath to react for 3 hours, pass Ce in an acidic water system 4+ Initiation of free radical polymerization, graft polymerization of DMAEMA at -OH of cellulose, to obtain amine-containing DMAEMA monomer grafted on the surface of cellu...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The cellulose (cellulose) obtained after pulverization of the paper plate prepared with wood chips as raw materials, the preparation of cellulose-g-PDMAEMA (sample 3), and the test of the adsorption performance of sample 3
[0044] In a 100ml single-mouth bottle, add 40ml ultrapure water, 2.0g (NH 4 ) 2 Ce(NO 3 ) 6 And 3mL of nitric acid with a mass concentration of 65%-68%, fully dissolve it, and then add 0.5g of cellulose fibers with a diameter of 1μm-100μm processed by a pulverizer, fully stir and disperse, bubble with nitrogen for 30 minutes, and add 2mL of monomer DEA, continue to purge nitrogen for 10 minutes. After sealing, place it in a 20℃ water bath to react for 24 hours, and pass Ce in an acidic water system. 4+ Initiate free radical polymerization, graft polymerize DEA at -OH of cellulose, obtain DEA monomer containing amine group on the surface of cellulose, and control grafting about 8wt% of PDEA containing amine group. The reaction was terminated by introduc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com