Active carbon-silicon aerogel complex for removing volatile organic pollutants
A volatile organic and silicon airgel technology, which is applied in the fields of alkali metal compounds, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem of high specific surface area and porosity, low mechanical strength, and large mass transfer resistance and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing adsorption capacity, low cost, and reducing mass transfer resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
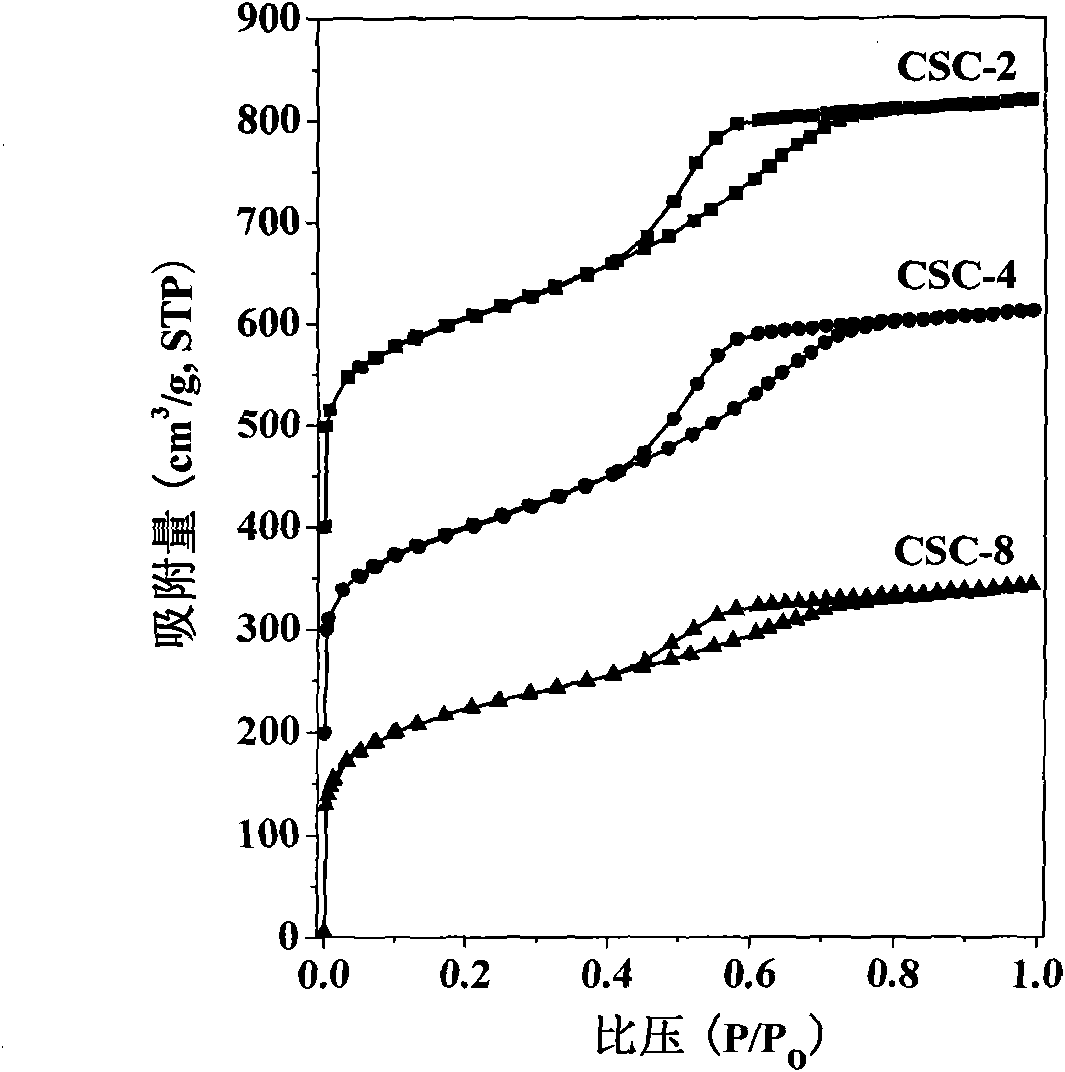
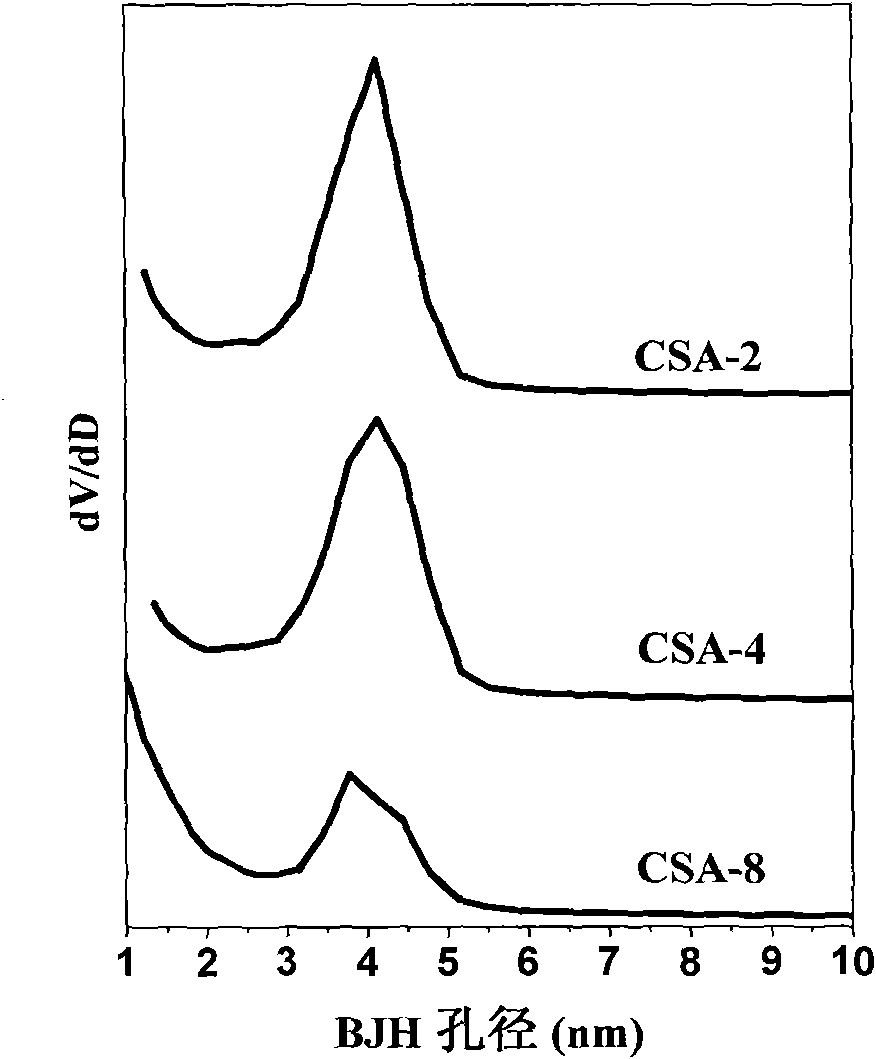
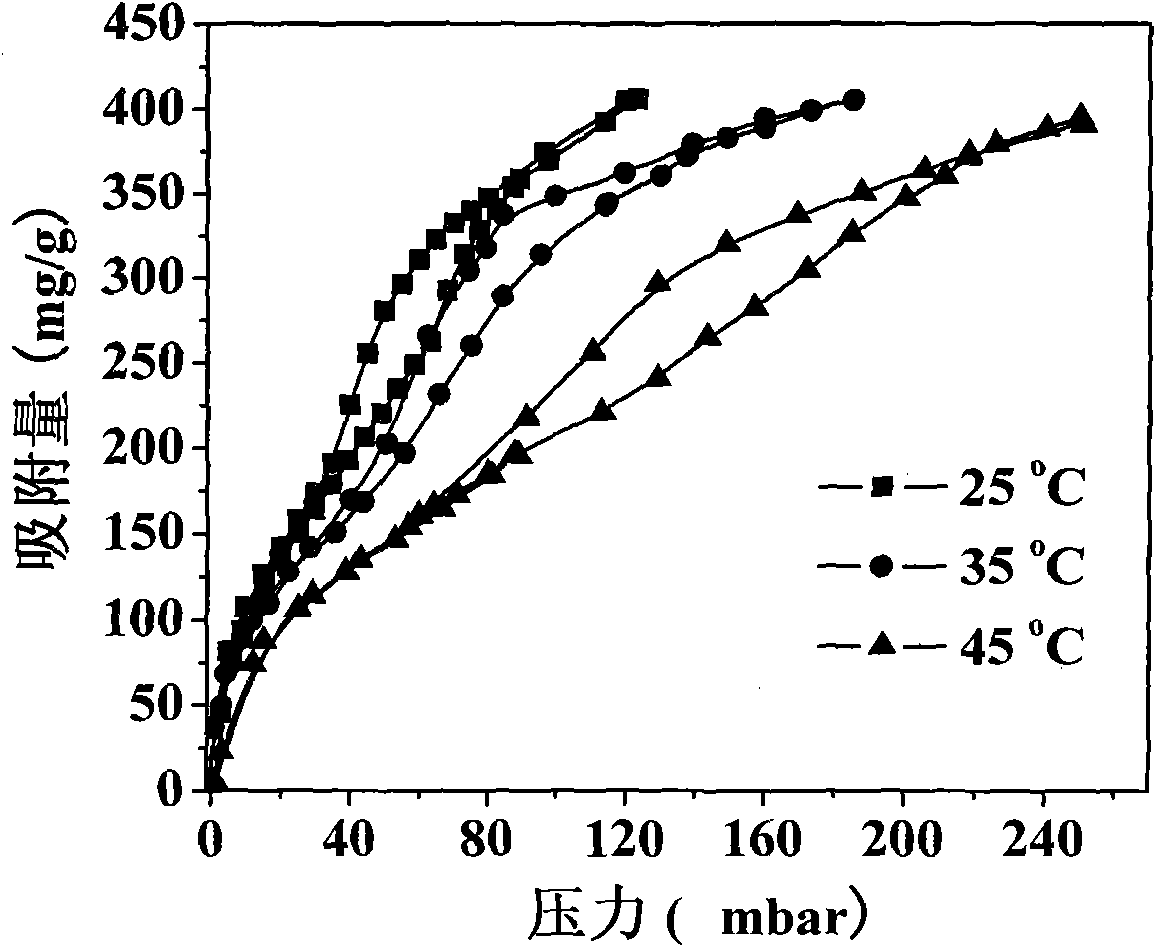
[0022] Example 1: 10 mL of water glass was diluted 4 times with deionized water, and ion-exchanged with a strong acid type cation exchange resin to obtain a silicic acid solution. Under the condition of magnetic stirring, 1 mol / L ammonia water was added dropwise to the silicic acid solution until the pH value rose to 5, and then stood still after stirring. Add 1g of activated carbon powder just before the gel is formed, stir evenly and let it stand for aging. The wet gel was solvent-exchanged with absolute ethanol and n-hexane in turn, and then surface hydrophobized modification was carried out with n-hexane solution containing 20% trimethylchlorosilane. The obtained gel was dried at 60°C, 80°C, 120°C and 180°C under normal pressure for 6 hours to obtain the activated carbon-silica airgel composite CSA-2.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: 10 mL of water glass was diluted 4 times with deionized water, and ion-exchanged with a strong acid type cation exchange resin to obtain a silicic acid solution. Under the condition of magnetic stirring, 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide was added dropwise to the silicic acid solution until the pH value rose to 5, and then left to stand after stirring. Add 2g of activated carbon powder just before the gel is formed, stir evenly and let it stand for aging. The wet gel was solvent-exchanged with absolute ethanol and n-hexane in turn, and then surface hydrophobized modification was carried out with n-hexane solution containing 20% trimethylchlorosilane. The obtained gel was dried at 60°C, 80°C, 120°C and 180°C under normal pressure for 6 hours to obtain the activated carbon-silica airgel composite CSA-4.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3: 10 mL of water glass was diluted 4 times with deionized water, and ion-exchanged with a strong acid type cation exchange resin to obtain a silicic acid solution. Under the condition of magnetic stirring, 1 mol / L ammonia water was added dropwise to the silicic acid solution until the pH value rose to 5, and then stood still after stirring. Add 4g of activated carbon powder just before the gel is formed, stir evenly and let it stand for aging. The wet gel was solvent-exchanged with absolute ethanol and n-hexane in sequence, and then the surface of the wet gel was hydrophobized with a n-hexane solution containing 20% methyltriethoxysilane. The obtained gel was dried at 60°C, 80°C, 120°C and 180°C under normal pressure for 6 hours to obtain the activated carbon-silica airgel composite CSA-8.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com