Method for preparing battery grade indium hydroxide and indium oxide
An indium hydroxide and battery-level technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, gallium/indium/thallium compounds, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate concentration of raw materials and precipitants, low purity of indium hydroxide and indium oxide , uneven fluidity and other issues, to achieve good economic feasibility, low cost, and control the effect of reaction speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
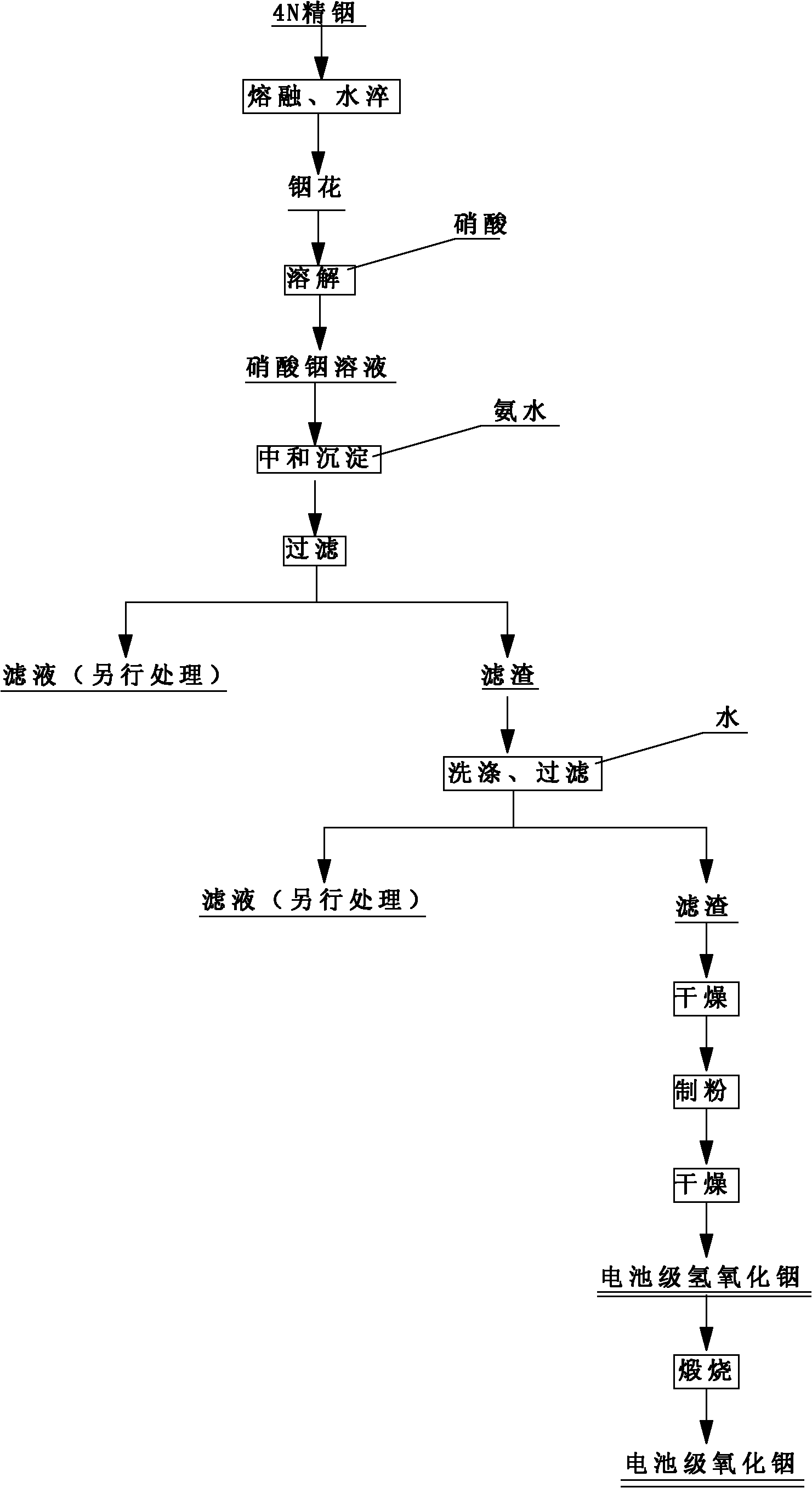
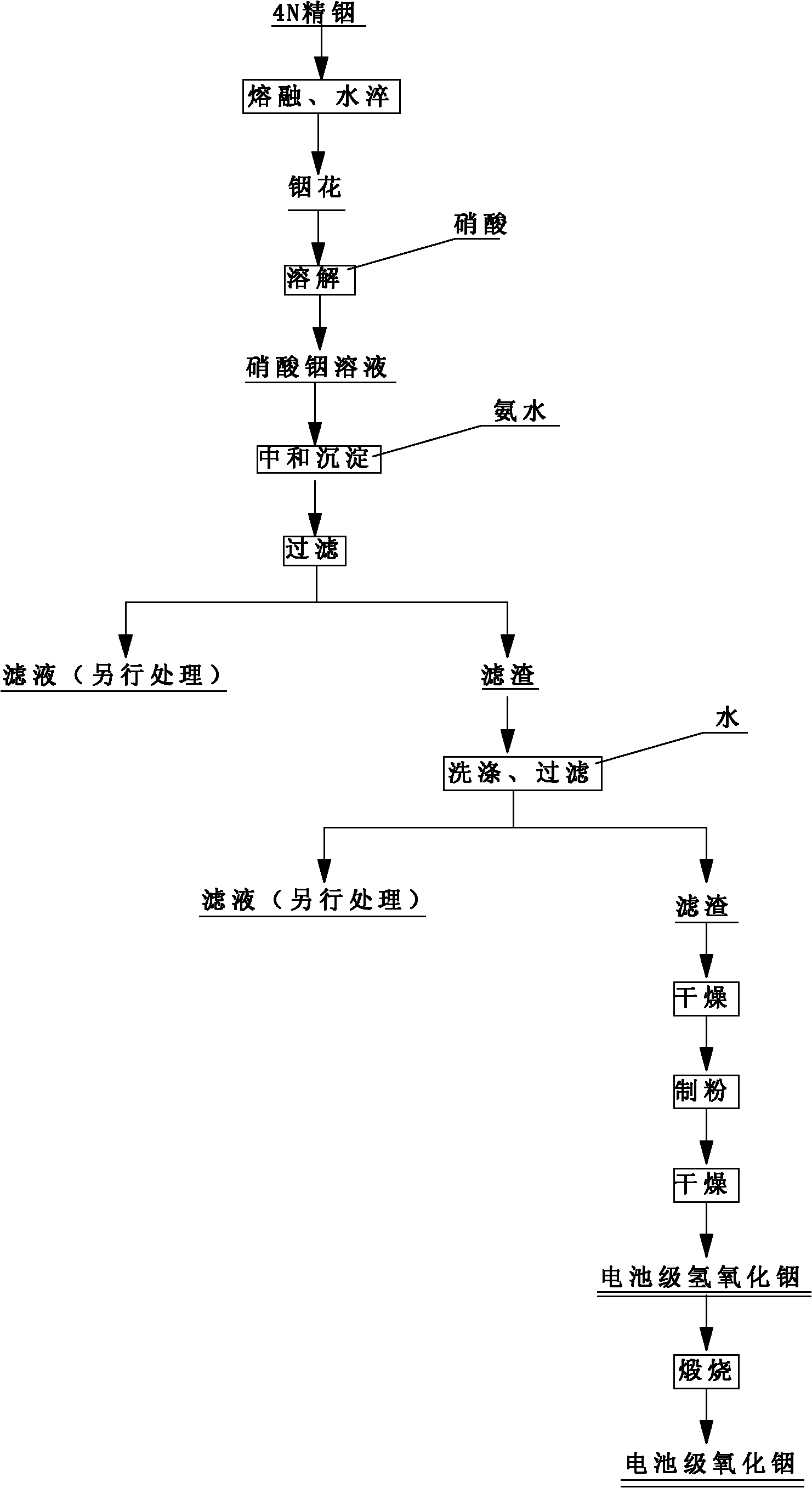
[0051] Melt 500g of 4N indium at 160°C, quench with water to obtain indium flower, take it out and react with nitric acid, that is, slowly add about 500mL of nitric acid with a concentration (wt%) of 68% under constant stirring, and add an appropriate amount of conductivity less than 500us / cm, soluble SiO 2 Less than 0.02mg / L of water, get In 3+ The concentration is 1.5 mol / L indium nitrate solution; 450 mL of ammonia water with a mass concentration of 27% and 1350 mL of water are prepared at a volume ratio of 1:3 to obtain an ammonia solution with a weight concentration of 6.2%. The above-mentioned indium nitrate solution and ammonia solution are simultaneously added with a conductivity of less than 500us / cm and soluble SiO under constant stirring conditions. 2 In a reactor with water lower than 0.02 mg / L as the bottom liquid, the temperature of the reaction system is controlled at 90°C, the process pH is 4.0, and the end pH is 5.0. After the addition, react for 30 minutes and ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Melt 500g of 4N indium at 180℃, quench with water to obtain indium flower, take it out and react with nitric acid, that is, slowly add about 500mL of nitric acid with a concentration (wt%) of 68% under constant stirring, and add an appropriate amount of conductivity less than 500us / cm, soluble SiO 2 Less than 0.02mg / L of water, get In 3+ The concentration is 1.0 mol / L indium nitrate solution; 450 mL of ammonia water with a weight concentration of 27% and 900 mL of water are prepared at a volume ratio of 1:2 to obtain an ammonia solution with a weight concentration of 8.3%. The above-mentioned indium nitrate solution and ammonia solution are simultaneously added with a conductivity of less than 500us / cm and soluble SiO under constant stirring conditions. 2 In a reactor with water less than 0.02 mg / L as the bottom liquid, the temperature of the reaction system is controlled to 80°C, the process pH is 4.5, and the end pH is 5.2. After the addition, react for 40 minutes and f...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Melt 500g of 4N indium at 200℃, quench with water to obtain indium flower, take it out and react with nitric acid, that is, slowly add about 500mL of nitric acid with a concentration (wt%) of 68% under constant stirring, and add an appropriate amount of conductivity less than 500us / cm, soluble SiO 2 Less than 0.02mg / L of water, get In 3+ The concentration is 0.5 mol / L indium nitrate solution; 450 mL of ammonia water with a weight concentration of 27% and 450 mL of water are prepared at a volume ratio of 1:1 to obtain an ammonia solution with a weight concentration of 12.8%. Add the above-mentioned indium nitrate solution and aqueous ammonia solution under constant stirring conditions with a conductivity of less than 500us / cm and soluble SiO 2 In a reactor with water lower than 0.02 mg / L as the bottom liquid, the temperature of the reaction system is controlled at 60°C, the process pH is 5.0, and the end pH is 6.0. After the addition, react for 50 minutes and filter to obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com