Method for recycling heavy metal pollution wastes
A recycling method and waste technology, which is applied in the field of harmless resource recycling, can solve the problem of no separation and recycling of various heavy metals, and achieve the effect of wide process adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
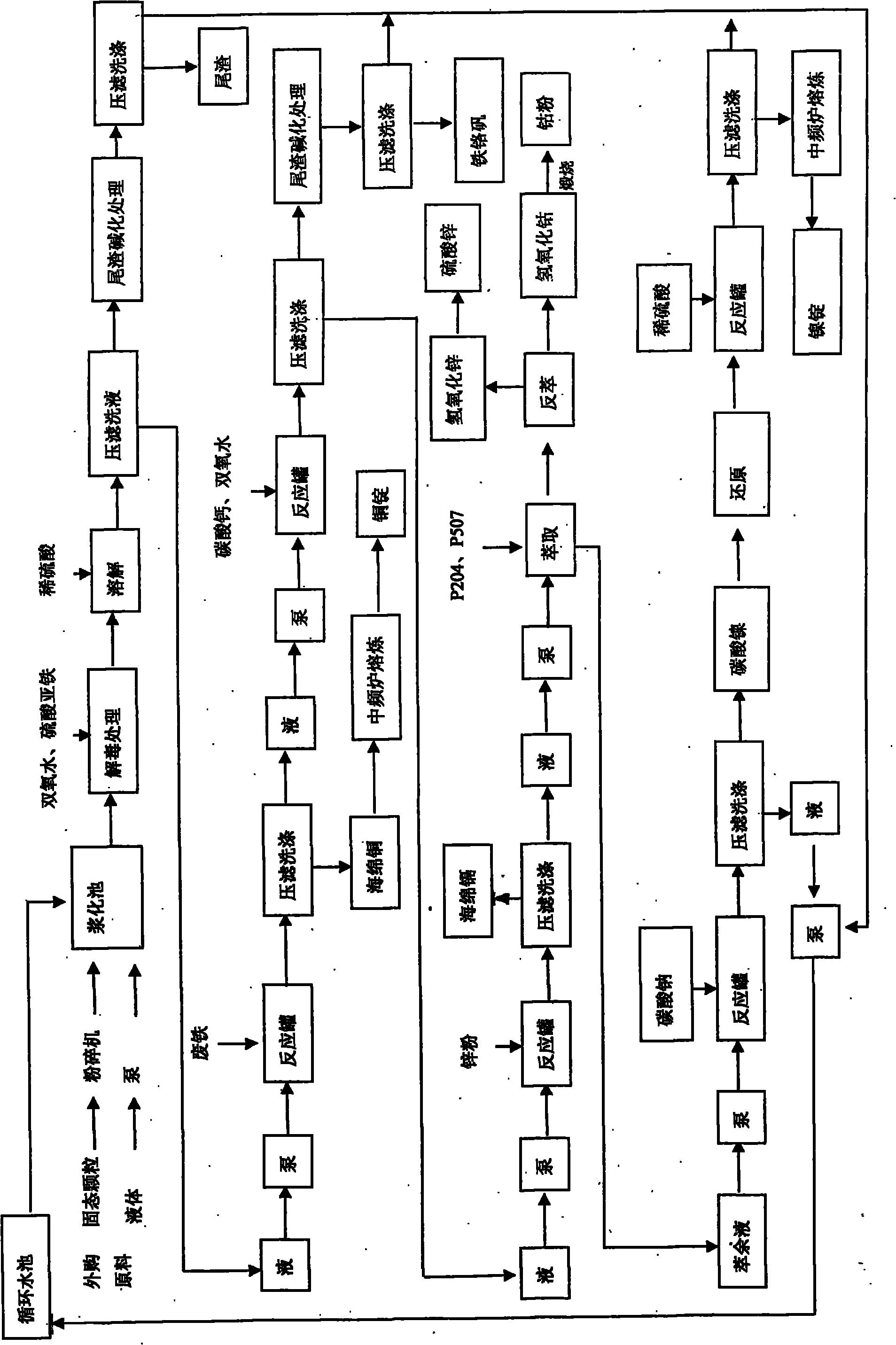
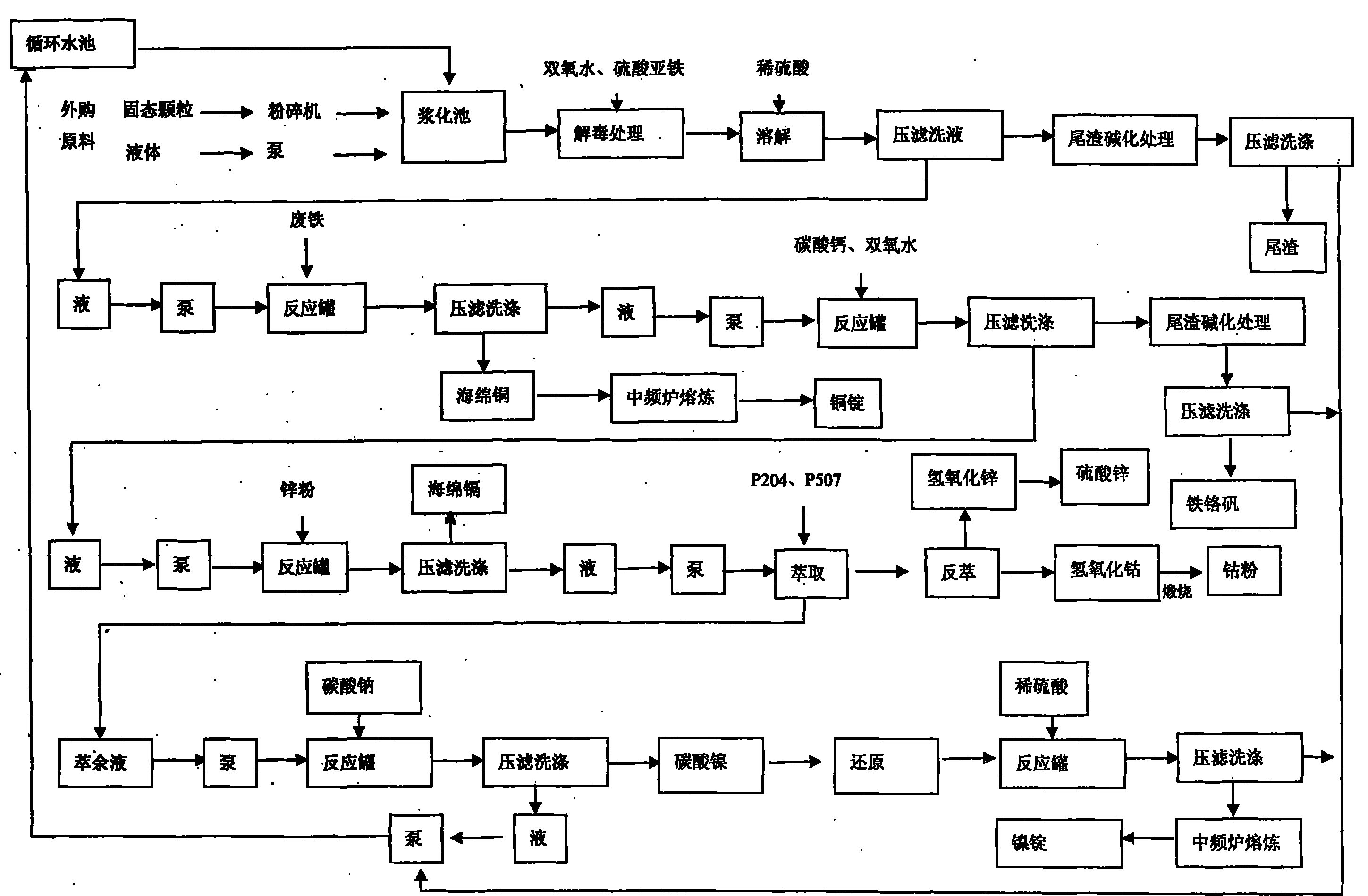
[0052] One embodiment comprises the following steps: 1) Raw material pulping: 1 ton of solid bulk raw material is crushed and crushed and put into the pulping tank, and 3 tons of water is added to make slurry (if it is muddy raw material or waste liquid, it can be directly put into the pulping tank ). 2) Acid leaching and dissolving: concentrated sulfuric acid (concentration is 98%) in the sulfuric acid reaction tank is slowly dripped into water from the top and diluted to dilute sulfuric acid with a concentration of 20% to 30%. The reaction tank is equipped with a mechanical stirrer, and the temperature is controlled below 30°C by controlling the stirring speed and the dripping speed of concentrated sulfuric acid. The prepared dilute sulfuric acid flows into the reaction tank containing the mixed liquid product of step 1 by using the drop, and the pH value is adjusted to 1.0-2.5 , the compounds of nickel, cobalt, copper, zinc, chromium, and cadmium in the raw materials are di...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Steps 1 to 5 are the same as in Example 1, and the following steps are added after step 5: a) extraction: the filtrate of step 5 is sent to the extraction system, separated by P204 and P507; b) producing nickel and cobalt powder: extracting Add 1.4 tons of sodium carbonate liquid with a concentration of 7%-10% to the raffinate, adjust the pH value to 7.8-9.0, press filter to obtain nickel carbonate, dry and heat at 600-800°C for reduction, the optimal reducing agent is starch or Materials with reducing properties of carbon and hydrogen, after washing, melt and cast to obtain 0.05 tons of nickel ingots; the extract obtained in the extraction step is subjected to back extraction to obtain cobalt liquid and zinc liquid, and the cobalt liquid is added with a concentration of 10% to 15% sodium hydroxide Precipitate the liquid, adjust the pH value to 7.8-8.5, press filter and wash to obtain cobaltous hydroxide, dry and calcinate to obtain 0.03 tons of cobalt powder; the filtra...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Repeat the same steps in Example 2, and increase the following steps on the basis of Example 2: the gained zinc solution is added with a concentration of 10% to 15% sodium hydroxide liquid to adjust the pH to 7.0-7.8, and it is washed by pressure filtration to obtain hydrogen oxide Zinc, 0.25 tons of zinc sulfate is obtained after acidification treatment; the filtrate is recycled.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com