Controlled-release multilayer drug-loaded artificial bone and preparation method thereof
A technology of artificial bone and drug loading, which is applied in the fields of medical science, bone implants, and medical devices, and can solve the problems of no relevant reports on 3D printing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Preparation of isoniazid-rifampicin controlled-release drug-loaded artificial bone
[0048] 1) Select L-polylactic acid (molecular weight: 100k / GPC) as the carrier material, pulverize it with a pulverizer, screen the powder with a particle size of about 150 μm, and mix it with excipients polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose E50 by 96 : 2: 2 (mass ratio) fully mix and set aside;
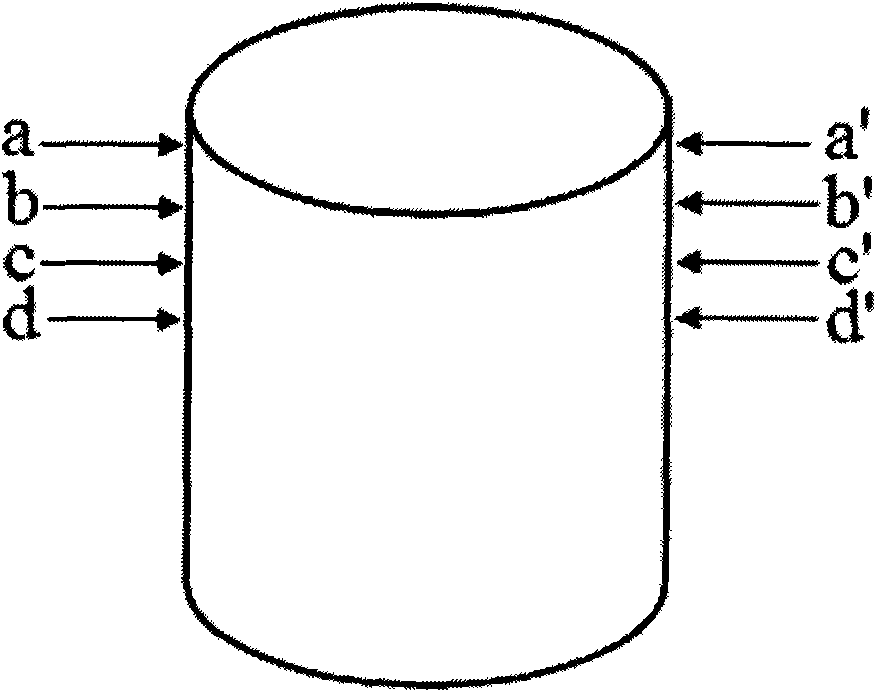
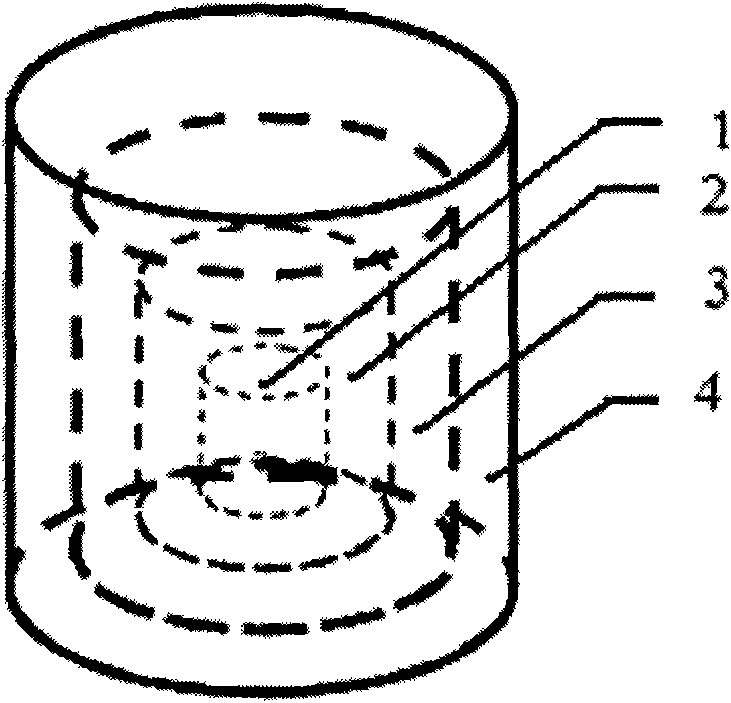
[0049] 2) Two anti-tuberculosis drugs with different mechanisms of action, isoniazid and rifampicin, are selected for use (in terms of design, these two drugs are placed on the second and fourth layers and the first and third layers respectively, and the design is a two-drug sequential release, also known as double-drug double-peak release, hierarchical structure see figure 2 ;)
[0050] 3) Take 80ml of acetone, 8ml of ethanol, 12ml of distilled water and 0.5ml of glycerin and mix them in the container, then add 1g of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 1.5g of sodium lauryl sulfate ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Preparation of levofloxacin single-drug controlled-release drug-loaded artificial bone
[0063] Select L-polylactic acid (molecular weight: 100k / GPC) as the carrier material, pulverize it with a pulverizer, screen the powder with a particle size of about 150 μm, and mix it with excipients polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose E50 at a ratio of 96:2 : 2 (mass ratio) fully mix and set aside. Levofloxacin was selected as a representative drug, placed on the second and fourth layers respectively, and designed as a single-drug pulse release. Take 80ml of acetone, 8ml of ethanol, 12ml of distilled water and 0.5ml of glycerin and mix them in the container, then add 1g of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 1.5g of sodium lauryl sulfate and 0.2g of sodium chloride to fully dissolve, and prepare a bonding liquid. 20ml was injected into print head 1 (i.e. blank ink cartridge) for later use, and another 20ml of the above-mentioned adhesive liquid was added, and 3g of levofl...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Preparation of levofloxacin-tobramycin controlled-release drug-loaded artificial bone
[0067] Select L-polylactic acid (molecular weight: 100k / GPC) as the carrier material, pulverize it with a pulverizer, screen the powder with a particle size of about 150 μm, and mix it with excipients polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose E50 at a ratio of 96:2 : 2 (mass ratio) fully mix and set aside. Two antibiotics with different mechanisms of action, levofloxacin and tobramycin, were selected as representative drugs, placed in layers 2 and 4 and layers 1 and 3 respectively, and designed as a double-drug sequential release (also known as double-drug double-peak release) . Take 80ml of acetone, 8ml of ethanol, 12ml of distilled water and 0.5ml of glycerin and mix them in the container, then add 1g of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 1.5g of sodium lauryl sulfate and 0.2g of sodium chloride to fully dissolve, and prepare a bonding liquid. Add 3g of tobramycin to 20ml to p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com