Method for polyethylene to graft glycidyl methacrylate
A technology of branching methacrylic acid and glycidyl ester, which is applied in the field of grafting, can solve the problems of cumbersome processing, harsh reaction conditions, and difficult recycling, and achieve the effects of simple processing, high grafting rate, and convenient recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
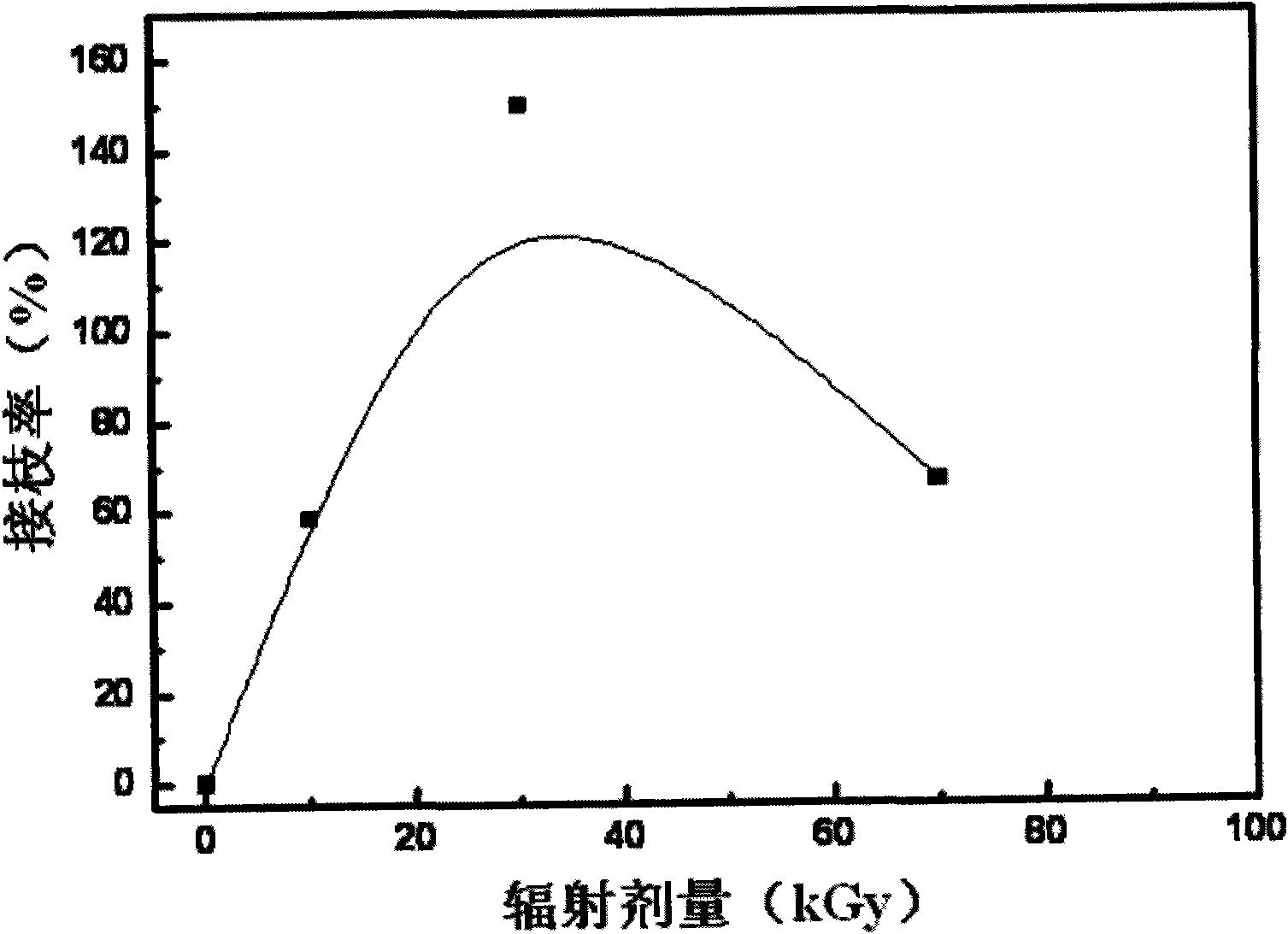
[0025] The influence of embodiment 1 radiation dose on grafting rate
[0026] Polyethylene non-woven fabric grafted with glycidyl methacrylate, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) Use electron beams to irradiate PE non-woven fabrics at room temperature in air, and the radiation doses are 10kGy, 30kGy, and 70kGy;
[0028] (2) Add GMA, 0.5% Tween-20 and water by 5% by volume, the amount of water used is to make the total volume of the system 100mL, and stir for 1 hour to make the GMA disperse evenly;
[0029] (3) Add 0.2 g of pre-radiation PE non-woven fabric, add a vent valve, vent nitrogen to remove oxygen, and then seal;
[0030] (4) The above reaction system was stirred and reacted at 100 rpm in a water bath at 55°C for 15 minutes;
[0031] (5) Stop the reaction, take out the grafted non-woven fabric, extract it with acetone and put it into a vacuum drier for drying.
[0032] Calculate the grafting rate under different radiation doses, the results are as follows ...
Embodiment 2
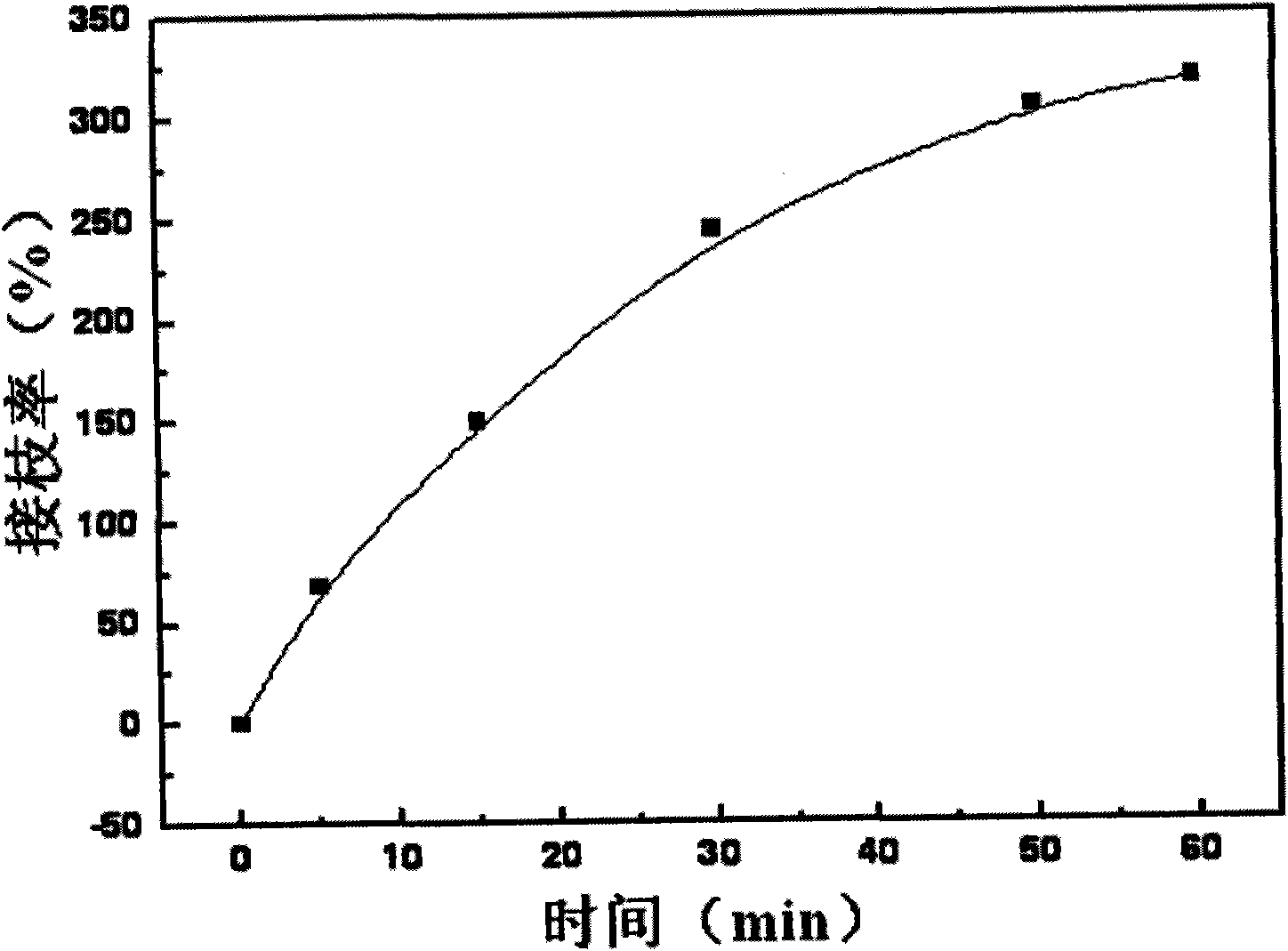
[0033] The influence of embodiment 2 grafting reaction time on grafting rate
[0034] Polyethylene non-woven fabric grafted with glycidyl methacrylate, comprising the following steps:
[0035] (1) Use electron beams to irradiate PE non-woven fabrics at room temperature in air, and the radiation dose is 30kGy;
[0036] (2) GMA, 0.5% Tween-20 and water were added at a volume ratio of 5%, and the amount of water used was to make the total volume of the system 100 mL. Stir for 1 hour to disperse the GMA evenly;
[0037] (3) Add 0.2 g of pre-radiation PE non-woven fabric, add a vent valve, vent nitrogen to remove oxygen, and then seal;
[0038] (4) Stir the above system in a water bath at 55° C. at a speed of 100 rpm and react for a certain period of time;
[0039] (5) Stop the reaction, take out the grafted non-woven fabric, extract it with acetone and put it into a vacuum drier to dry.
[0040] Calculate the grafting rate under different grafting reaction time, the result is ...
Embodiment 3
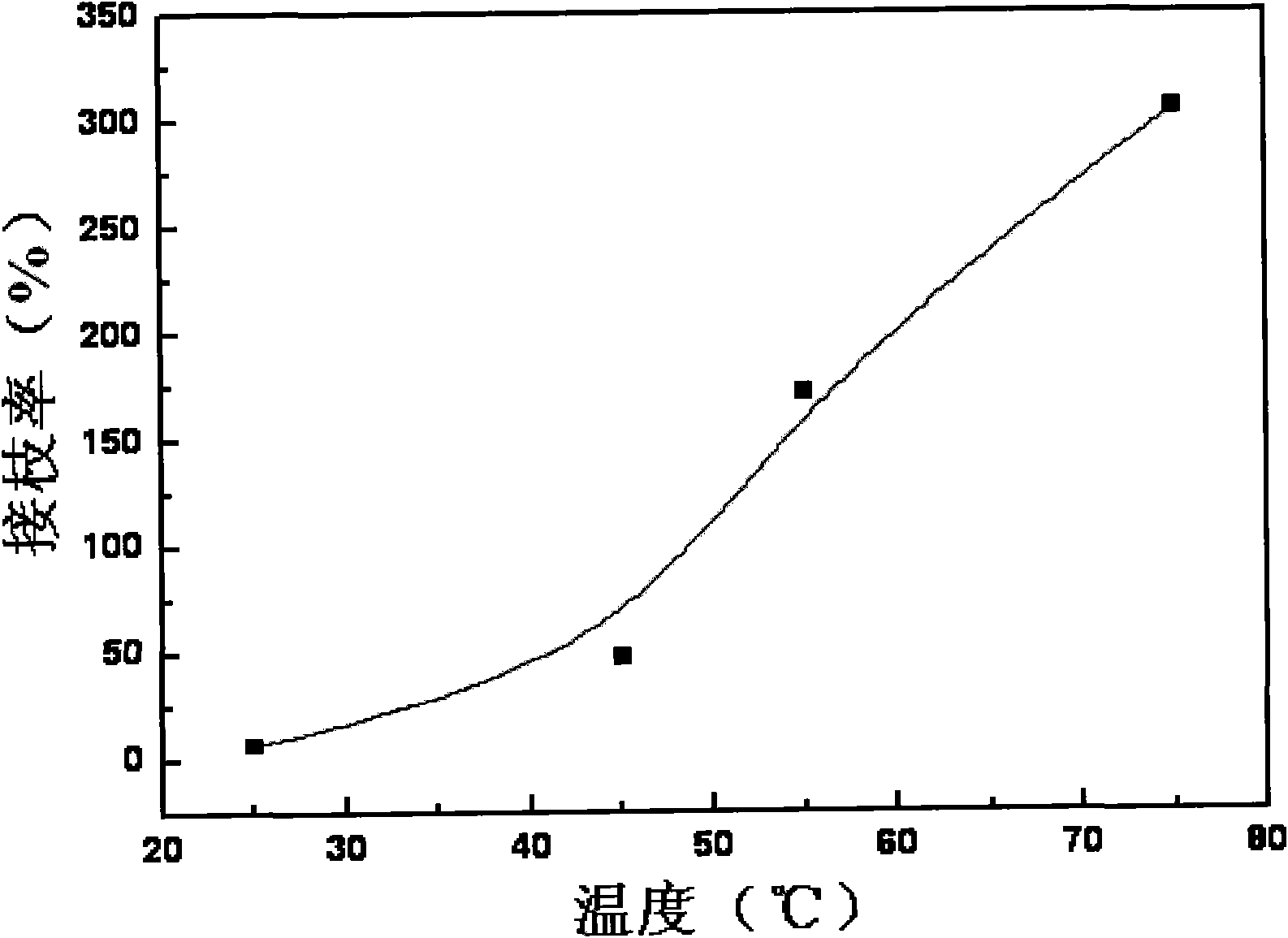
[0041] The influence of embodiment 3 temperature on grafting rate
[0042] Polyethylene non-woven fabric grafted with glycidyl methacrylate, comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) Use electron beams to irradiate PE non-woven fabrics at room temperature in air, and the radiation dose is 30kGy;
[0044] (2) GMA, 0.5% Tween-20 and water were added at a volume ratio of 5%, and the amount of water used was to make the total volume of the system 100 mL. Stir for 1 hour to disperse the GMA evenly;
[0045] (3) Add 0.2g of pre-irradiated PE non-woven fabric, add a vent valve, vent nitrogen to remove oxygen, and then seal;
[0046] (4) The above system was stirred and reacted at 100 rpm in a water bath at 25°C, 45°C, 55°C, and 75°C for 15 minutes;
[0047] (5) Stop the reaction, take out the grafted non-woven fabric, extract it with acetone and put it into a vacuum drier to dry.
[0048] Calculate the grafting rate at different grafting reaction temperatures, the results are as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com