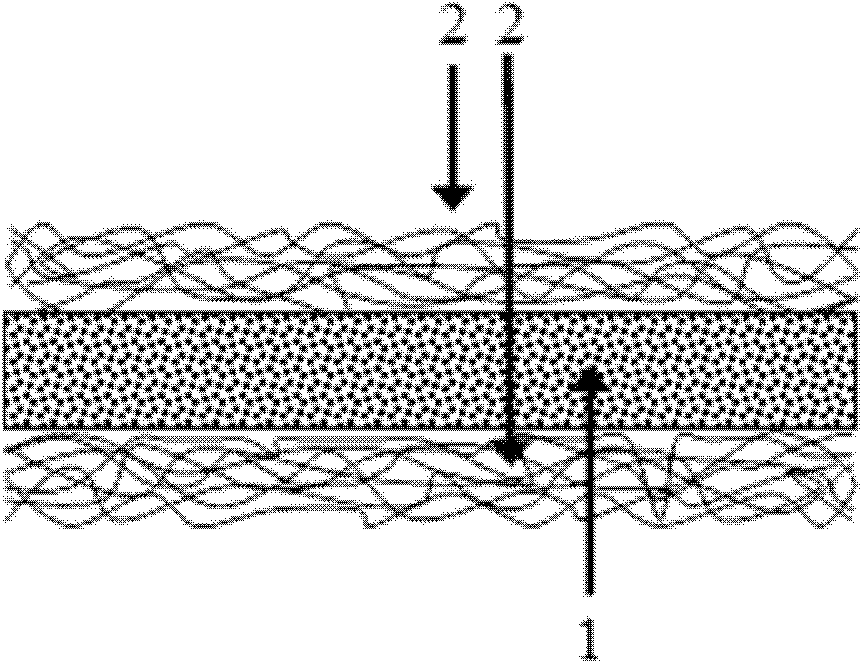
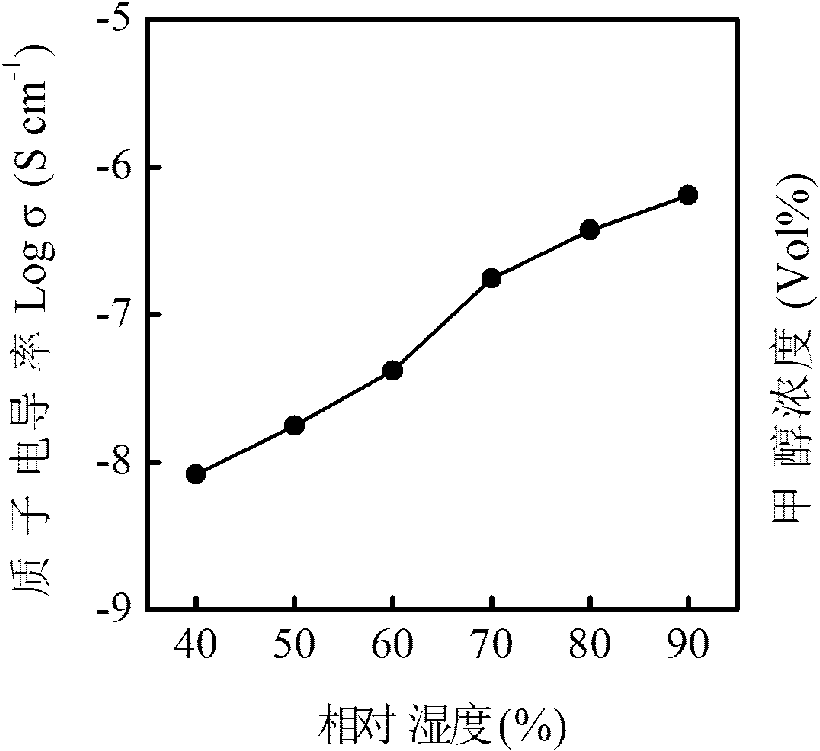
Free-standing sandwich structure composite proton conducting film and preparation method thereof
A proton-conducting membrane and proton-conducting technology, applied in structural parts, solid electrolyte fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the complexity of membrane electrode preparation and application limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Step 1: Prepare a sacrificial layer. Poly(p-styrenesulfonic acid) (PSS, Aldrich) was dissolved in deionized water to prepare a 5 wt% aqueous solution of PSS. Place the substrate on a spin coater at 3000 rpm for 1 minute to spin coat the PSS sacrificial layer.
[0041] Step 2: Prepare the organic layer. A polymer of formaldehyde, (chloromethyl)oxirane and 2-methylphenol (PCGF, Aldrich) was mixed with polyethyleneimine (PEI, Aldrich) in chloroform at a mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare 1 wt% solution. Spin-coat the PEI / PCGF organic layer on the substrate obtained in step 1 at 3000 rpm for 1 minute.
[0042] Step 3: Prepare the inorganic layer. Ethyl orthosilicate: n-propanol: water: hydrochloric acid: C 16 h 33 (OC 2 h 4 ) 10 OH (CEO, Aldrich) = 1: 11.4: 5: 0.004: 0.1 ratio preparation (CEO) SiO 2 Sol. Spin coat surfactant-containing SiO at 3000 rpm for 1 min 2 layer on the substrate obtained in step 2.
[0043] Step 4: Prepare the organic layer. Coating material...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Step 1: Prepare a sacrificial layer. Dissolve PSS in deionized water to prepare a 20 wt% PSS aqueous solution. Place the substrate on a spin coater at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute to spin coat the PSS sacrificial layer.
[0047] Step 2: Prepare the organic layer. PCGF and PEI were mixed in chloroform at a mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare a 50 wt% solution. Start the spin coater, and coat the PEI / PCGF organic layer on the substrate obtained in step 1.
[0048] Step 3: Prepare the inorganic layer. First, tetraethyl orthosilicate, deionized water, and hydrochloric acid were mixed according to the ratio of 1:4:4×10 -3 The molar ratio was vigorously stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Then according to 5%P 2 o 5 -95% SiO2 2 The molar percentage of phosphoric acid was slowly added to the solution and stirred for 20 minutes. The prepared sol was dropped on the substrate in step 2, held at 1000 rpm for 1 minute, spin-coated to obtain a phosphosilicate layer.
[0049] S...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Step 1: Prepare a sacrificial layer. Dissolve PSS in deionized water to prepare a 0.1 wt% PSS aqueous solution. Put the substrate on the spin coater, keep it at 100 rpm for 5 minutes, start the spin coater, and coat the PSS sacrificial layer.
[0054] Step 2: Prepare the organic layer. PCGF and PEI were mixed in chloroform at a mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare a 0.1 wt% solution. Start the spin coater at 1000 rpm, hold for 1 minute, and spin coat the PEI / PCGF organic layer on the substrate obtained in step 1.
[0055] Step 3: Prepare the inorganic layer. zirconium n-butoxide: acetylacetone: water: propanol: surfactant F127 (BASF Corporation) = 1:5:5:20:0.01 ratio to prepare the sol. Dilute zirconium n-butoxide in butanol in proportion, add acetylacetone and water, stir at room temperature for 1h; surfactant F127 was dissolved in 5 times the volume of butanol and stirred at room temperature for 1 h; the above two solutions were mixed and stirred continuously at room ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com