Clean regeneration process for ion exchange fiber material
A technology of ion exchange fiber and process, applied in the field of functional polymer materials, can solve the problems of sucrose production system pollution, increase production cost, cost increase, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, pollution avoidance and high regeneration rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
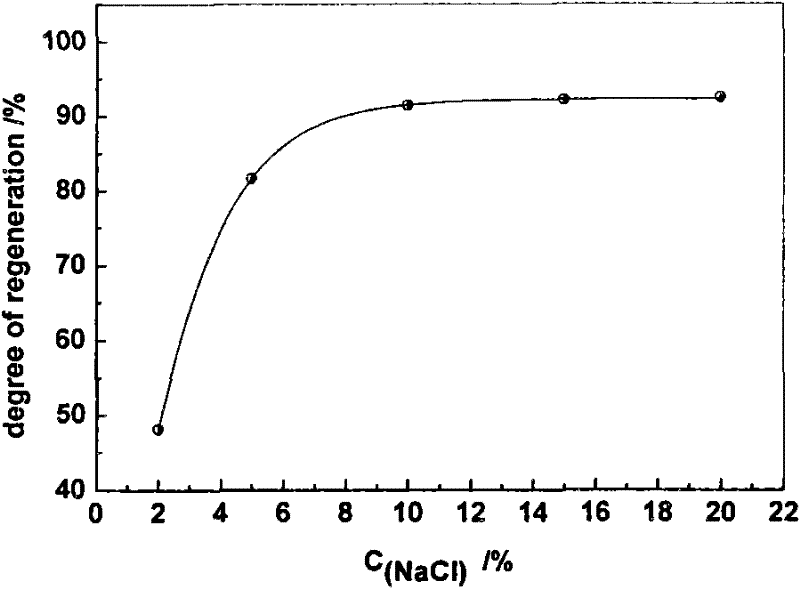
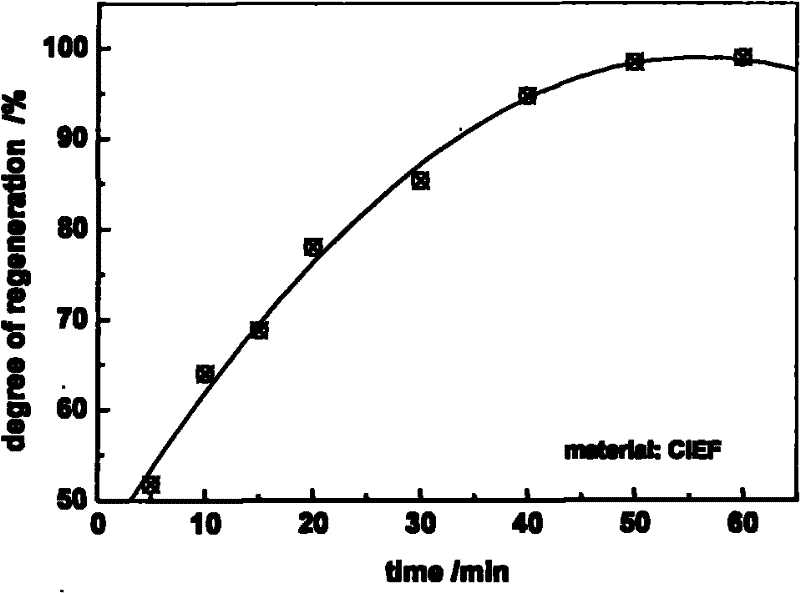
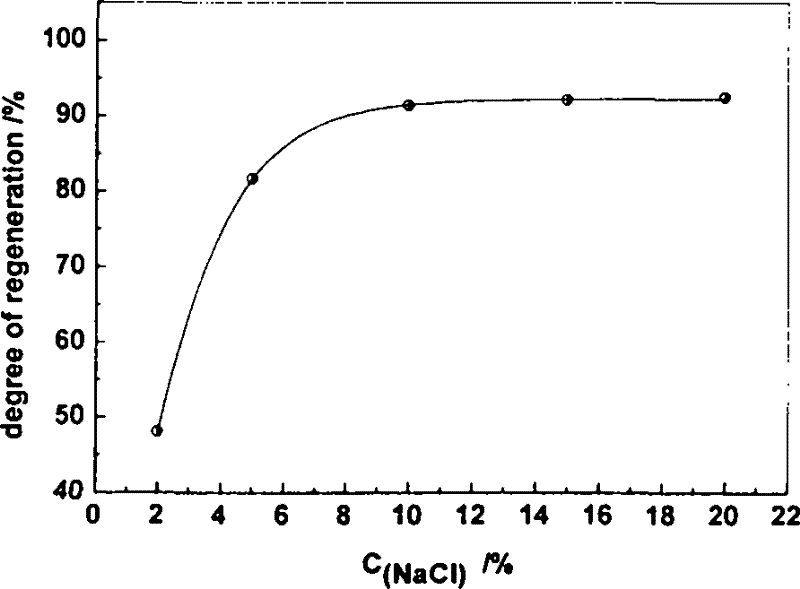
[0019] Weigh 0.5 g of polypropylene-based cation exchange fibers into a weighing bottle, and vacuum-dry to constant weight. Alternately soak the material with 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide and 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid to activate the functional groups. Soak the pretreated fiber material in 50 mL of a 1.0% solution containing calcium and magnesium ions in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, and vibrate at 30° C. for 2 hours in a constant temperature oscillator. Filter out the exchanged fiber material, measure the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the solution before and after soaking by titration, and calculate the amount of calcium and magnesium ions adsorbed and exchanged per gram of fiber. Rinse the fibers until neutral, soak them in 50 mL of 10.0% food-grade NaCl solution prepared in advance, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the food-grade NaCl solution to pH 6, and shake in a constant temperature oscillator at 70°C for 1 hour. Titrate the concentration of calcium and ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Weigh 0.5 g of polyacrylonitrile-based cation exchange fibers into a weighing bottle, and vacuum-dry to constant weight. Alternately soak the material with 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide and 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid to activate the functional groups. Soak the pretreated fiber material in 50 mL of a 1.0% solution containing calcium and magnesium ions in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, and vibrate at 30° C. for 2 hours in a constant temperature oscillator. Filter out the exchanged fiber material, measure the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the solution before and after soaking by titration, and calculate the amount of calcium and magnesium ions adsorbed and exchanged per gram of fiber. Rinse the fiber until it is neutral, soak it in 50 mL of 15.0% food-grade NaCl solution prepared in advance, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the food-grade NaCl solution to pH 5, and shake it in a constant temperature oscillator at 90°C for 1 hour. Titrate the concentration of ca...
Embodiment 3
[0023] Weigh 0.5 g of polypropylene-based cation exchange fibers into a weighing bottle, and vacuum-dry to constant weight. Alternately soak the material with 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide and 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid to activate the functional groups. Soak the pretreated fiber material in 50 mL of a 1.0% solution containing calcium and magnesium ions in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, and vibrate at 30° C. for 2 hours in a constant temperature oscillator. Filter out the exchanged fiber material, measure the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the solution before and after soaking by titration, and calculate the amount of calcium and magnesium ions adsorbed and exchanged per gram of fiber. Rinse the fibers until neutral, soak them in 20.0% 50mL food-grade NaCl solution prepared in advance, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the food-grade NaCl solution to pH 5, and shake in a constant temperature oscillator at 70°C for 1 hour. Titrate the concentration of calcium and magn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com