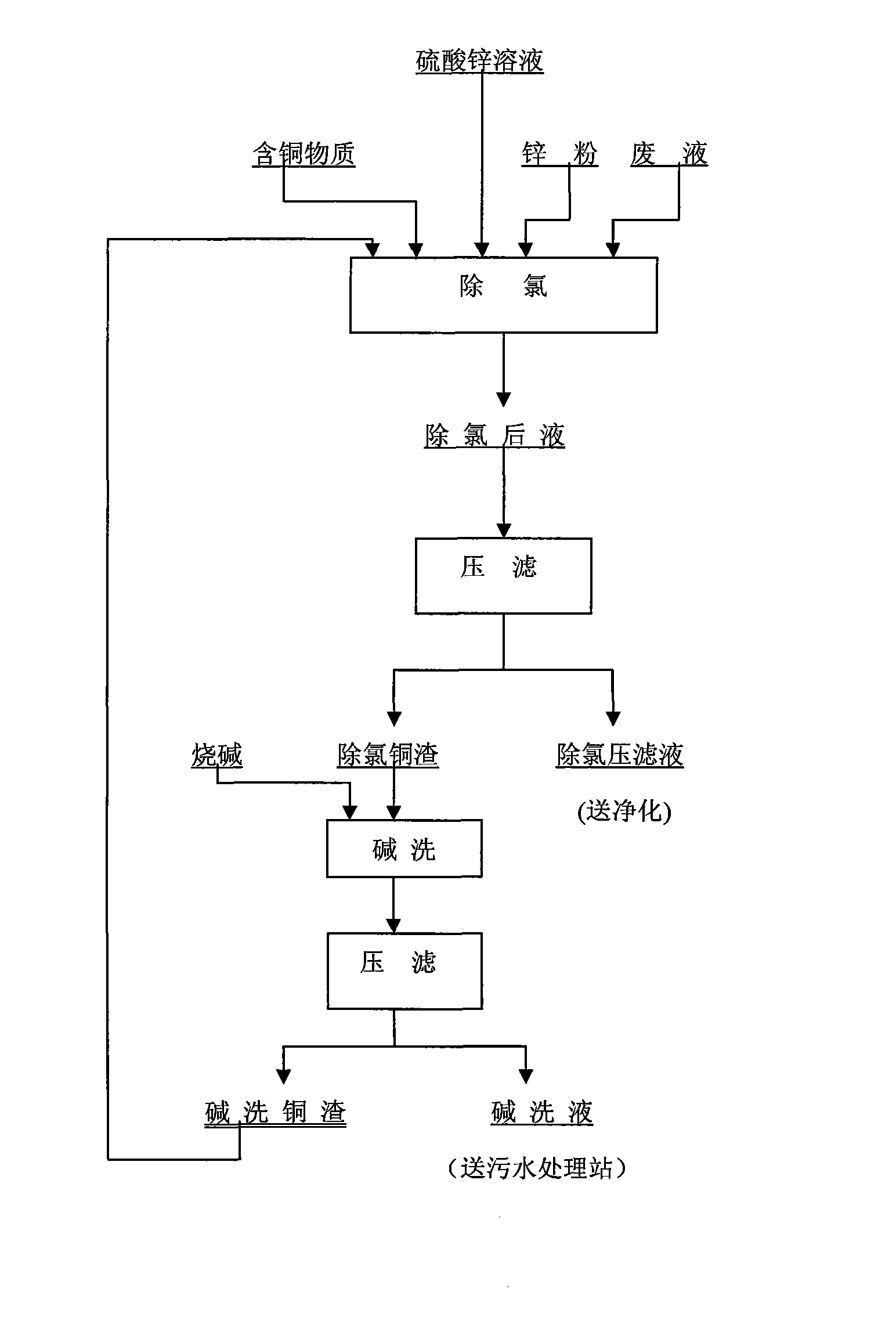
Method for circularly removing chlorine in zinc sulphate solution by copper slag
A technology of zinc sulfate solution and copper slag, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to guarantee dechlorination effect, difficult process control, high production cost, etc., achieve good dechlorination effect, less reagent consumption, Less interference from external factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Before copper slag is produced, the dechlorinated copper ions come from copper sulfate. In this example, only copper sulfate is added.
[0038] Chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution to be dechlorinated: Cl 1.36g / l, Zn 130g / l, Cu 0.2g / l, Fe 0.025g / l, Cd 0.7g / l; chemical composition of solid copper sulfate: Cu 20.1% ,; Electrolytic waste: H 2 SO 4 175g / l. The production process conditions are shown in Table 1:
[0039] Table 1: Process conditions for removing ammonia in zinc sulfate solution
[0040] Alkali washing copper slag
Intake (kg / h)
copper sulfate added
Quantity (kgh)
electrolytic waste stream
Quantity (m 3 / h)
Addition amount of zinc powder
(kg / h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Flow (m 3 / h)
temperature reflex
(℃)
0
540
0.09
28
30
40
[0041] Chlorine removal results of zinc sulfate solution:
[0042] The chemical composition of zinc sulfate so...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The chemical composition of a batch of zinc sulfate solution to be dechlorinated: Cl 1.1g / l, Zn 140g / l, Cu 0.3g / l, Fe 0.02g / l, Cd 0.8g / l; alkaline cleaning copper slag is the last operation Return, its chemical composition: Cu 33.5%, Cl 3.2%; electrolytic waste solution: H 2 SO 4 170g / l. The production process conditions are shown in Table 2:
[0048] Table 2: Process conditions for removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
[0049] Alkali washing copper slag
Intake (kg / h)
copper sulfate added
Quantity(kg / h)
electrolytic waste stream
Quantity (m 3 / h)
Addition amount of zinc powder
(kg / h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Flow (m 3 / h)
temperature reflex
(℃)
46
0
0.1
4
40
65
[0050] The result of chlorine removal by zinc sulfate solution is:
[0051] The chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution after chlorine removal: Cl 0.22g / l, Zn 138g / l, Cu 2.1g / l, Fe0.0...
Embodiment 3
[0055] When the copper ions in the returned copper slag are insufficient, additional copper sulfate is properly supplemented. This is the case in this case.
[0056] The chemical composition of the zinc sulfate solution to be dechlorinated is: Cl 1.15g / l, Zn 130g / l, Cu 0.3g / l, Fe 0.2g / l, Cd 1.2g / l; the chemical composition of the alkaline cleaning copper slag: Cu 35.3%, Cl 3.4%; copper sulfate liquid Cu 40g / l. The production process conditions are shown in Table 3:
[0057] Table 3: Process conditions for removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
[0058] Alkali washing copper slag
Intake (kg / h)
copper sulfate added
Quantity (kgh)
electrolytic waste stream
Quantity (m 3 / h)
Addition amount of zinc powder
(kg / h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Flow (m 3 / h)
temperature reflex
(℃)
45
1
0.15
1.5
20
90
[0059] Chlorine removal results of zinc sulfate solution:
[0060] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com