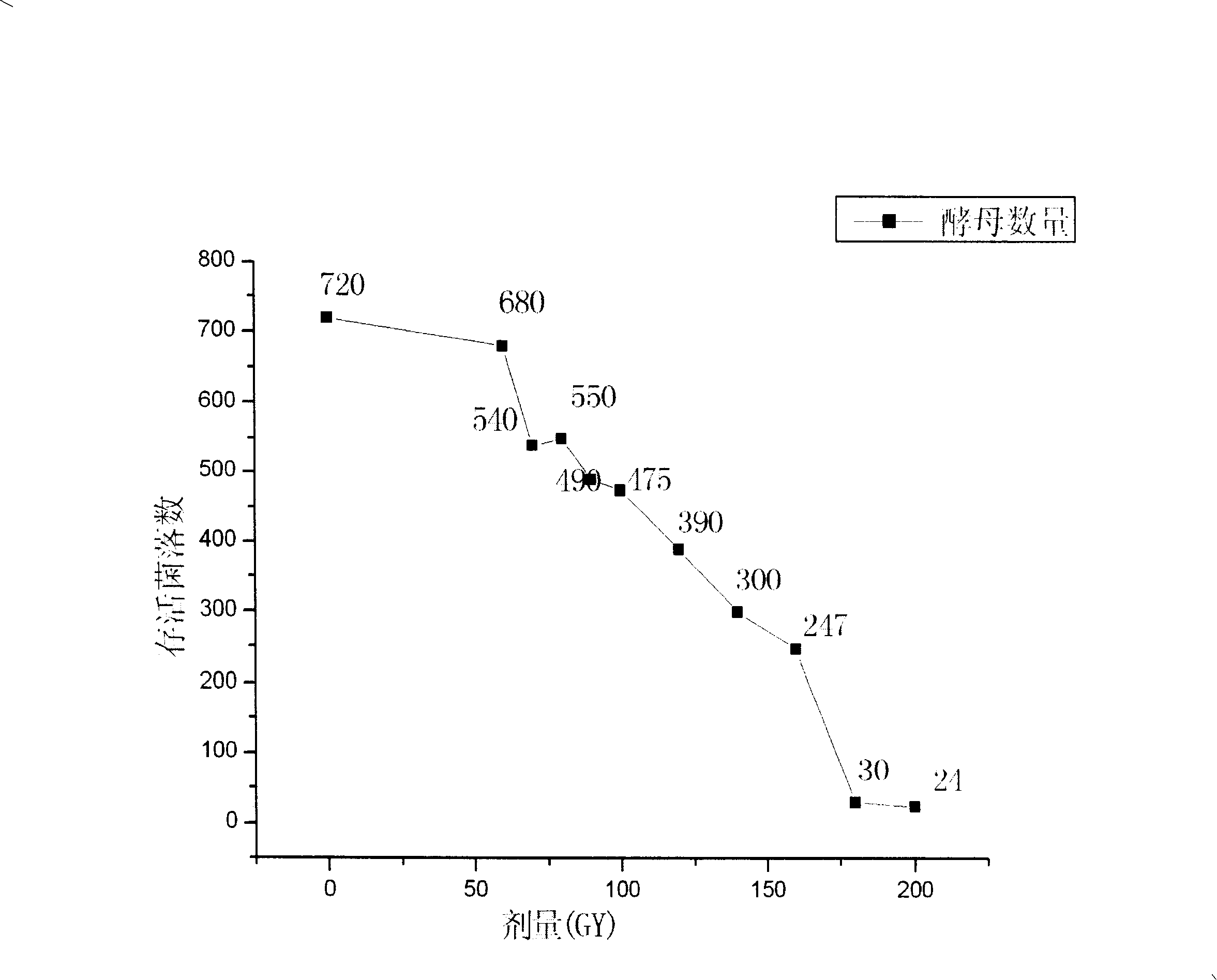Optimizing method of high temperature resistant distillery yeast
A technology of alcoholic yeast and optimization methods, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and treatment of microorganisms with electricity/wave energy, can solve problems such as long cycle, low temperature tolerance, and single optimization method, and achieve Strong fermentation power, stable performance, and the effect of improving economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Treatment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with high dose rate pulsed electron beams
[0028] Preparation of irradiated samples: Inoculate the starting strain Saccharomyces cerevisiaewo (purchased from Sigma) into 100ml liquid YPD medium, cultivate at 36°C, activate for 18 hours, then take 0.5ml bacterial solution into EP (eppendorf) tube, centrifuge at 5000r / min, repeated three times. The samples were pretreated by freeze-drying and vacuum-drying at room temperature.
[0029] Set different irradiation doses (0-200Gy) respectively, and measure the survival curve of yeast ( figure 1 ), after the yeast was irradiated and diluted to spread on the plate, the number of colonies in each plate was recorded 24 hours later. The result is as figure 1 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that with the increase of the irradiation dose, the number of yeast colony survival has an overall downward trend, but the decline in the survival curve from 70Gy to 100Gy ten...
Embodiment 2
[0031] High temperature acclimatization of sample after embodiment 2 irradiation
[0032] The four groups of irradiated yeast samples obtained in Example 1 were respectively cultured in YPD liquid medium at 36°C for 4h, then inoculated into 100ml YPD liquid medium respectively, enriched and cultured at 41°C for 48h, diluted and then coated with YPD plate. Cultivate at 41°C, take unirradiated yeast as a control, and record the colony growth every day. And through multiple times of high-temperature acclimatization and screening (that is, culture for three days at a culture temperature of 36°C, pick out well-grown, round and full-bodied colonies, and then culture for three days under the culture conditions that the transfer culture temperature is increased by 0.5°C, repeat the above steps until the temperature is raised to the point where the strain cannot grow.)
[0033] Finally, strains resistant to high temperature 43.5°C, 43°C, 42.5°C, and 42°C were obtained for each group r...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3 repeated experiments
[0035] Adopt the method of embodiment 1 and 2, carry out irradiation time to departure bacterial strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae and be respectively 10s, 12s, 15s, 17s, 20s, 22s, 25s, and irradiation dose rate is respectively 10s 9 Gy / s, 1.2X10 9 Gy / s, 1.5X10 9 Gy / s, 1.7X10 9 Gy / s, 2X10 9 Gy / s, 2.2X10 9 Gy / s and 2.5X10 9 Gy / s irradiation treatment and high temperature acclimatization screening, two groups were set up for each dose rate. As a result, each group could normally grow more than 20 single colonies in the YPD solid medium plate at 41 °C, that is, all of them can obtain high temperature resistance. Strains above 41°C. This shows that the method of the present invention optimizes the high temperature resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has good repeatability, and can obtain Saccharomyces cerevisiae with high temperature resistance of at least 41°C.
[0036] Example 3 Analysis of ethanol content in the fermentation o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com