Novel modification-specific signal Conus superfamily toxin and uses thereof
A post-translational modification and conch technology, which is applied to the new signal cono P-superfamily toxin with post-translational modification and its application field, can solve the problems of in vitro expression of rare conotoxin genes and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Separation and purification of signal conotoxin lt9b, identification by mass spectrometry and Edman degradation sequencing
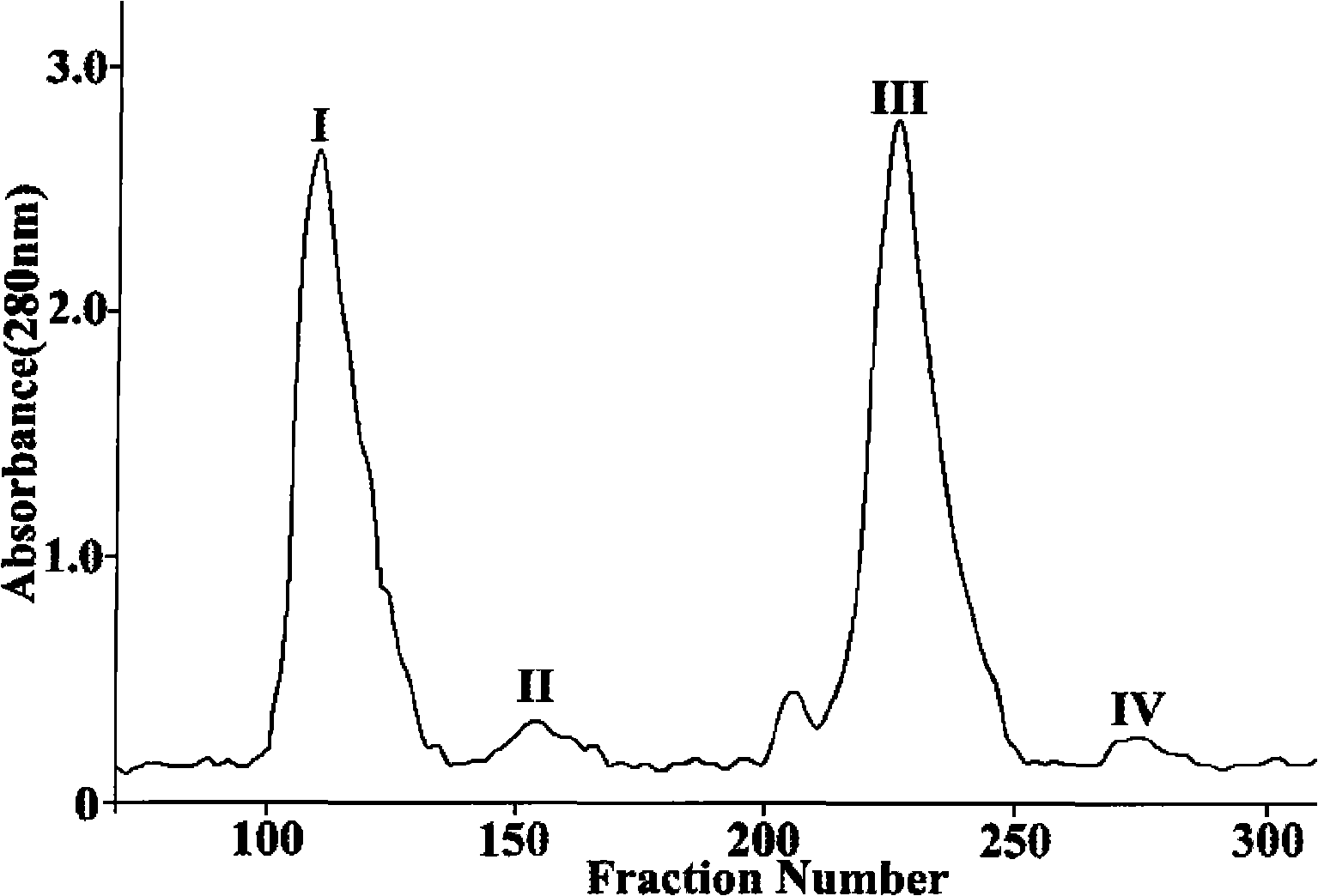
[0034] Place the freshly separated venom tube of the South China Sea signal Cono snail in a petri dish, cut it on ice, and extract it with extraction buffer (100mmol / L NaCl, 50mmol / L Tris-HCl, pH 8.8) for 30 min, 4°C, 12000g centrifugation Collect the supernatant at 30 min, repeat extraction and centrifugation three times, combine the supernatants, separate them by Sephadex-G25 Fine, and detect four absorption peaks at a wavelength of 280 nm (see figure 1 ). The peak II sample separated and collected by Sephadex-G25 Fine, after ion exchange chromatography, detected five absorption peaks at 215nm wavelength (see figure 2 ), separately collected and further separated by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography.
[0035] Ion exchange chromatography peak IV was further purified by reversed-phase HPLC, and the spectrum obtained un...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: The effect of signal conotoxin lt9b on sodium ion channels
[0040] In order to observe the effect of this P-superfamily conotoxin on TTX-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels, we selected rat DR6 cells as the experimental object. After DR6 cells form a whole-cell recording mode, under voltage clamp conditions, the cell membrane potential is clamped at -80mV, and then given a single pulse stimulation with a duration of 50ms and a depolarization voltage of -10mV to induce TTX-sensitive sodium currents . After applying the toxin, give the same stimulation repeatedly and observe the effect of the toxin on the inward current.
[0041] 500nM lt9b has a significant inhibitory effect on TTX-sensitive sodium current, and the maximum inhibition rate is 49.60±2.61% (n=3). After lt9b partially inhibited the sodium current, the shape of the current was consistent with the shape of the control current, indicating that they did not significantly change the dynamic characteri...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Experimental method of central analgesic effect on physiological model
[0044] Basic scheme: mouse hot plate method
[0045] Select 100 NIH mice, weighing 20←2g, all females. Before the experiment, the mice were screened. The mice were placed on a hot plate pain meter heated to 55°C in advance, and the time from when the mouse was put on the hot plate to the appearance of hind feet licking was recorded with a stopwatch as the mouse’s pain threshold. Twice, the mice whose pain threshold did not exceed 20s were selected as qualified candidates for formal experiments. The mice after screening were randomly divided into 4 groups, namely the blank control group and the low, medium and high dose groups of lt9b samples, with 10 mice in each group. At the beginning of the experiment, intraperitoneal injection was performed. The low, medium and high dose groups of lt9b were given 0.07 mg / kg, 0.14 mg / kg, and 0.28 mg / kg, respectively. The blank control group was given an e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com