Panax japonicus polysaccharides, preparation method and use thereof
A technology of bamboo ginseng polysaccharides and bamboo ginseng, which can be used in food preparation, application, allergic diseases, etc., can solve the problems of polysaccharides that cannot be extracted and curative effect restrictions, and achieve a simple and easy method, easy operation, and wide source of raw materials Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Use ethyl acetate and acetone to remove fat and small molecular impurities from the dried and crushed bamboo ginseng produced in Enshi, Hubei. After vacuum drying, take 100-1000 g of the dried solid and wash it with water for 2-5 times. After centrifugation, the precipitate is extracted with high-pressure hot water at 100-150°C for 2-4 times, each time for 0.5-1 hour. The extracted slurry was centrifuged again, and the solution was concentrated with a rotary evaporator, and a small amount of n-octanol was added to remove air bubbles during concentration. The concentrated solution was deproteinized by the Sevag method, then ammonia water was added to adjust the pH value of the solution to 7-10, and H 2 o 2 1 to 4 days for decolorization. After the solution is decolorized, it is then frozen at 0-50°C for 2-12 hours, and then melted at 0-80°C to denature and precipitate the starch, centrifuge and destarch the solution, and then dialyze the solution with tap water and dis...
Embodiment 2
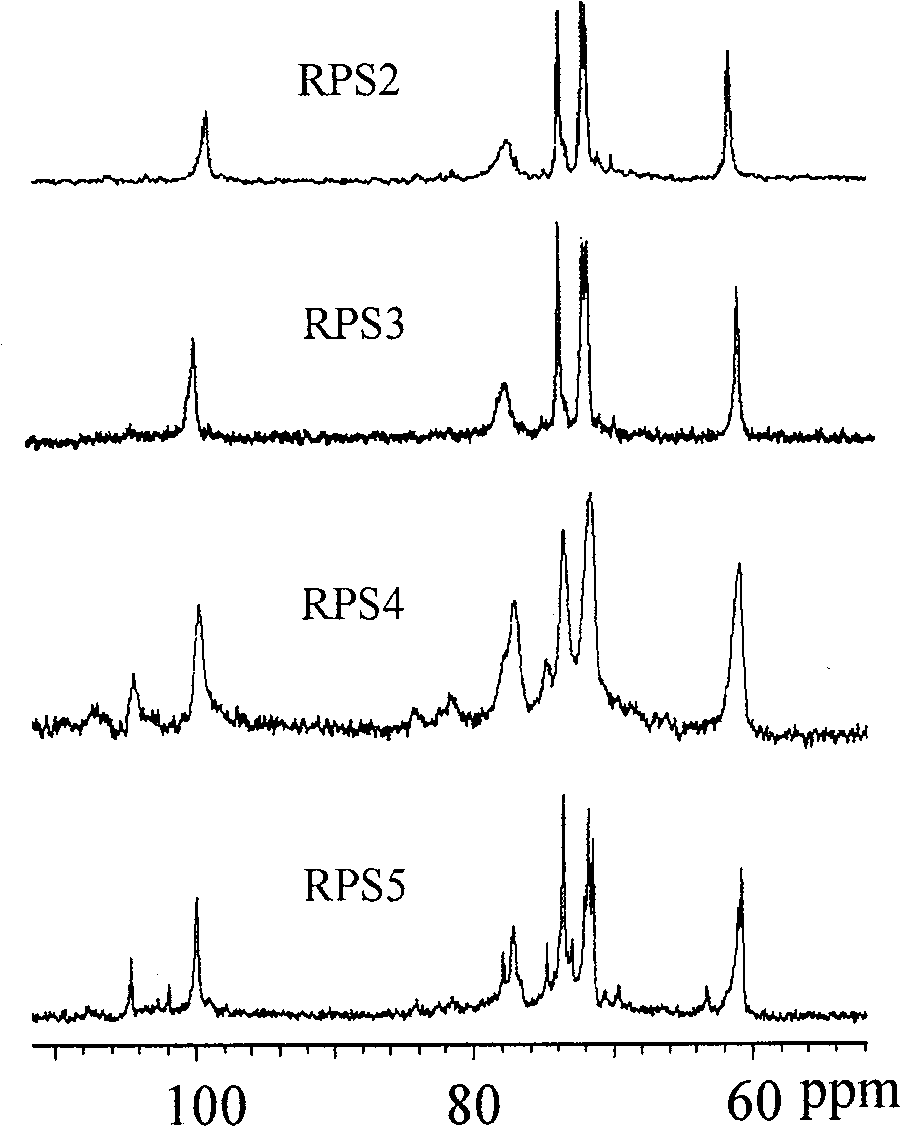
[0022] The bamboo ginseng residue extracted with hot water in Example 1 was treated with concentrations of 0.1-2M NaOH and 0.01-0.1M NaBH at -10-75°C 4 The aqueous solution is stirred and extracted for 1-12 hours, and the solution is immediately neutralized with glacial acetic acid to a pH value of 6.5-7.5 after centrifugation. Repeat the extraction 2 to 6 times. When the solution was concentrated, n-octanol was added to defoam. After deproteinization, decolorization, and dialysis by the method in Example 1, polysaccharide samples RPS3 and RPS4 were obtained by freeze-drying. The transmission electron microscope images are as follows Figure 4 with Figure 5 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0024] With NaOH and NaBH in embodiment 2 4 The residue of Panax ginseng after aqueous extraction is soaked and extracted with 40-88% formic acid at -10-25°C for 0.5-2h, and after centrifugation, the clear liquid is neutralized with 20%-40% NaOH aqueous solution until the pH is 6.5-7.5. Repeat the extraction 2 to 3 times. After the solution was concentrated and left to stand, a large amount of salt crystallized, the salt crystallization was separated by centrifugation, the solution was decolorized and dialyzed, and then freeze-dried to obtain the polysaccharide sample RPS5. The transmission electron microscope picture is shown in Image 6 .
[0025] Table 1 shows the elemental analysis results of the polysaccharides of Panax ginseng prepared above. The weight average molecular weight of bamboo ginseng polysaccharide (M w ), molecular weight distribution (M w / M n ), molecular mean square radius of rotation (2 > z 1 / 2 ) and intrinsic viscosity ([η]) and other physical an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com