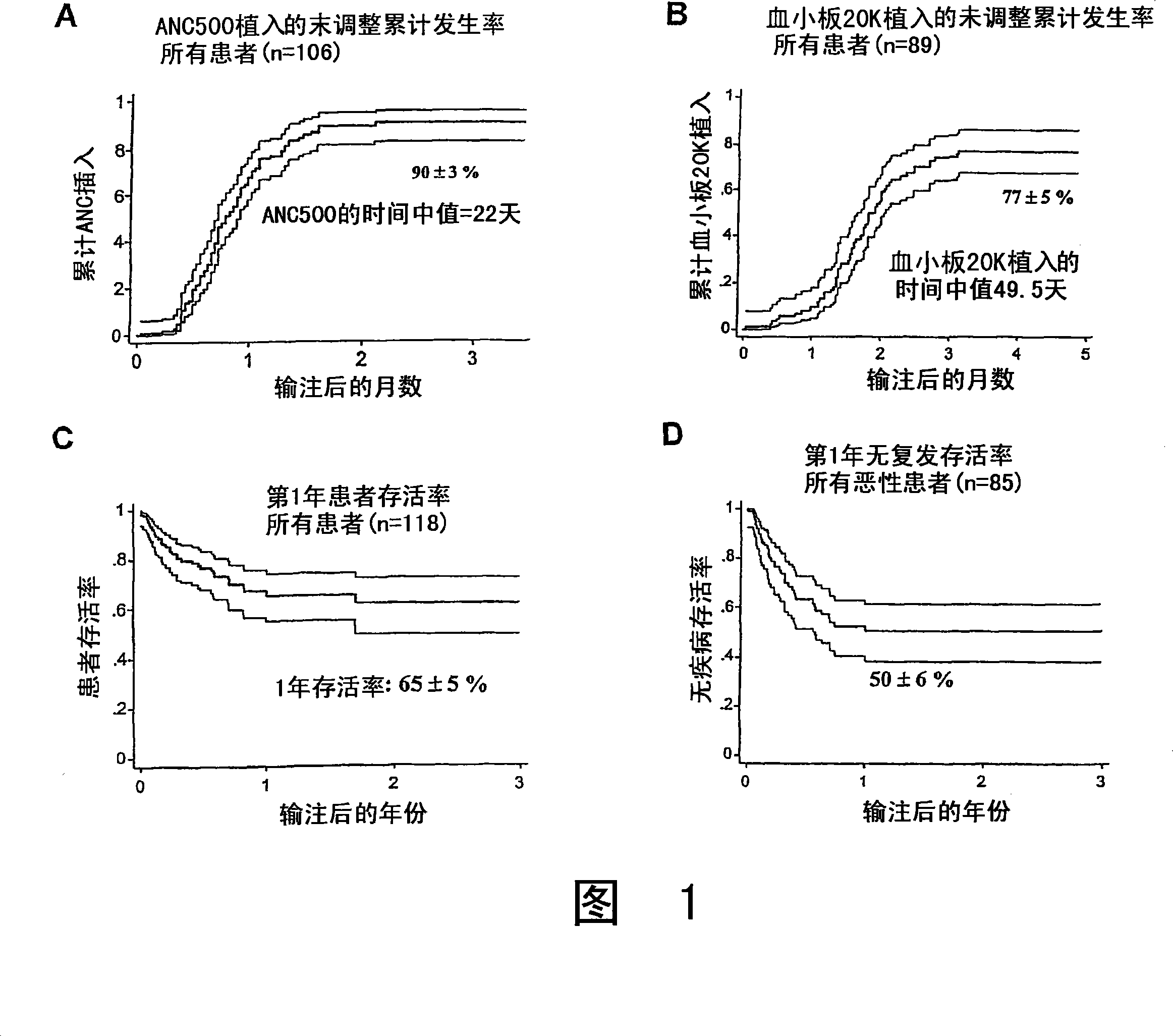
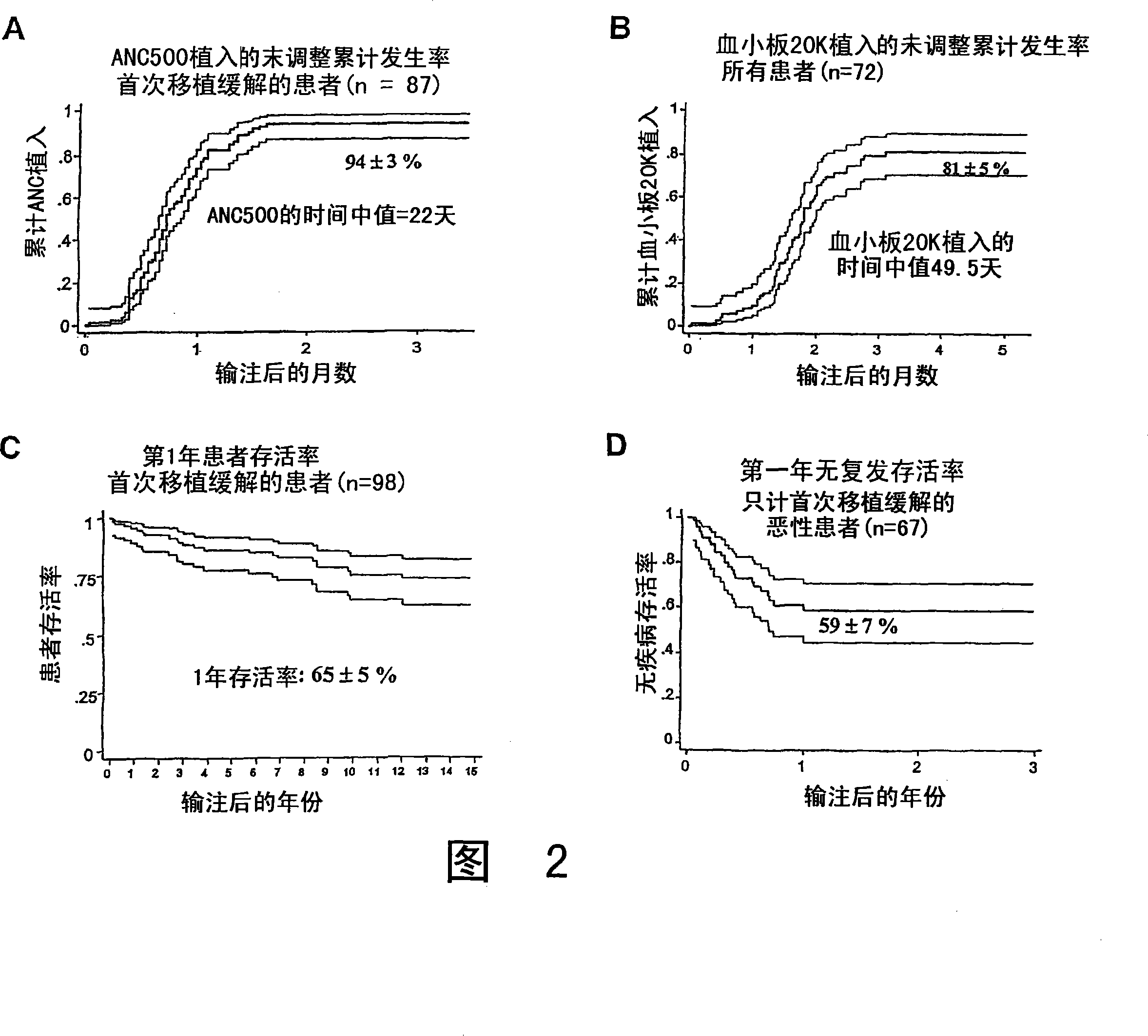
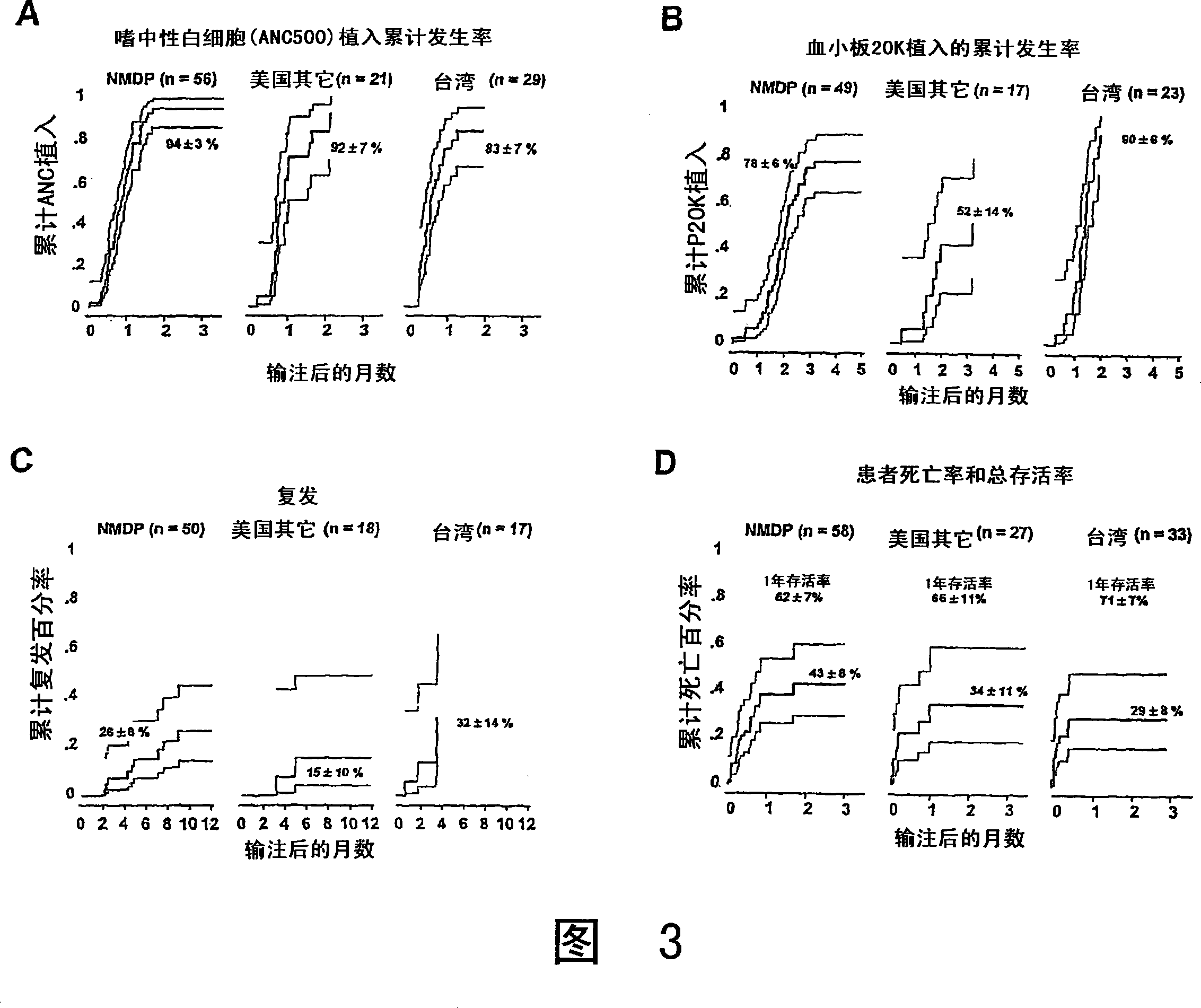
Plasma-depleted, non-red blood cell-depleted umbilical cord blood compositions and methods of use
A composition and technology of red blood cells, which can be applied in the fields of application, preservation of human or animal bodies, and medical raw materials derived from mammals, can solve the problems of cord blood stem cell supply shortage, high cost, and insufficient number of cells, etc., and achieve overall survival rate The effect of increasing, reducing the incidence rate, and reducing the mortality rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0131] Example 1. Exemplary Plasma Depletion Umbilical Cord Blood Unit
[0132] The present embodiment provides an exemplary cord blood (UCB) composition substantially depleted of plasma but not red blood cells.
[0133] Standard cryoprotectant volume: about 60ml plasma depletion unit uses about 15ml cryoprotectant.
[0134] If CV=volume of cord blood collected, AV=volume of anticoagulant (for example, between about 23-about 35ml), PV=volume of plasma-depleted cord blood, PAV=volume of anticoagulant after processing, and APV=anticoagulant To remove the volume of umbilical cord blood from coagulant plasma, an exemplary UCB composition of the present invention contains:
[0135] PV=60ml×(CV / (CV+AV));
[0136] PAV=60ml×(AV / (CV+AV));
[0137] PV+PAV=APV=60ml; and
[0138] Volume before freezing = APV + cryoprotectant volume = 60 ml + 15 ml = 75 ml.
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2. Removal of umbilical cord blood unit plasma increases hematocrit and red blood cell concentration
[0140] This example illustrates that processing and collecting umbilical cord blood (UCB) according to the method of the present invention increases the hematocrit (ie, the percentage of red blood cells in the final volume) and red blood cell (RBC) concentration of UCB units.
[0141] The UCB collected from 488 newborns was first tested to determine the hematocrit ("PRE-HCT%") and RBC concentration ("PRE-RBC(10 6 / μl)”), and then the plasma removal process described herein. After processing, the hematocrit ("POST-HCT%") and RBC concentration ("POST-RBC(10 6 / μl)”) and white blood cell concentration (“POST-WBC(10 3 / μl)”). As shown in Table 3, processing UCB units by plasmapheresis according to the methods described herein can substantially increase hematocrit and RBC concentration.
[0142] Table 3. 488 cord blood units before and after processing
[0143] ...
Embodiment 3
[0145] Example 3. Comparison of plasma-depleted, red blood cell-depleted, and whole blood cord blood units
[0146] This example compares the plasma-depleted cord blood composition of the present invention with whole blood and HES red blood cell depletion units.
[0147] Hematocrit:
[0148] The average hematocrit of plasma depleted (PD) cord blood (UCB) units is about 1.8 times that of whole blood units or red blood cell depleted (RD) units. In terms of volume, the hematocrit of a given unit corresponds to the percentage of red blood cells (RBC). Without intending to be limited to any specific theory, the PD UCB unit of the present invention has a higher hematocrit, which is beneficial to provide better cryoprotective properties and / or improved clinical effects.
[0149] Hematocrit
PD blood
RD blood
≤40%
≥50%
≤50%
[0150] Red blood cell concentration:
[0151] The average RBC concentration of PD units is about 1.8 tim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com