Gene chip for analyzing microbial group structure and function under acid environment
A microbial community and gene chip technology, which is applied in the field of gene chips for analyzing the structure and function of microbial communities in an acidic environment, can solve problems such as low sensitivity, limited types of fluorescent dyes, and limited types of microorganisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
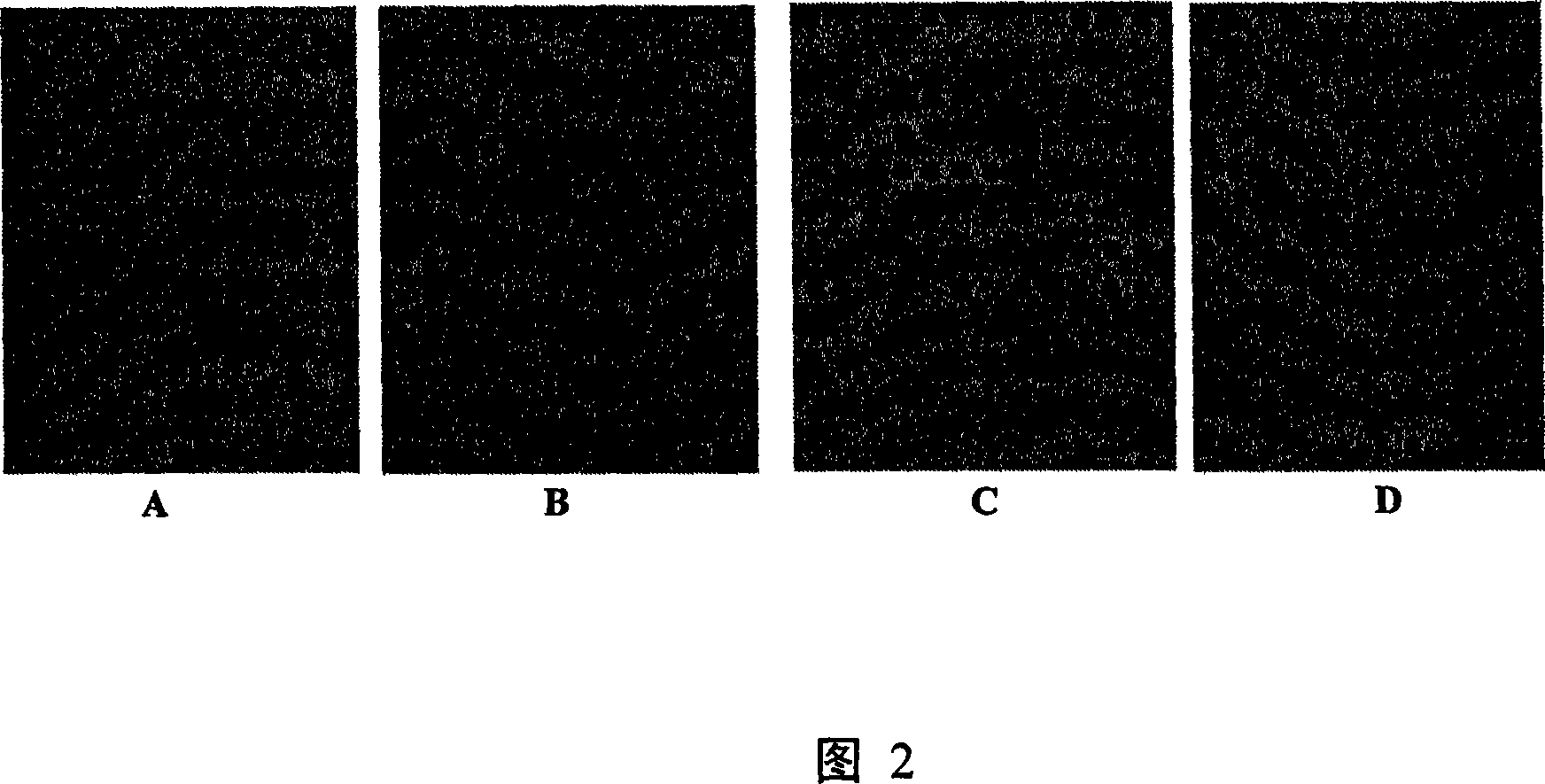
[0249] Example 2: Chip hybridization specificity assessment
[0250] Select the 16s rDNA contained in the chip, the ferrous oxidase gene (iro), the gyrB gene encoding the B subunit of DNA helicase, the pufM gene encoding the M subunit of the photosynthetic reaction center complex, and the cbbQ gene as target sequences to detect the chip Hybridization specificity of probes. After these genes were amplified by PCR method, the products were purified using a purification kit. The PCR purified products of all genes were mixed in equal amounts, labeled with cy3 fluorescent dyes, and hybridized with oligonucleotide chips at 50°C. The results showed that the chips Strong fluorescent signals were generated at the probe positions corresponding to these five genes (as shown in Figure 1), and no non-specific cross-hybridization with non-target genes was found on the chip. It shows that there is a strong specificity between the specific oligonucleotide probe and its corresponding target g...
Embodiment 3
[0252] Example 3: Sensitivity detection of chip hybridization
[0253] Use the pure genomic DNA of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 23270 to detect the sensitivity of the chip of the present invention, the pure genomic DNA of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 23270 is diluted according to certain concentration gradient (concentration is respectively 0.2,1,5,25,50,100,250,500 and 750ng) and hybridized with the chip after labeling with cy3. From the results of chip hybridization analysis, we can find that all A.f genes have strong signals between 25-750ng gradients (see Figure 2), and most of the gene signals can be detected in 5ng genomic DNA hybridization but a small part The probes have only very weak hybridization signals, and we only detected few gene signals when 0.2 and 1ng of genomic DNA were used as labeled templates for hybridization. Therefore, according to the results of chip gradient hybridization experiments, we determined that the detection limit of the chip for purel...
Embodiment 4
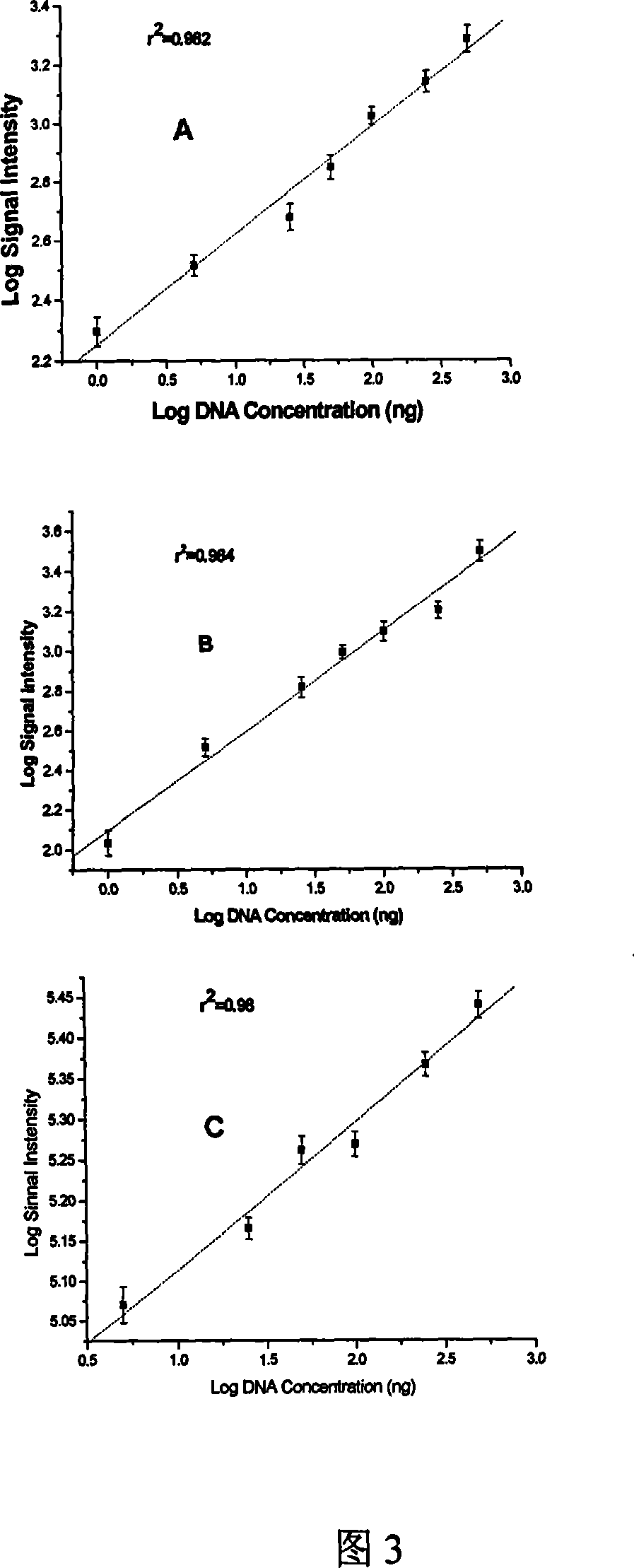
[0254] Example 4: Quantitative performance of functional gene chip
[0255] The ability of the chip for nucleic acid quantification was evaluated by measuring the relationship between the target DNA concentration and the hybridization signal of the chip. As mentioned above, the pure Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 23270 genomic DNA was labeled with cy3 and hybridized with the chip according to the gradient dilution. Each concentration of DNA was prepared in three parallel hybridizations. The signal corresponding to each probe was averaged, and the DNA The logarithmic value of the concentration and the logarithmic value of the fluorescence signal intensity were plotted (see Figure 3). For the ferrous oxidase gene, there was a strong linear correlation (r 2 =0.982), the same linear correlation also exists with the 16s rRNA gene probe. In addition, a strong linear relationship (r 2 = 0.98). This result indicated that chip hybridization has a quantitative effect on DNA in a spe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com