Circulating hot tube type radiator
A radiator and heat exchange tube technology, applied in the field of heat dissipation of electronic devices, can solve the problems of low production efficiency, high requirements on the accuracy of the outer diameter of the heat pipe, and high cost and price of the heat pipe
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
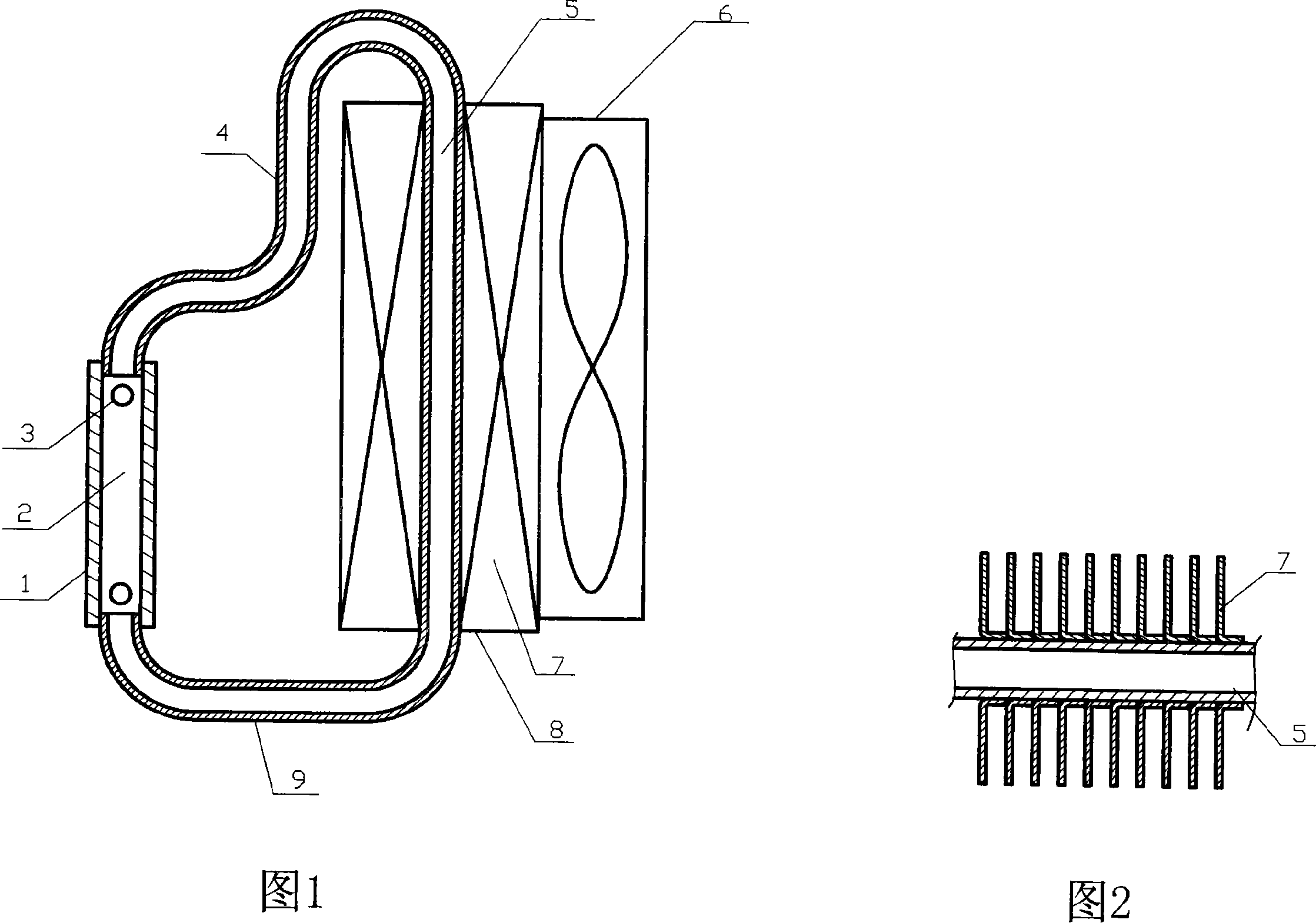
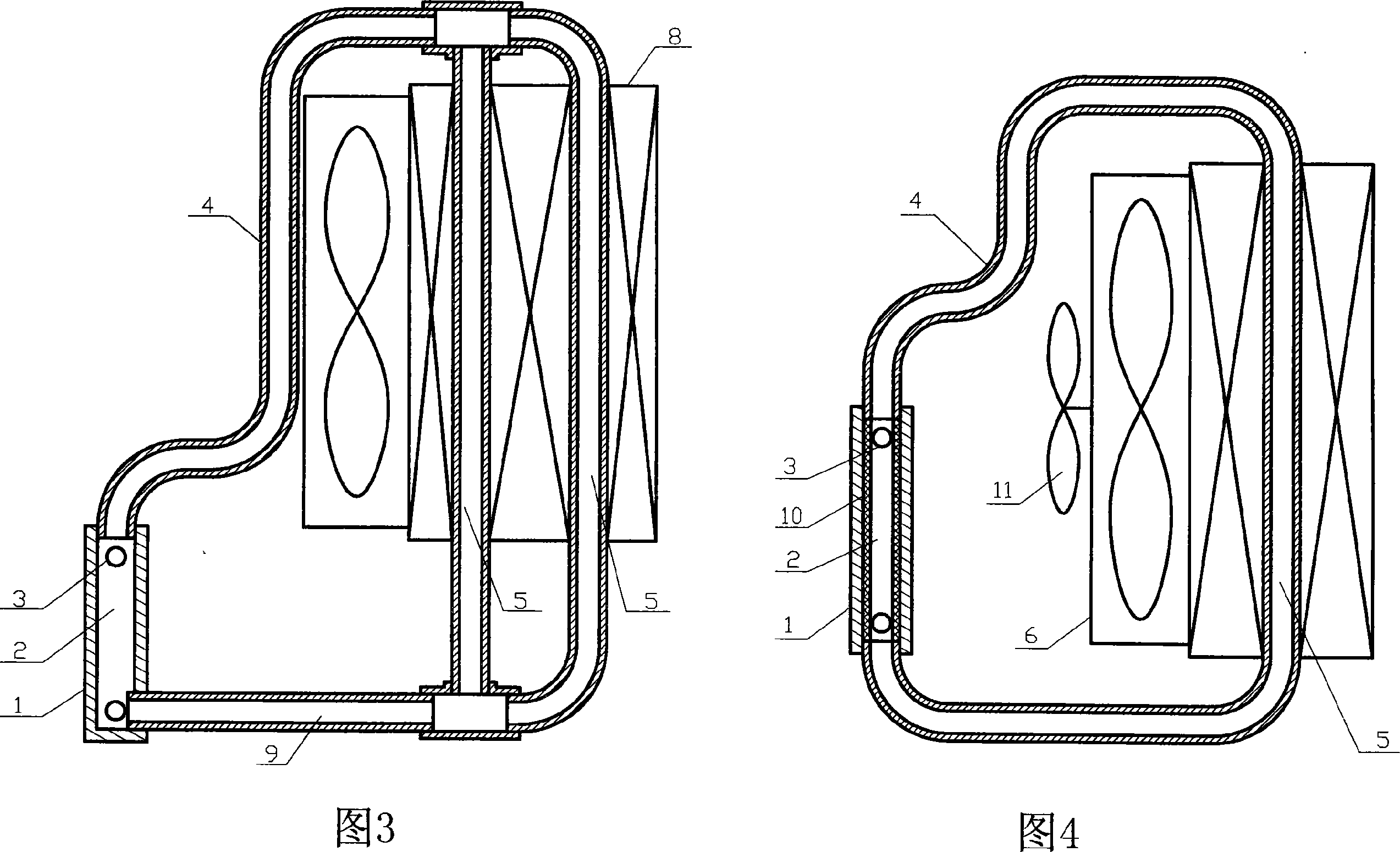
[0020] The CPU in the computer is usually placed vertically, and the radiators shown in Figures 1, 3 and 4 are placed vertically in accordance with the heat dissipation surface of the heating device. The heat-absorbing blocks (1) are all located at the lower end of the radiator, which is beneficial to the area of the evaporation channel (2) in the heat-absorbing block (1) being wetted by the liquid working medium, which is conducive to evaporation and heat transfer , which is also conducive to reducing the inner area of the liquid working medium submerged in the heat exchange tube (5), which is beneficial to condensation and heat transfer. In the radiator shown in Figure 3, the air heat exchanger (8) is higher than the heat-absorbing block (1), so when the evaporating channel (2) is completely submerged by the liquid working fluid, no air remains in the heat exchange tube (5). Liquid working medium, this design is good for evaporation heat transfer and condensation heat tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com