Glass-glass composite optical wave guide
A composite light and glass technology, applied in the field of optical waveguide, can solve the problem that the function of the functional glass substrate 2 cannot be fully exerted, and achieve the effects of multi-functionality, large design and production, and miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
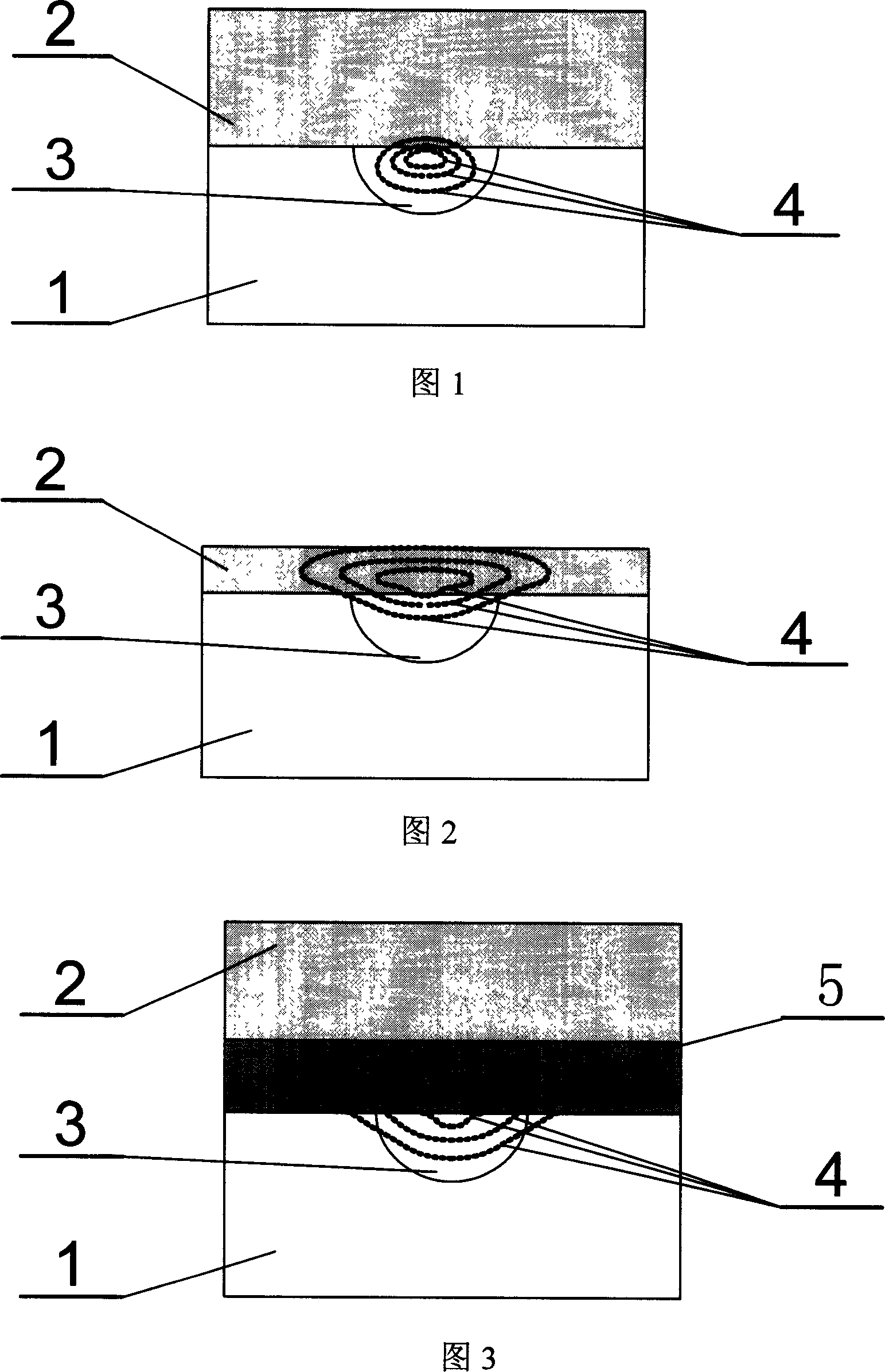
[0024] Embodiment 1: Composite optical waveguide structure see Figure 3, the main process steps
[0025] The glass substrate 1 is made of silicate optical glass material, and the functional glass substrate 2 is made of phosphate glass doped with rare earth. The main manufacturing steps of the glass-glass composite optical waveguide structure:
[0026] (A) Preparation of light guide region 3 on glass substrate 1
[0027] ·Using microfabrication technology to fabricate strip-shaped optical waveguide masks on glass substrates to obtain ion-exchange windows with a width of the order of microns;
[0028] ·Molten salt ion exchange process is used to make strip optical waveguide, and the ion exchange temperature is 300-400°C;
[0029] • Annealing of optical waveguides.
[0030] (B) Preparation of light confinement region 3 on functional glass substrate 2
[0031] · Fabricate the light confinement region 5 on the functional glass substrate 2 by using molten salt ion exchange techn...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: The composite optical waveguide structure is shown in Figure 4, the main process steps
[0035] The glass substrate 1 is made of silicate optical glass material, and the functional glass substrate 2 is made of phosphate glass doped with rare earth. The main manufacturing steps of the glass-glass composite optical waveguide structure:
[0036] (A) Preparation of light guide region 3 on glass substrate 1
[0037] ·Using microfabrication technology to fabricate strip-shaped optical waveguide masks on glass substrates to obtain ion-exchange windows with a width of the order of microns;
[0038] ·Molten salt ion exchange process is used to make strip optical waveguide, and the ion exchange temperature is 300-400°C;
[0039] • Annealing of optical waveguides.
[0040] (B) Preparation of light confinement region 3 on functional glass substrate 2
[0041] ·Using microfabrication technology to fabricate the mask of the strip optical waveguide on the glass subst...
Embodiment 3
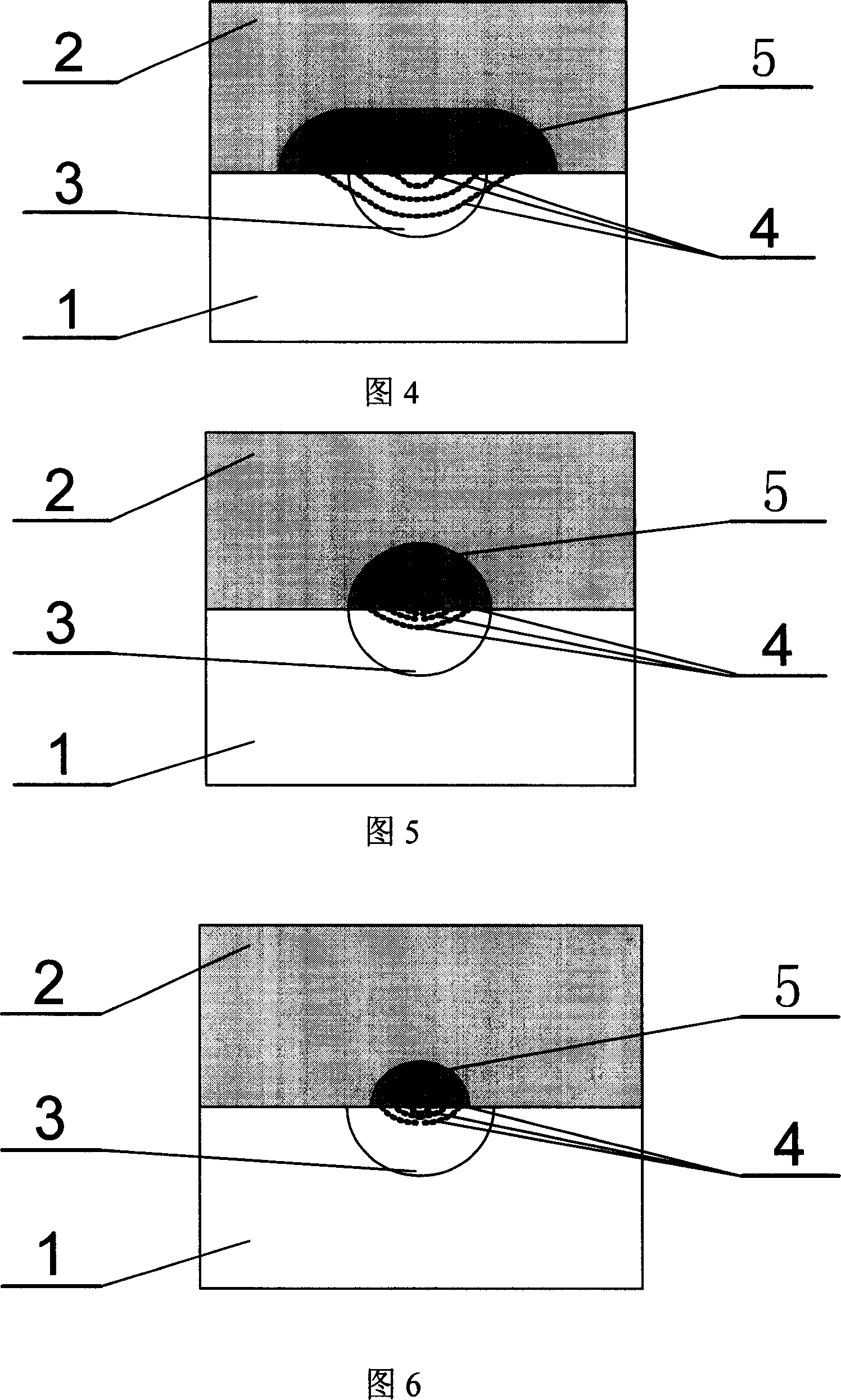
[0045] Embodiment 3: Composite optical waveguide structure see Figure 5 and Figure 6, the main process steps
[0046] The glass substrate 1 is made of silicate optical glass material, and the functional glass substrate 2 is made of phosphate glass doped with rare earth. The main manufacturing steps of the glass-glass composite optical waveguide structure:
[0047] (A) Preparation of light guide region 3 on glass substrate 1
[0048] ·Using microfabrication technology to fabricate strip-shaped optical waveguide masks on glass substrates to obtain ion-exchange windows with a width of the order of microns;
[0049] ·Molten salt ion exchange process is used to make strip optical waveguide, and the ion exchange temperature is 300-400°C;
[0050] • Annealing of optical waveguides.
[0051](B) Preparation of light confinement region 3 on functional glass substrate 2
[0052] ·Using microfabrication technology to fabricate strip-shaped optical waveguide masks on glass substrates t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com