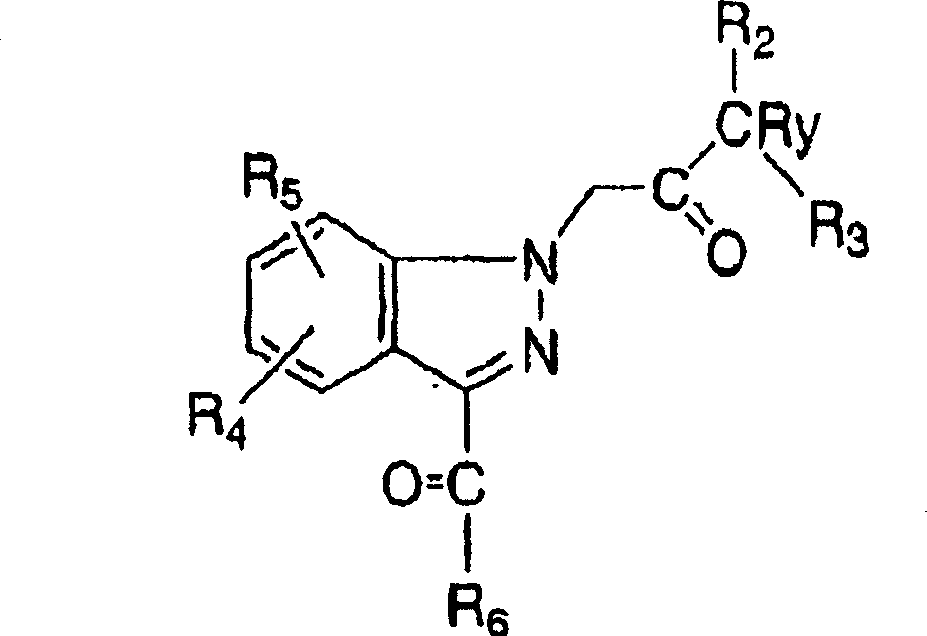
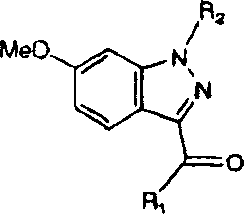
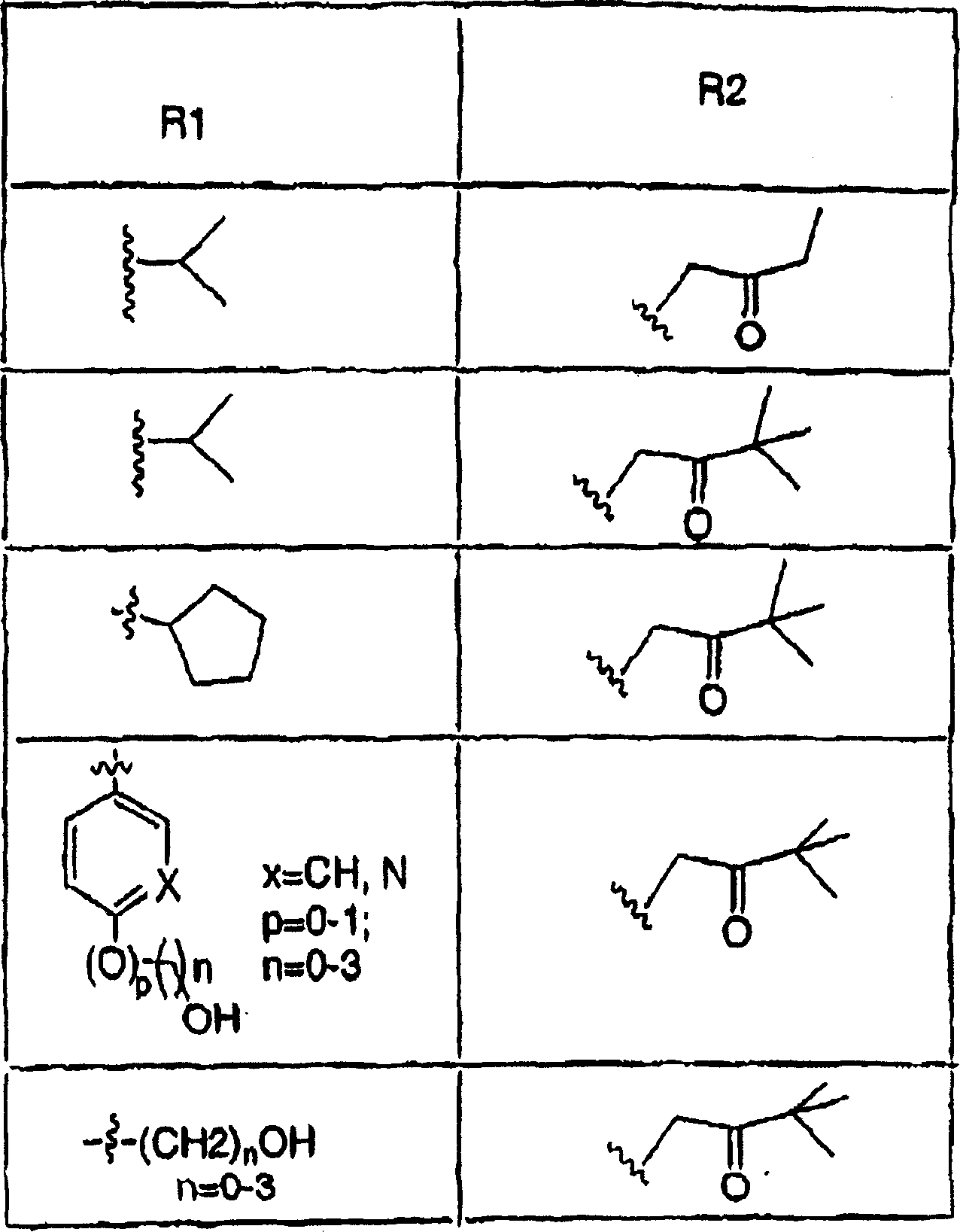
Ophthalmic compositions for treating ocular hypertension
A technology of compounds and mixtures, which can be used in drug combinations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic chemistry, etc., and can solve problems such as unsatisfactory efficacy and side effects, and increased
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0092]
[0093] A 500 ml flask was charged with 336 mmol (13.44 g; 60%) of sodium hydride. 150 ml of DMSO was added under an argon atmosphere, and then 32 ml of ethyl cyanoacetate (2.2 eq; 352 mmol) were added dropwise at 50°C. After complete addition, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature over 1 hour. 30 g of the nitrobenzene derivative (160 mmol) were added in powder form. The reaction mixture was heated at 90° C. for 8 hours in a closed system. Acidification and standard work-up gave a crude oily residue which was purified on a silica gel column to give 39 g of the desired crystalline product, which was decarboxylated to give the following benzonitrile. 38 g of SM obtained above were dissolved in 400 ml of 1N sodium carbonate. The homogeneous solution was stirred at room temperature for two days. Thin layer chromatography analysis indicated that the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was acidified and extracted with ethyl acetate (100ml×4). ...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0096]
[0097] 10 g of the benzonitrile derivative were dissolved in 20 ml of THF and then diluted with 50 ml of methanol. The reaction mixture was transferred to a pressure tube, palladium-carbon (10% by weight / 10 mol%) was added, and the reaction mixture was hydrogenated at 40 psi. After the amount of hydrogen necessary to reduce the nitro group has been consumed, the reaction is stopped. TLC analysis indicated that the spots had been transformed spots. The reaction mixture was filtered through a pad of celite, and the filtrate was concentrated to a solid and used directly in the next step. The crude aniline derivative (52 mmol) was dissolved / suspended in 2N hydrochloric acid (150 ml), cooled to 5°C, and then 5.4 g of sodium nitrite in 10 ml of aqueous solution was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour and gradually warmed to room temperature. TLC analysis showed that SM had been consumed and a new spot was formed. The reaction mixture was extracted with...
preparation Embodiment 3
[0099]
[0100] Weigh 4.15 g of indazole and the azeotropic water and 2 toluene (100 ml) washes, and remove the toluene azeotrope by rotary evaporation. Dry well under high vacuum and flush with argon. Dissolve in 40 ml dry THF and 92 ml dry ether under argon atmosphere. Cool to 5 °C in an ice-water bath. Charge 3 equivalents of isopropylmagnesium chloride ((6 ml) in 2M THF) and stir at room temperature for 0.5 hours. 1N Hydrochloric acid (240ml) was added carefully and stirred for 1 hour. The progress of the reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography. Extraction with ethyl acetate and rotary evaporation yielded the desired product.
[0101] LCMS[M+H]=219
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com