Non-vacuum smelting casting tech. of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy and Cu-Zr alloy
A non-vacuum, cu-cr-zr technology, applied in the field of non-vacuum casting process, can solve the problems of large equipment investment, low production efficiency, high price, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing costs and improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
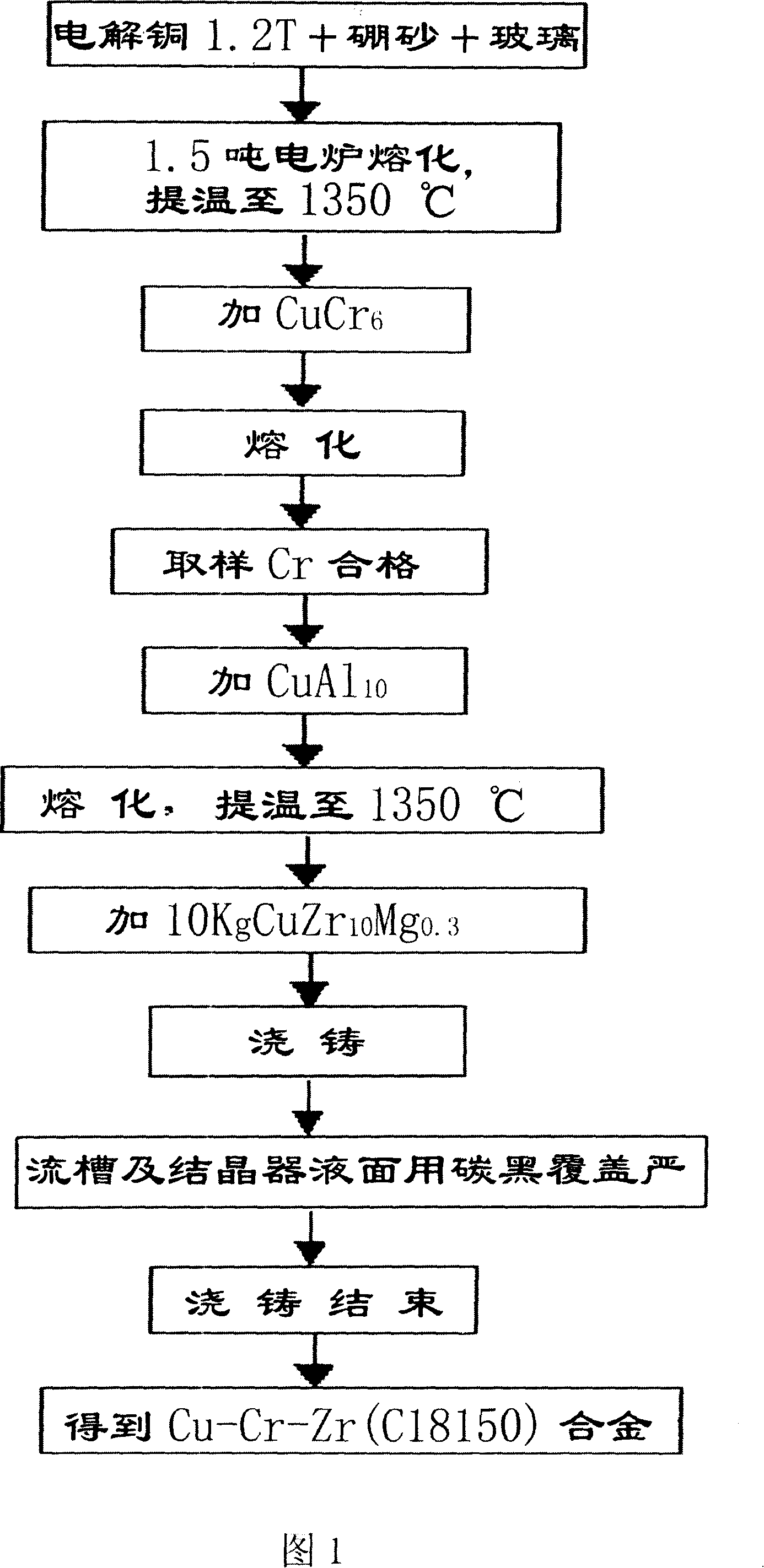
[0027] As shown in Figure 1, the non-vacuum casting process of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy of the present invention, it carries out by following steps:
[0028] a. First make CuCr from easily oxidized elements such as Cr, Zr, Al and Mg 6 、CuZr 10 Mg 0.3 、CuAl 10 Master alloy, as the raw material for subsequent addition;
[0029] b. Select 1.2 tons of standard cathode copper that meets the quality requirements, add it to a 1.5-ton power frequency induction furnace, and add enough dehydrated borax and glass as a covering agent at the same time. The weight ratio of borax and glass is 3:1, and melt the electrolytic copper , the covering agent is covered on the copper melt to avoid direct contact with the air; the temperature of the molten copper water is increased to about 1350 ° C ~ 1400 ° C, and CuCr is added 6 For the master alloy, when it is melted, take a sample to analyze the chemical composition of Cr, and the weight ratio of the ingredients is 1.0%; after the element is qualified, ...
Embodiment 2
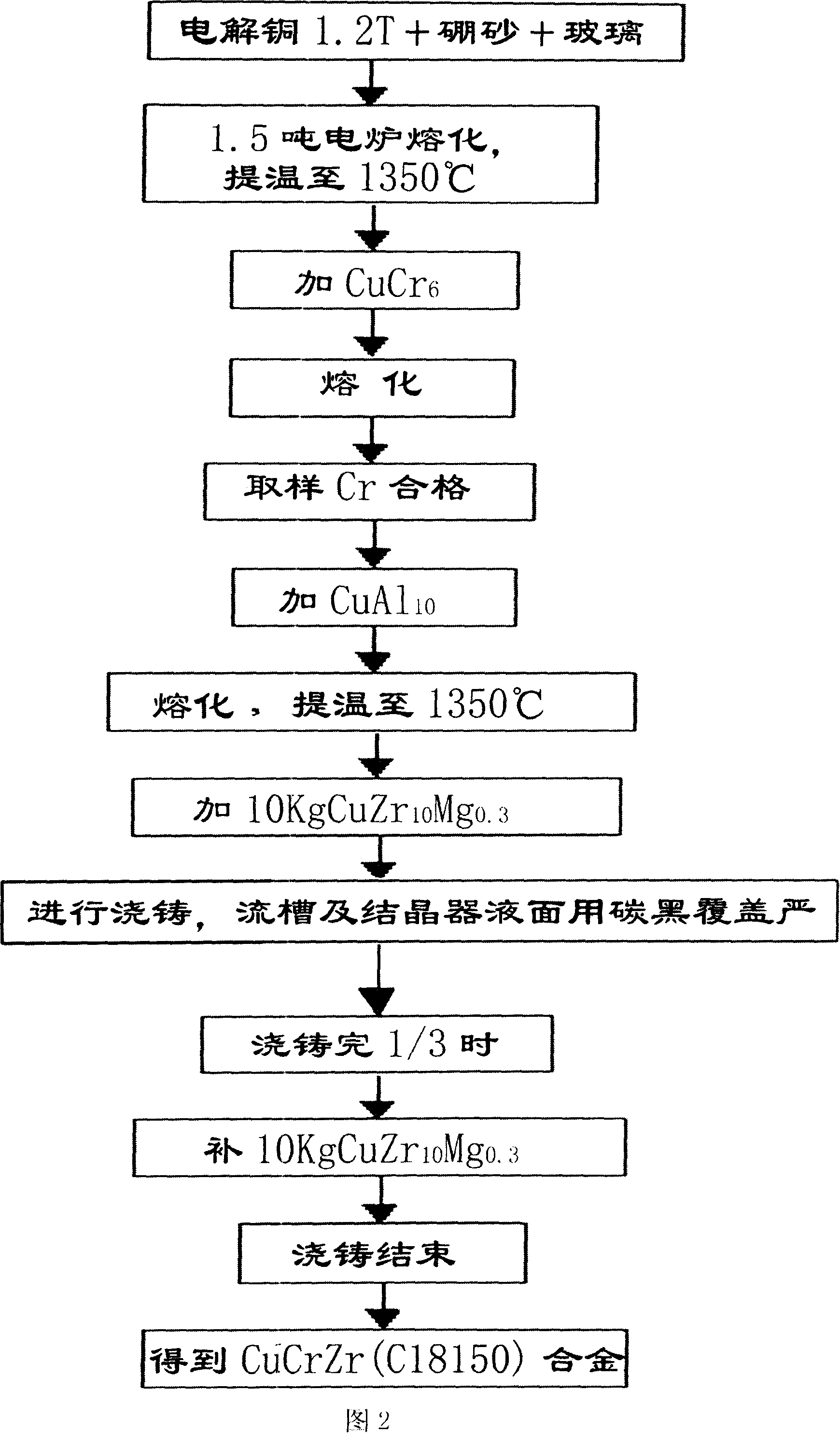
[0031] As shown in accompanying drawing 2, the non-vacuum casting technique of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy of the present invention, it carries out according to the following steps:
[0032] a. First make Cr, Zr, Al, Mg into CuCr 6 、CuZr 10 Mg 0.3 、CuAl 10 master alloy for use;
[0033]b. Select 1.2 tons of standard cathode copper that meets the quality requirements, add it to a 1.5-ton power frequency induction furnace, and add enough dehydrated borax and glass as a covering agent at the same time. The weight ratio of borax and glass is 3:1, and melt the electrolytic copper Finally, add covering agent to avoid direct contact with copper melt and air;
[0034] c. Raise the temperature of the molten copper water to about 1350°C ~ 1400°C, and add CuCr 6 Master alloy, wait for it to melt, take a sample to analyze the chemical composition of Cr, control by partial lower limit (batching weight ratio 0.7%);
[0035] d. After the Cr element is qualified, use special iron pliers to clamp the...
Embodiment 3
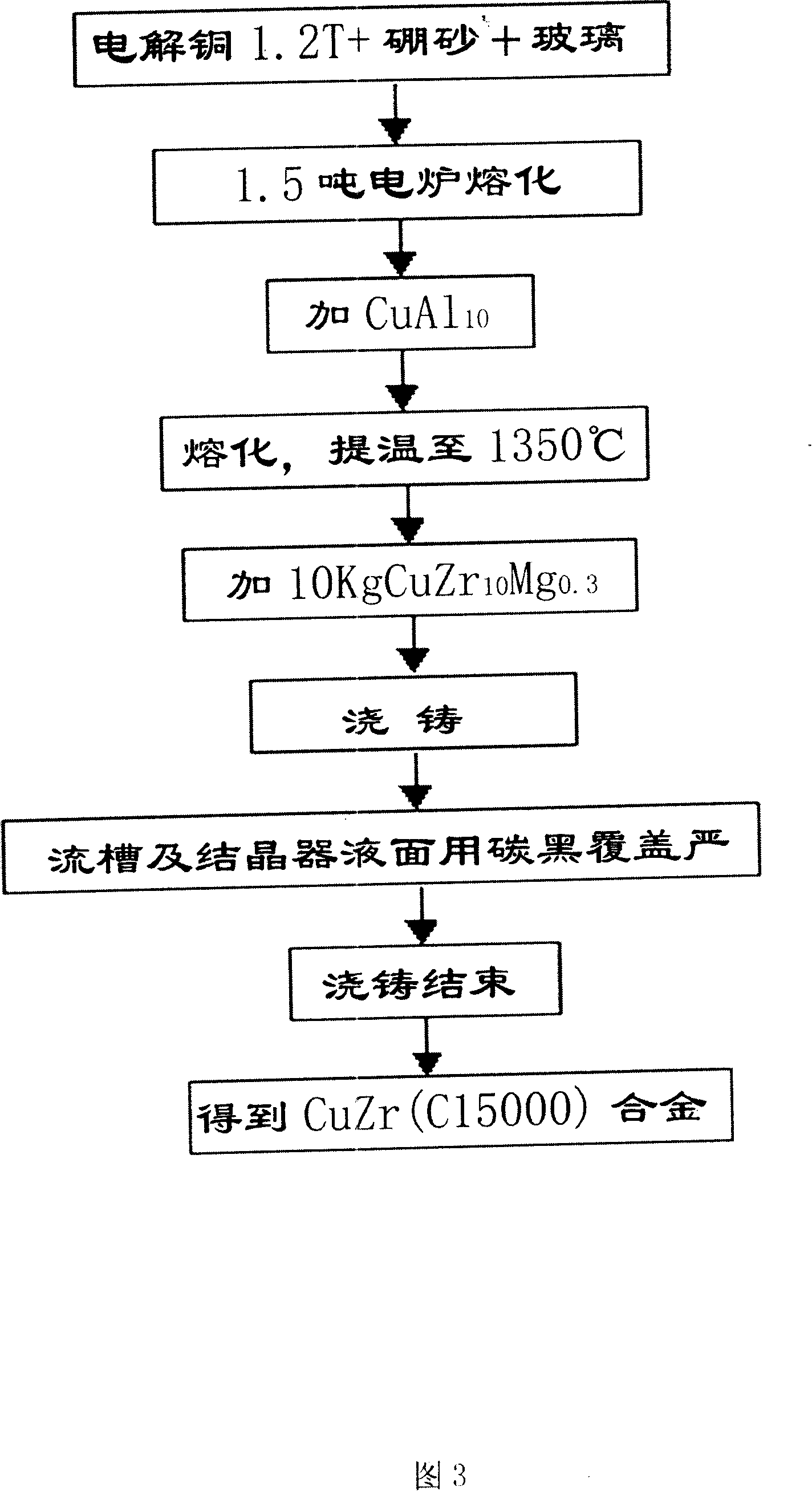
[0040] The preparation technology of Cu-Zr alloy of the present invention is as follows, see as shown in Figure 3:
[0041] a. First make Zr, Al, Mg easily oxidizable elements into CuZr 10 Mg 0.3 、CuAl 10 Master alloy, as the raw material for subsequent addition;
[0042] b. Select 1.2 tons of standard cathode copper that meets the quality requirements, add it to a 1.5-ton power frequency induction furnace, melt the electrolytic copper, and add enough dehydrated borax and glass as a covering agent at the same time. The weight ratio of borax and glass is 3:1 , the covering agent is covered on the copper melt to avoid direct contact with the air; when the temperature rises to 1350-1400°C, use special iron pliers to clamp the calculated CuAl 10 For the intermediate alloy, quickly insert it 50mm below the liquid surface, slowly loosen the pliers, so that Al is fully melted into the Cu melt, and the weight ratio of Al is controlled at 0.25%; when the temperature rises to 1350-14...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com