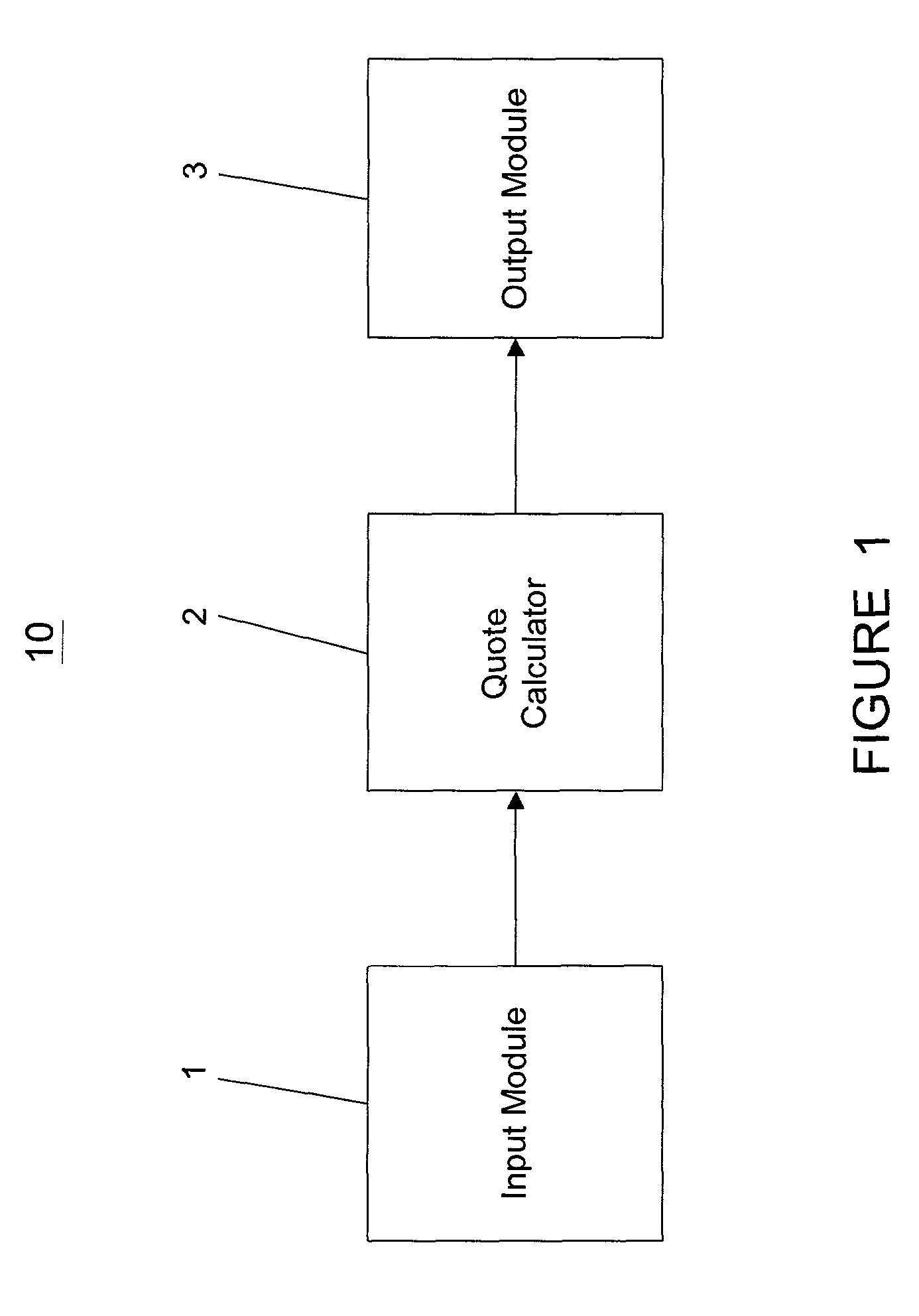
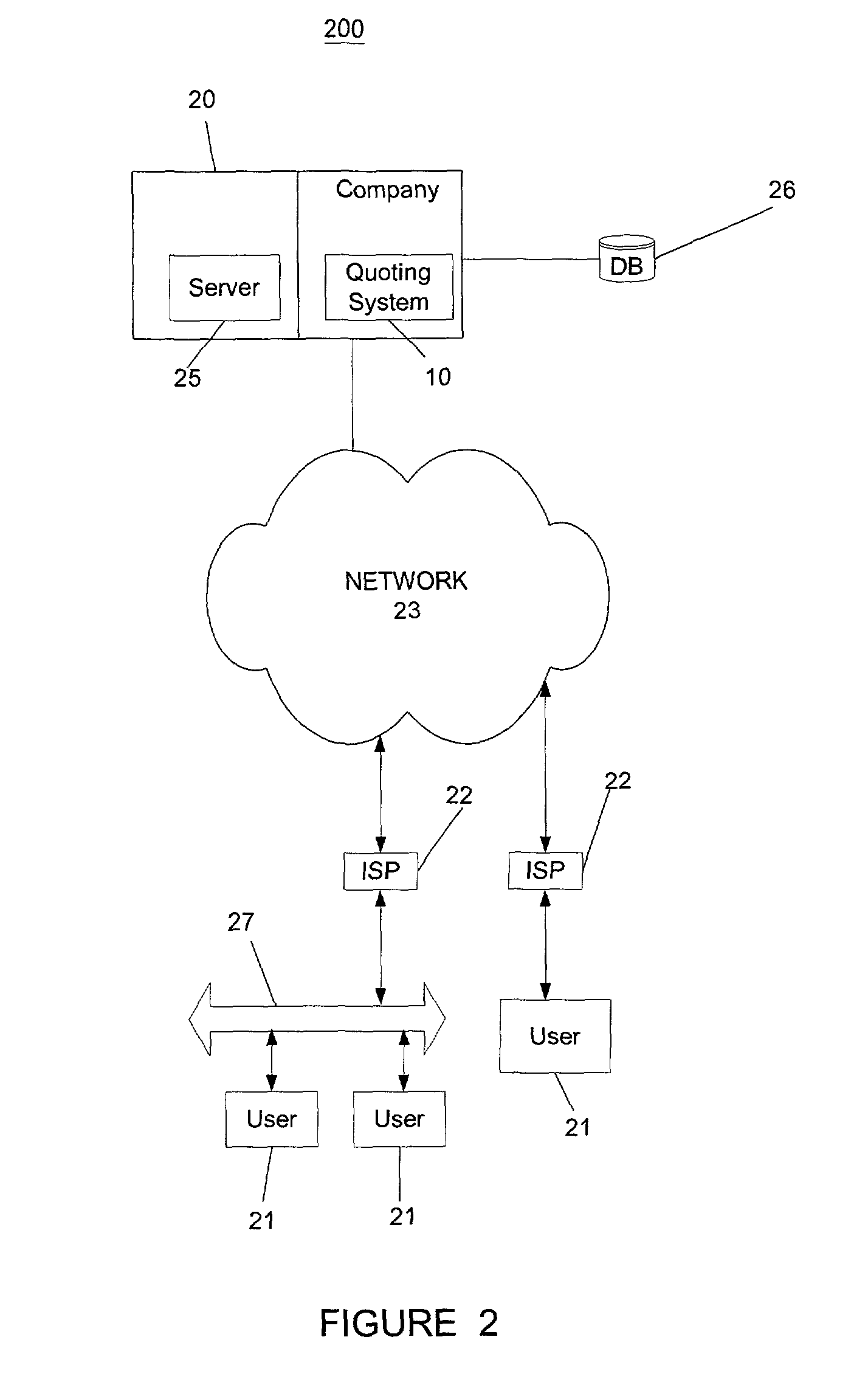
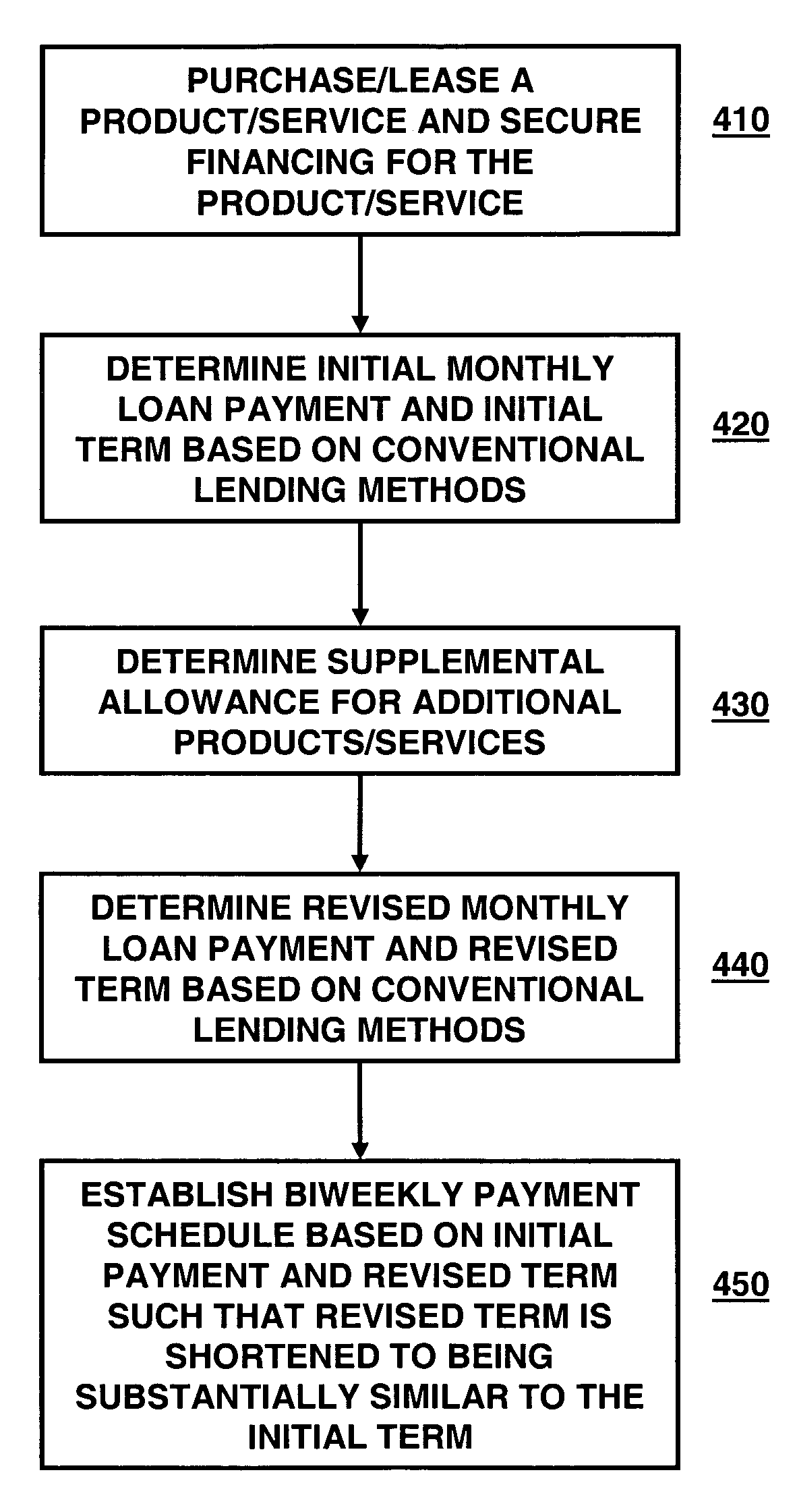
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Payment schedule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
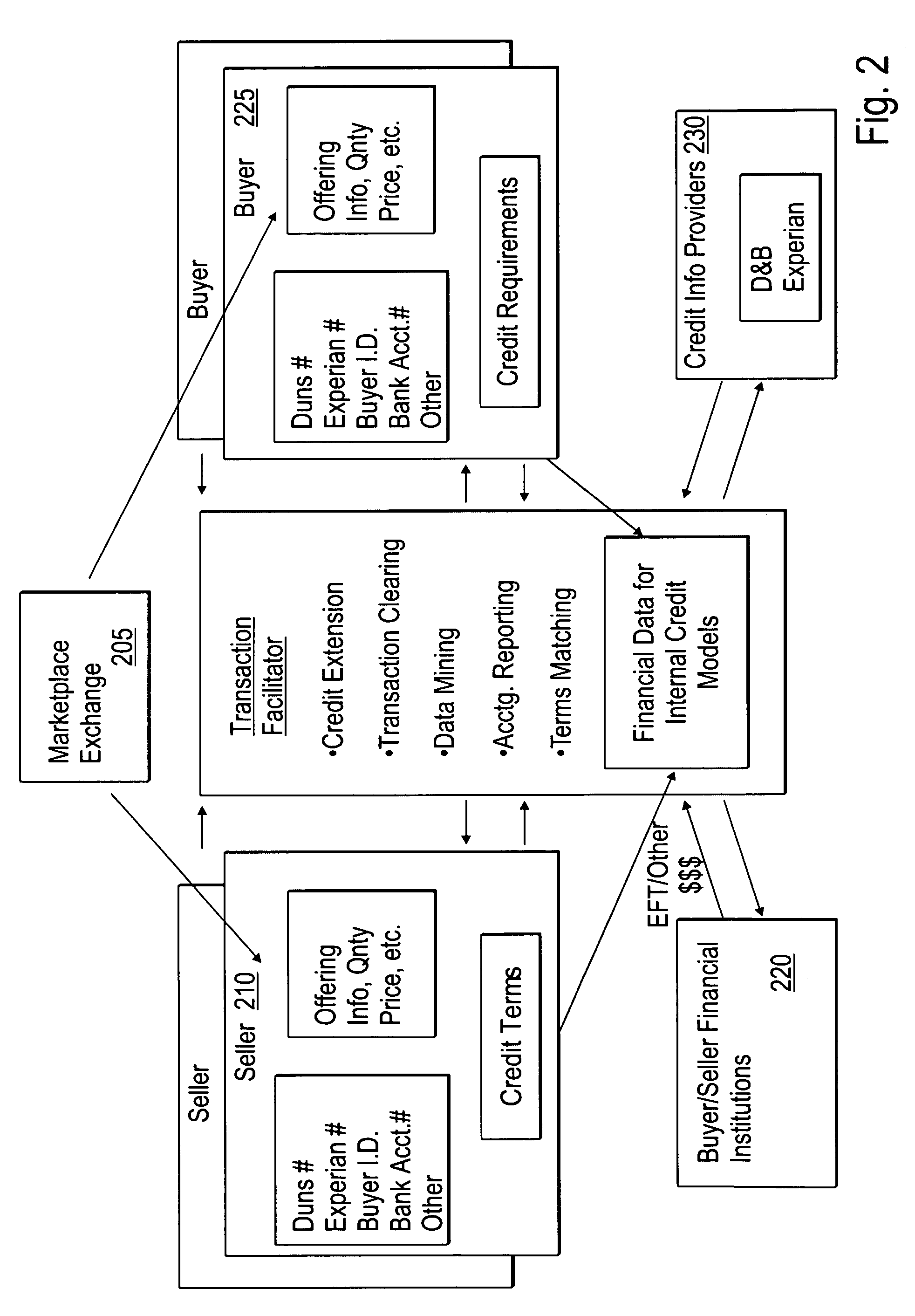
The payment schedule of financial instruments defines the dates at which payments are made by one party to another on for example a bond or derivative. It can be either customised or parameterised.
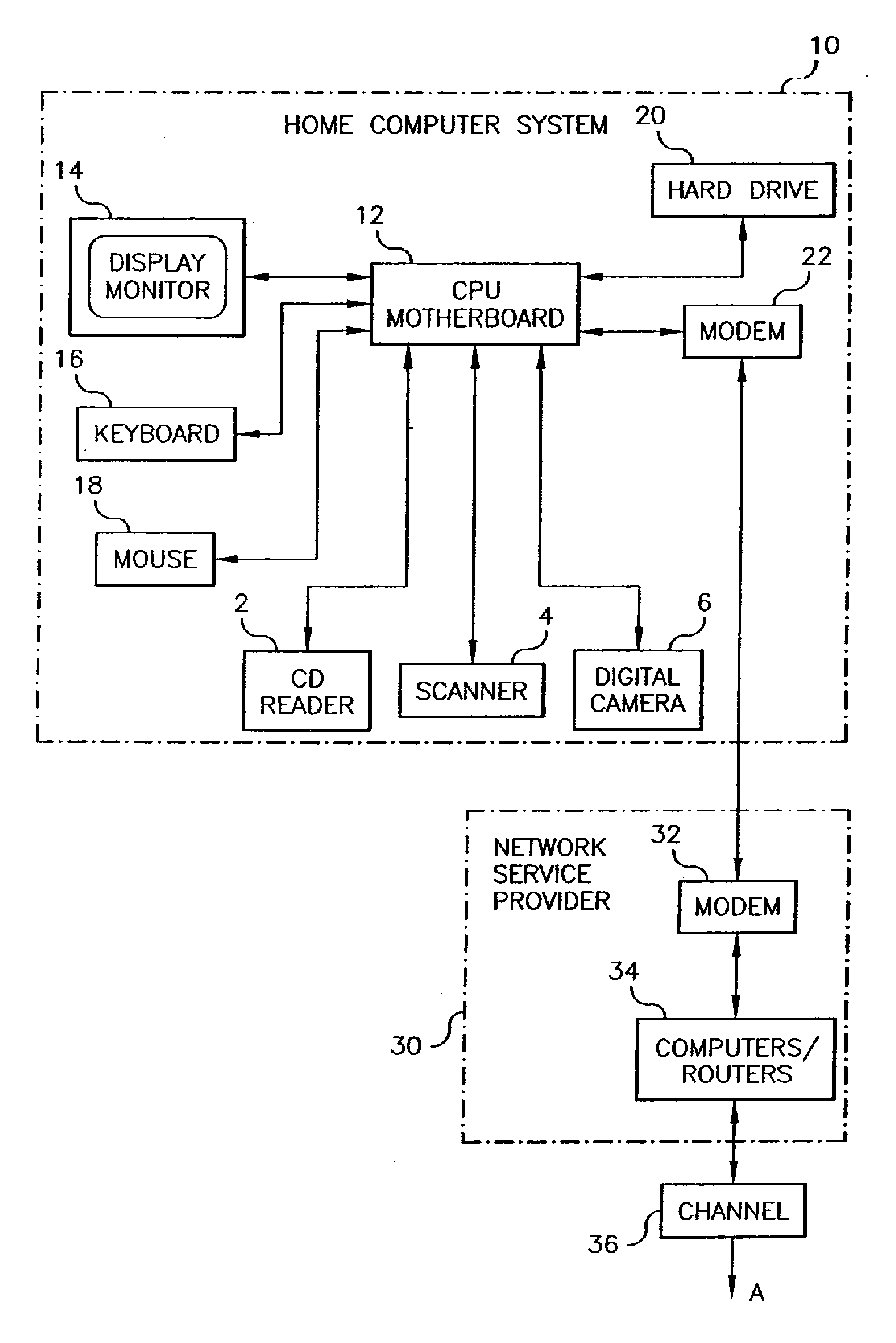
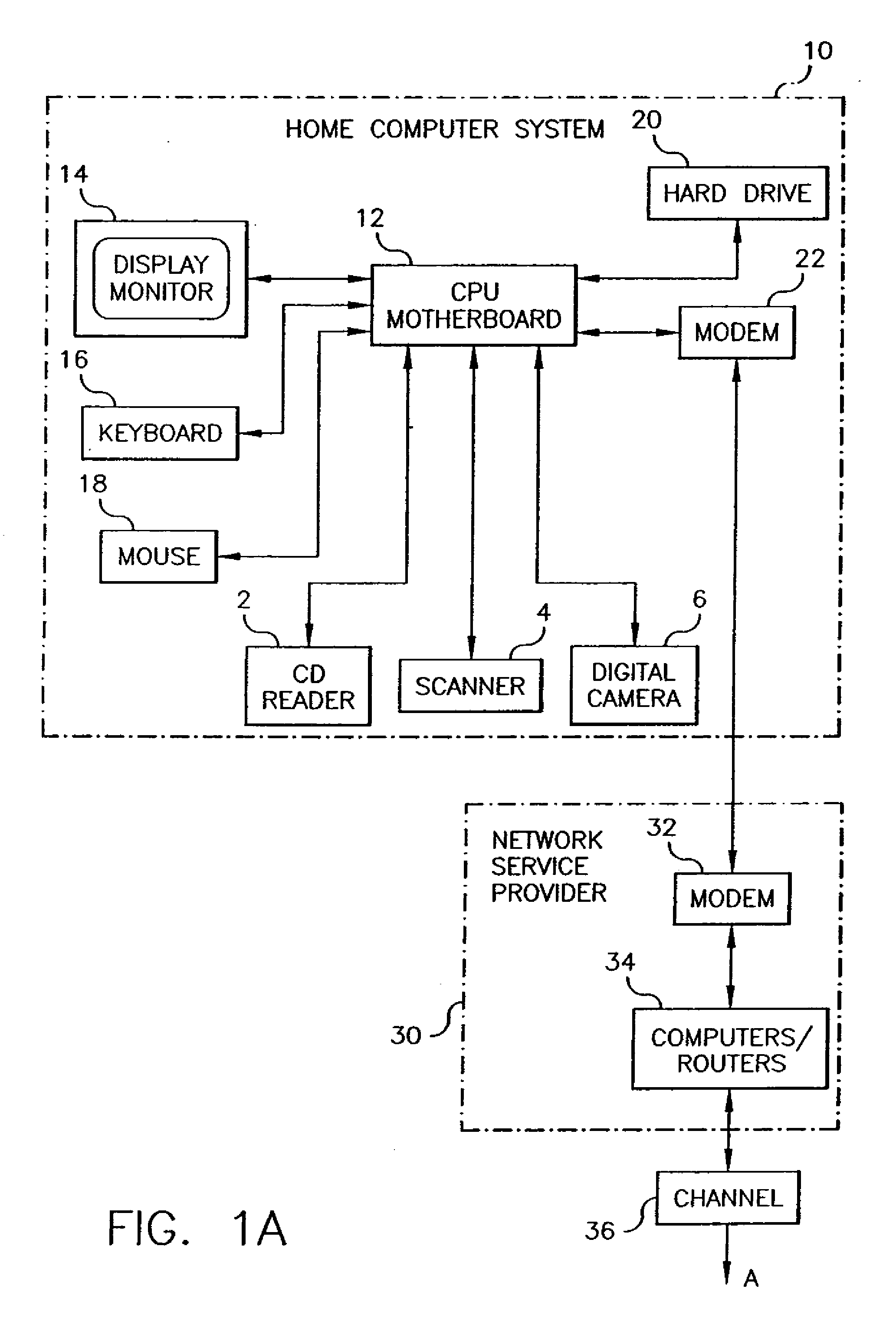
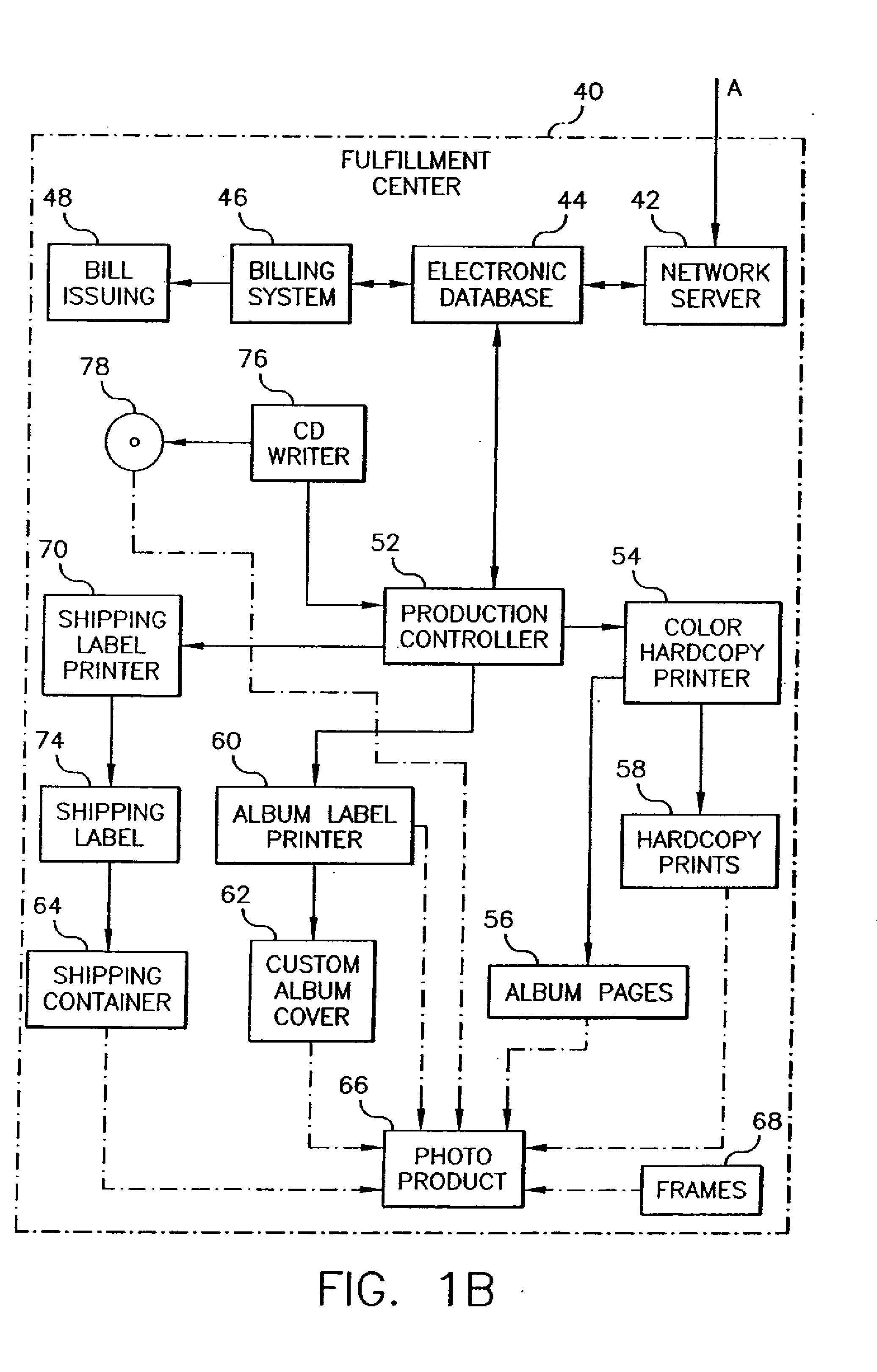
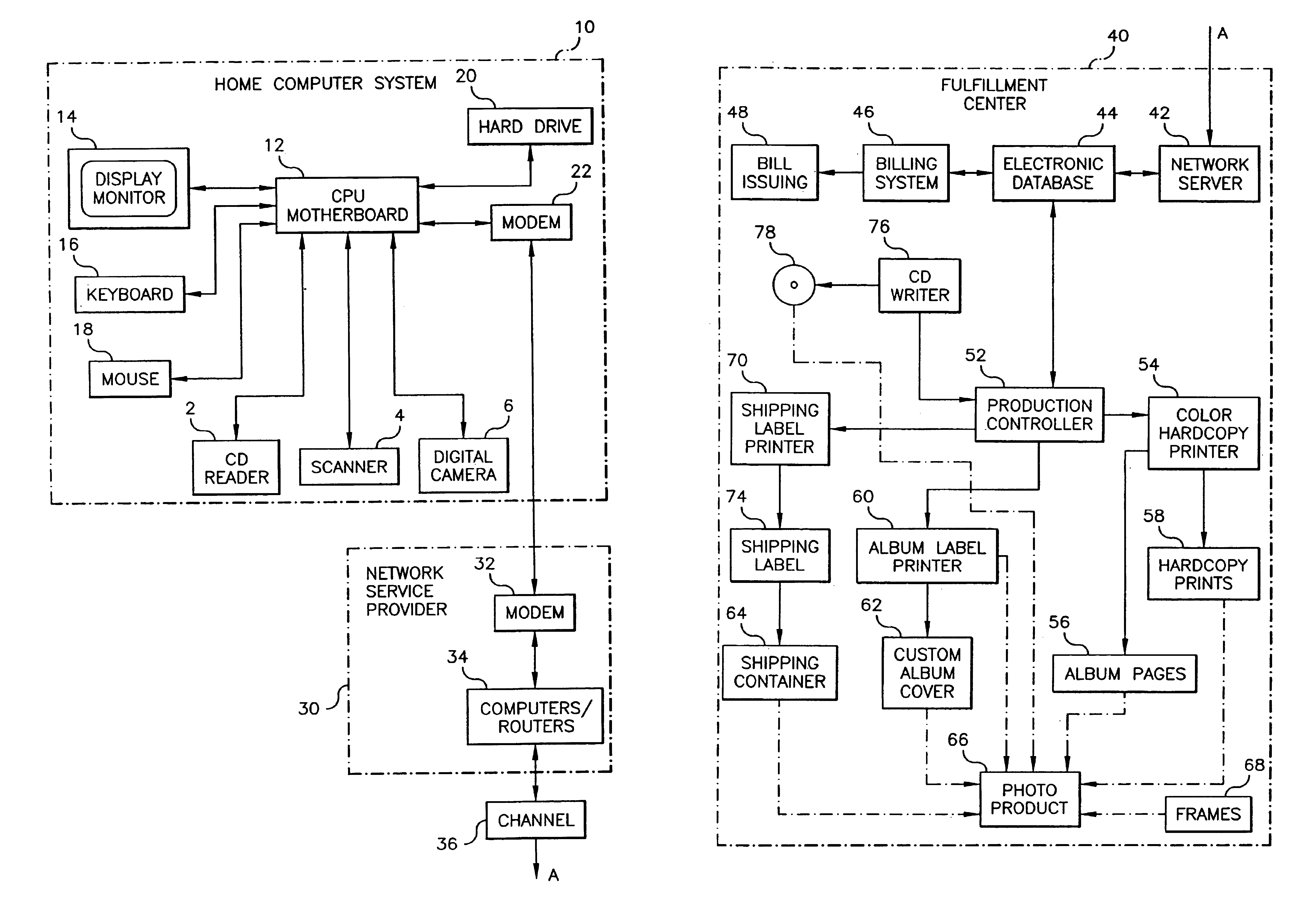
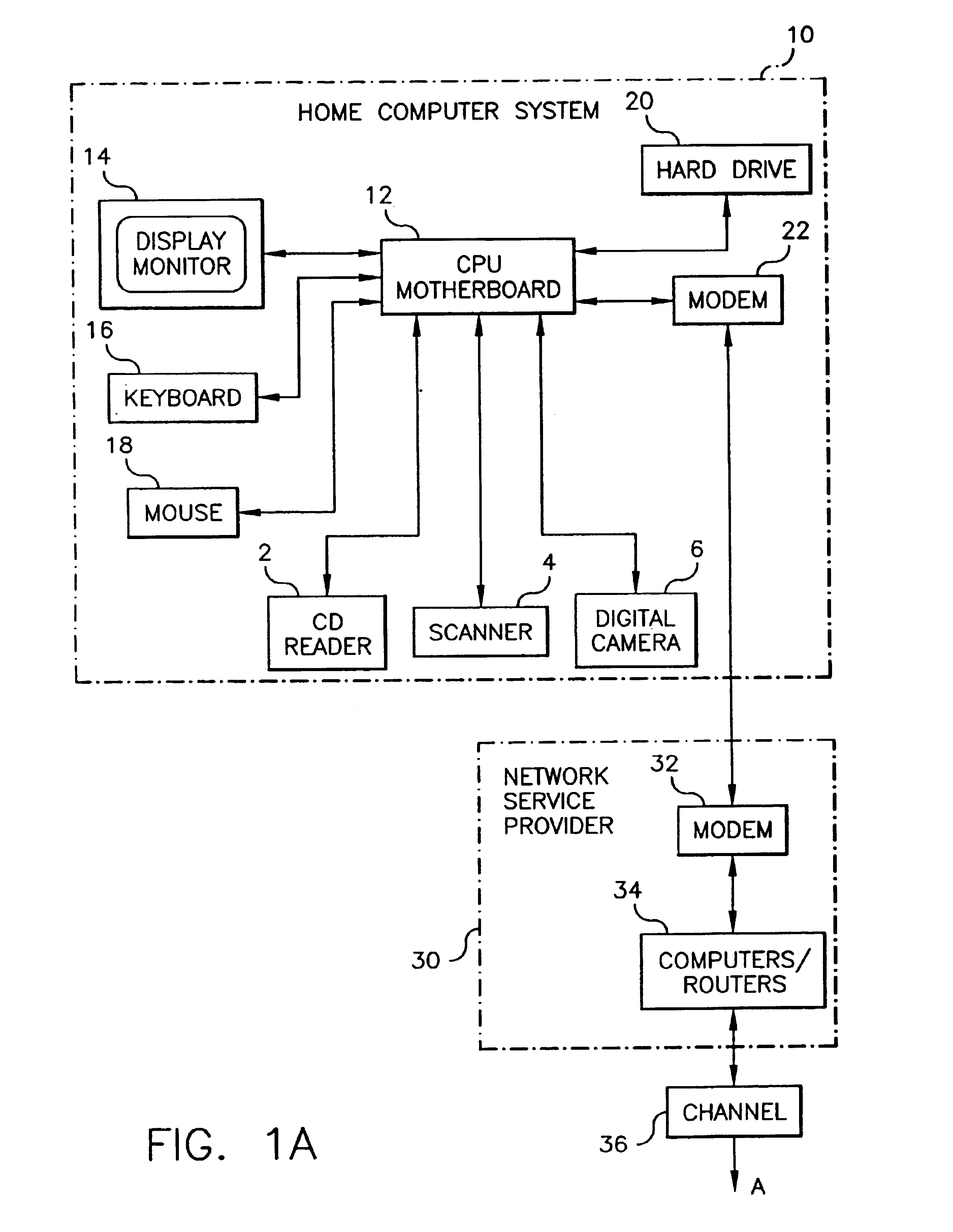
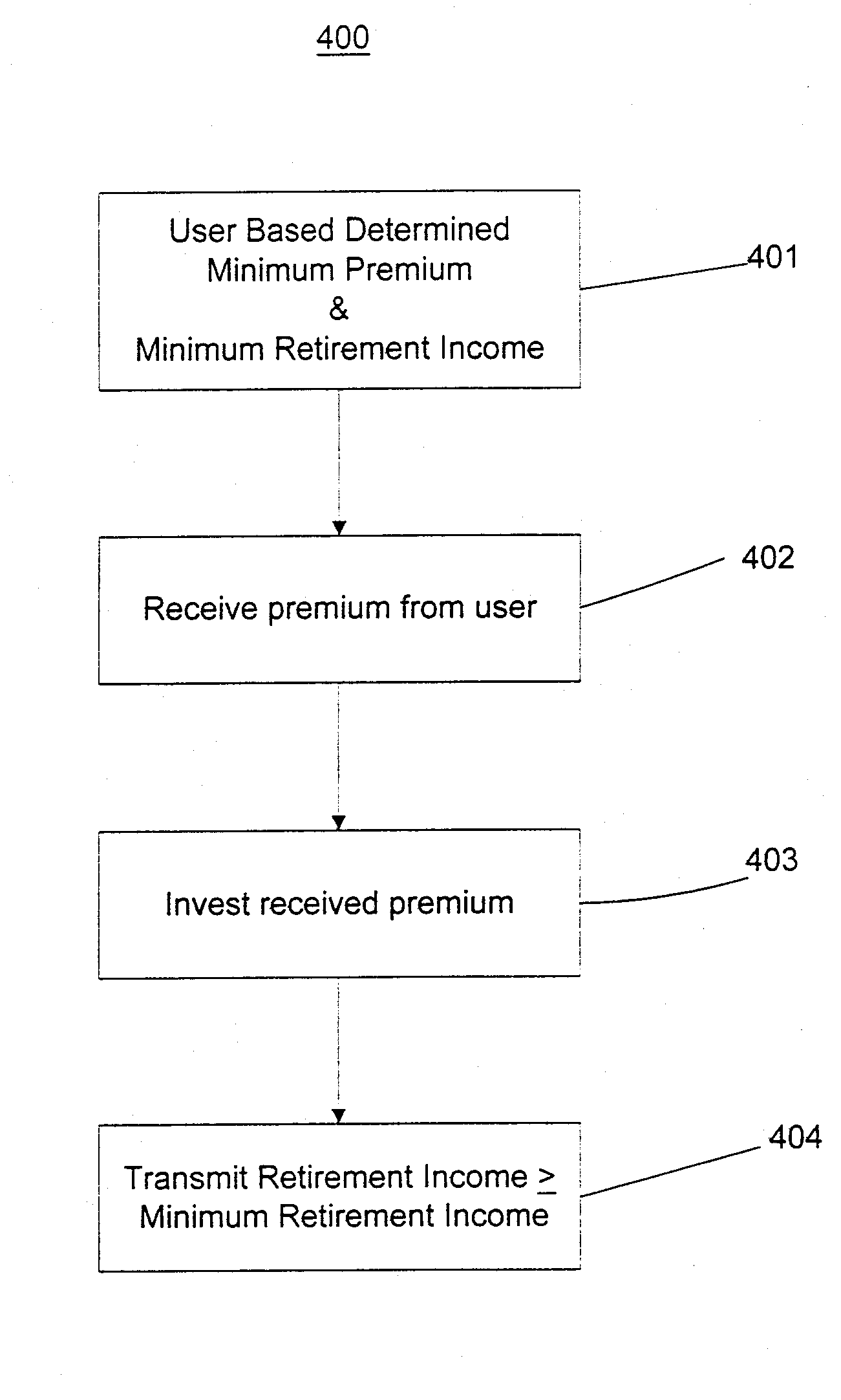
Method and system for portable retirement investment
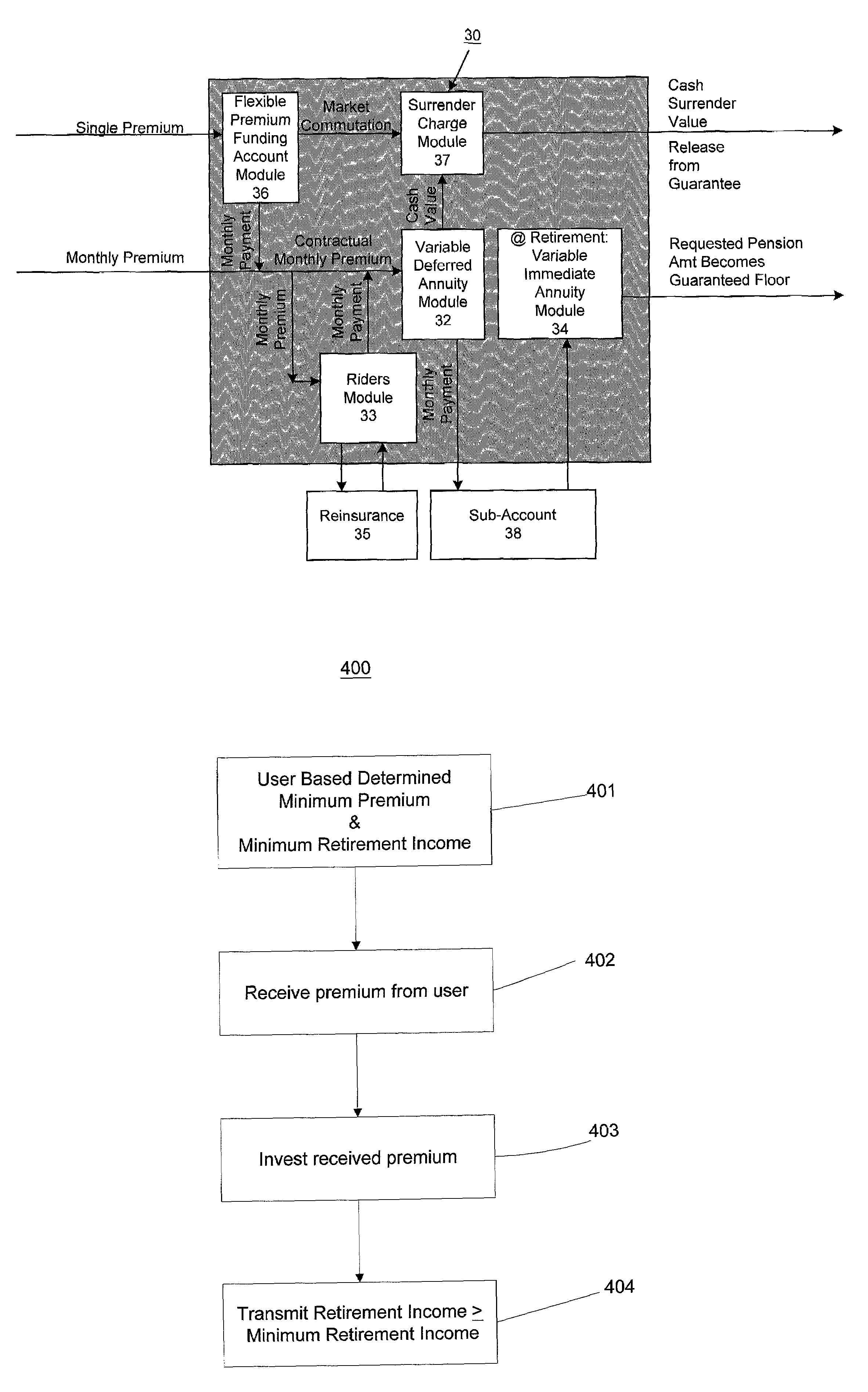
A process and a system for providing a user with a plurality of periodic retirement income payments is disclosed. The process comprises the steps of receiving an input including two of a retirement date, a minimum retirement income amount and a defined premium payment amount for payment over a plurality of preset payment intervals. The process also includes the steps of calculating the other one of the retirement date, the minimum retirement income amount and the defined premium payment amount for an accumulation period defined by the retirement date and a current age of the user; receiving a premium payment amount from the user during the accumulation period; investing the received premium payment amount in an account in a manner consistent with one or more predefined objectives during the accumulation period to realize a retirement income amount. The process further includes the step of transmitting the retirement income amount to at least one of the user and a designated receiver at a designated time after the end of the accumulation period. The retirement income amount includes a predetermined guaranteed minimum retirement income if the received premium payments are received according to a preset premium payment schedule.
Owner:GENWORTH HLDG
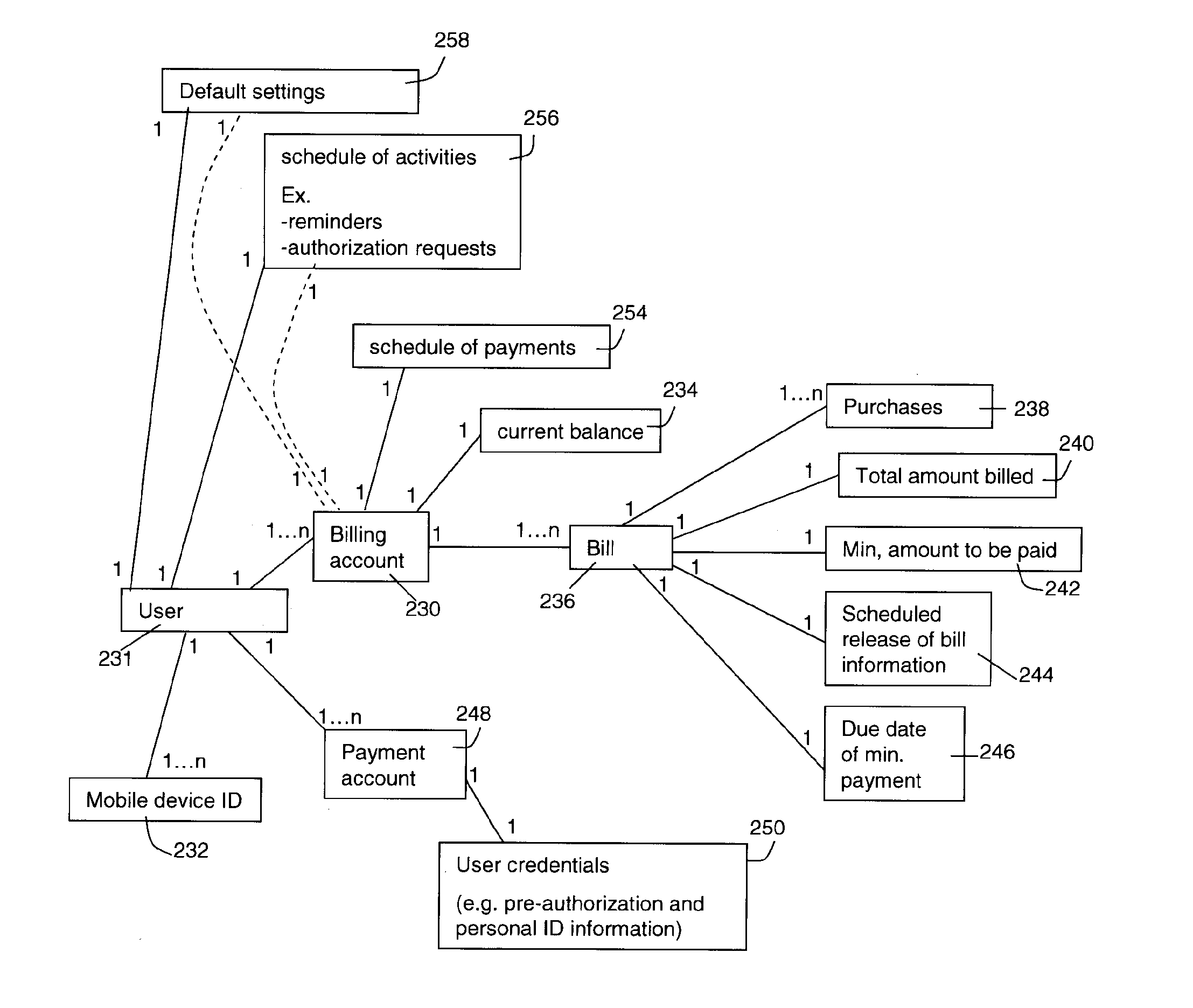
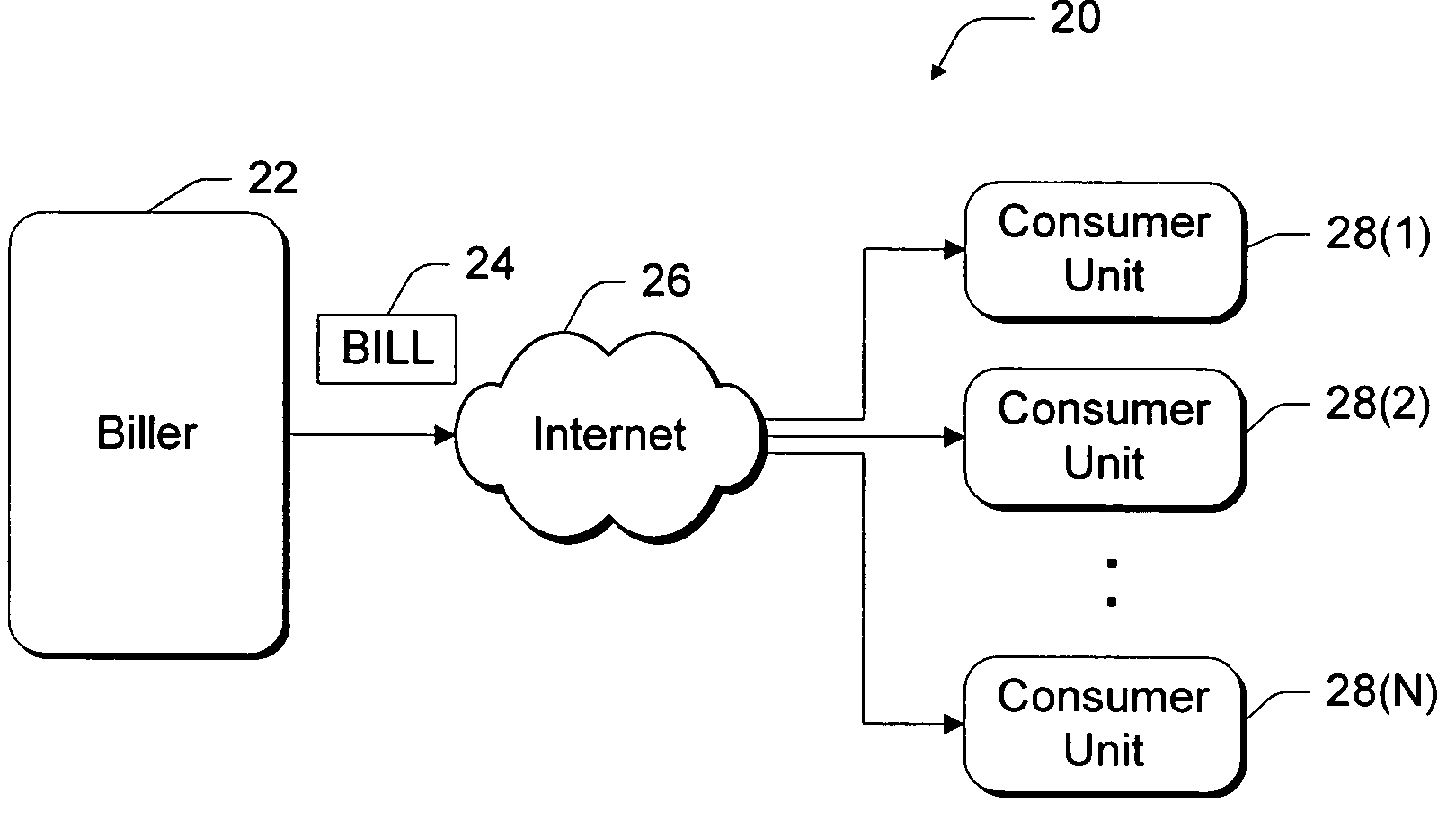
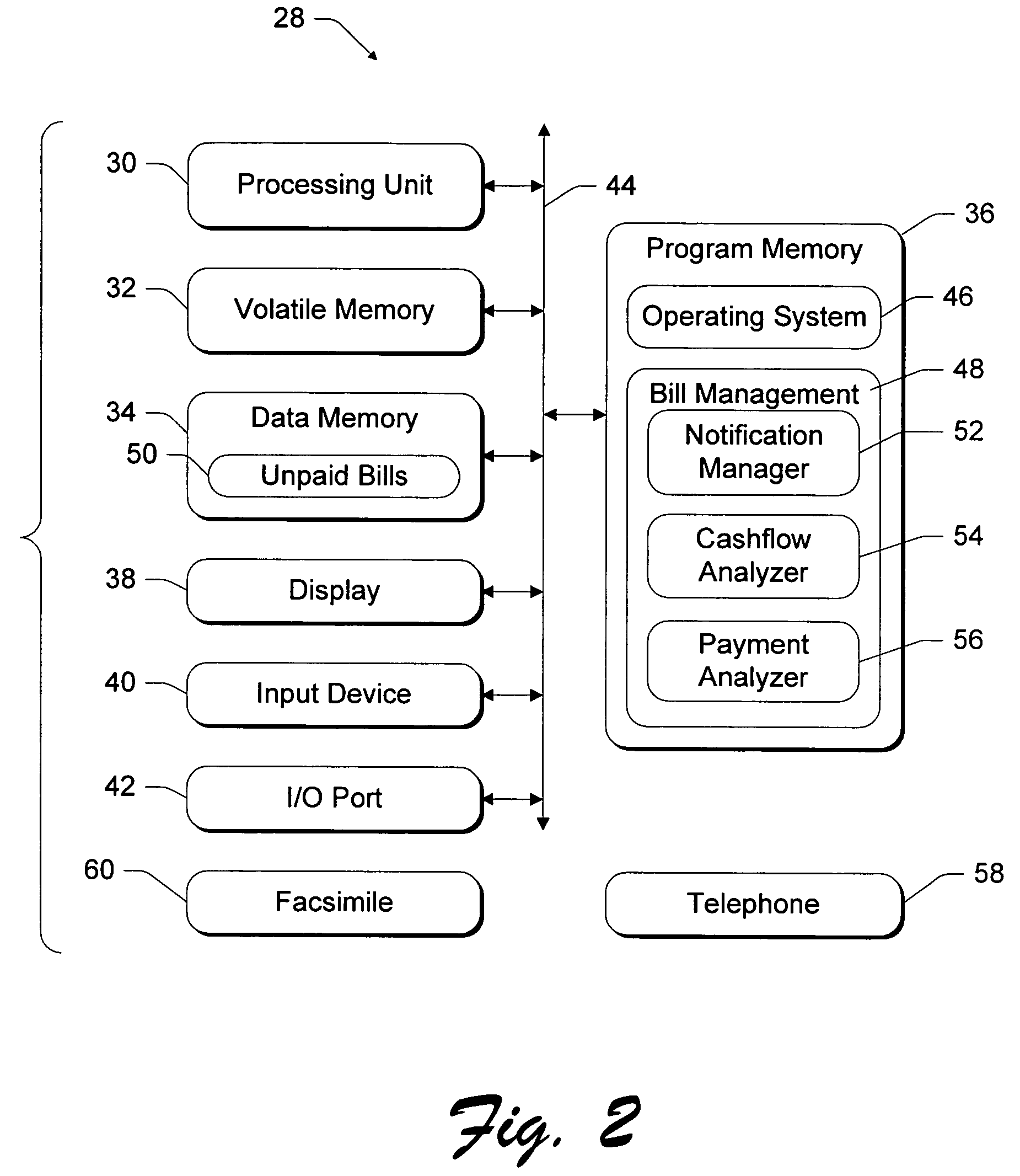
Consumer-based system and method for managing and paying electronic billing statements
InactiveUS6839687B1Minimizes overdraftMaximize balanceComplete banking machinesFinancePayment scheduleGraphics
A consumer-based bill management and payment system is configured to receive, analyze, manage and pay electronic billing statements received from the biller over the Internet. The system includes a notification manager that detects when the electronic bill arrives and notifies the consumer. The bill is stored in memory with other unpaid electronic bills. According to another aspect of the invention, the system has a cashflow analyzer that enables the consumer to coordinate the unpaid electronic bills according to different payment schedules for a bill payment cycle (e.g., a month). The goal of the manipulation is to permit the consumer to analyze how the different payment schedules affect the consumer's cashflow with an aim toward minimizing overdraft during the bill payment cycle. The cashflow analyzer can automatically compute an optimized payment schedule that minimizes overdraft of the consumer's account, while maximizing the balance to generate the most interest. When the consumer desires to pay a particular bill, the bill is presented to the consumer through a graphical user interface (UI). The bill management and payment system supports a payment analyzer to enable the consumer to determine how much of the electronic bill to pay. The payment analyzer provides a venue to challenge certain items on the bill.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
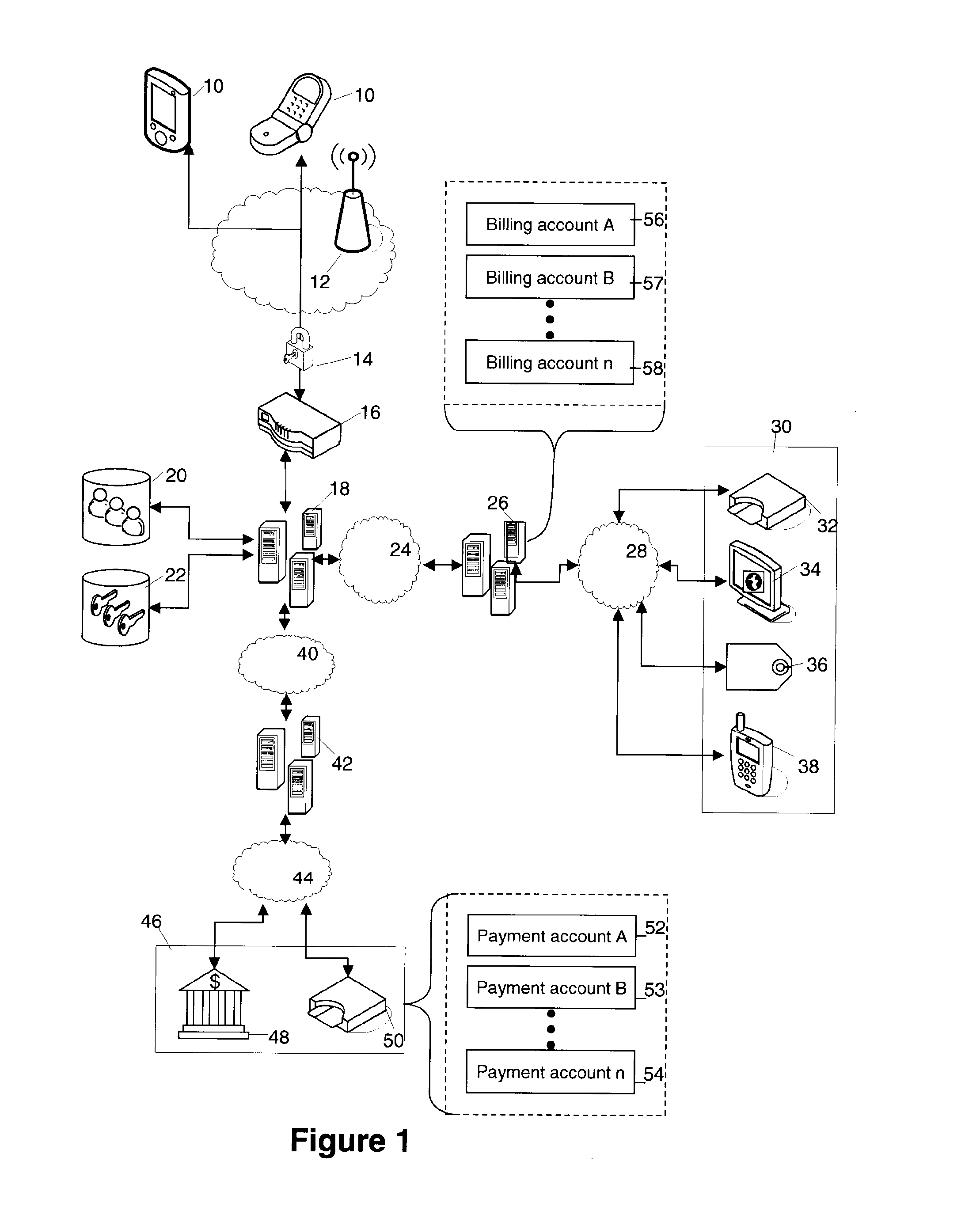
Secure billing system and method for a mobile device
A system and method are provided for scheduling the payments of bills. An authorization server is provided to be in communication with one or more payment servers and a mobile device. The authorization server receives bills from a billing account, and each of the payment servers can make payments to the billing account. A mobile billing manager, residing on at least the mobile device, detects a new bill and then displays a graphical user interface (GUI) on the mobile device. Through the GUI, selection inputs are received, the selection inputs being associated with paying a first amount at a first date from a first payment account. Based on the payment schedule, the mobile billing manager, through the authorization server, instructs the payment server to make payments.
Owner:XTREME MOBILITY INC
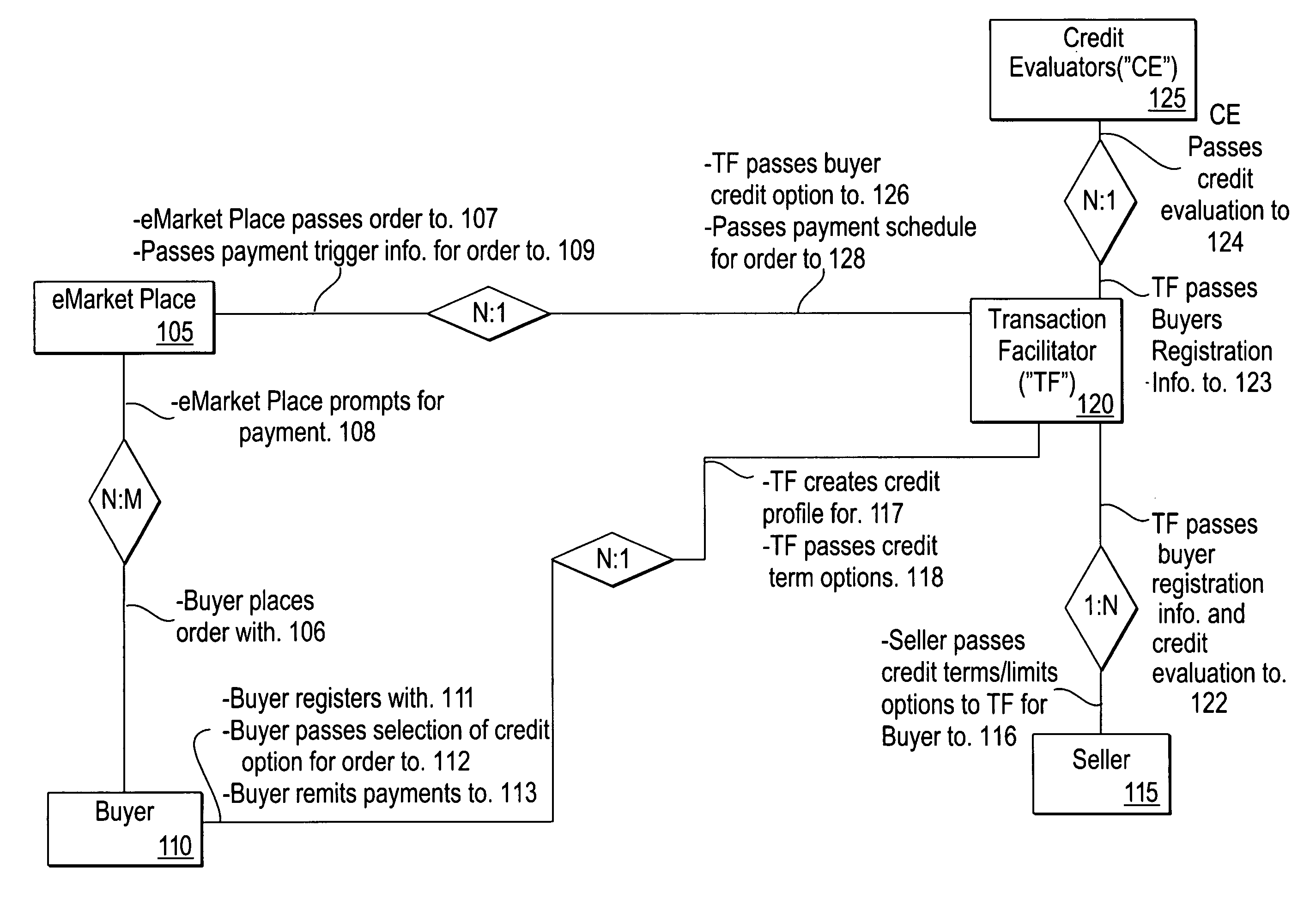
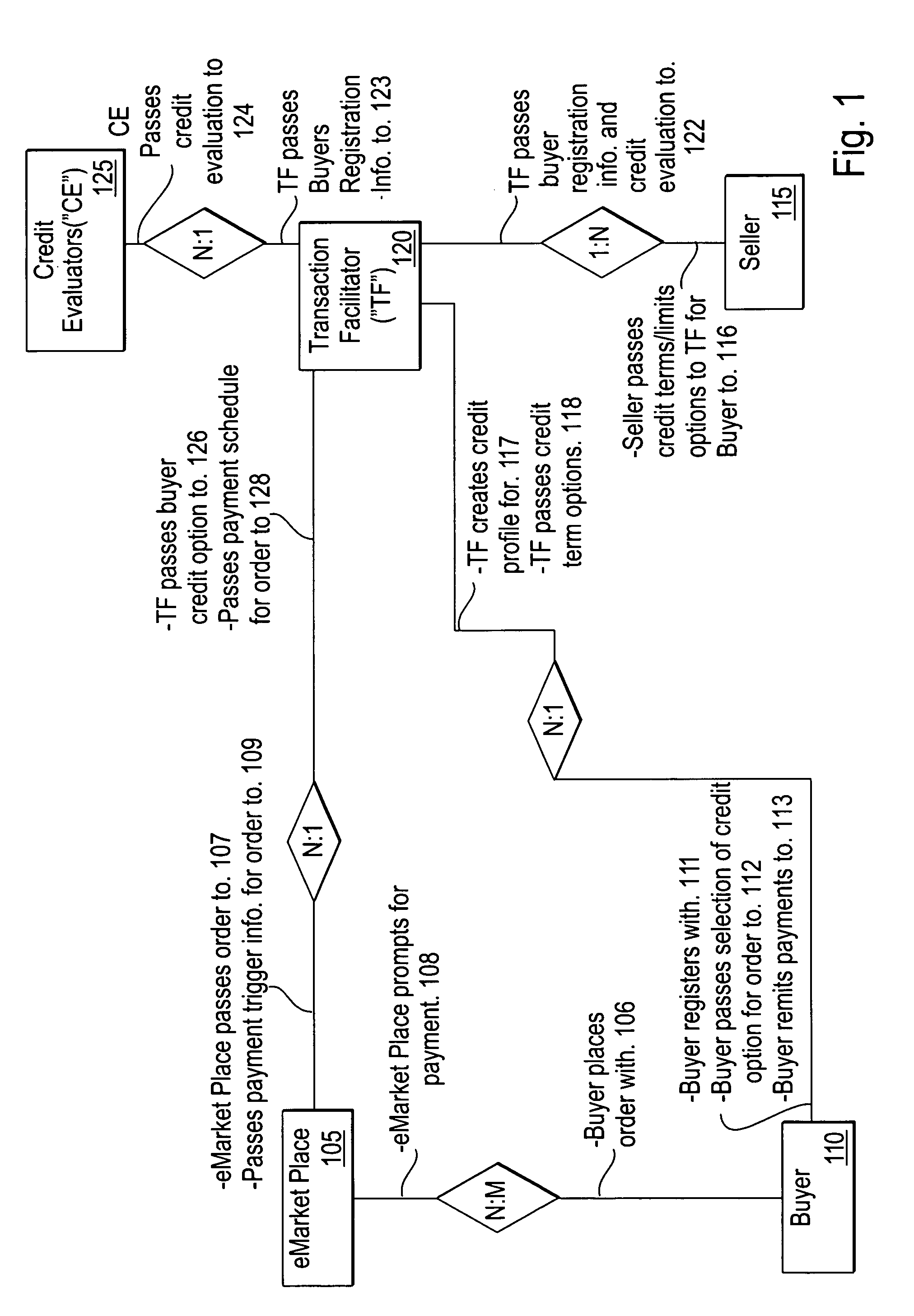
System and method for automated credit matching
The invention includes a method of financing eCommerce purchases including: receiving over the Internet buyer registration information. Then evaluating a credit rating for the buyer and passing over the Internet the credit rating to a seller, and then receiving over the Internet from the seller seller's credit options for the buyer. The next steps are determining other credit provider's credit options for the buyer, creating a database of the credit options for the buyer. After receiving over the Internet an order for the buyer, then querying the database with query criteria specific to the order, thereby resulting in a report of credit options for the buyer for the order. Passing over the Internet the report to the buyer; receiving over the Internet the buyer's selection of a credit option; passing over the Internet a payment schedule for the buyer to an intermediary; and receiving payment remitted from the buyer.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
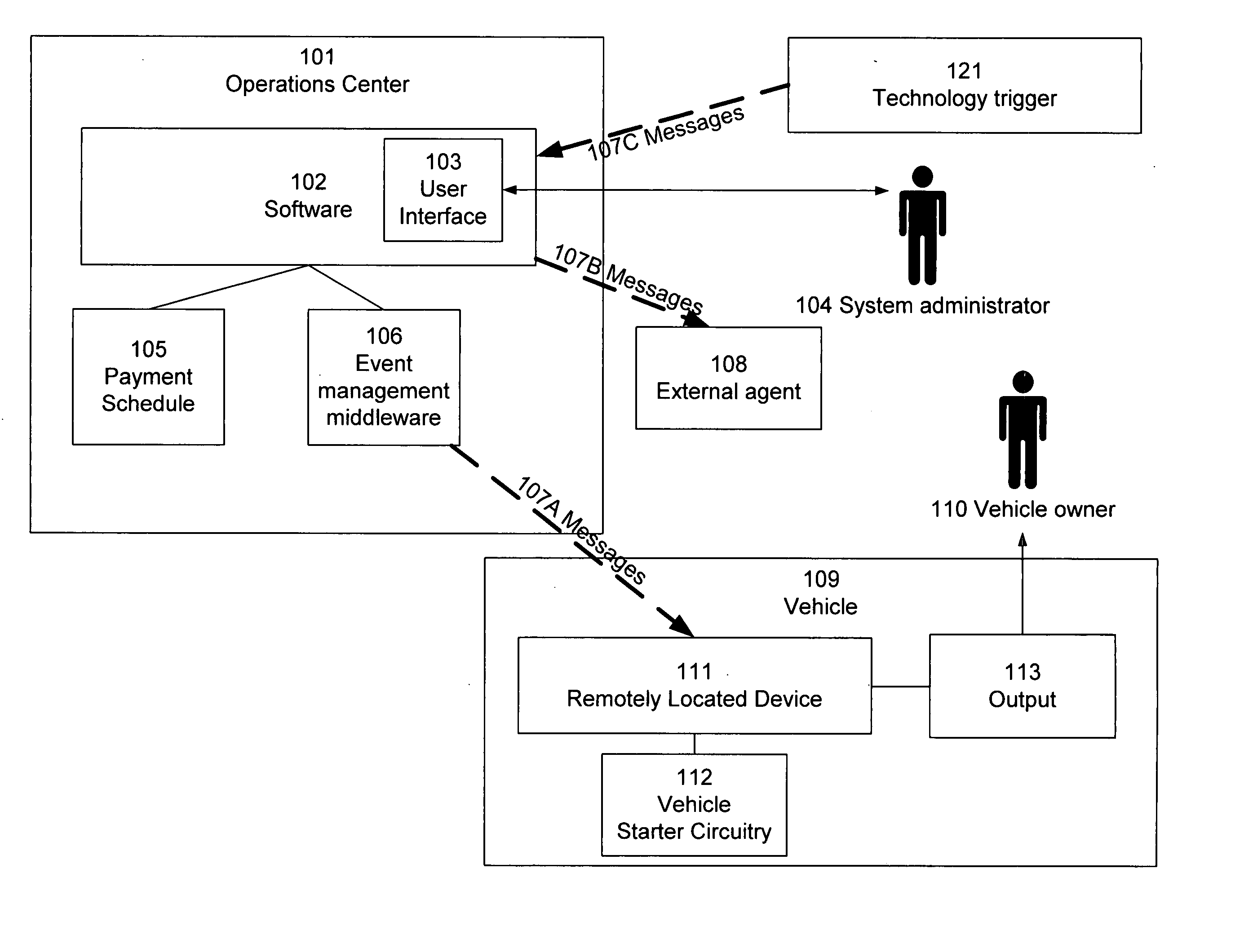
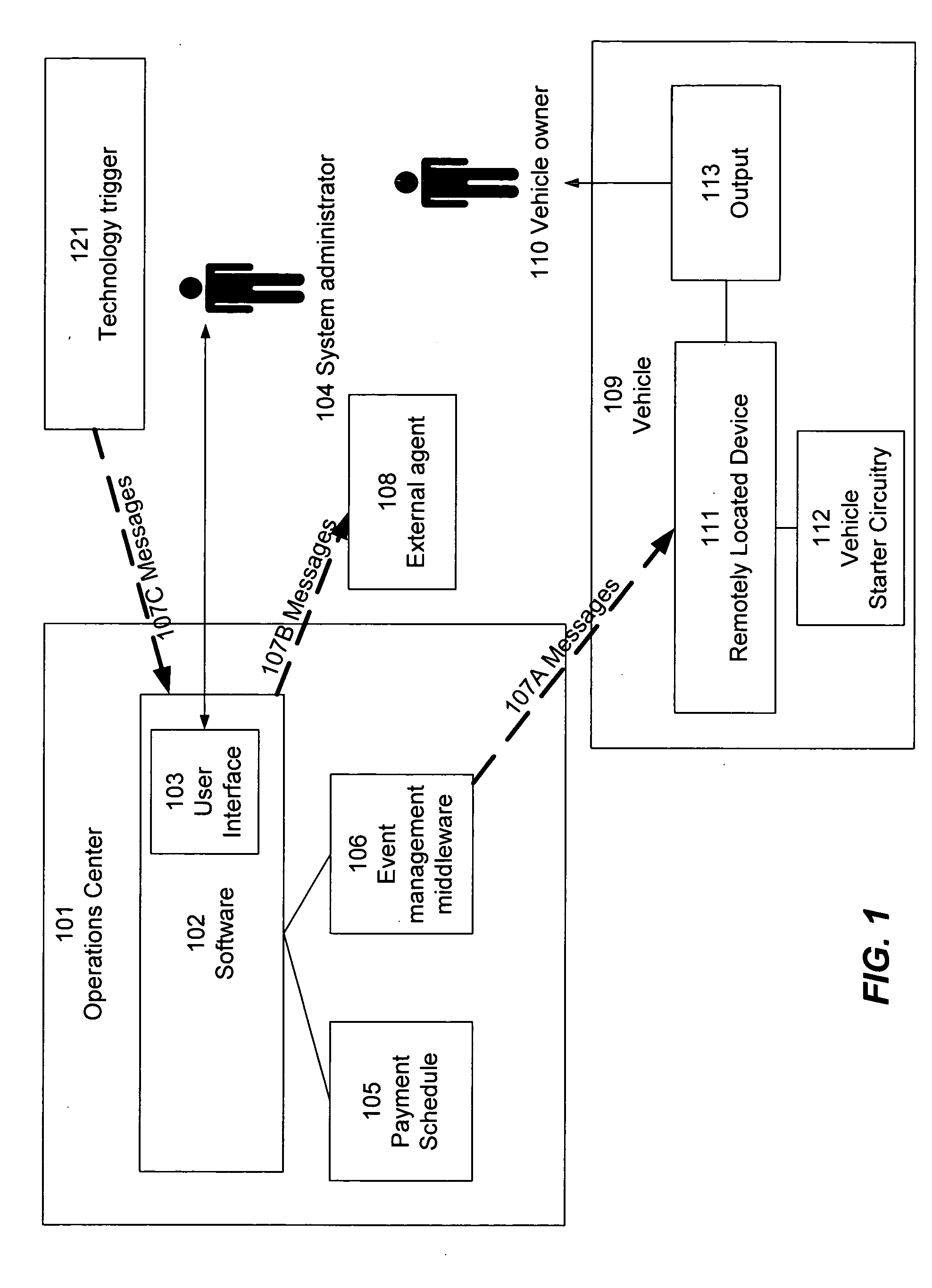
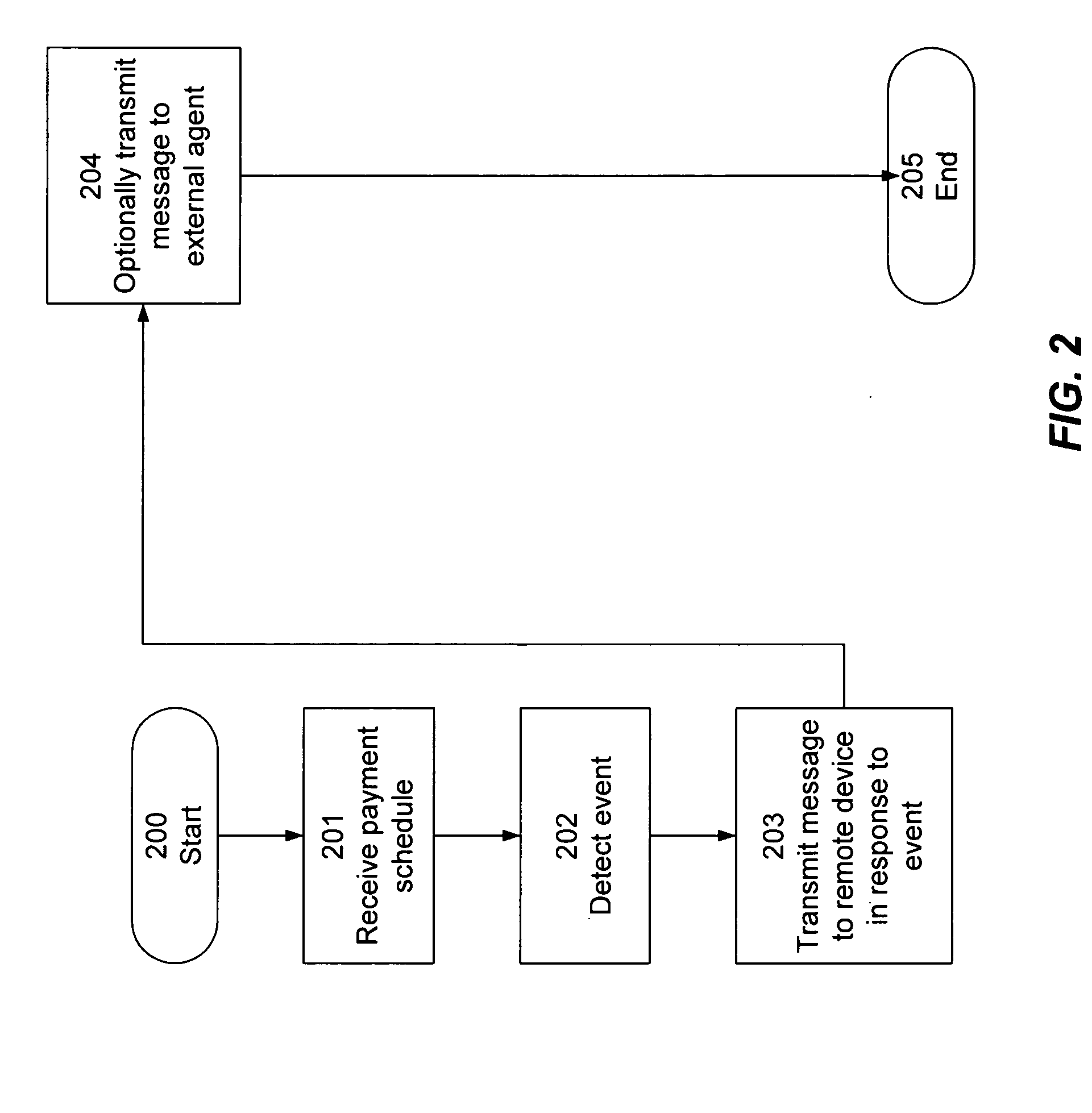
Enforcing payment schedules
InactiveUS20070194881A1Reduce dependenceIncrease flexibilityDigital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesPayment scheduleEngineering
Owner:GORDONHOWARD ASSOC INC
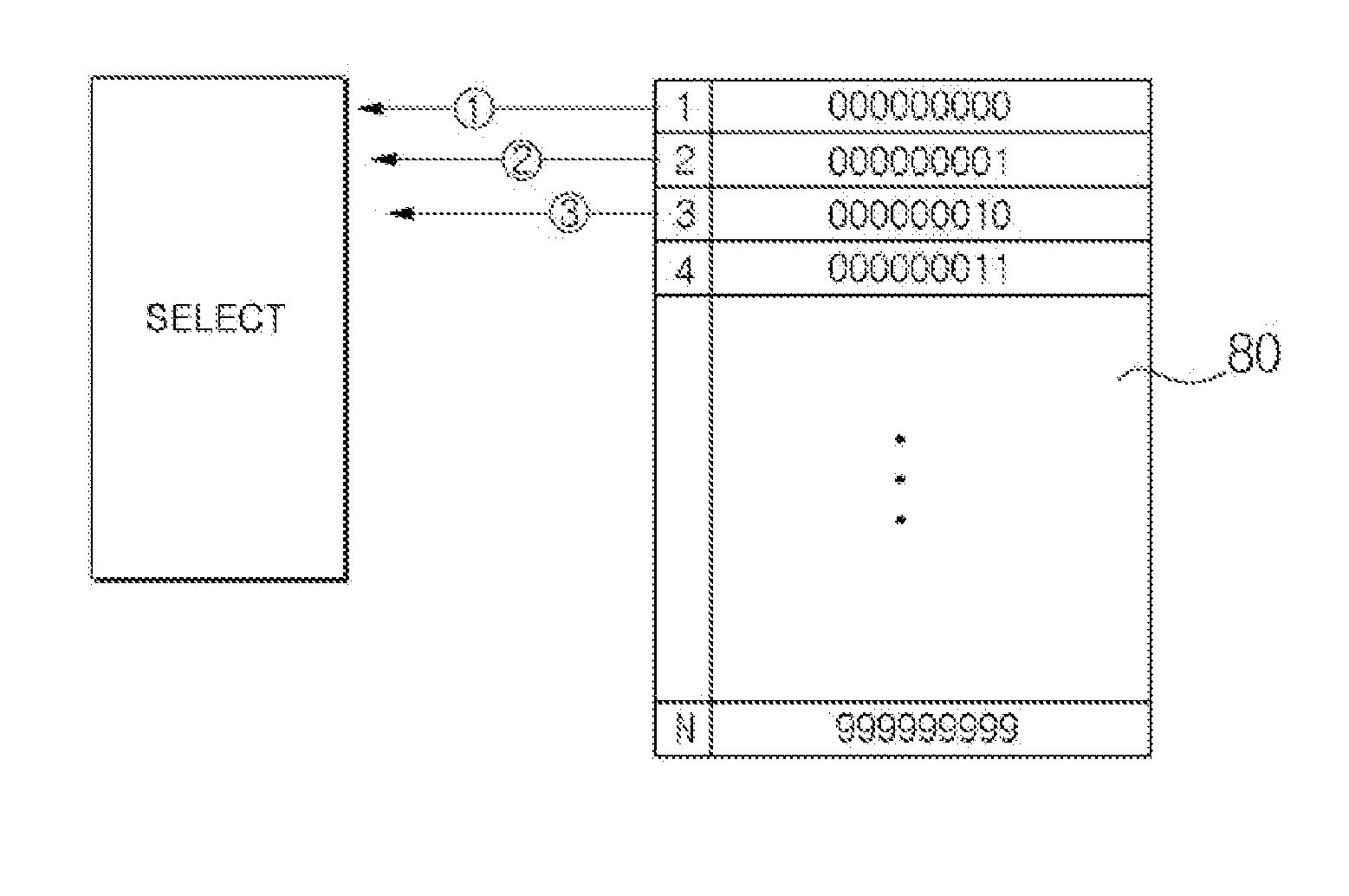
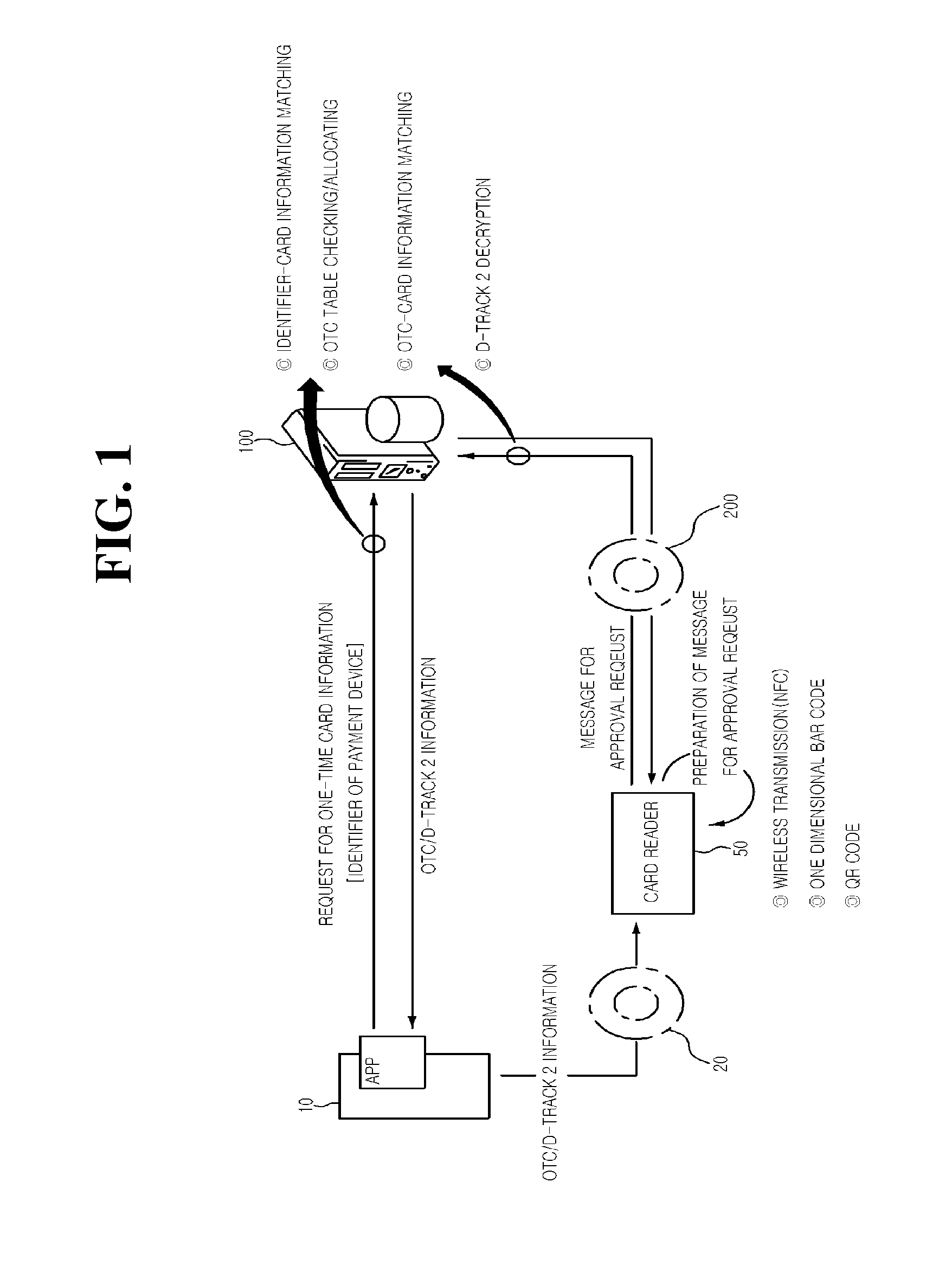
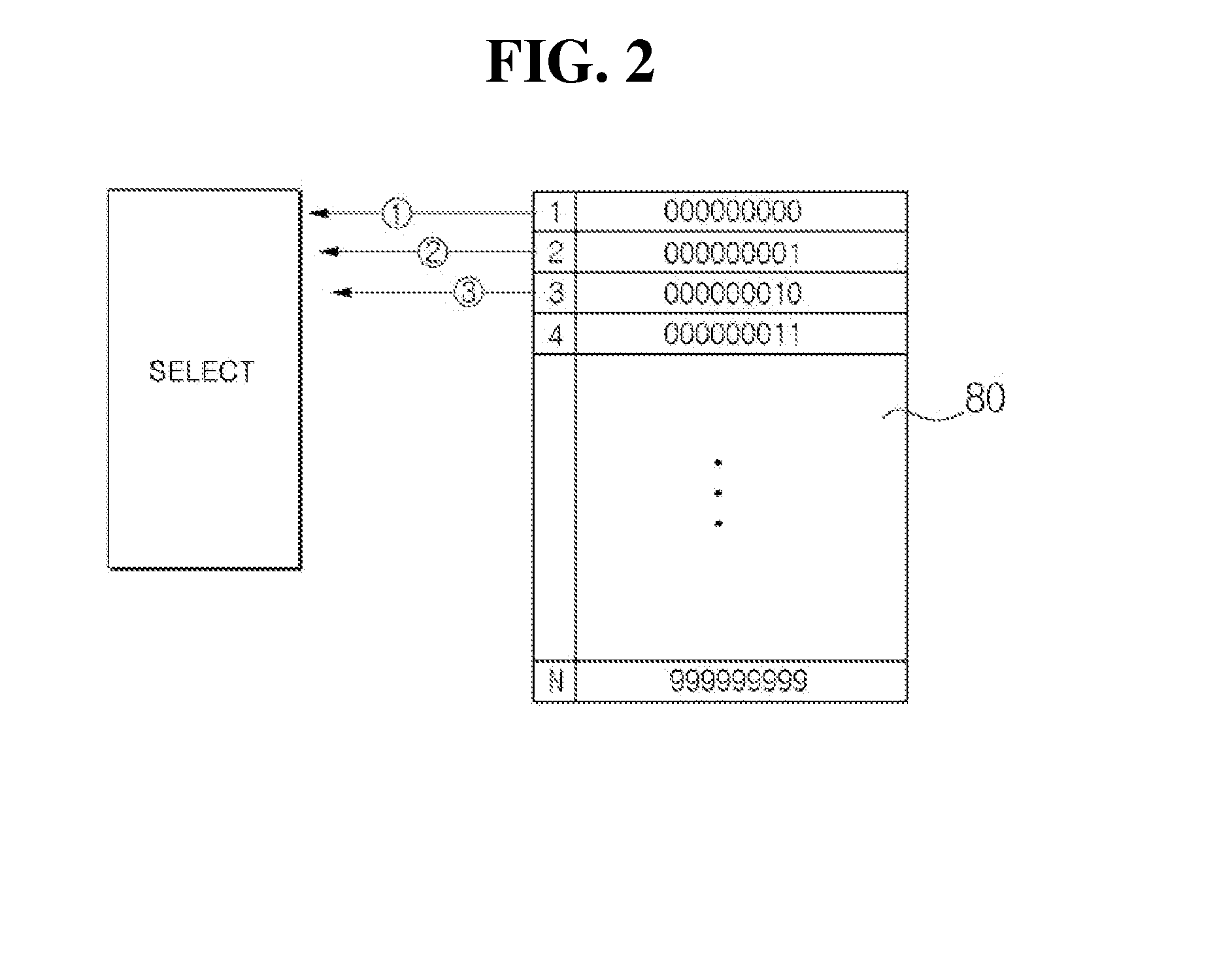
Payment method using one-time card information
ActiveUS20140258135A1Environment safetyImprove securityFinanceCryptography processingPayment scheduleTime information
Provided is a payment method using one-time information, which is performed by a payment system network-connected to a relay server and a payment device and having actual card information, the method including: receiving a payment schedule message from the payment device; publishing a Bank Information Number in response to the payment schedule message, generating one-time card information not including the actual card information, and providing the generated one-time card information to the payment device; judging validity of a message for approval request transmitted from the relay server according to whether or not a difference between a first time when the one-time card information is returned through the relay sever and a second time when the one-time card information is provided to the payment device satisfies a predetermined reference time; and determining whether or not the message for approval request is approved according to a judgment result of the validity.
Owner:SHINHAN CARD +5
Billing method for pump usage
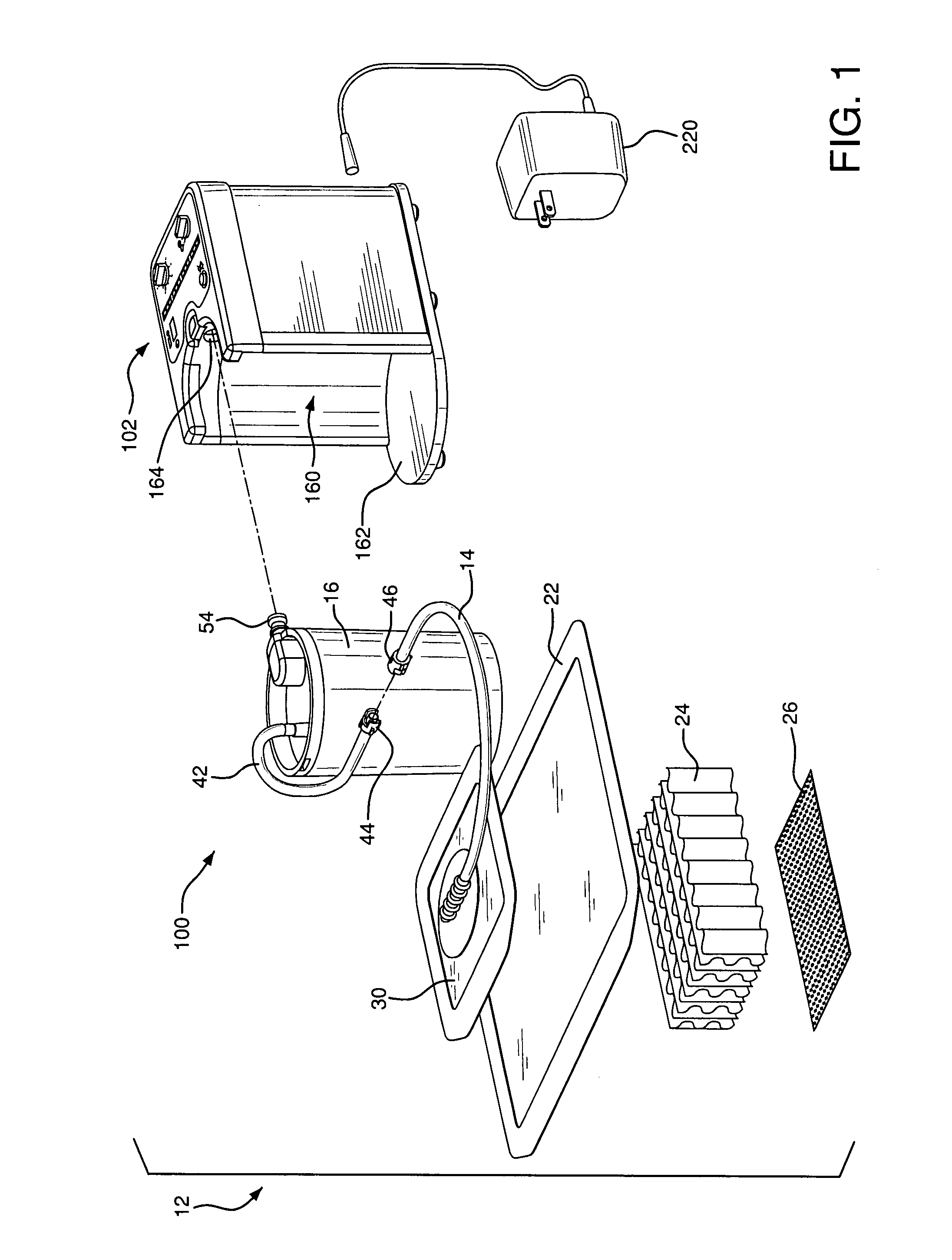
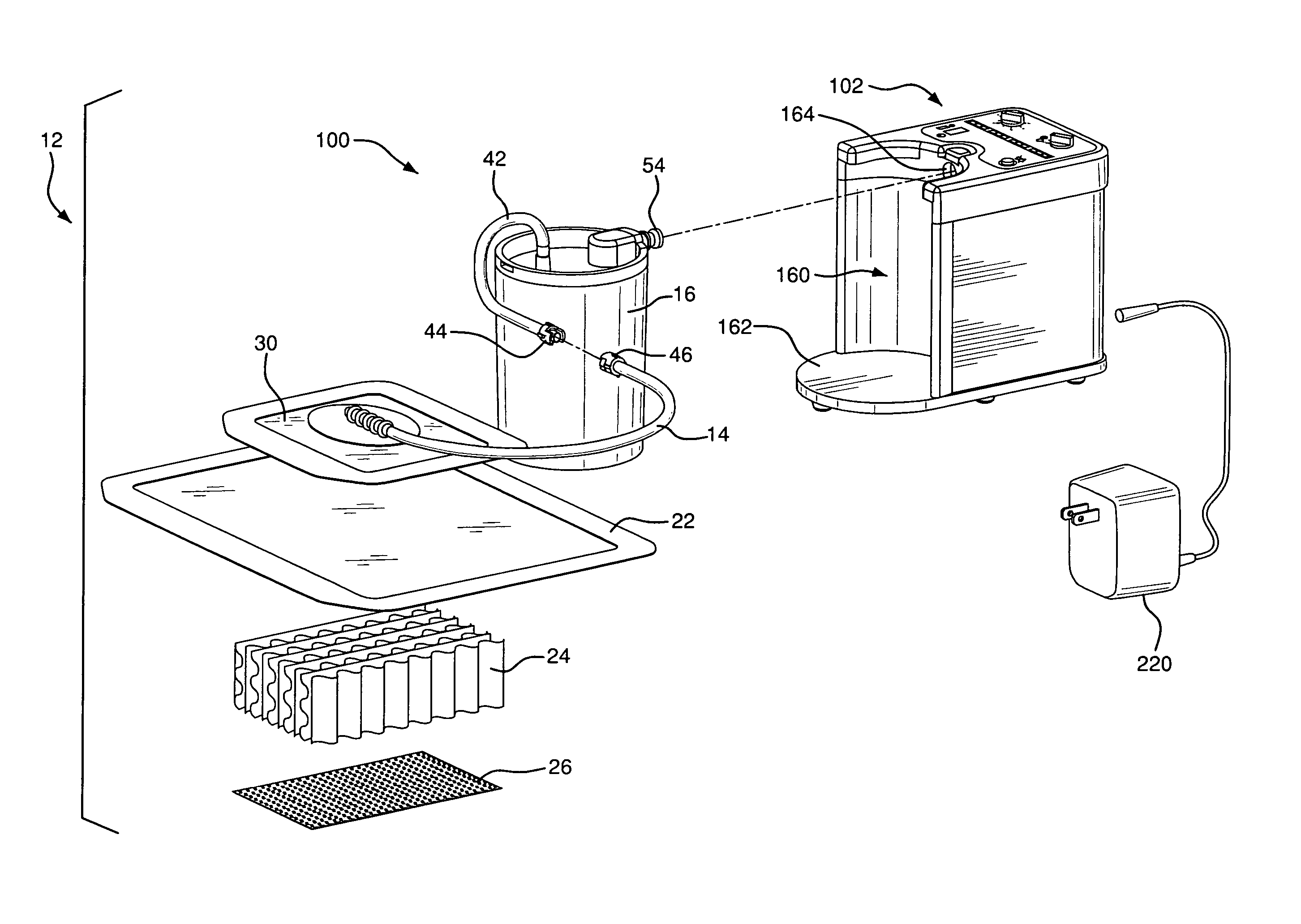
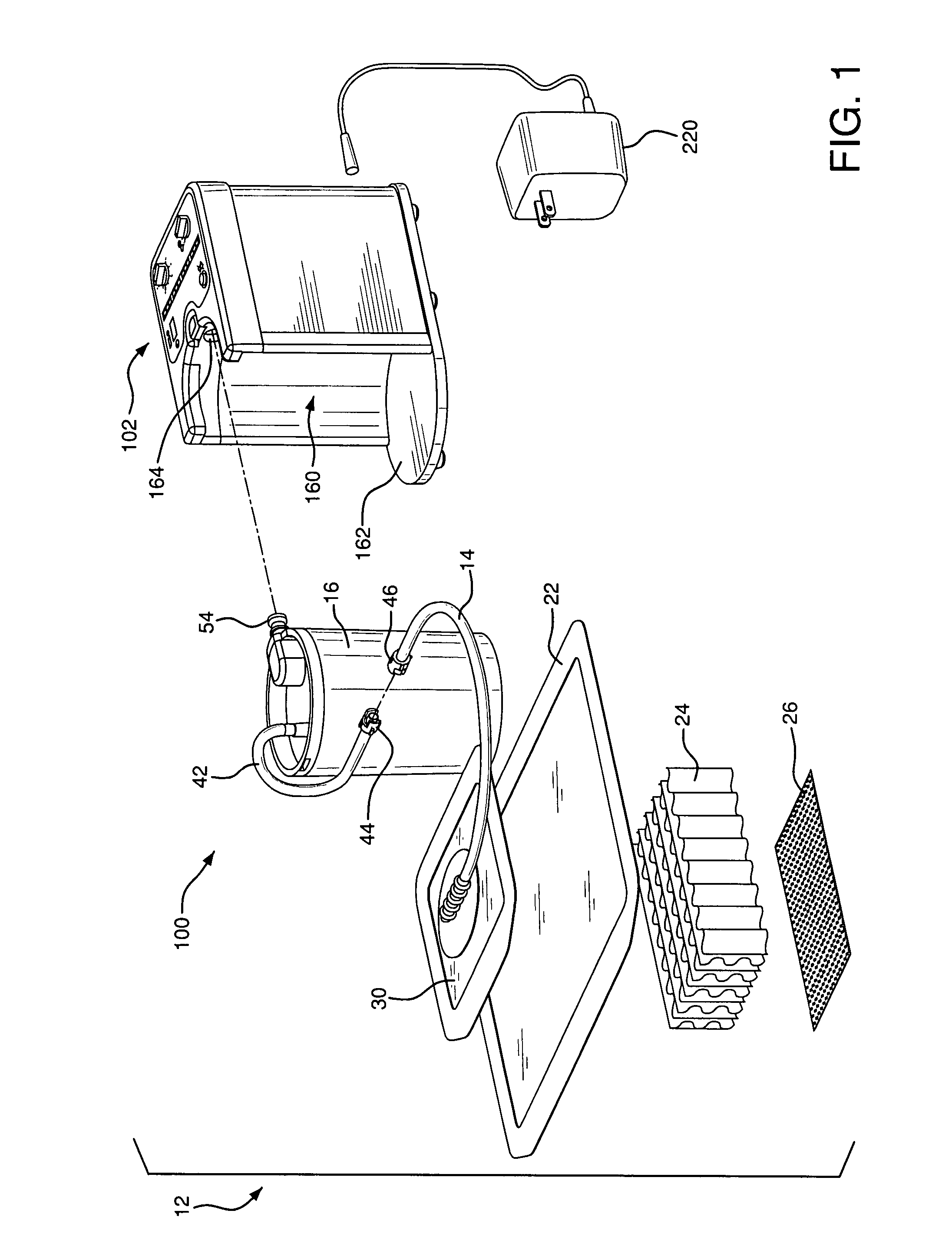
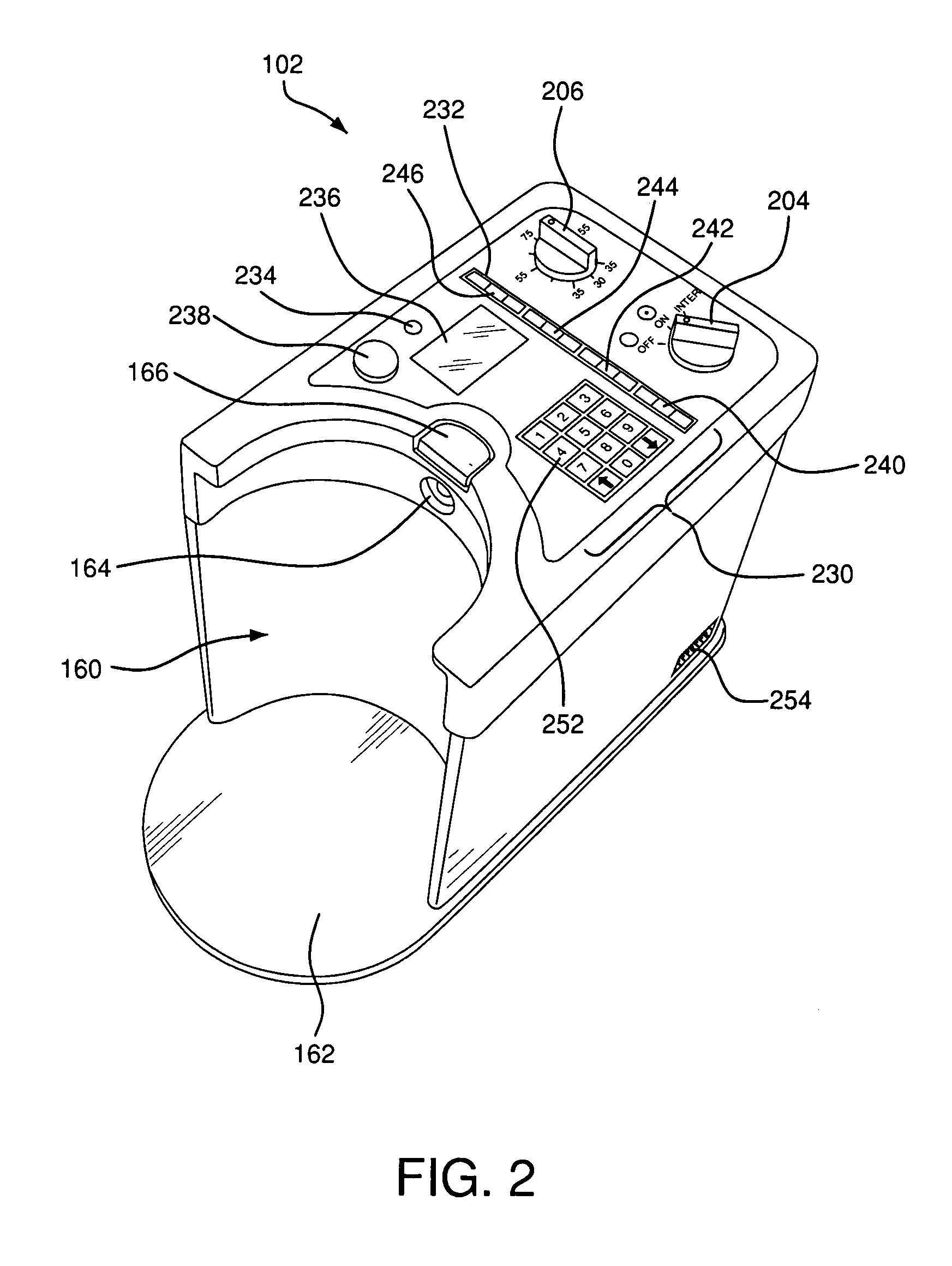
InactiveUS20080005000A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical devicesPayment scheduleUnit of time
Disclosed are methods of leasing or billing for the usage of a portable suction pump adapted for use in a suction-assisted would treatment system. The pump has means for recording time units corresponding to periods of time when the pump is operating and for providing reports of usage time. The pump further has means for detecting that the wound treatment system is operating normally so as to be compliant with standards for suction wound treatment, and for recording and reporting time of normal operation or compliant usage. The methods include leasing the pump at a payment schedule that is based upon the amount of actual usage time or the amount of compliant usage time. The lease payment may include an amount of pre-paid time units such that unused time units can be credited to a new or renewed lease for a replacement pump. The billing methods can also be based in whole or in part on a planned maintenance schedule for the pump.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
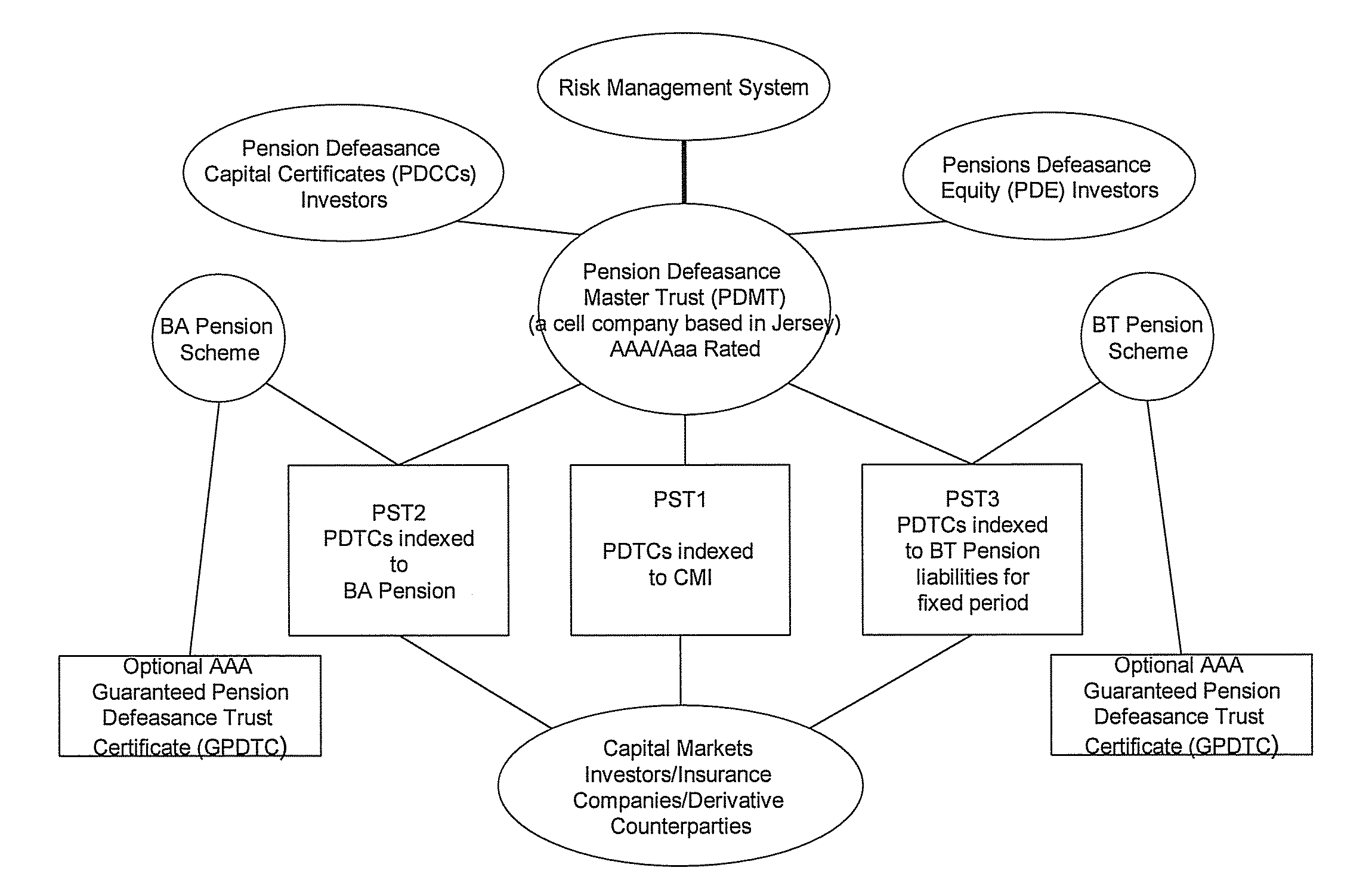
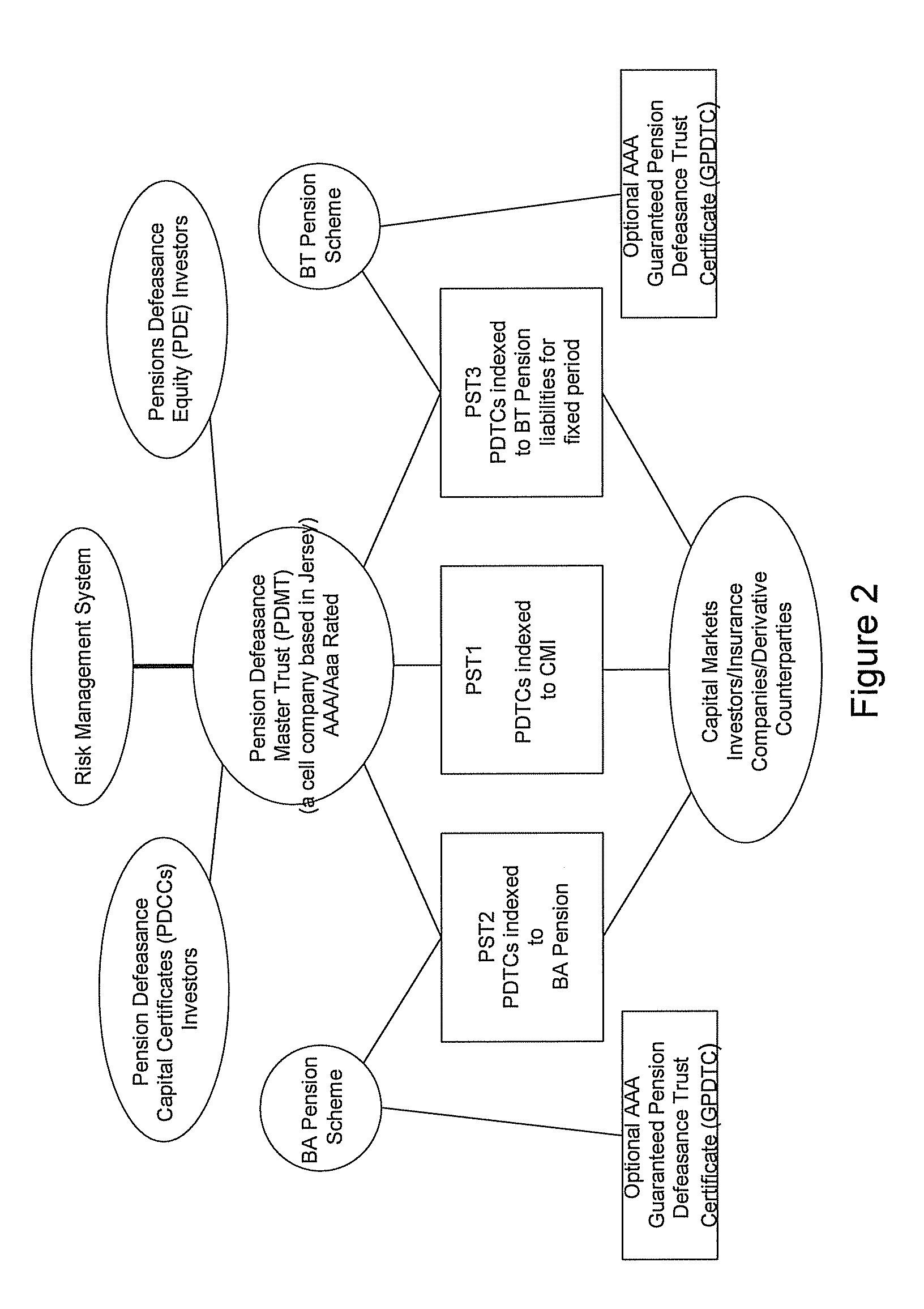
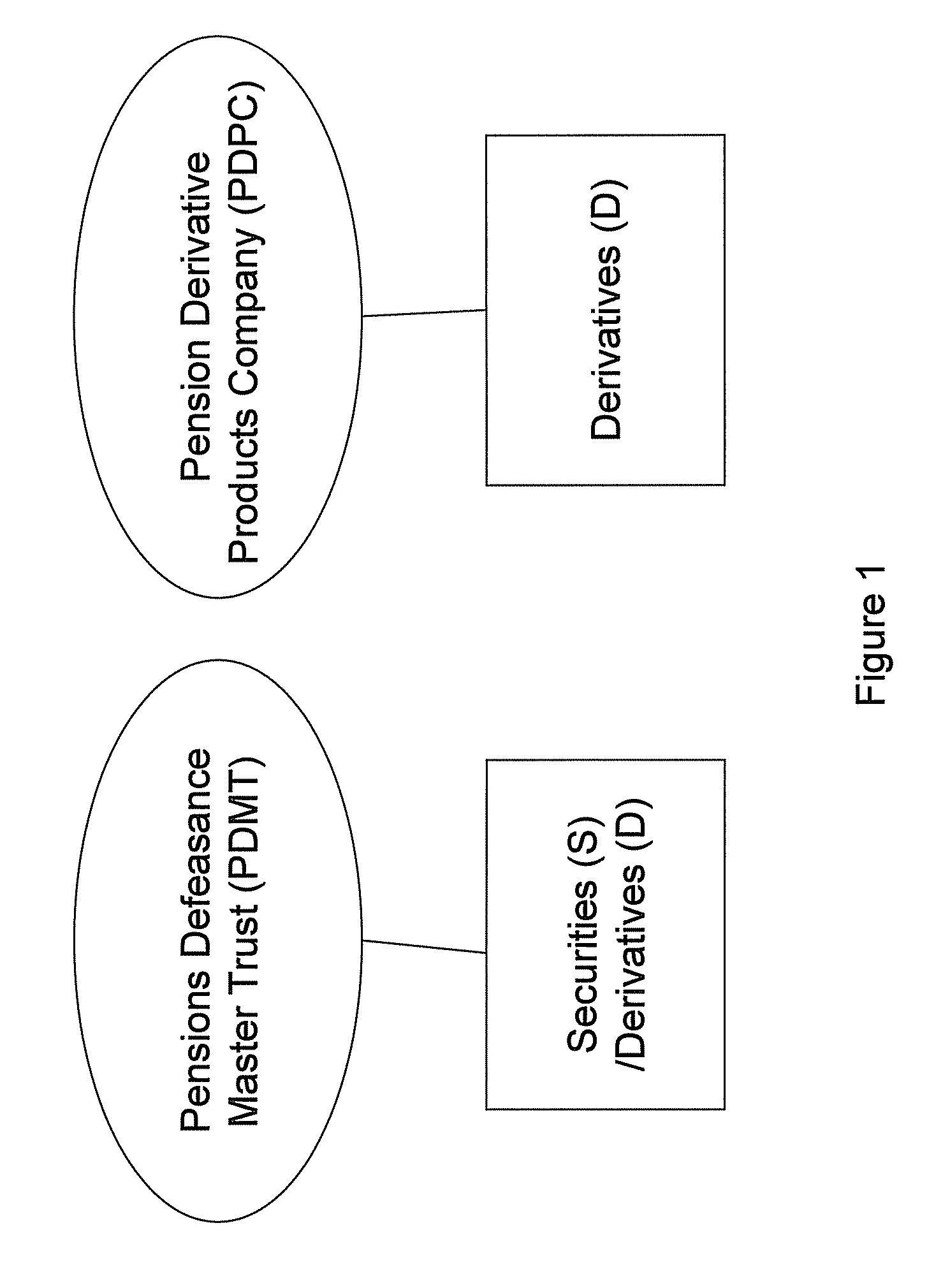
Pension Fund Systems
InactiveUS20100121783A1Reduce riskAccurately projecting the expected longevityFinanceFuzzy logic based systemsTime schedulePayment schedule
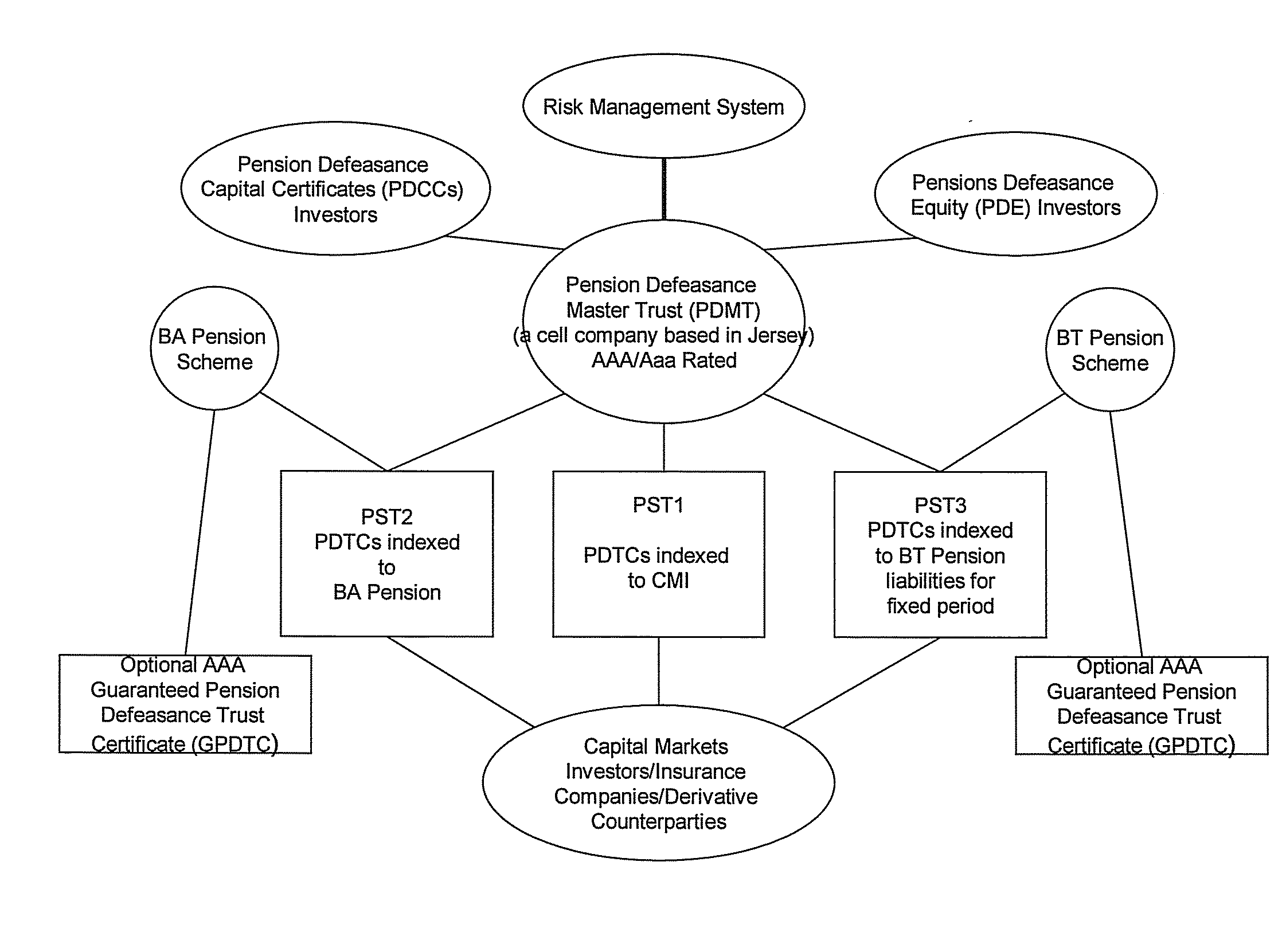
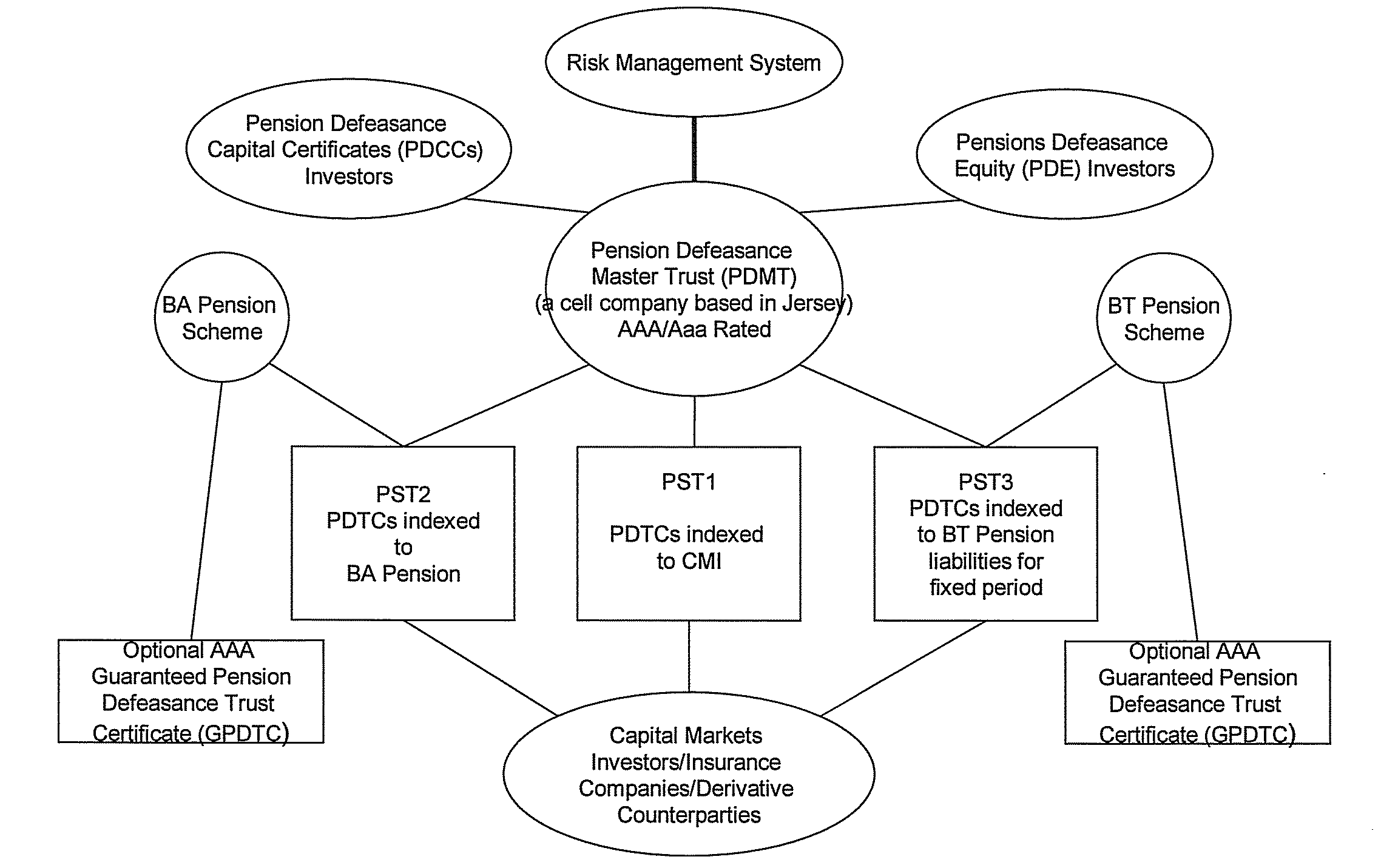
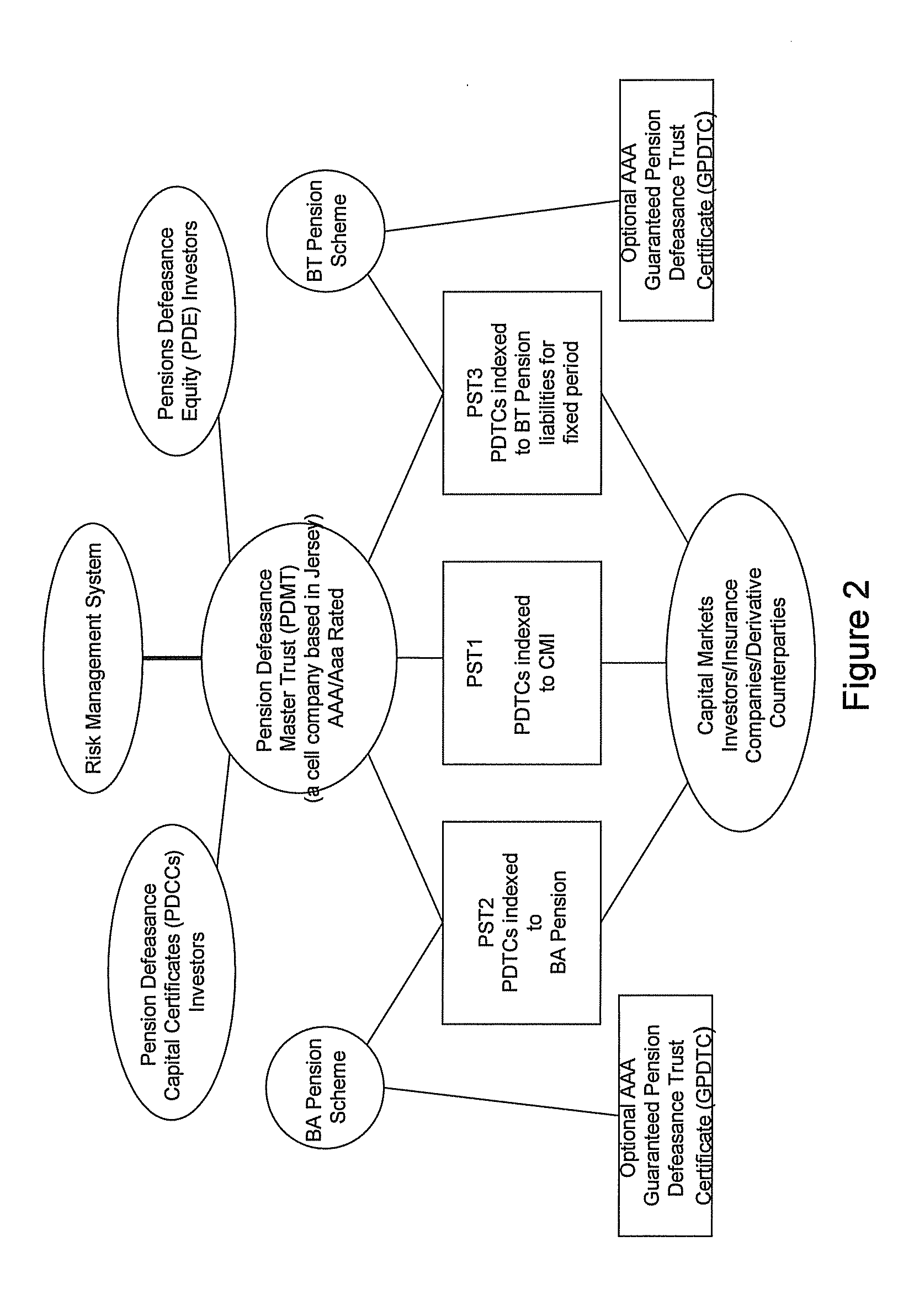
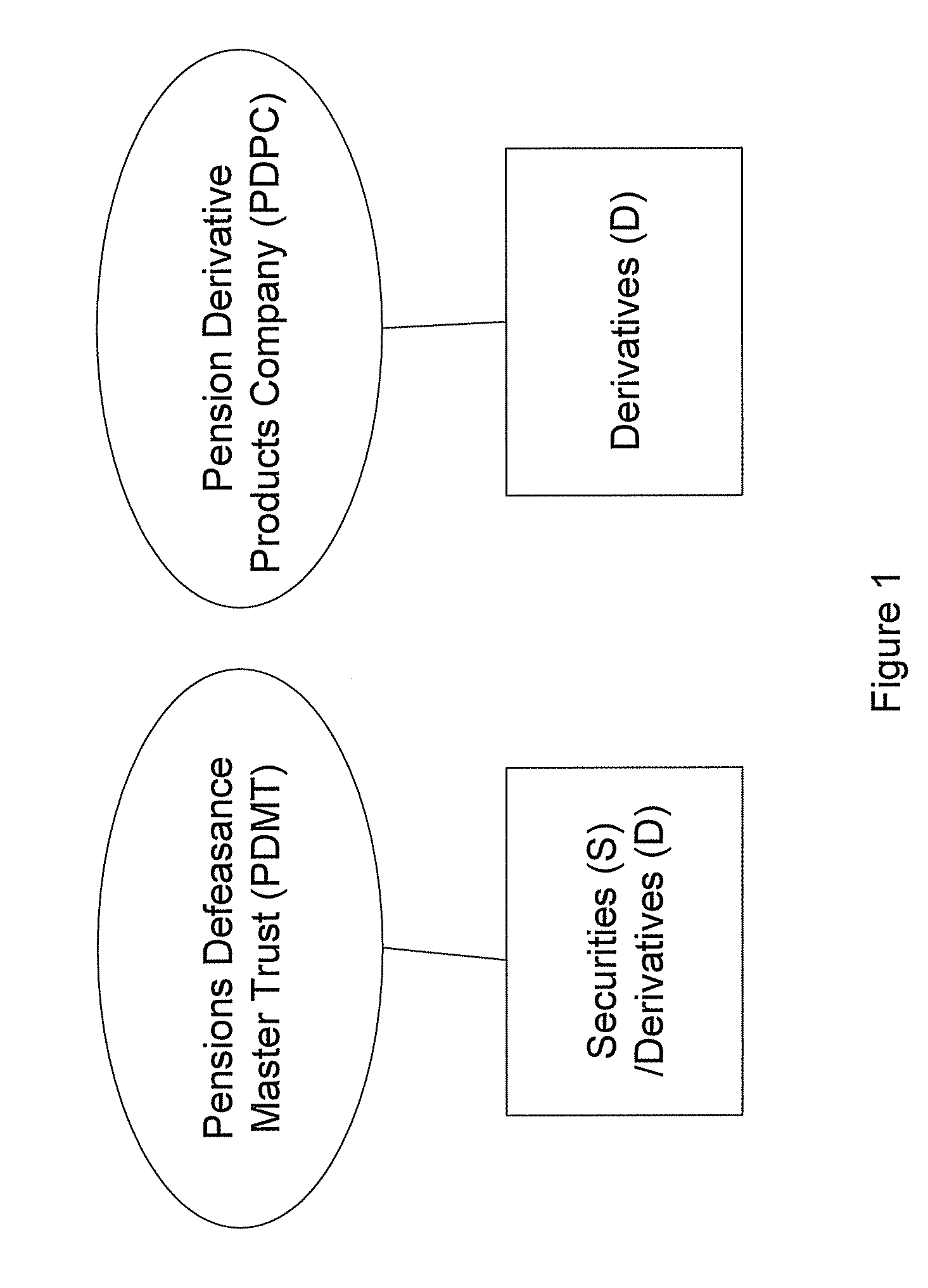
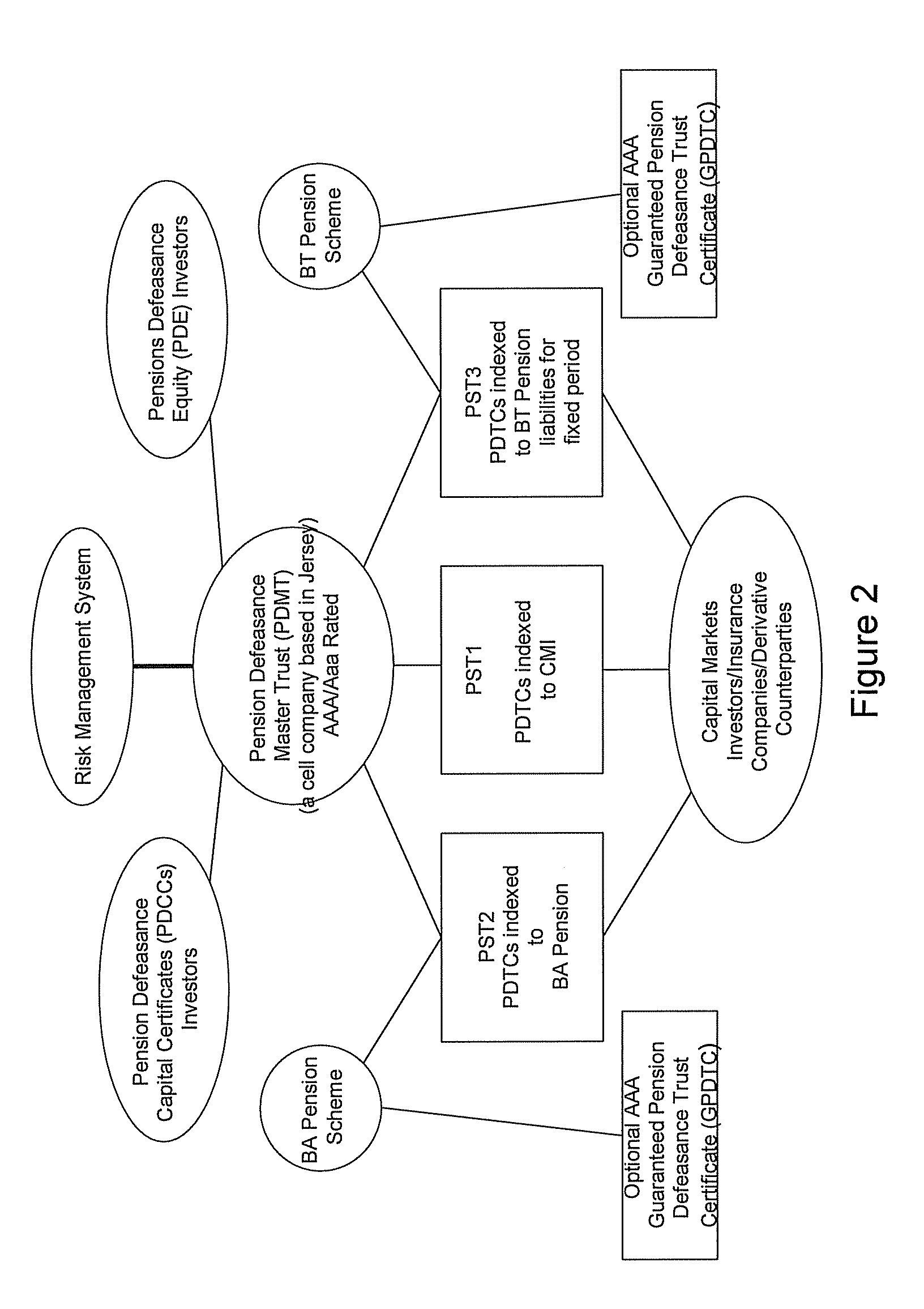
There is provided a computer-implemented method of estimating a capital reserve requirement to cover the longevity risk exposure of a financial instrument in the case of a future longevity shock, the financial instrument undertaking to pay to an investor sums according to a payment schedule of amounts arranged to match with the future cash flow obligations of a pension scheme to at least a portion of its members. The method comprises: (a) calculating, using computing apparatus, an expected payment schedule of the financial instrument by calculating what the cash flow obligations of the pension scheme to its relevant members would be in the case of an expected longevity scenario for the pension scheme membership occurring; (b) calculating, using computing apparatus, a present value of the financial instrument in the case of a stressed longevity scenario for the pension scheme membership in which a longevity-related shock to the expected longevity scenario of the pension scheme membership occurs; and (c) calculating, using computing apparatus and using the calculations of the expected payment schedule and a present value of the financial instrument in the case of a stressed longevity scenario, an estimate of the longevity capital reserve required to ensure that the future cash flow obligations of the financial instrument would be covered in the event that the stressed longevity scenario were to occur.
Owner:PENSIONS FIRST GROUP
Ace up poker game
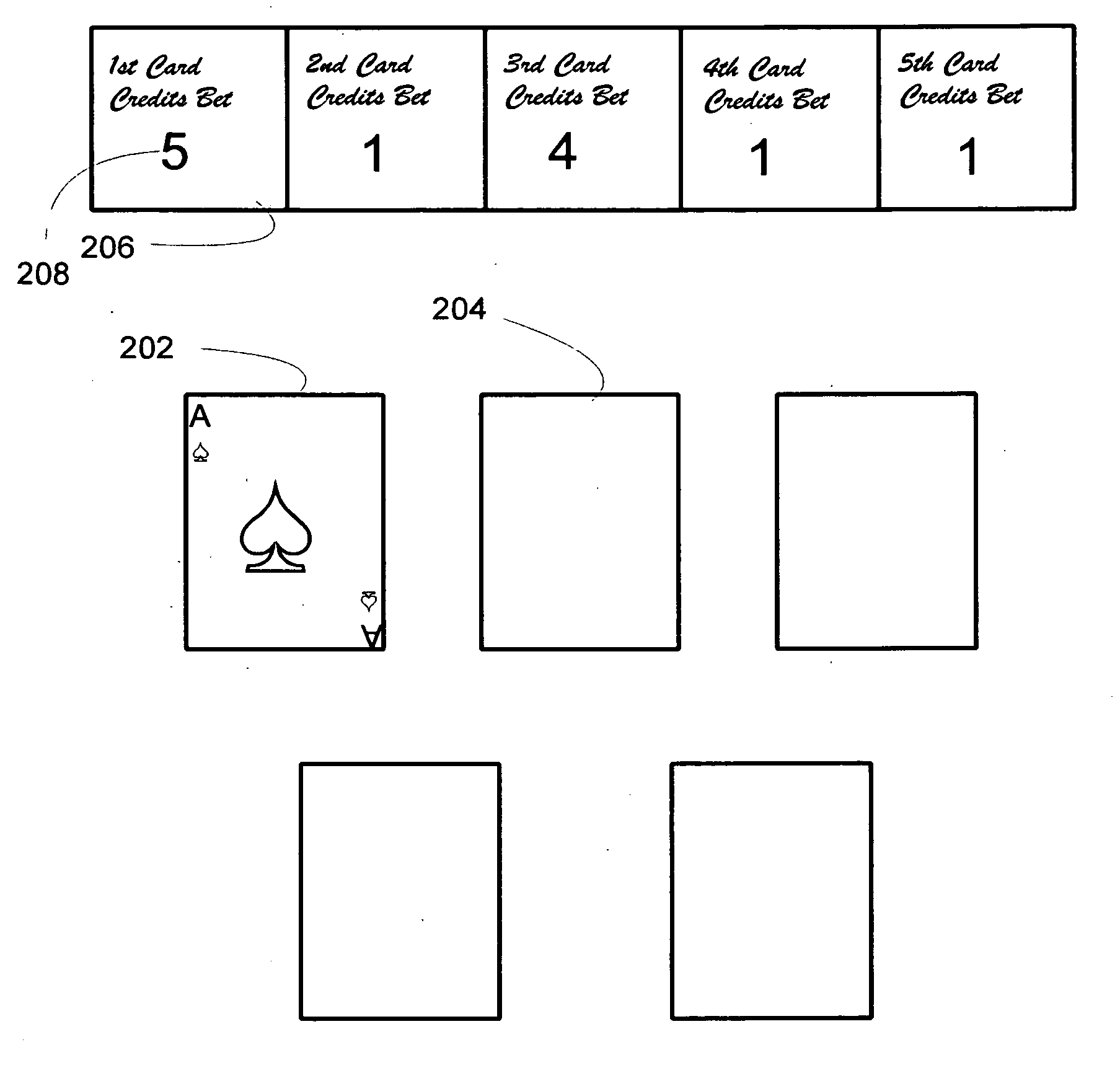
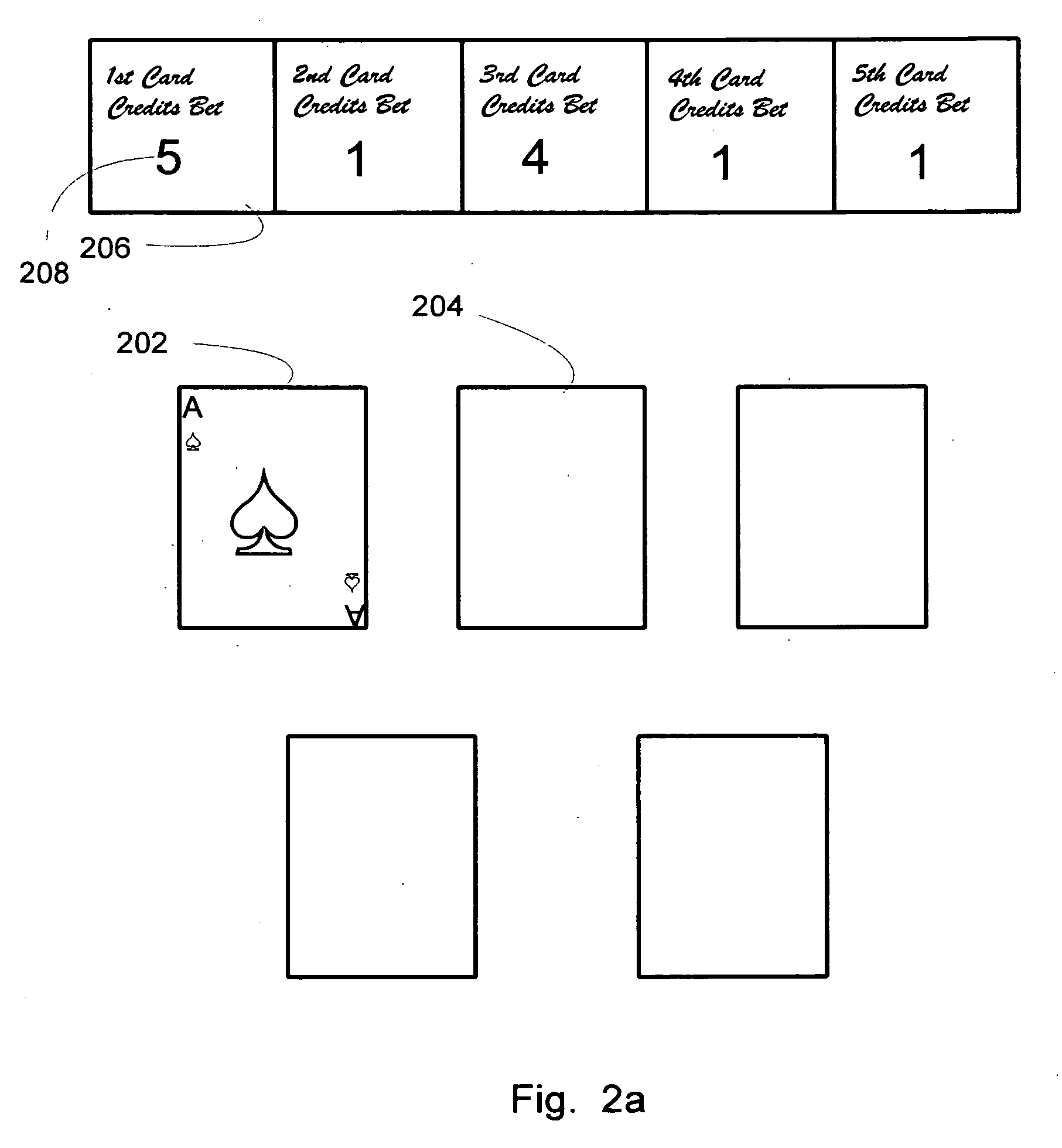
InactiveUS20080161085A1Great payoutLarge payoutBoard gamesCard gamesComputer hardwarePayment schedule
A poker game with physical cards or on an electronic gaming device may be played in which the aces are promoted up a payout schedule so as to provide greater payout than aces normally are accorded based upon pure statistical likelihood of the ace hand occurring. Multiple rounds of poker play against a pay table may be carried out, with the rounds progressing from one card to a defined number of cards such as 5 or 7, with wagers on each or some rounds. A single card poker hand pay schedule may be used, with the Ace of Spaces accorded a larger payout than other aces, and three community cards may be used to speed play at a table with multiple players playing against the modified pay table.
Owner:ACES UP GAMING INC
Pension Fund Systems
InactiveUS20100121785A1Not at risk of errorIncrease relative volatilityFinanceTime schedulePayment schedule
There is provided a method of securitizing a pension fund associated with a pension scheme, comprising: calculating, using data processing apparatus, the expected liabilities of a pension scheme to at least a portion of its members taking into account an expected mortality of the scheme members; issuing from a securities issuing entity a financial instrument which undertakes to pay to an investor a cash flow according to a payment schedule, said expected liabilities being establishing as the initial payment schedule of a financial instrument; exchanging financial instrument with assets held by pension fund; and supporting the securities issuing entity in issuing the financial instrument by providing risk capital to the securities issuing entity; wherein the risk capital is initially provided by at least three separate equity investor entities. One of the equity investor entities may be the corporate sponsor of the pension scheme. Alternatively the risk capital is initially provided by the corporate sponsor of the pension scheme.
Owner:PENSIONS FIRST GROUP
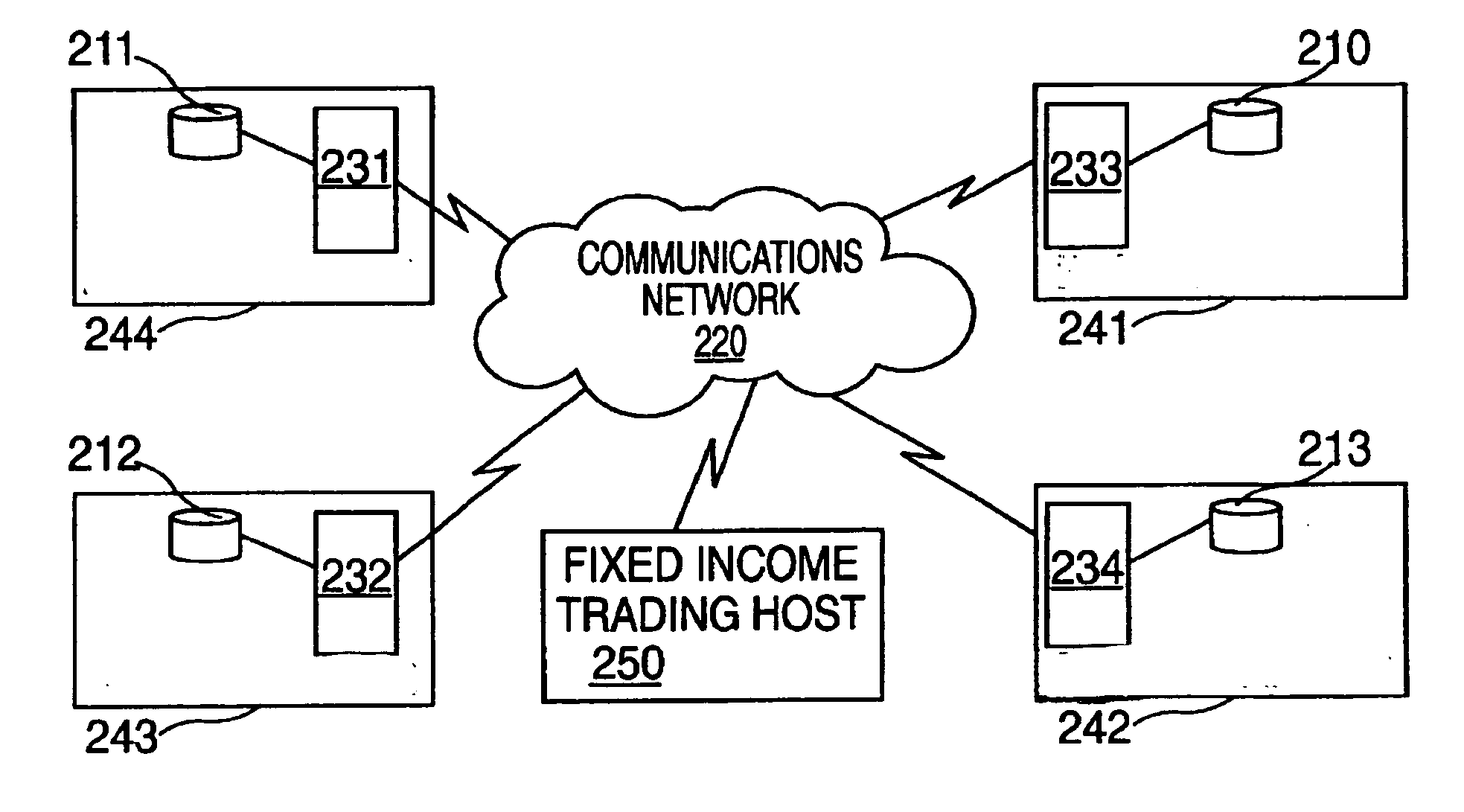
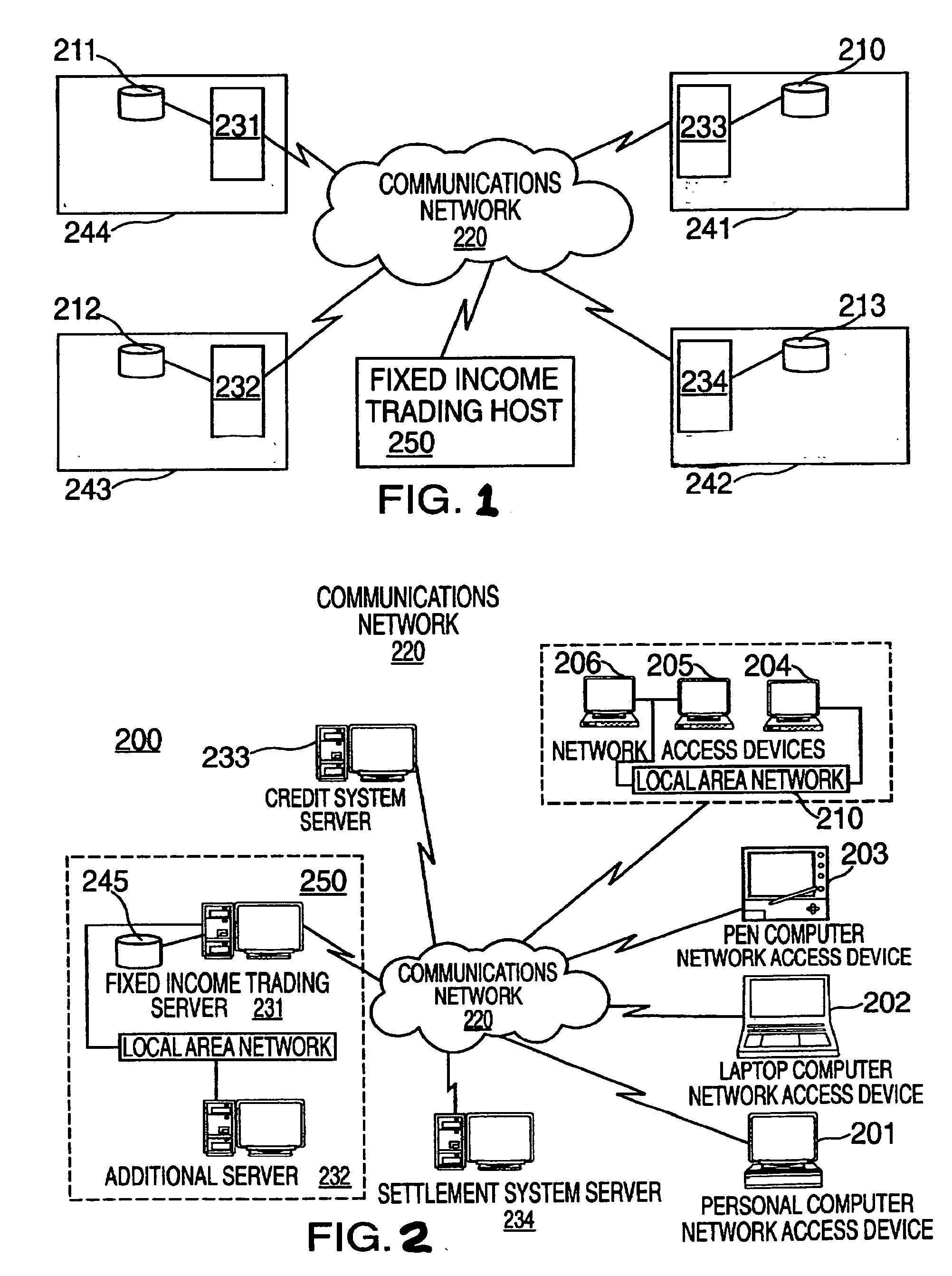
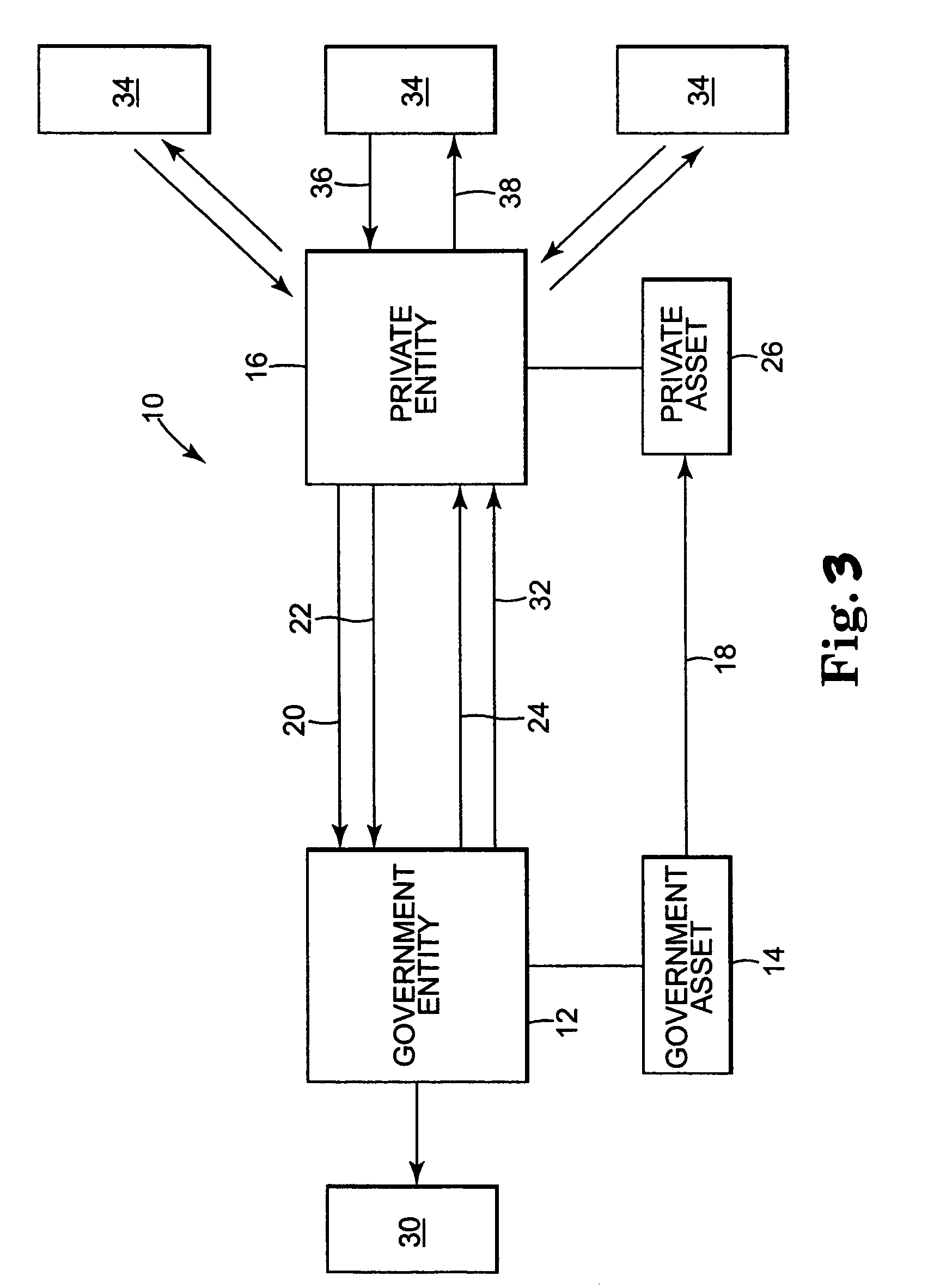
Investment vehicle secured by government assets and electronic trading system for same
A computer system trades investment vehicles secured by governmental assets via a computerized network. A computer server is accessible with a network access device via a communications network. Executable software stored on the server is executed to transmit data relating to trading investment vehicles secured by governmental assets; to receive an instruction to buy or sell an investment vehicle secured by governmental assets; and to transmit a live order from an investor, wherein the live order is related to the instruction to buy or sell an investment vehicle secured by governmental assets. A database of investment vehicle profiles is maintained that includes a term, a face value, a governmental guarantee to repay the face value at the end of the term, a payment schedule requiring periodic payments by the governmental entity comprising a percentage of the face value, and an allocation of appreciation of the pool of governmental assets during the term of the investment vehicle. The computer communications system can be a private network or the Internet.
Owner:REBIT
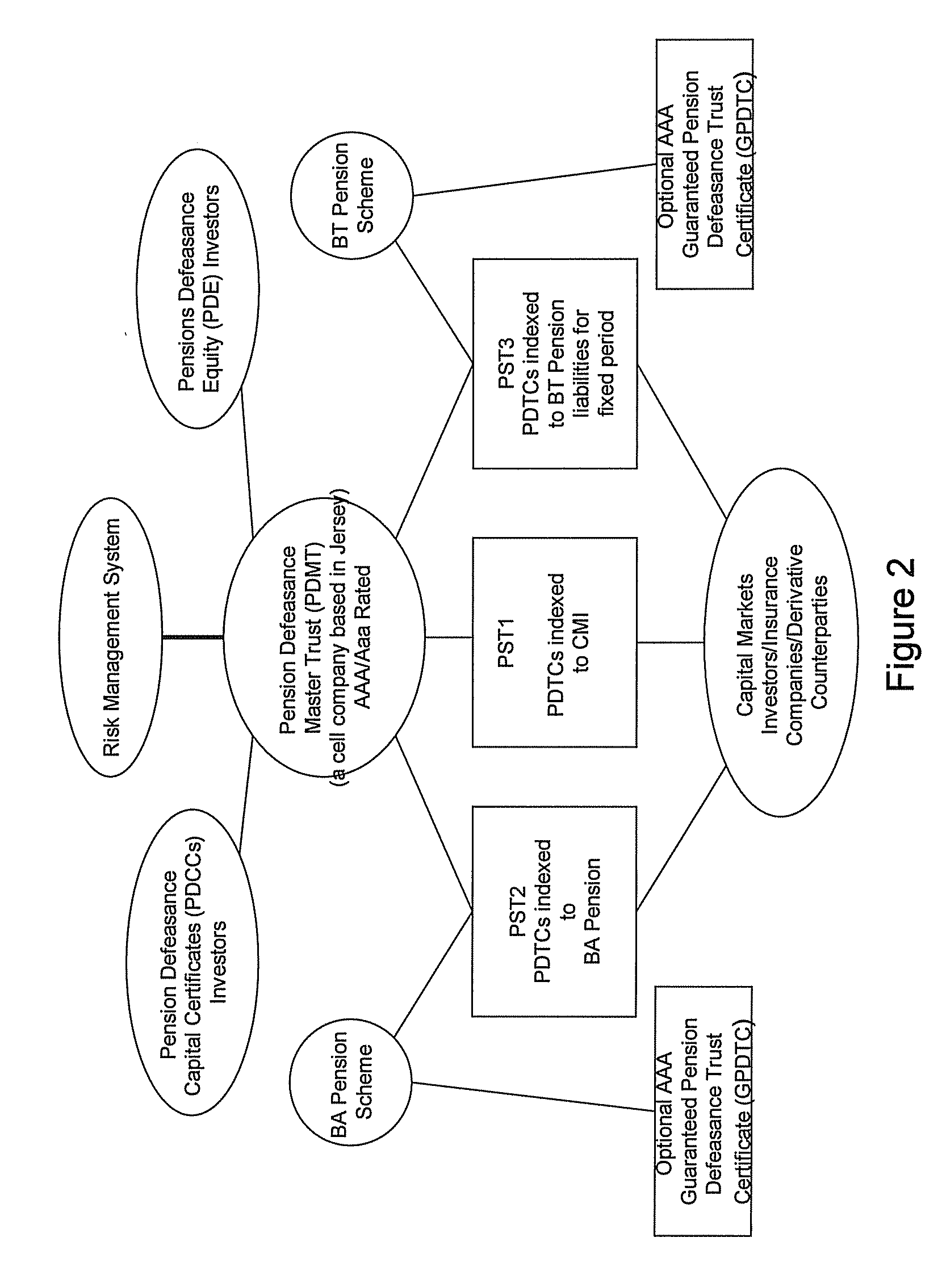
Pension Fund Systems
InactiveUS20100121784A1Minimize risk exposureMinimize or even eliminate the longevity basis risk exposureFinanceTime schedulePayment schedule
The invention provides a computer implemented method of establishing a longevity financial instrument, the method comprising: establishing, using computing apparatus, a set of parameters determining payment amounts to be made according to a payment schedule for the financial instrument such that the payment amounts relate to the future liabilities of a pension scheme to at least a portion of its members. The parameters may determine the payment amounts to match the a calculation of the future liabilities of the pension scheme to at least a portion of its members, taking into account the actual cumulative mortality experience of the pension scheme membership. The various embodiments of the method provide a number of longevity financial instruments that have different payment schedules that are advantageously arranged to match different risk profiles and can be used to satisfy pension scheme sponsors having different risk appetites. The invention also provides methods of issuing longevity financial instruments established thus, and providing such longevity financial instruments to investors. The invention also provides financial instruments thus established and issued.
Owner:PENSIONS FIRST GROUP
Consumer-based system and method for managing and paying electronic billing statements
InactiveUS20050065883A1Minimizing overdraftMinimizes overdraftFinanceDigital computer detailsPayment scheduleGraphics
A consumer-based bill management and payment system is configured to receive, analyze, manage and pay electronic billing statements received from the biller over the Internet. The system includes a notification manager that detects when the electronic bill arrives and notifies the consumer. The bill is stored in memory with other unpaid electronic bills. According to another aspect of the invention, the system has a cashflow analyzer that enables the consumer to coordinate the unpaid electronic bills according to different payment schedules for a bill payment cycle (e.g., a month). The goal of the manipulation is to permit the consumer to analyze how the different payment schedules affect the consumer's cashflow with an aim toward minimizing overdraft during the bill payment cycle. The cashflow analyzer can automatically compute an optimized payment schedule that minimizes overdraft of the consumer's account, while maximizing the balance to generate the most interest. When the consumer desires to pay a particular bill, the bill is presented to the consumer through a graphical user interface (UI). The bill management and payment system supports a payment analyzer to enable the consumer to determine how much of the electronic bill to pay. The payment analyzer provides a venue to challenge certain items on the bill.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
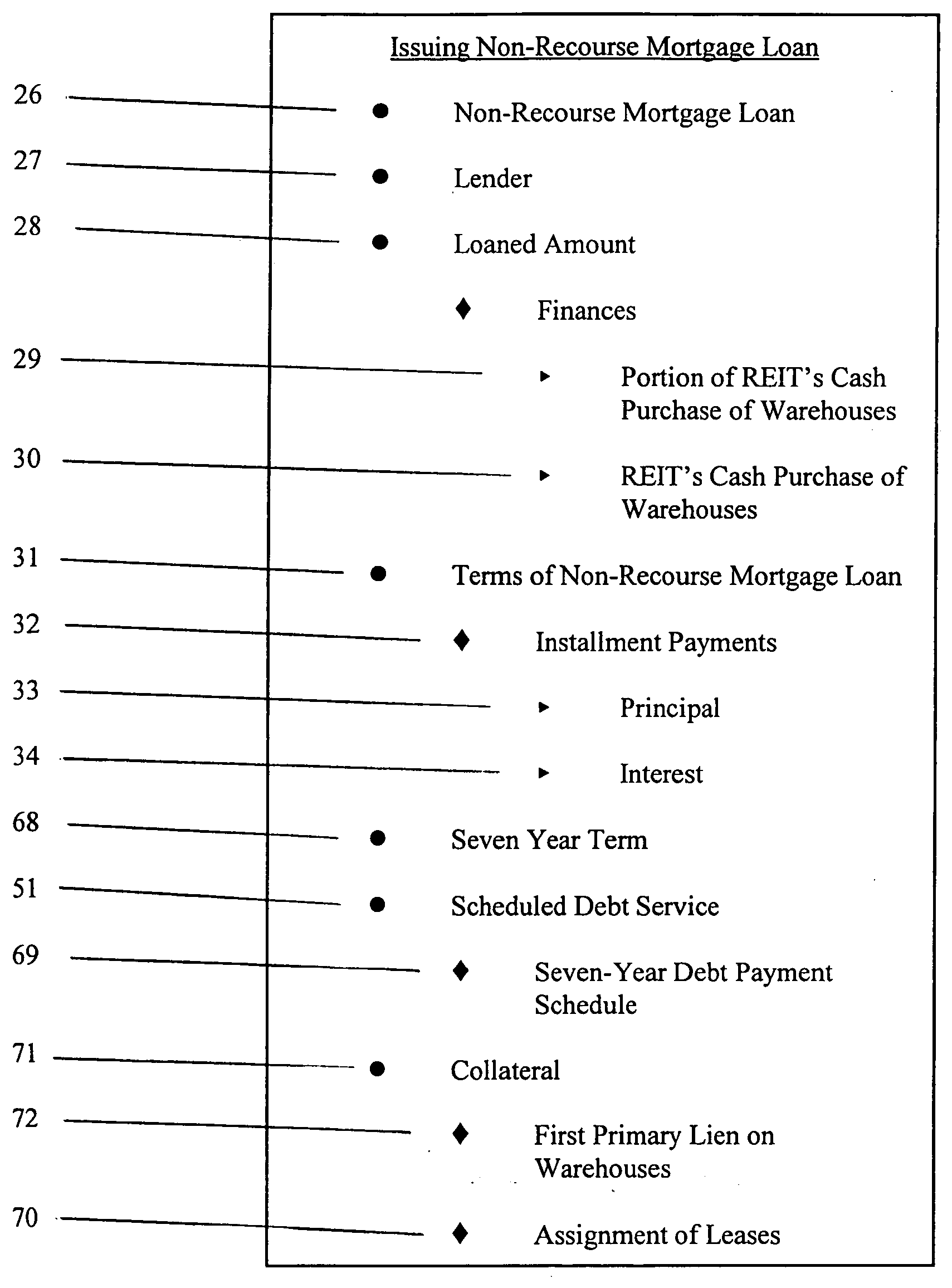
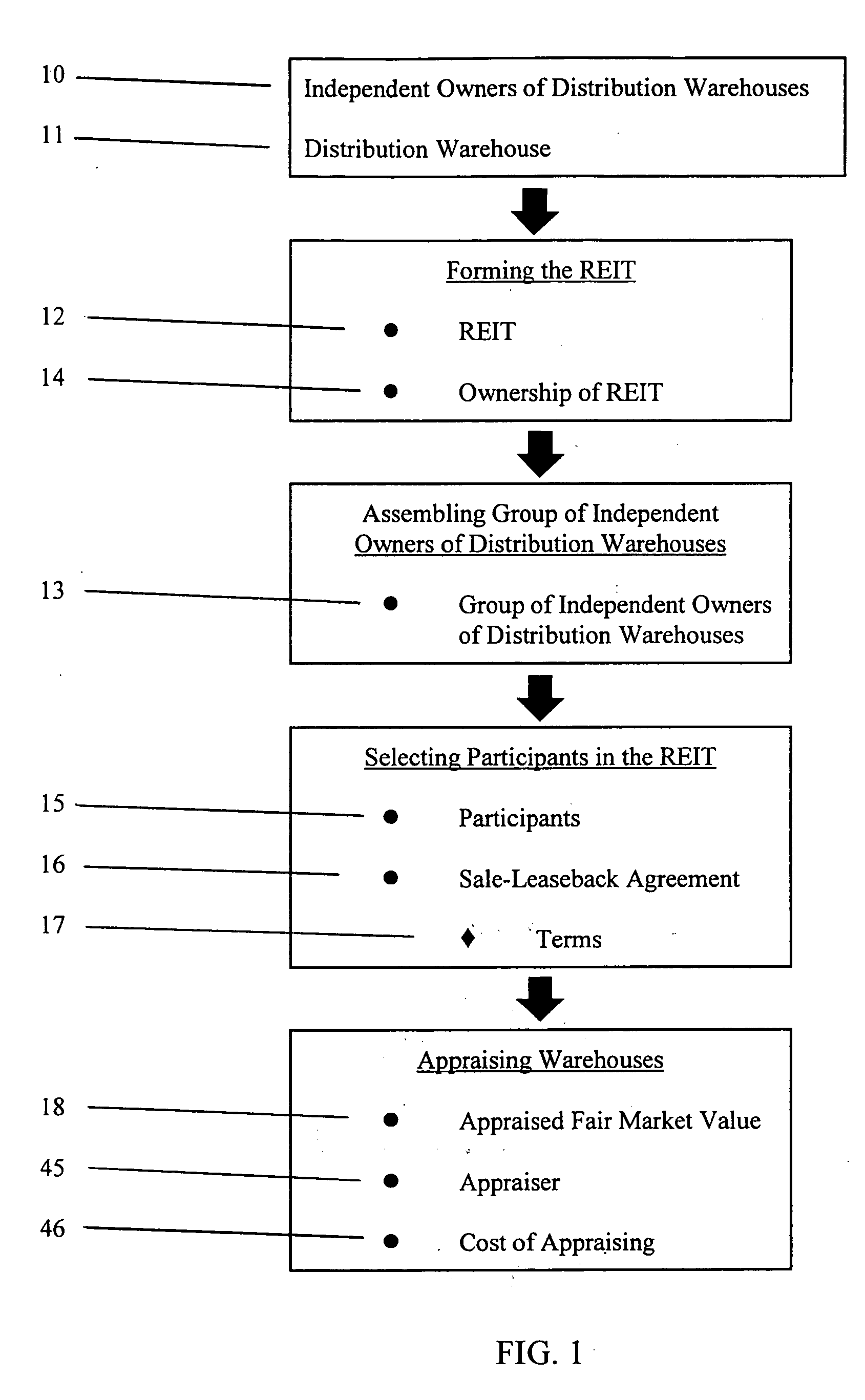
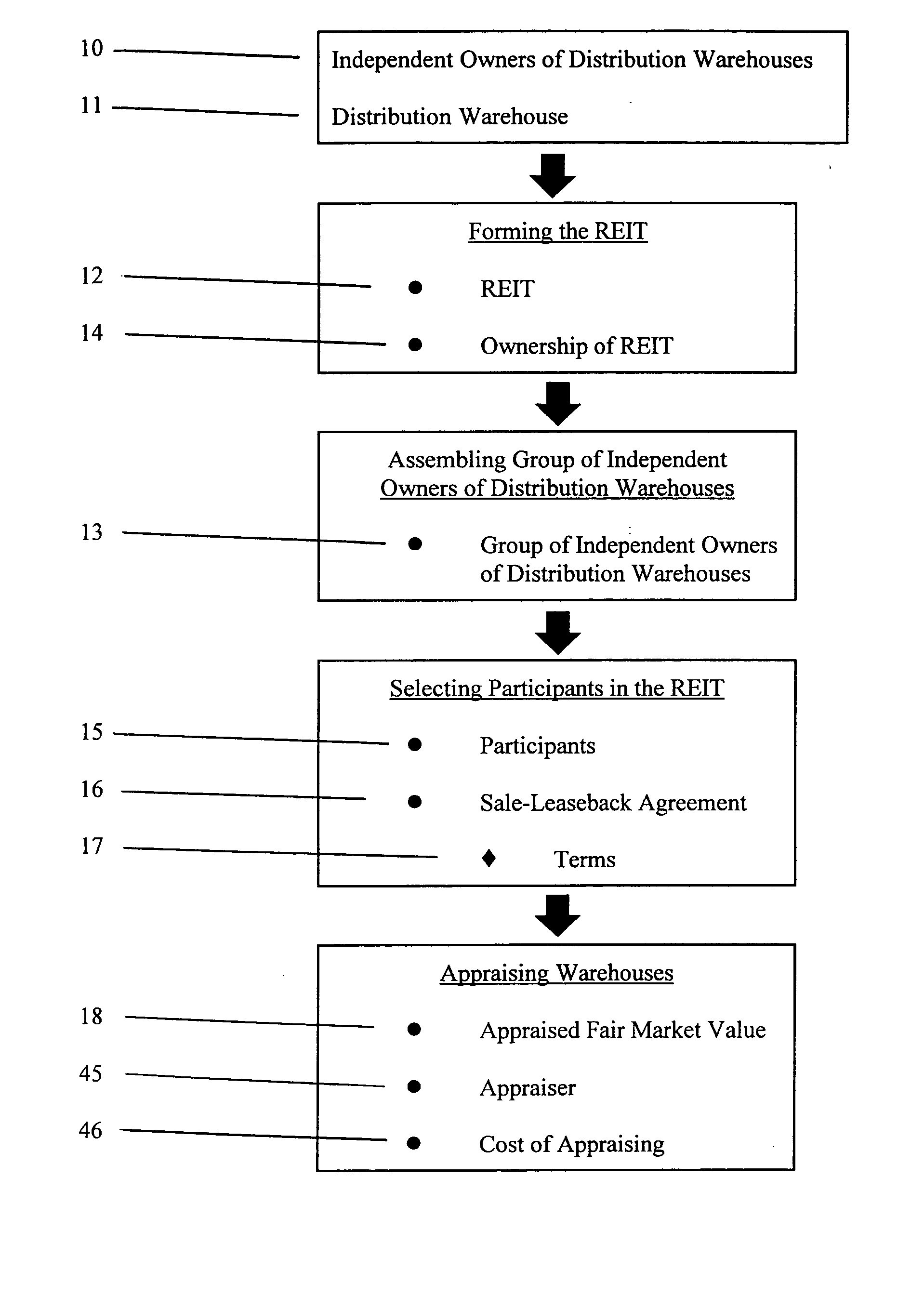
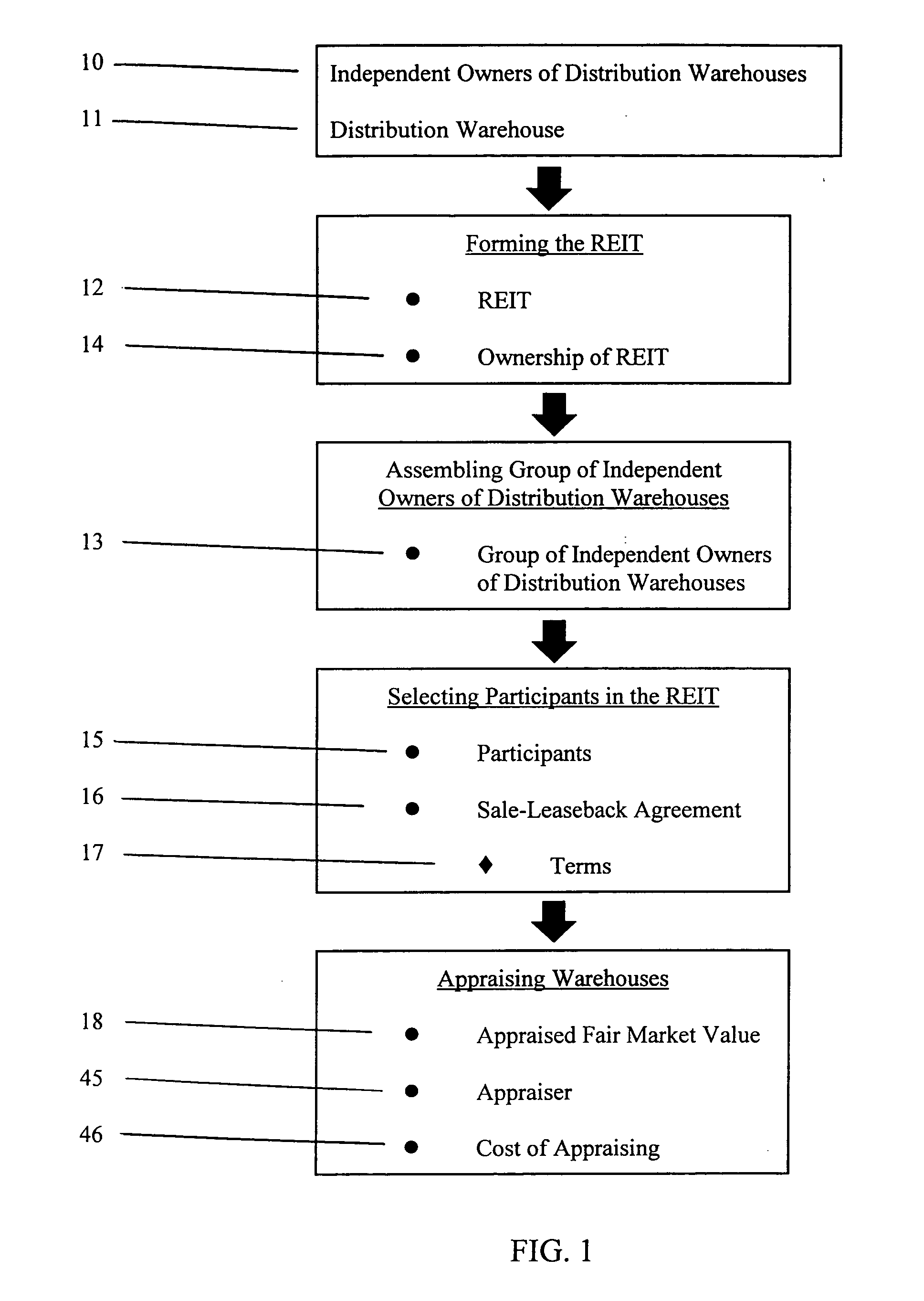
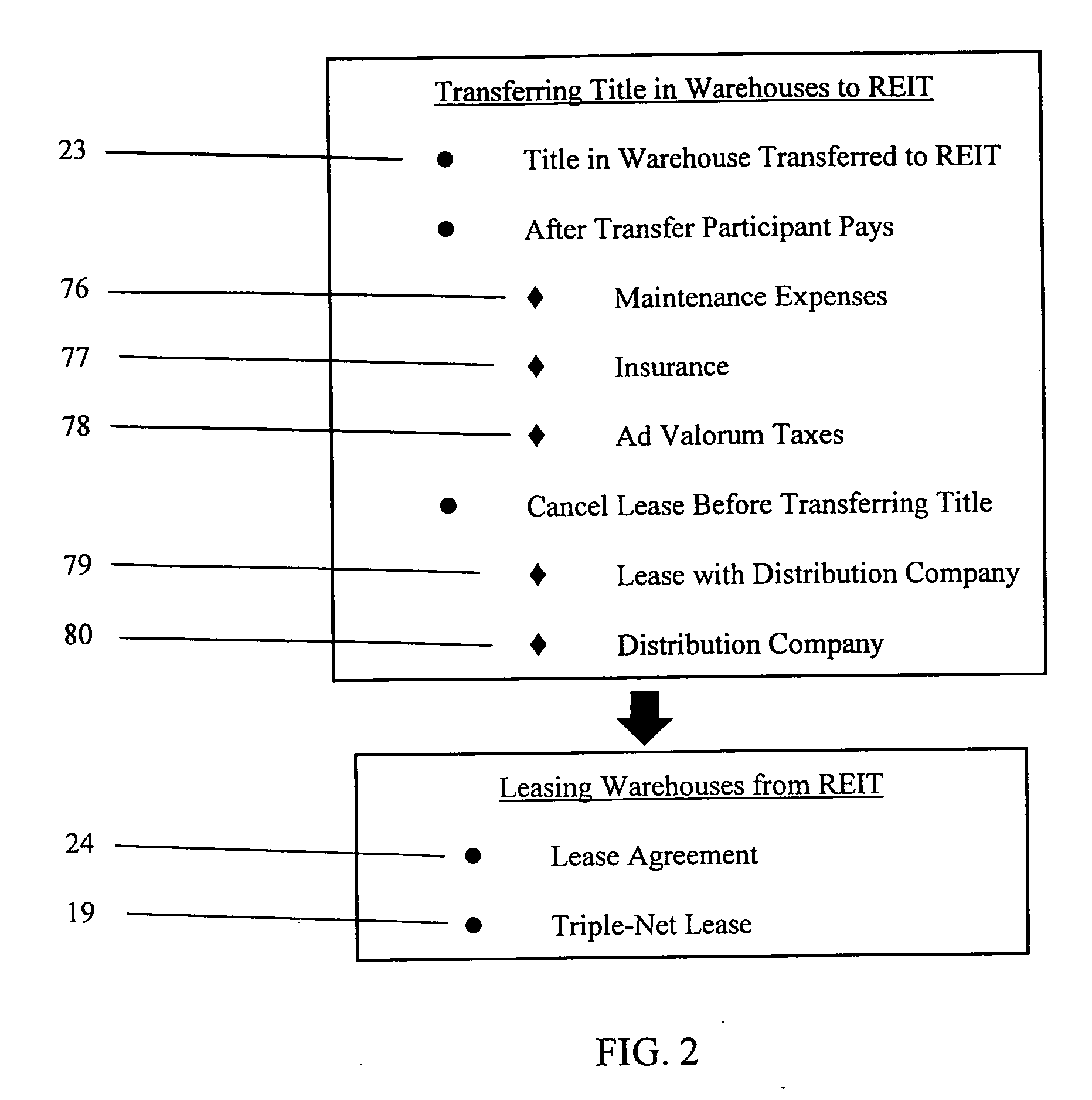
Method of consolidating independent owners of distribution warehouses into a real estate investment trust (REIT)
InactiveUS20050004861A1Improve the situationSaving interestFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsPayment scheduleOperations research
Methods of consolidating independent owners of distribution warehouses into a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) for purposes of achieving economics of scale, for obtaining favorable mortgage financing and for creating a vehicle to enable periodic refinancing and investment of proceeds from such refinancing in real estate opportunities. The REIT is formed and independent owners of distribution warehouses are assembled and selected to participate in the REIT. The participant enters in a sale-leaseback agreement with the REIT and transfers title in their warehouses to the REIT. The REIT finances the purchase of the warehouses by securing a non-recourse loan with at least a seven-year term, serviced on at least a seven-year debt payment schedule. On a periodic basis, preferably every seven years, each warehouse is reappraised, new leases entered into between the REIT and each participant, and new mortgage loans issued for each warehouse. The REIT invests proceeds from the new mortgage loans in real estate opportunities to produce investment revenue. The REIT distributes 90% of net earnings from the investment revenue to the participants.
Owner:BANCROFT ENTERPRISES
Billing method for pump usage
InactiveUS7933817B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical devicesPayment scheduleRunning time
Disclosed are methods of leasing or billing for the usage of a portable suction pump adapted for use in a suction-assisted would treatment system. The pump has means for recording time units corresponding to periods of time when the pump is operating and for providing reports of usage time. The pump further has means for detecting that the wound treatment system is operating normally so as to be compliant with standards for suction wound treatment, and for recording and reporting time of normal operation or compliant usage. The methods include leasing the pump at a payment schedule that is based upon the amount of actual usage time or the amount of compliant usage time. The lease payment may include an amount of pre-paid time units such that unused time units can be credited to a new or renewed lease for a replacement pump. The billing methods can also be based in whole or in part on a planned maintenance schedule for the pump.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
Method of consolidating independent owners of distribution warehouses into an investment corporation
InactiveUS20050080700A1Improve the situationSaving interestFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsComputer sciencePayment schedule
Methods of consolidating independent owners of distribution warehouses into an investment corporation for purposes of achieving economics of scale, for obtaining favorable mortgage financing and for creating a vehicle to enable periodic refinancing and investment of proceeds from such refinancing in real estate opportunities. The investment corporation is formed and independent owners of distribution warehouses are assembled and selected to participate in the investment corporation. The participant enters in a sale-leaseback agreement with the investment corporation and transfers title in their warehouses to the investment corporation. The investment corporation finances the purchase of the warehouses by securing a non-recourse loan with at least a seven to ten year term, serviced on at least a seven to ten year debt payment schedule. On a periodic basis, preferably every seven to ten years, each warehouse is reappraised, new leases entered into between the investment corporation and each participant, and new mortgage loans issued for each warehouse. The investment corporation invests proceeds from the new mortgage loans in investment opportunities to produce investment revenue.
Owner:BANCROFT ENTERPRISES
Pension fund systems
InactiveUS8533087B2Reduce riskAccurately projecting the expected longevityFinanceFuzzy logic based systemsTime schedulePayment schedule
There is provided a computer-implemented method of estimating a capital reserve requirement to cover the longevity risk exposure of a financial instrument in the case of a future longevity shock, the financial instrument undertaking to pay to an investor sums according to a payment schedule of amounts arranged to match with the future cash flow obligations of a pension scheme to at least a portion of its members. The method comprises: (a) calculating, using computing apparatus, an expected payment schedule of the financial instrument by calculating what the cash flow obligations of the pension scheme to its relevant members would be in the case of an expected longevity scenario for the pension scheme membership occurring; (b) calculating, using computing apparatus, a present value of the financial instrument in the case of a stressed longevity scenario for the pension scheme membership in which a longevity-related shock to the expected longevity scenario of the pension scheme membership occurs; and (c) calculating, using computing apparatus and using the calculations of the expected payment schedule and a present value of the financial instrument in the case of a stressed longevity scenario, an estimate of the longevity capital reserve required to ensure that the future cash flow obligations of the financial instrument would be covered in the event that the stressed longevity scenario were to occur.
Owner:PENSIONS FIRST GROUP
Processing system for recording media content
InactiveUS20080288378A1Specific information broadcast systemsPayment architectureTime schedulePayment schedule
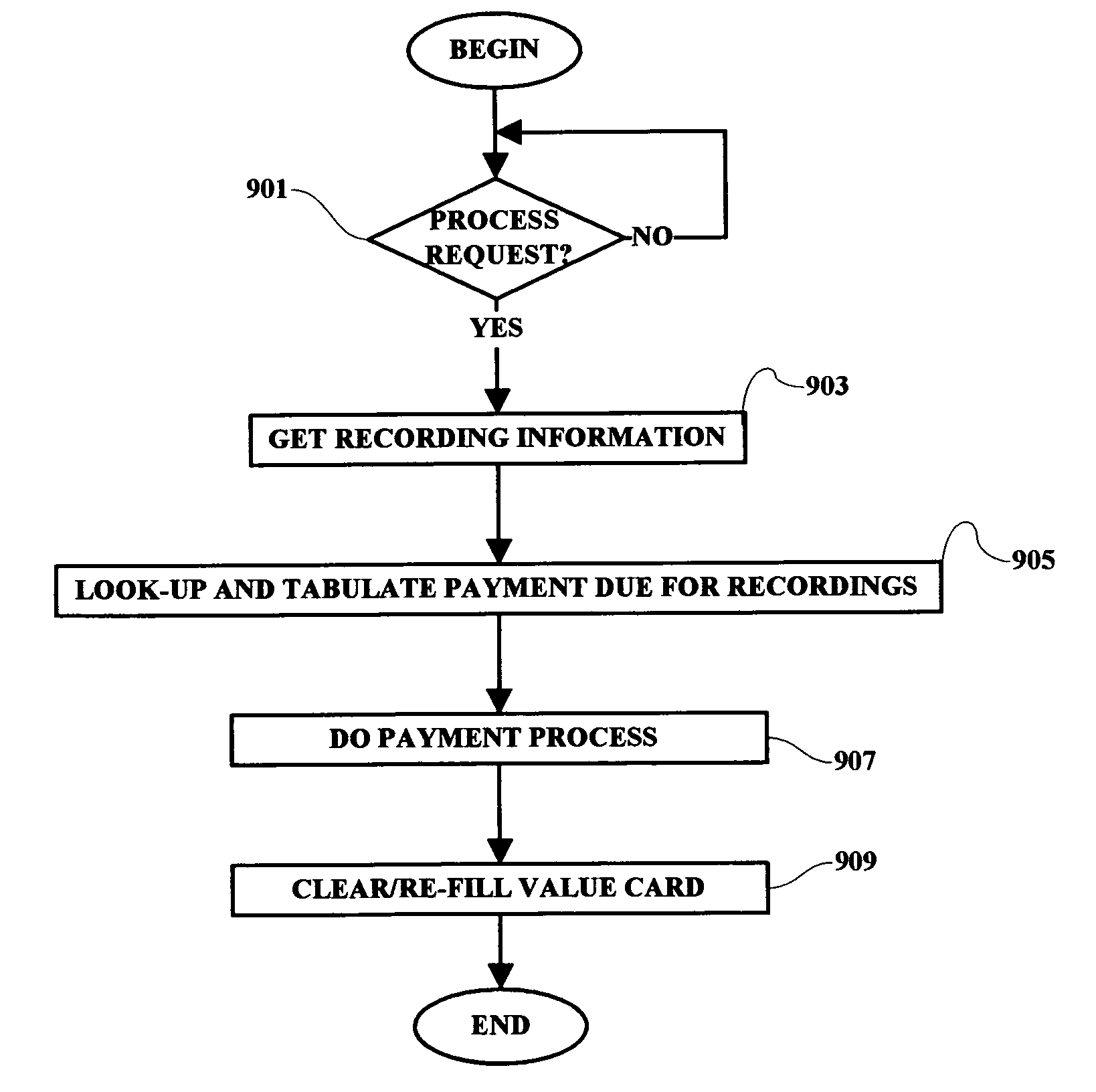
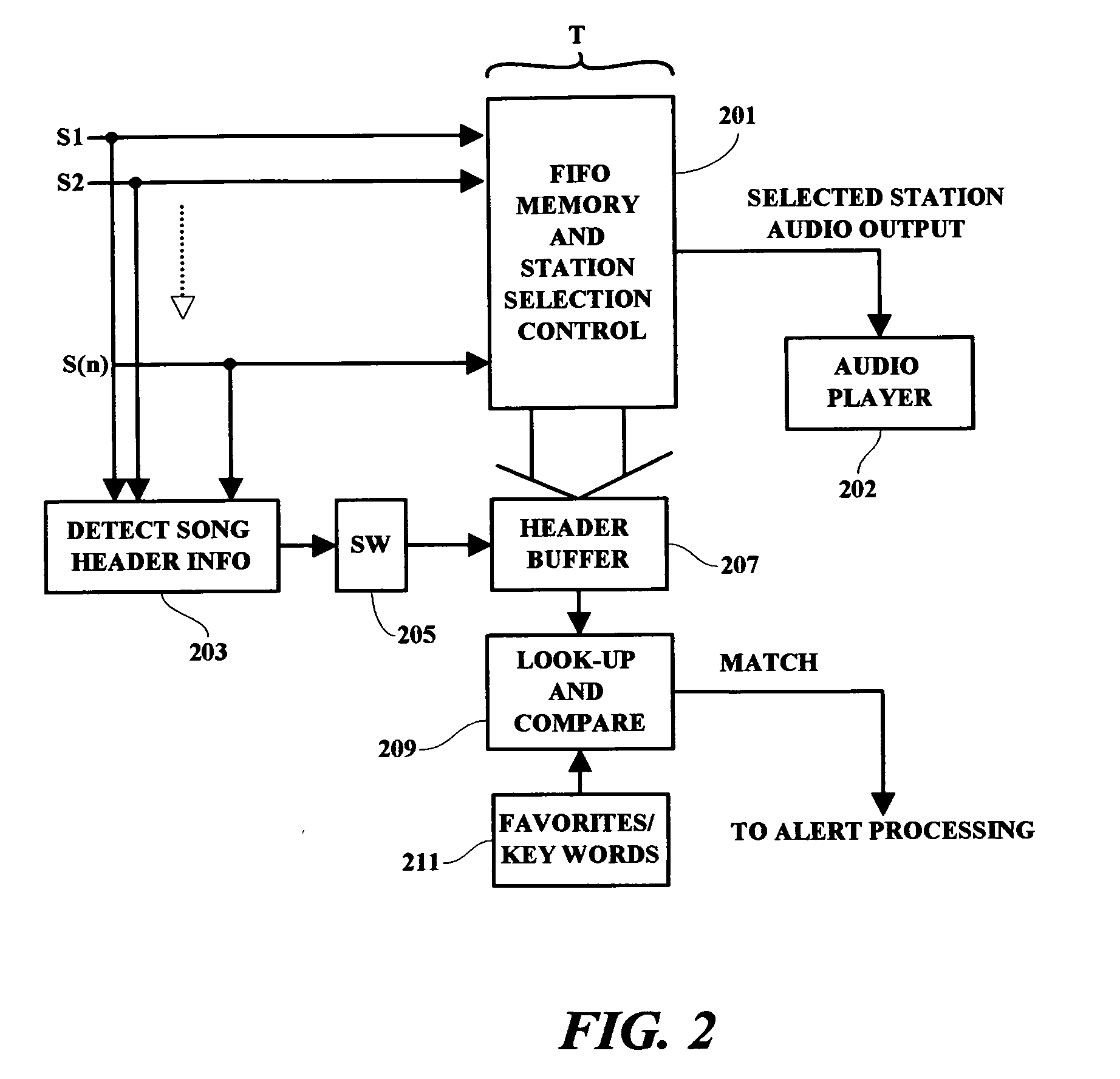
A method and system are provided in which a user is enabled to record, for example, a song or other radio and / or video content, on demand, and to account for and process appropriate payment for the use of the recorded content. The recorded material is saved and indexed by title and is retrievable for subsequent review, tabulation and / or playing at the user's convenience. In one example, a user is enabled to record received media content by pressing a single “ADD” button at any time while a favorite song is being received and played. The song then being played together with the title of the song or video presentation are then saved to memory for subsequent retrieval and playing. The received content is accounted for and tabulated and a payment for the use of the recorded song is processed by the user in accordance with a predetermined payment schedule.
Owner:IBM CORP
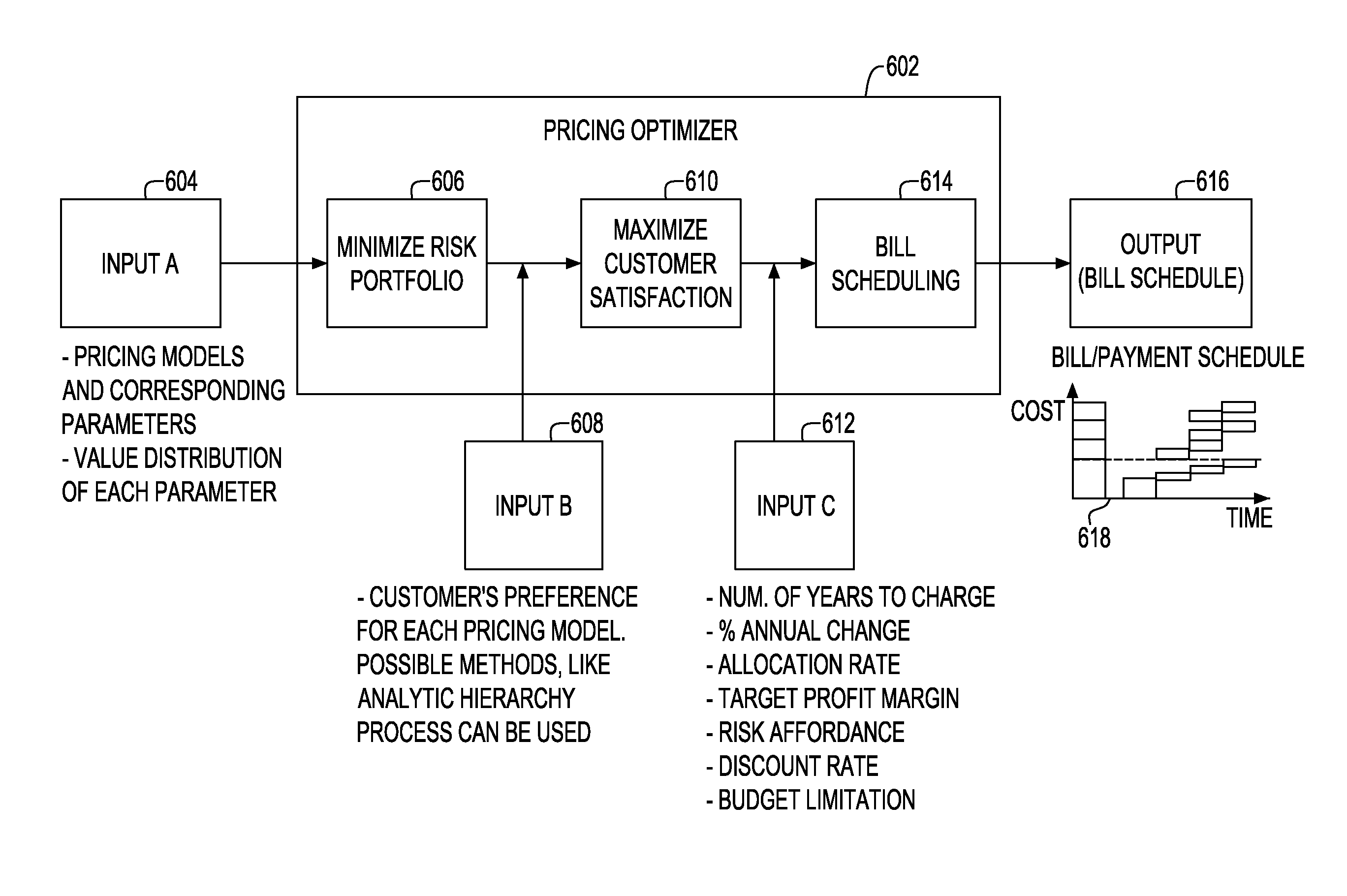
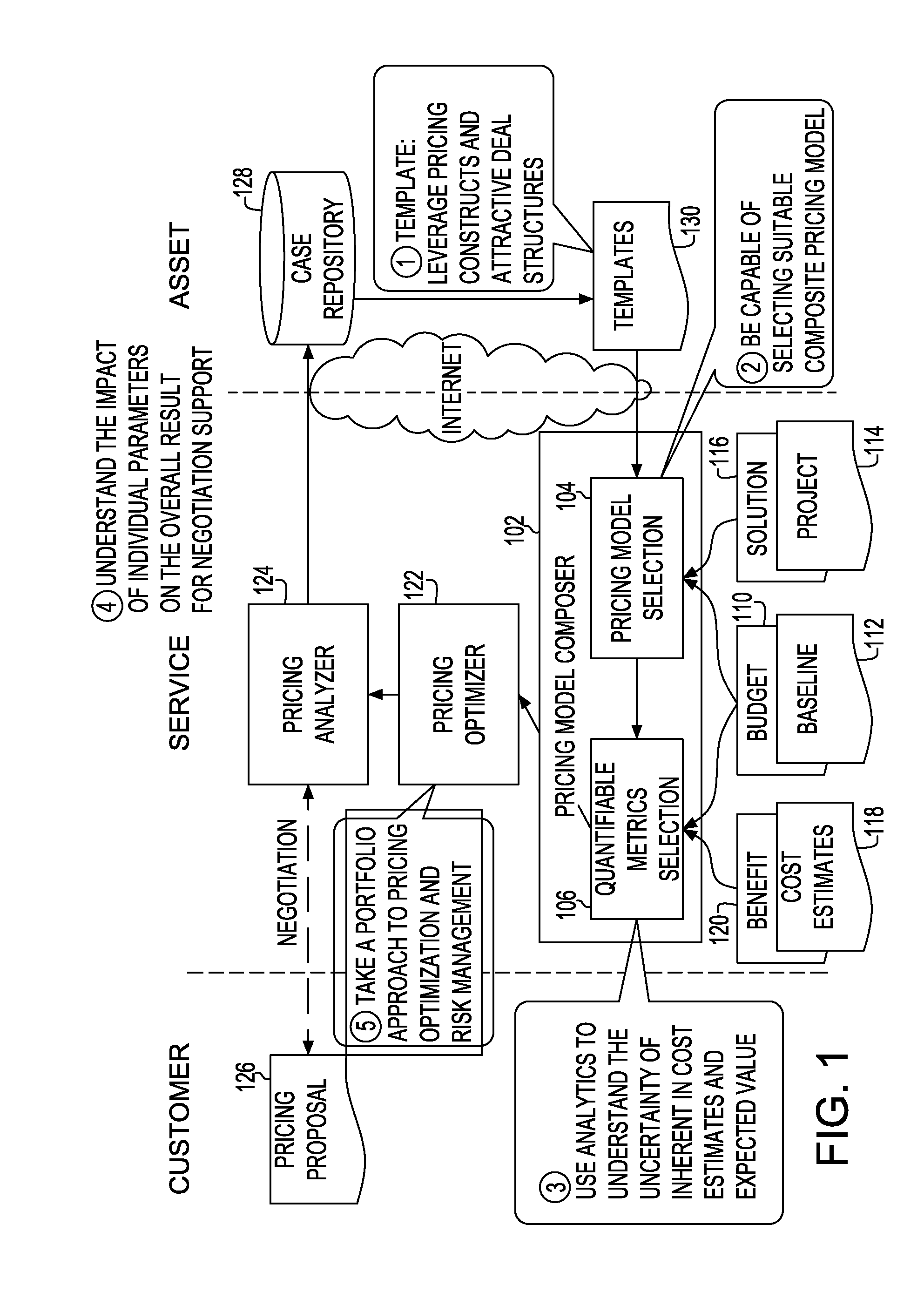
System and method for generating optimal bill/payment schedule
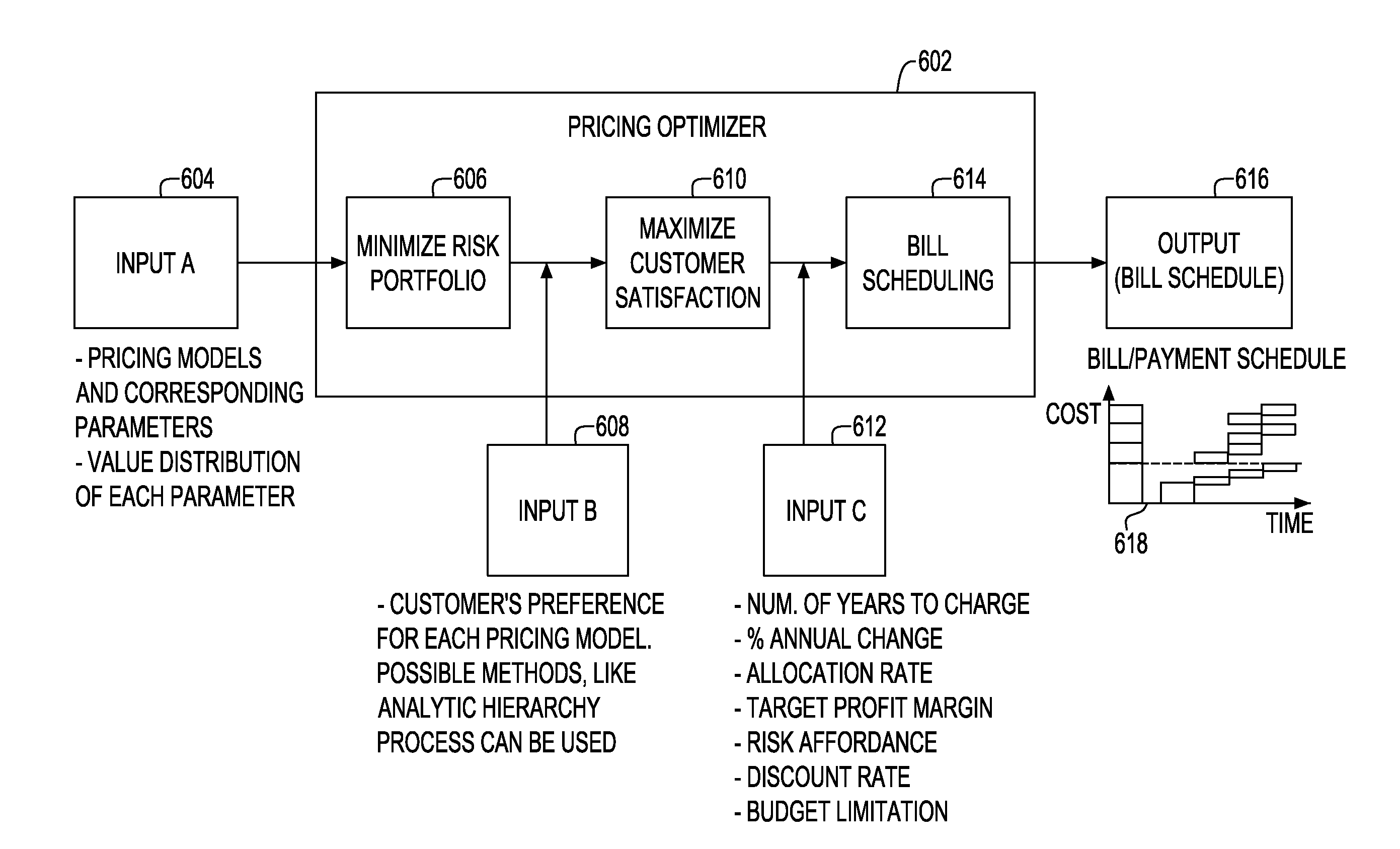
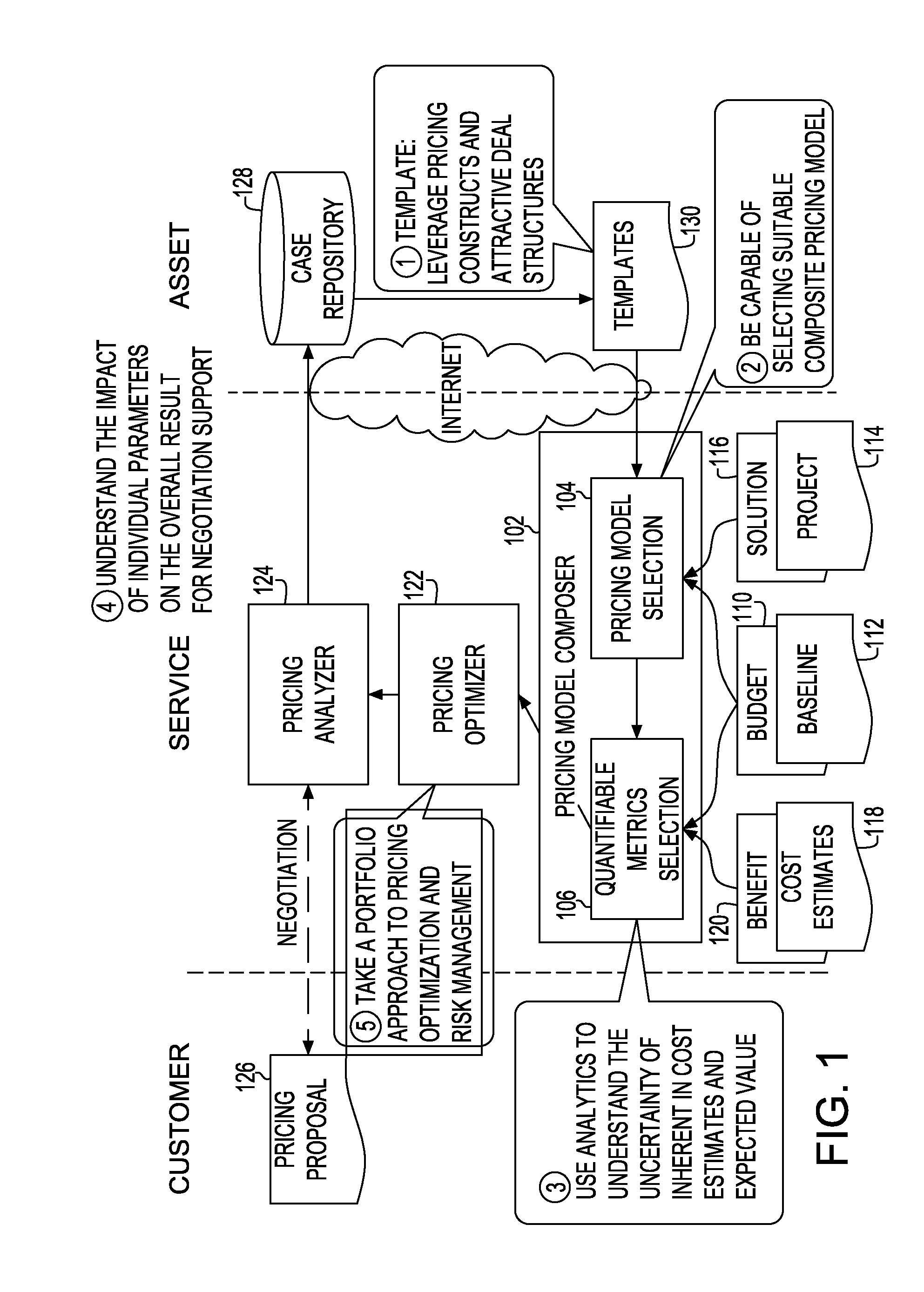
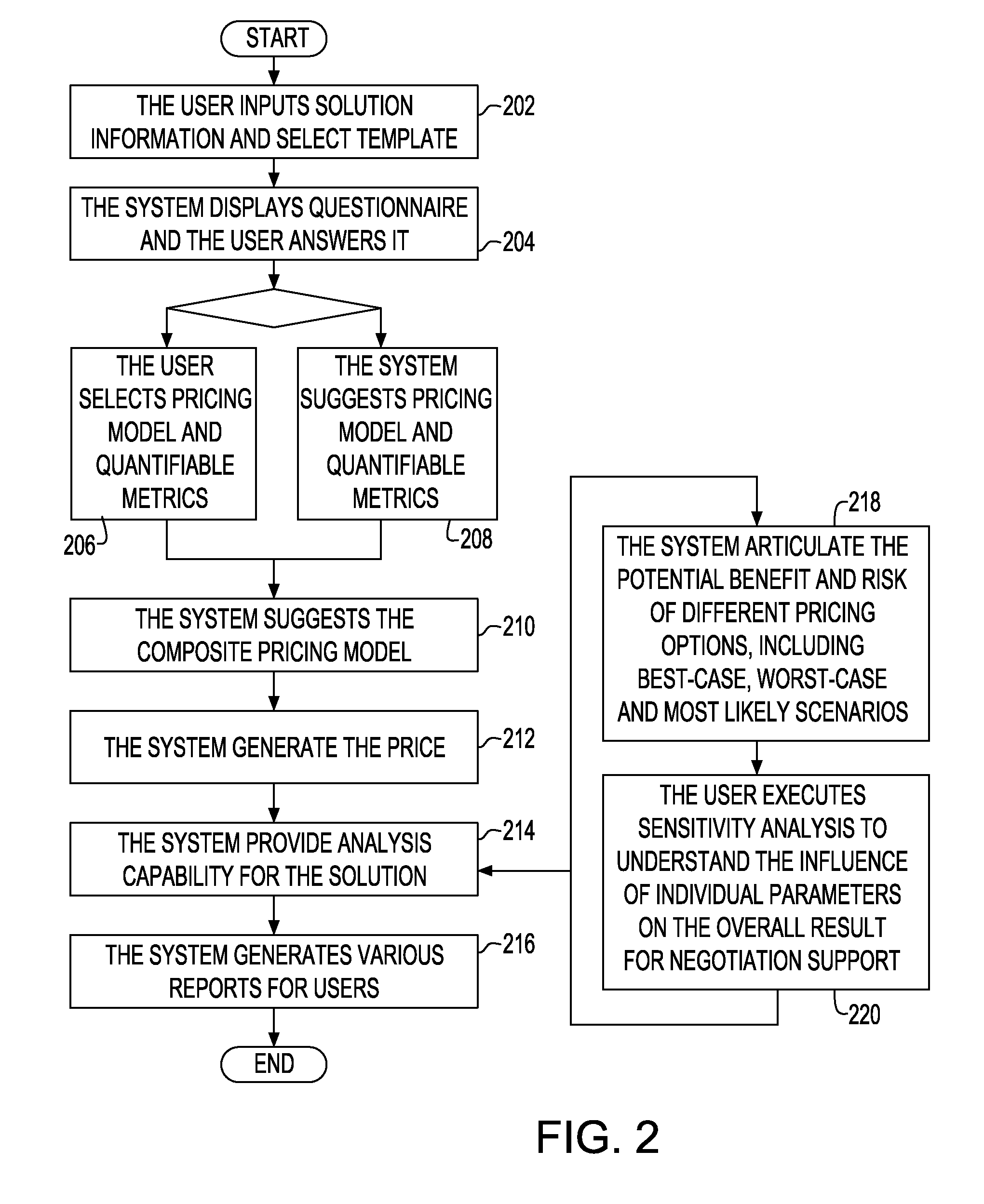
ActiveUS20090222366A1Risk minimizationComplete banking machinesMarket predictionsPayment scheduleTime schedule
A method and system for generating bill payment schedule utilizes a composite pricing module to generate payment schedule over a predetermined period of time. In one aspect, a fraction of each pricing model attributing to the composite pricing model is determined. A charge fee associated with said each pricing model based on said fraction and said total price to charge is determined. Price to charge during each time unit of the time period is allocated, based on budget over the time period, discount rate, target profit margin and risk affordance. Bill schedule is generated using the allocated price.
Owner:IBM CORP
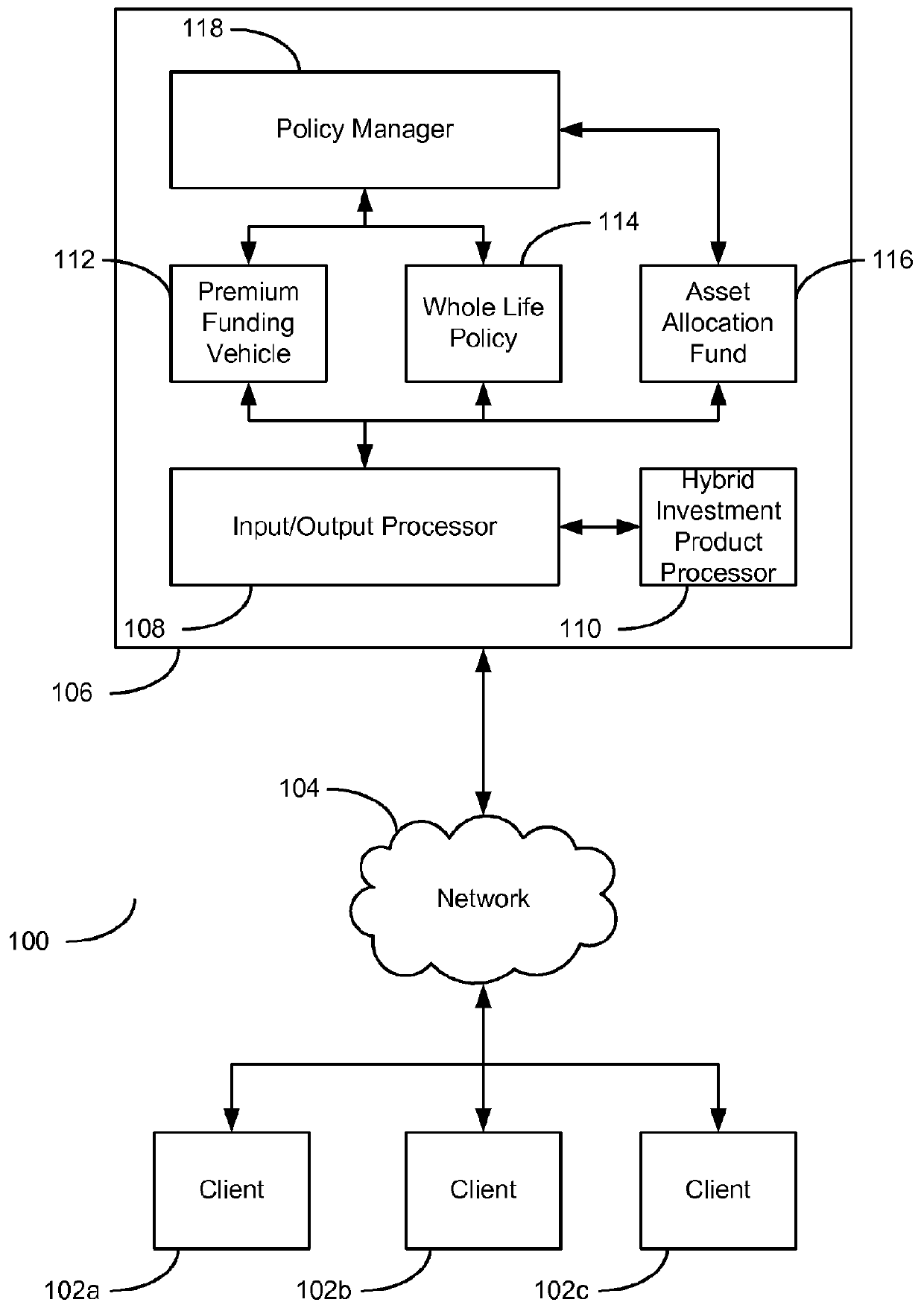
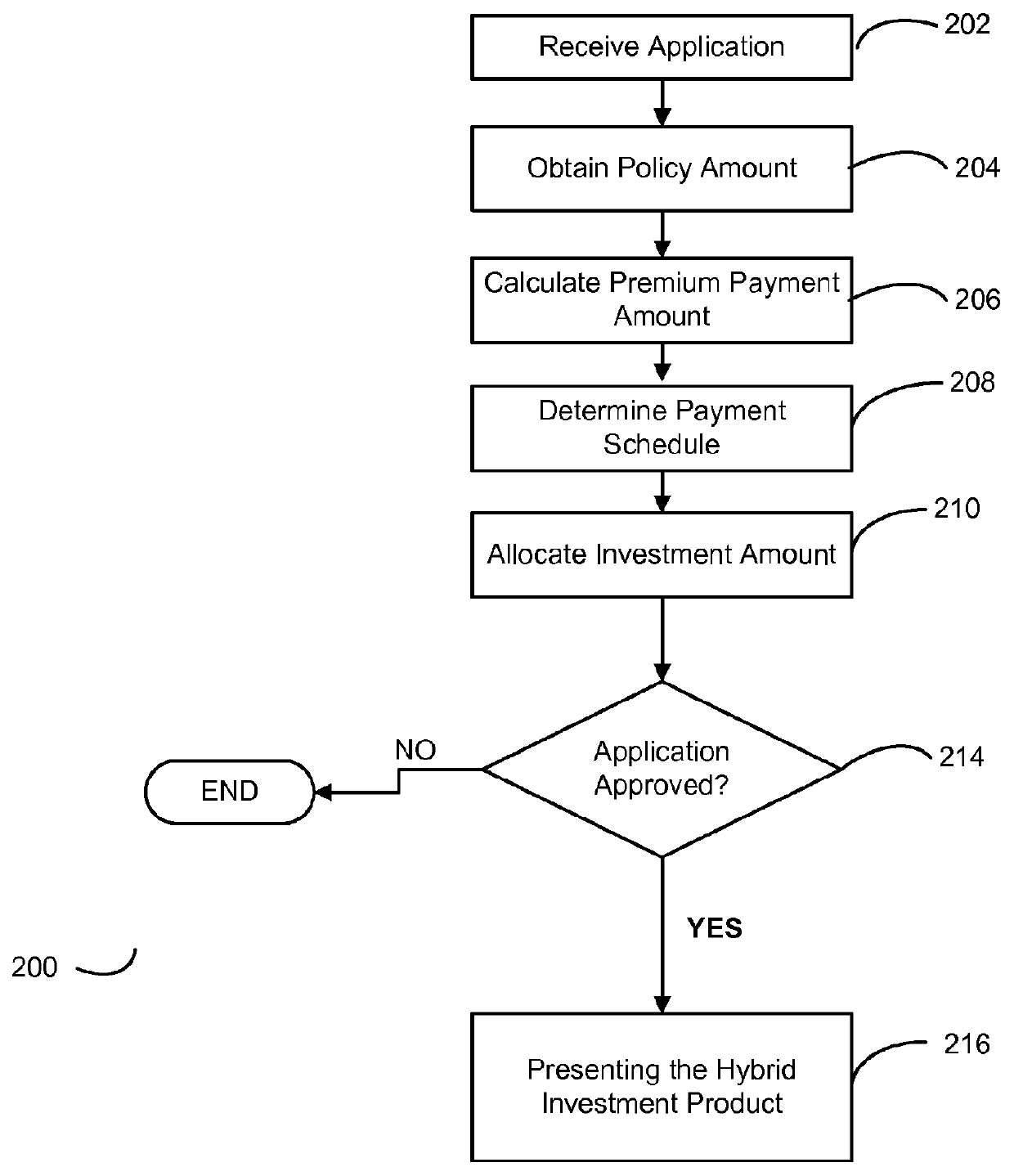
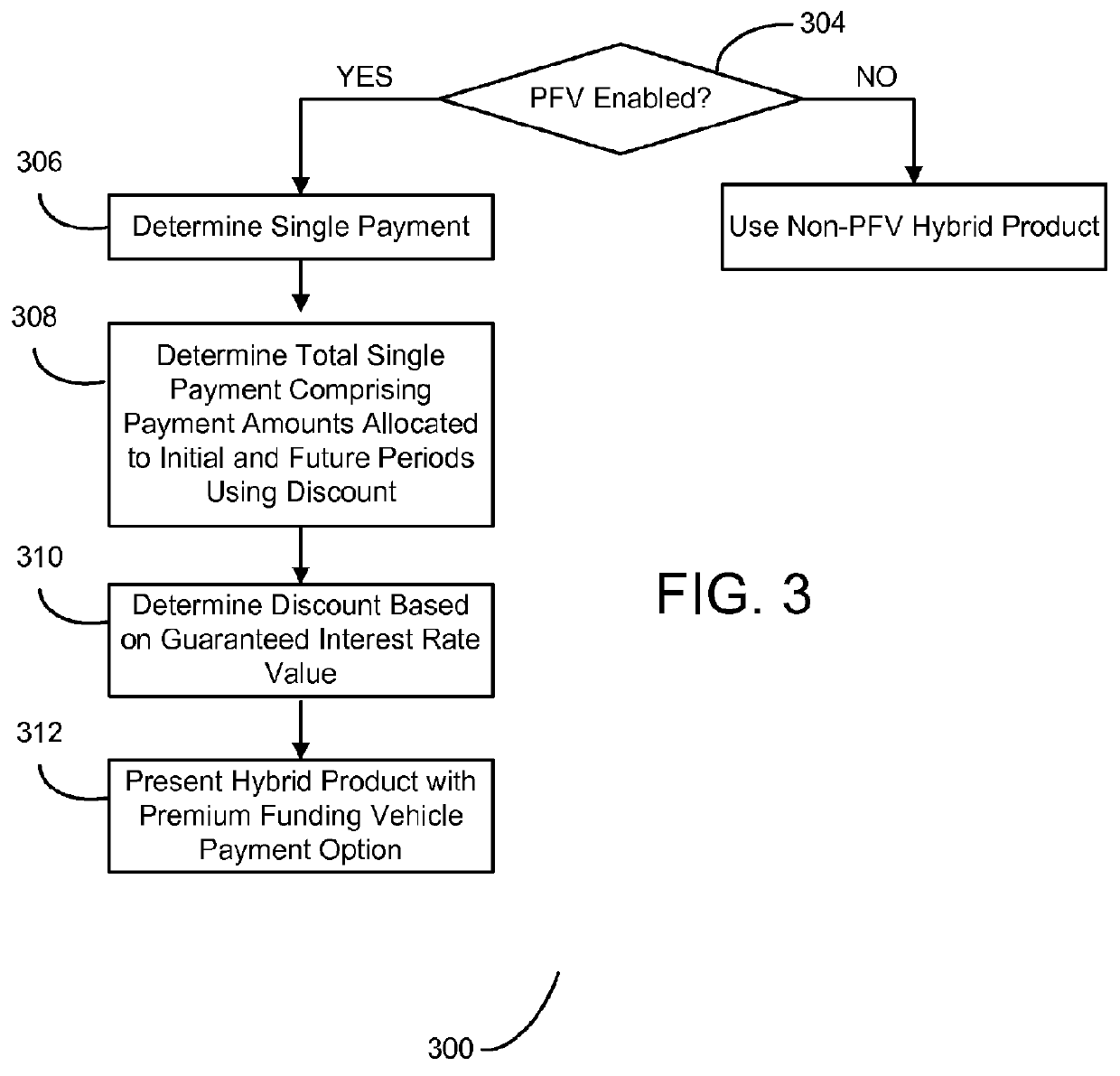
Systems and methods for providing an asset allocation whole life insurance option with a premium funding vehicle
The present invention provides methods, computer media and systems for providing a hybrid life insurance and non-life insurance investment product for an individual. Embodiments of the methods, computer media and systems include obtaining an initial investment amount for an investment product comprising a life insurance investment component and a non-life insurance investment component and a face amount of the life insurance investment component, calculating a premium payment amount for the life insurance investment component, determining a payment schedule for the premium payment amount, allocating a portion of the initial investment amount to the life insurance investment component and allocating a portion of the initial investment amount to the non-life insurance investment component, and presenting, based at least in part on the allocations of the initial investment amount to the life insurance investment component and to the non-life insurance investment component, the premium payment amount and the payment schedule, the life insurance investment component and the non-life insurance investment component as a combined investment product for an individual in a singular transaction.
Owner:NEW YORK LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY
System and method for guaranteeing minimum periodic retirement income payments using an adjustment account
A system and method for providing a user with a plurality of guaranteed minimum retirement income payments is disclosed. The system comprises a variable immediate annuity module to receive an income generating payment and to output a guaranteed minimum retirement income payment amount wherein the periodic retirement income payment amount is greater than, equal to, or less than a guaranteed minimum periodic retirement income payment amount if the income generating payments received are received according to a predetermined payment schedule, and wherein the predetermined guaranteed minimum periodic retirement income payment amount is defined by the user. The system also includes an adjustment module for comparing the periodic retirement income payment amount and the guaranteed minimum periodic retirement income payment amount, and for outputting to the user at least the guaranteed minimum periodic retirement income payment amount, the adjustment module storing a balance in an adjustment account if the periodic retirement income payment amount is less than the guaranteed minimum periodic retirement income payment amount.
Owner:GENWORTH HLDG
Method for financing a loan
A method for financing a product or service that includes determining a first loan amount and calculating a first periodic payment and a first term based on the first loan amount. The method further includes determining a supplemental allowance for a borrower and calculating a revised loan amount by summing the first loan amount and the supplemental allowance. Once the revised loan amount is determined, a revised periodic payment and a revised loan term based on said revised loan amount are determined; and the revised loan term is reduced by applying a second periodic payment schedule based one of the first periodic payment and the revised periodic payment.
Owner:DION PAUL E
Method and system for installment payment utilization
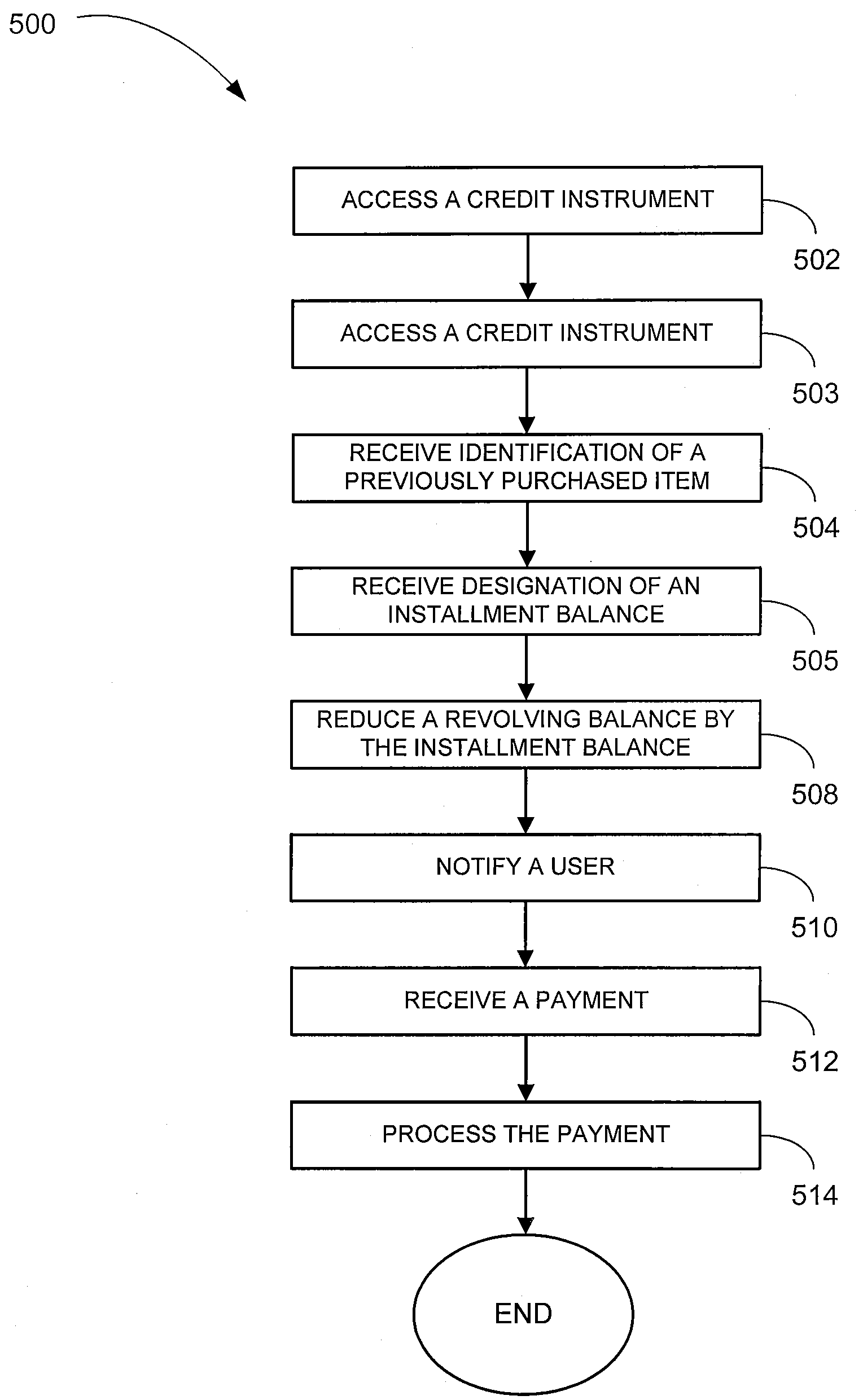
Methods and system for installment payment utilization are described. In one embodiment, a revolving balance of a credit instrument associated with a user may be accessed. The revolving balance may be at a revolving balance interest rate. An installment balance may be designated for the credit instrument. The installment balance may be associated with a payment schedule and a payment amount and be at a different interest rate than the revolving balance interest rate. The credit instrument may be updated responsive to the designation of the installment balance.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
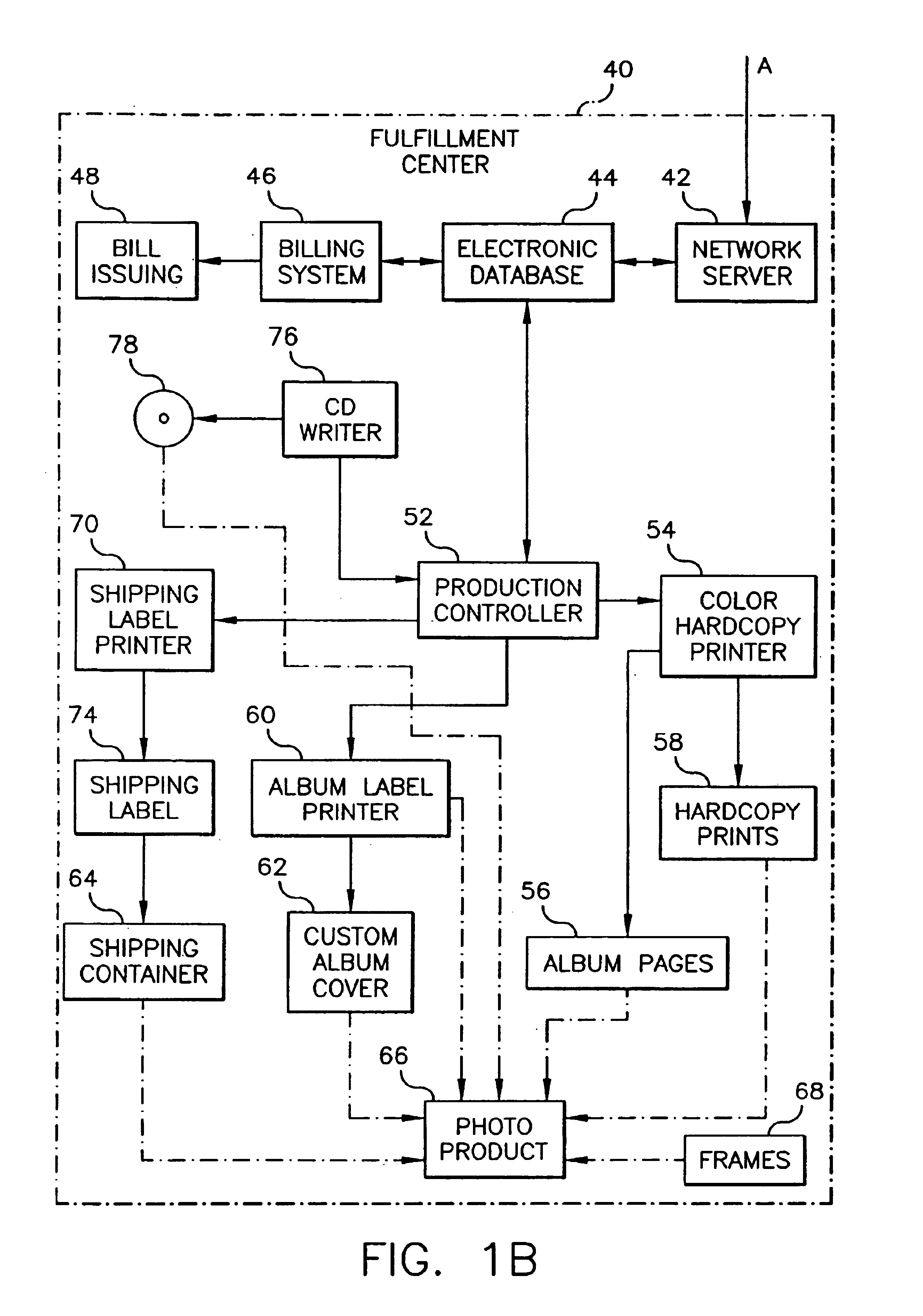
Providing multiple payment schedules for storing imags and utilizing the stored images
InactiveUS20090076964A1Low costCompensation costsDigitally marking record carriersPlaten pressesPayment scheduleTime schedule
A method of selecting images from a plurality of images previously stored by a user in a memory location of a service provider and ordering services to be provided utilizing the images includes establishing a service account for the user with the service provider to permit the user to have access to ordered services, receiving and storing a plurality of images along with a designated date in the memory location, and displaying image designators for at least a subset of the images for viewing by the user. The method also includes the user selecting at least one image to be utilized after viewing the displayed images, and selecting a service, receiving payment for the selected service for the selected image based upon a payment schedule that depends upon the designated date associated with the selected image, and providing the selected service using the selected image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Providing a discounted payment schedule for utilizing and deleting stored images
InactiveUS7136837B2Low costCompensation costsComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTime schedulePayment schedule
A method of selecting images from a plurality of images previously transferred from a user and stored by a service provider, and ordering services to be provided utilizing the images, including establishing an account for the user with the service provider to permit the user to have access to ordered services; receiving a plurality of images from the user and storing the plurality of images in an electronic database provided by the service provider; displaying image designators for at least a subset of the images for viewing by the user; the user selecting a service to be provided using at least one selected image from the plurality of images stored in the electronic database, providing a price and a lower discounted price for the selected service; and using the discounted price if the user deletes at least one of the plurality of images from the electronic database.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and system for portable retirement investment
Owner:GENWORTH HLDG
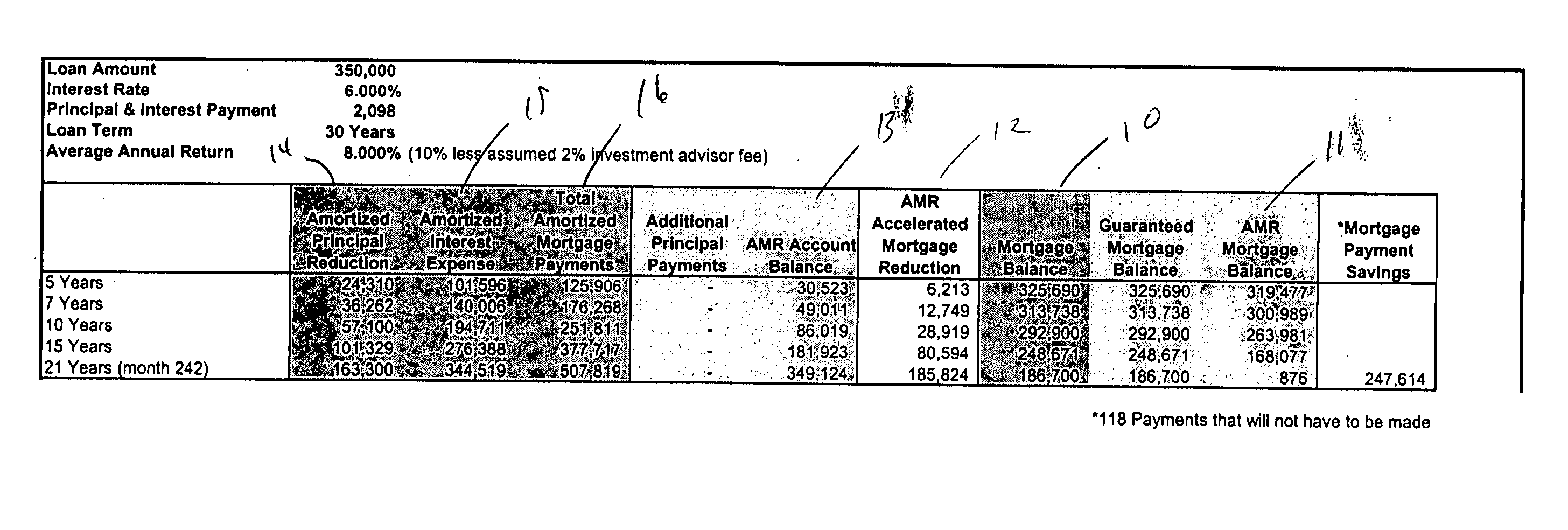
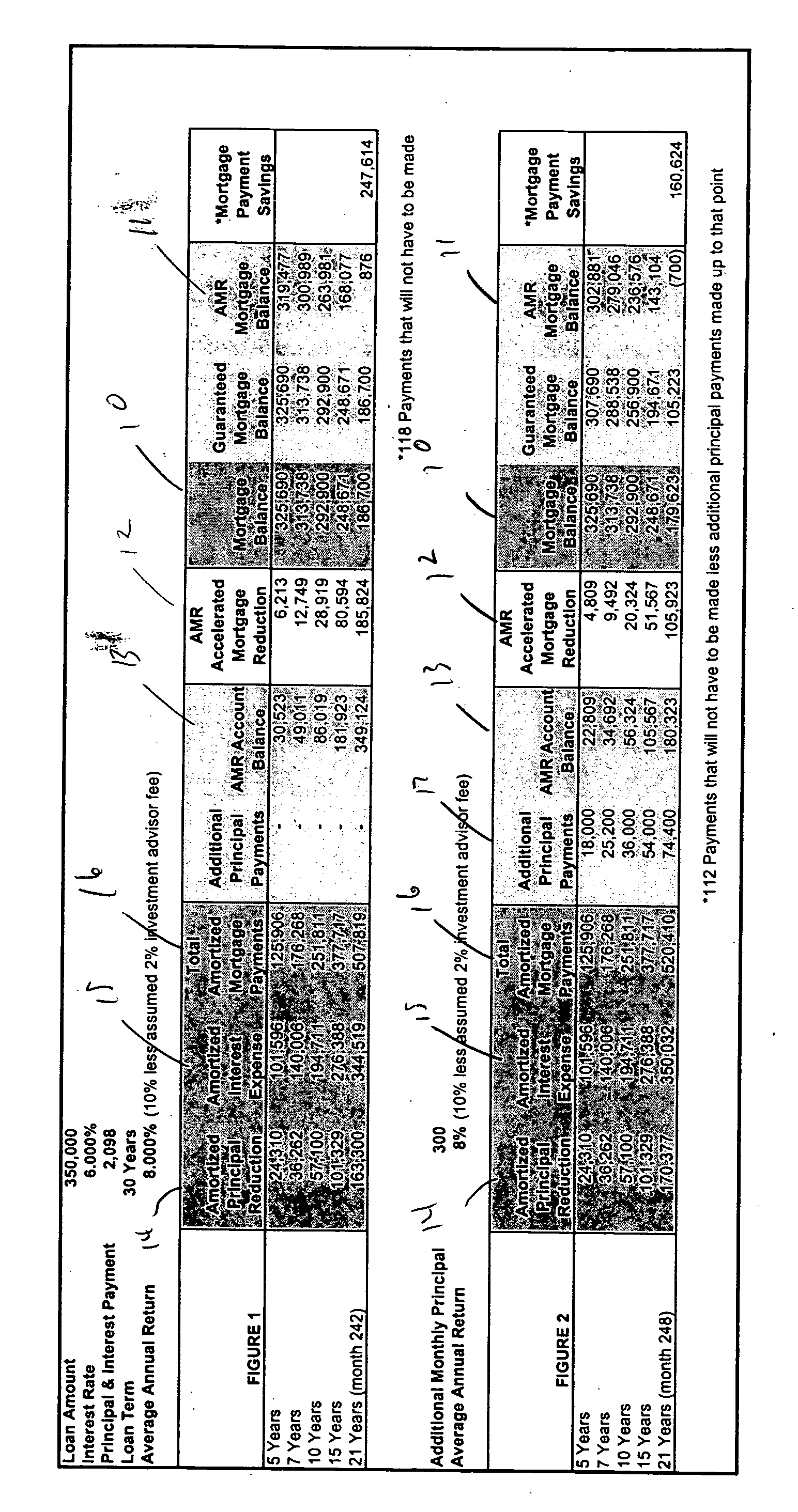
Methods for accelerated principal reduction
A method of reducing a principal amount of a loan. The method comprises determining a payment schedule of a series of payments for repaying the principal amount of the loan, each payment comprising a principal portion and an interest portion, receiving payments, and crediting the principal portion of received payments towards the principal amount of the loan. The method also comprises investing at least a part of the principal portion in a portfolio comprising at least one investment instrument and applying at least a part of any gains made from the portfolio to the principal amount of the loan.
Owner:DUNCOR
System and method for generating optimal bill/payment schedule
ActiveUS7979329B2Risk minimizationComplete banking machinesMarket predictionsPayment scheduleTime schedule
A method and system for generating bill payment schedule utilizes a composite pricing module to generate payment schedule over a predetermined period of time. In one aspect, a fraction of each pricing model attributing to the composite pricing model is determined. A charge fee associated with said each pricing model based on said fraction and said total price to charge is determined. Price to charge during each time unit of the time period is allocated, based on budget over the time period, discount rate, target profit margin and risk affordance. Bill schedule is generated using the allocated price.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Customizable and flexible payment plans
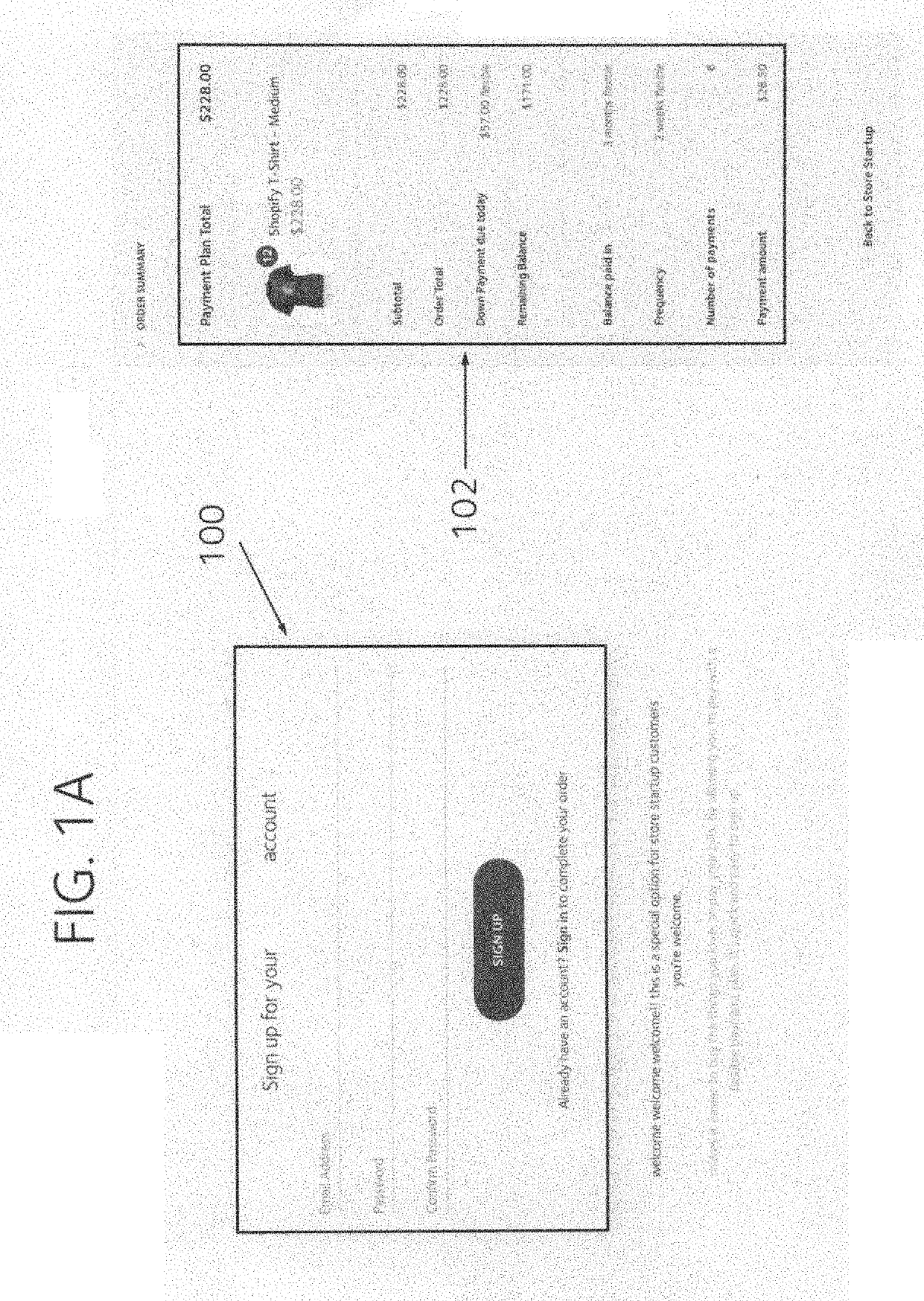
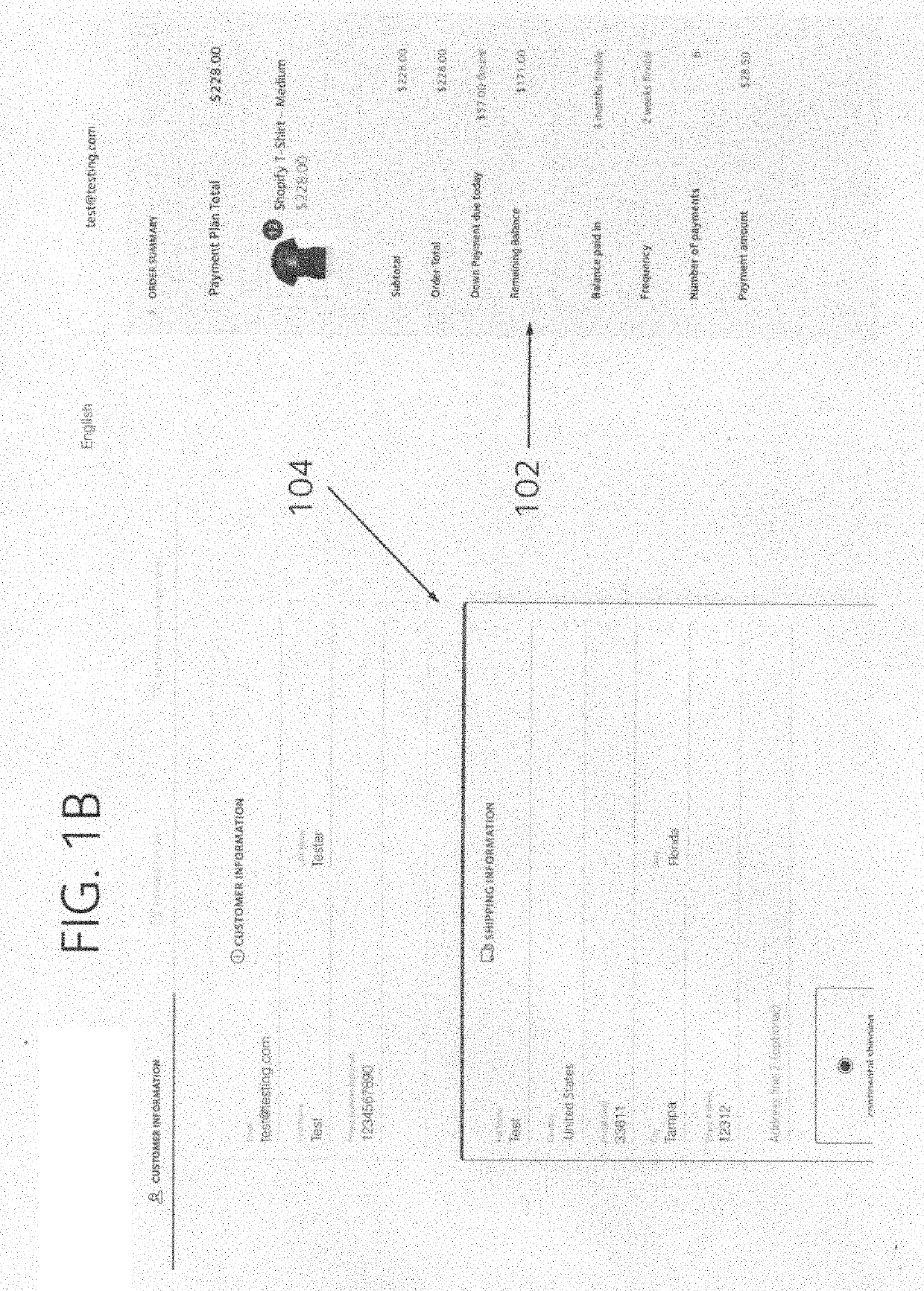
A software platform implementing a payment plan option for customers purchasing goods and services from a merchant website has an intuitive and transparent customer experience. The customer is able to calibrate down payment, frequency, and duration of the payment plan using user interface elements that show all values and periods being adjusted as the customer is making modifications to the payment plan. The platform allows the merchant to offer payment plans where customers can pay on specific days of the month. Customers can change payment plan terms after the plan has been agreed to and memorialized in a plan agreement containing the payment schedule. When terms have been changed, a replacement agreement is created and replaces the prior agreement. A plan can have automatic scheduled payments or manual payments. For manual payments, the merchant is able to select multiple manual plans for which he wants payments made and submit the batch of manual payments in parallel or concurrently.
Owner:PARTIALLY INC
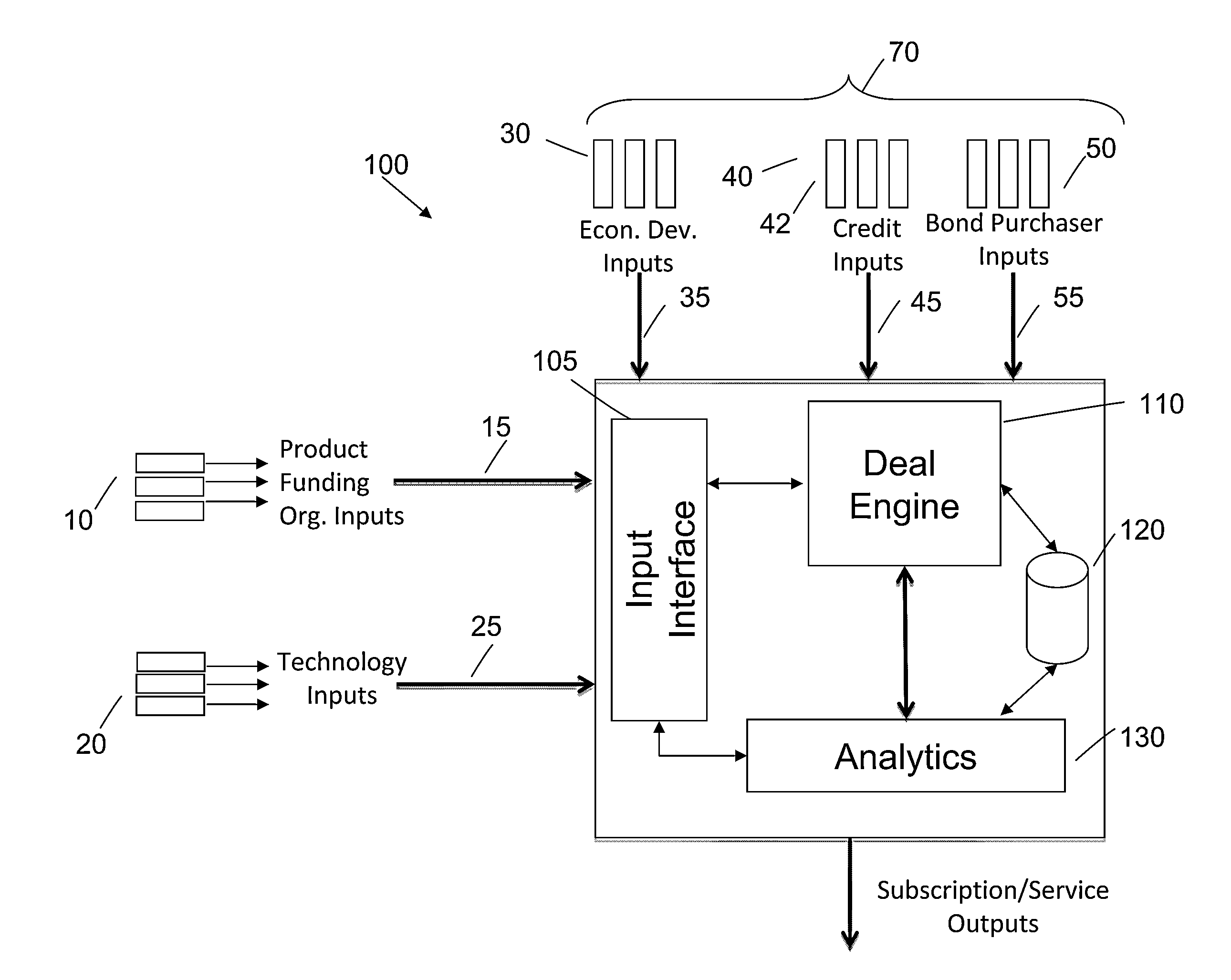
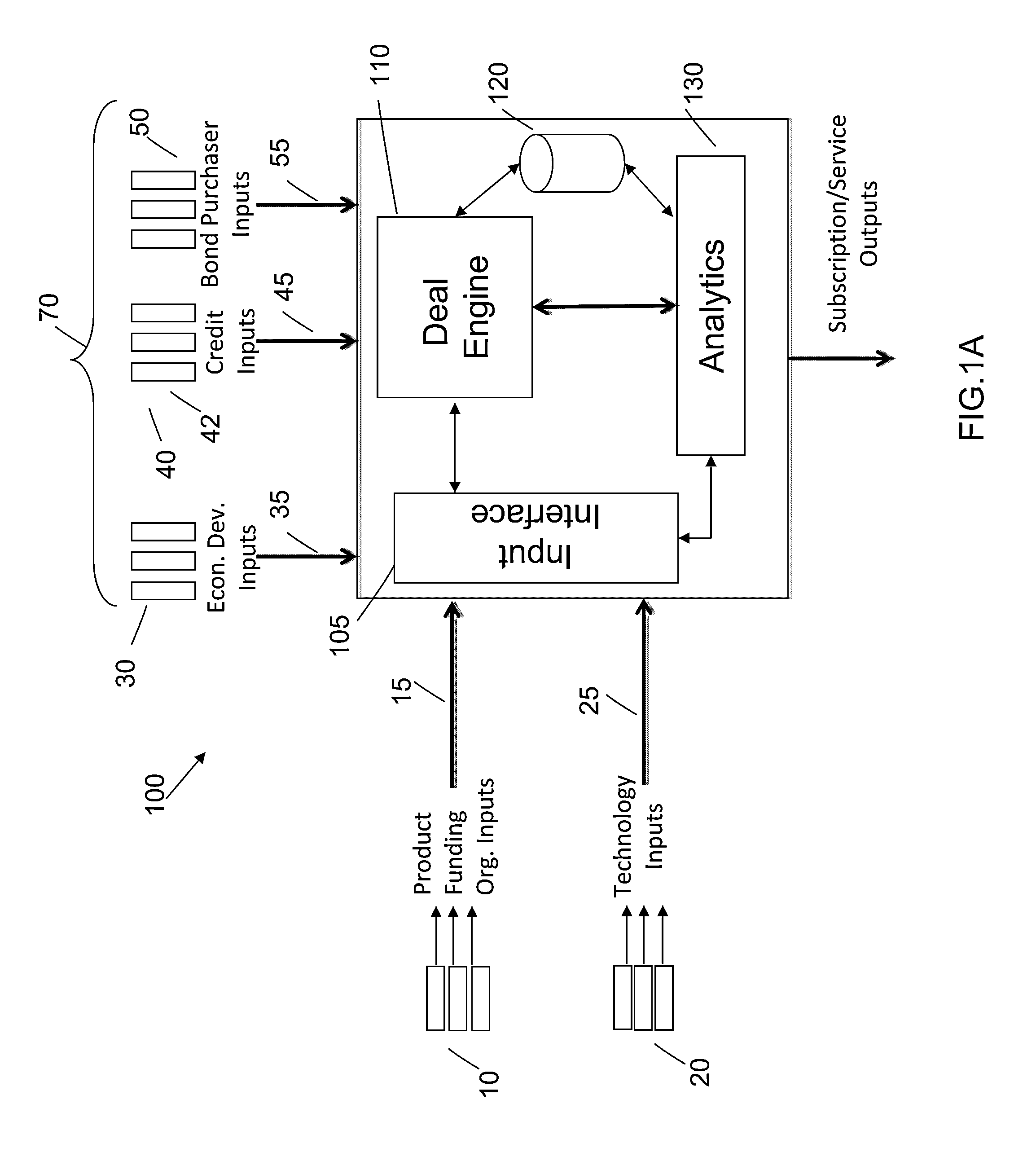
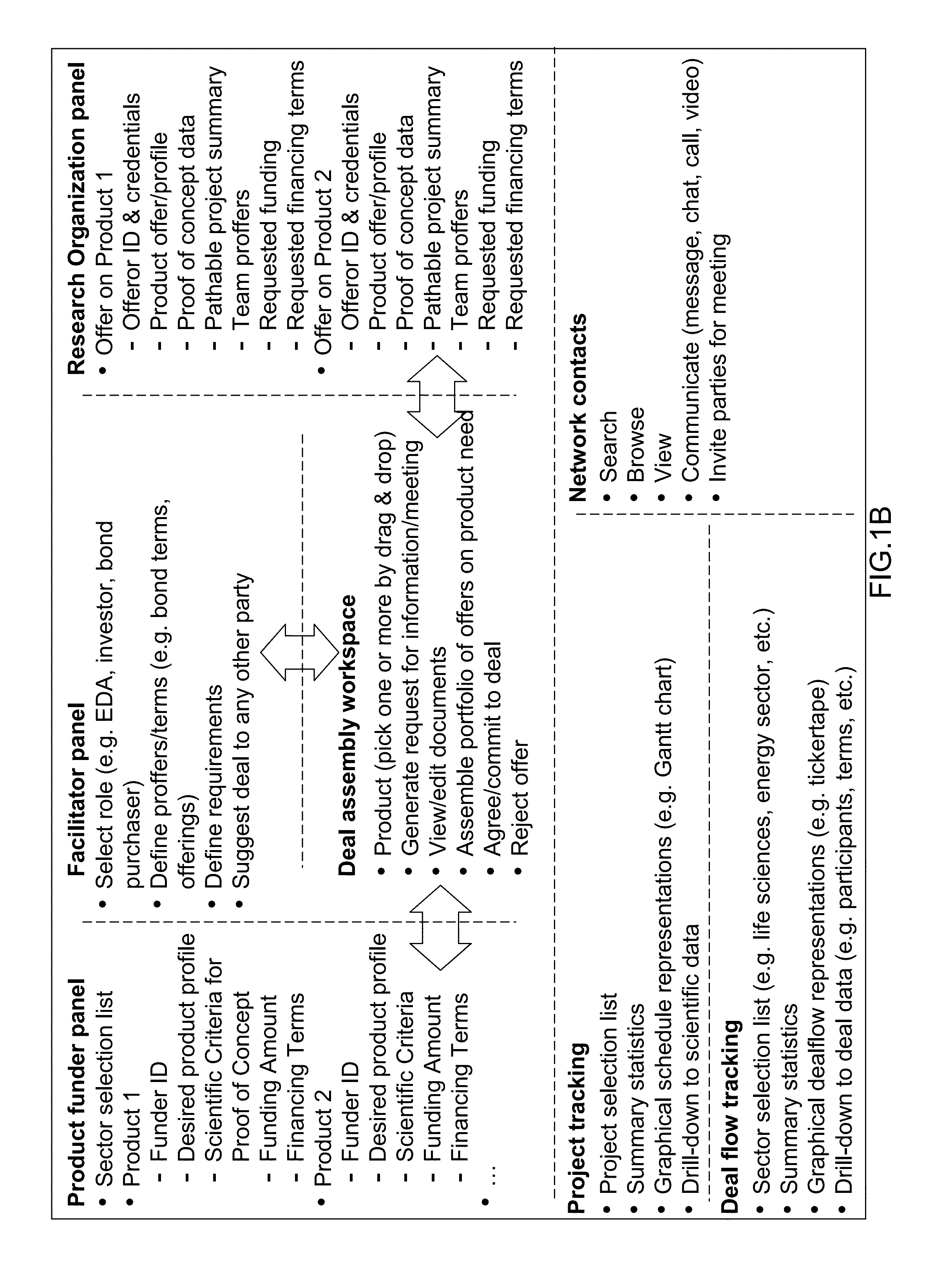
Systems, methods, and program products for innovation finance
A funding method and system provides funding at all stages of product development and manufacture. One or more of the funding organizations are matched with one or more of the securities issuing entities, and one or more of the securities issuing entities are matched with one or more of the pathable development projects, based at least in part on projected financial return, a schedule of tranches for the stages of the pathable development project, and a surety arrangement. One or more of the securities purchasing entities are matched with one or more securities issuing entities.
Owner:UNITHER VIROLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com