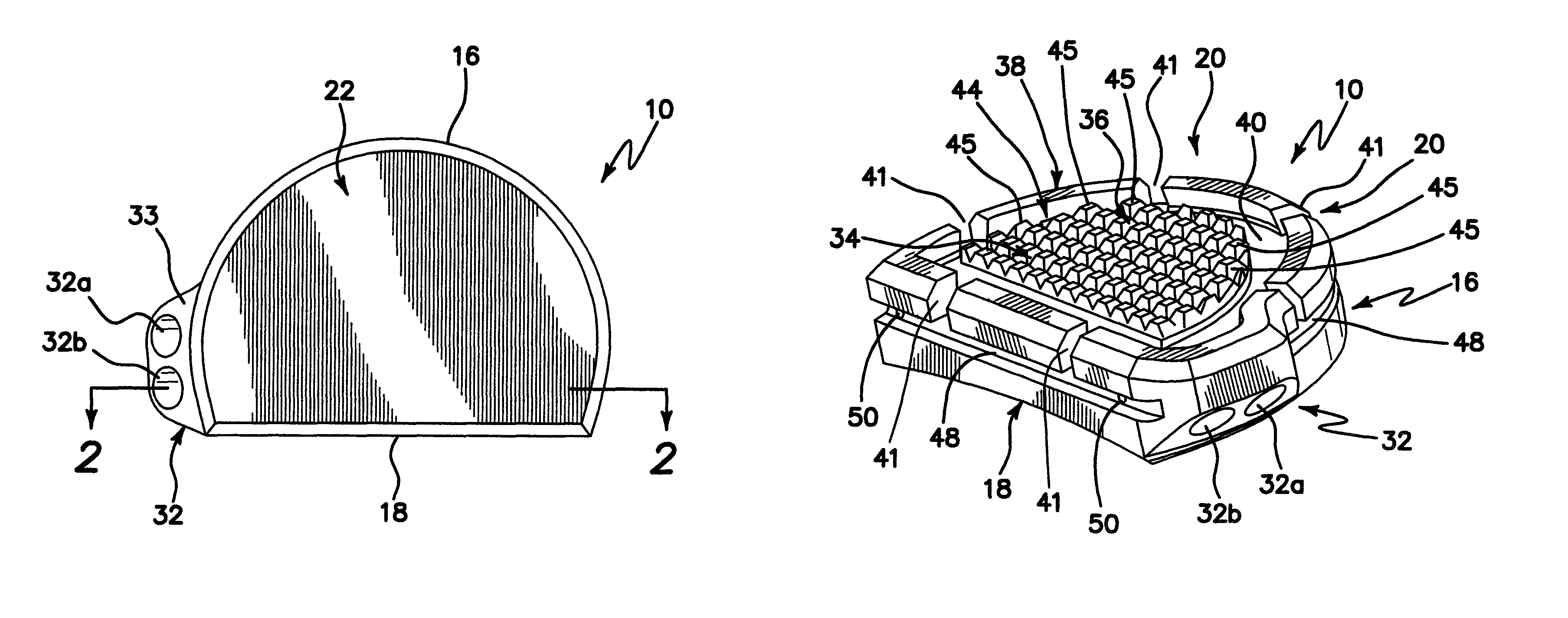
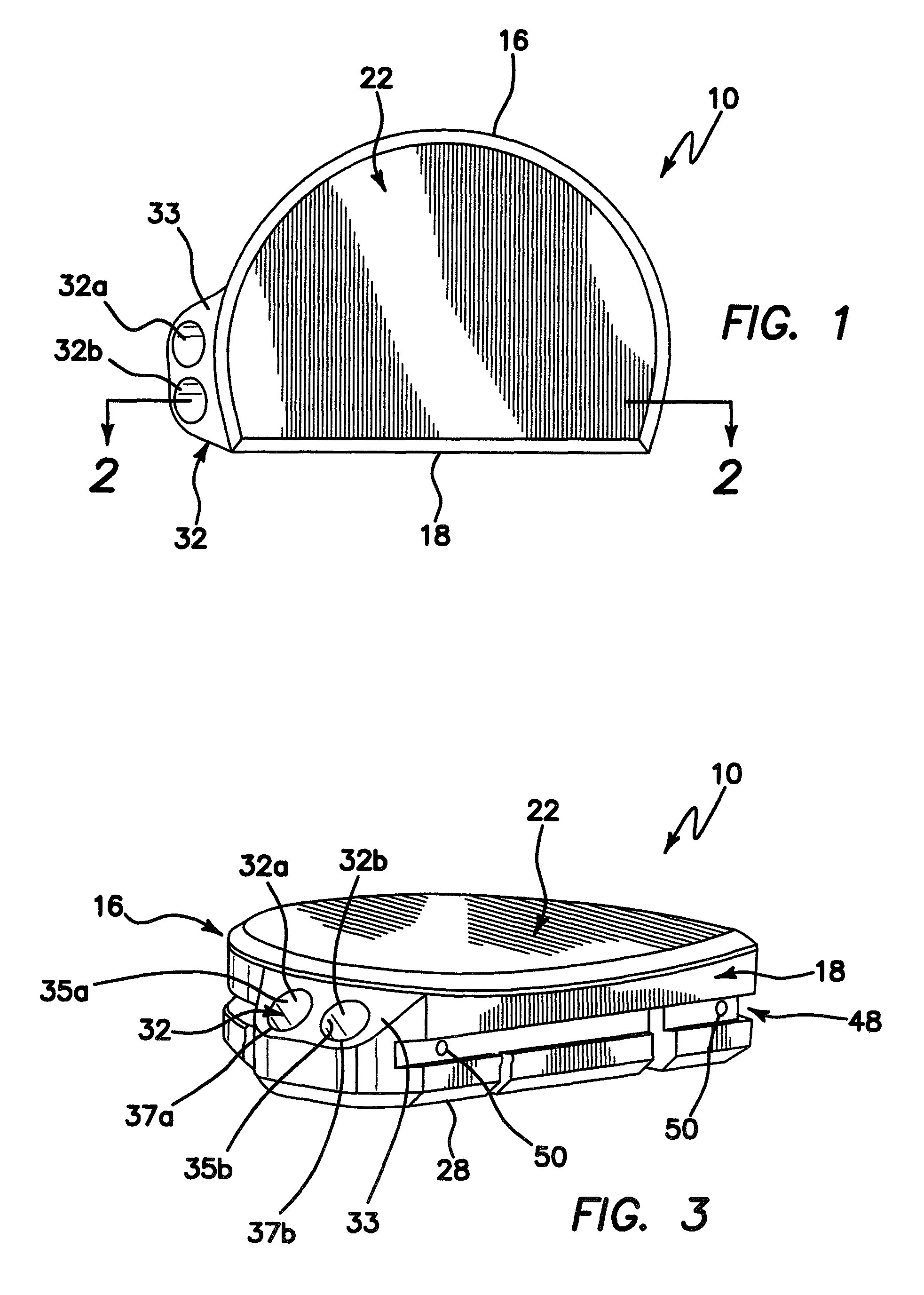
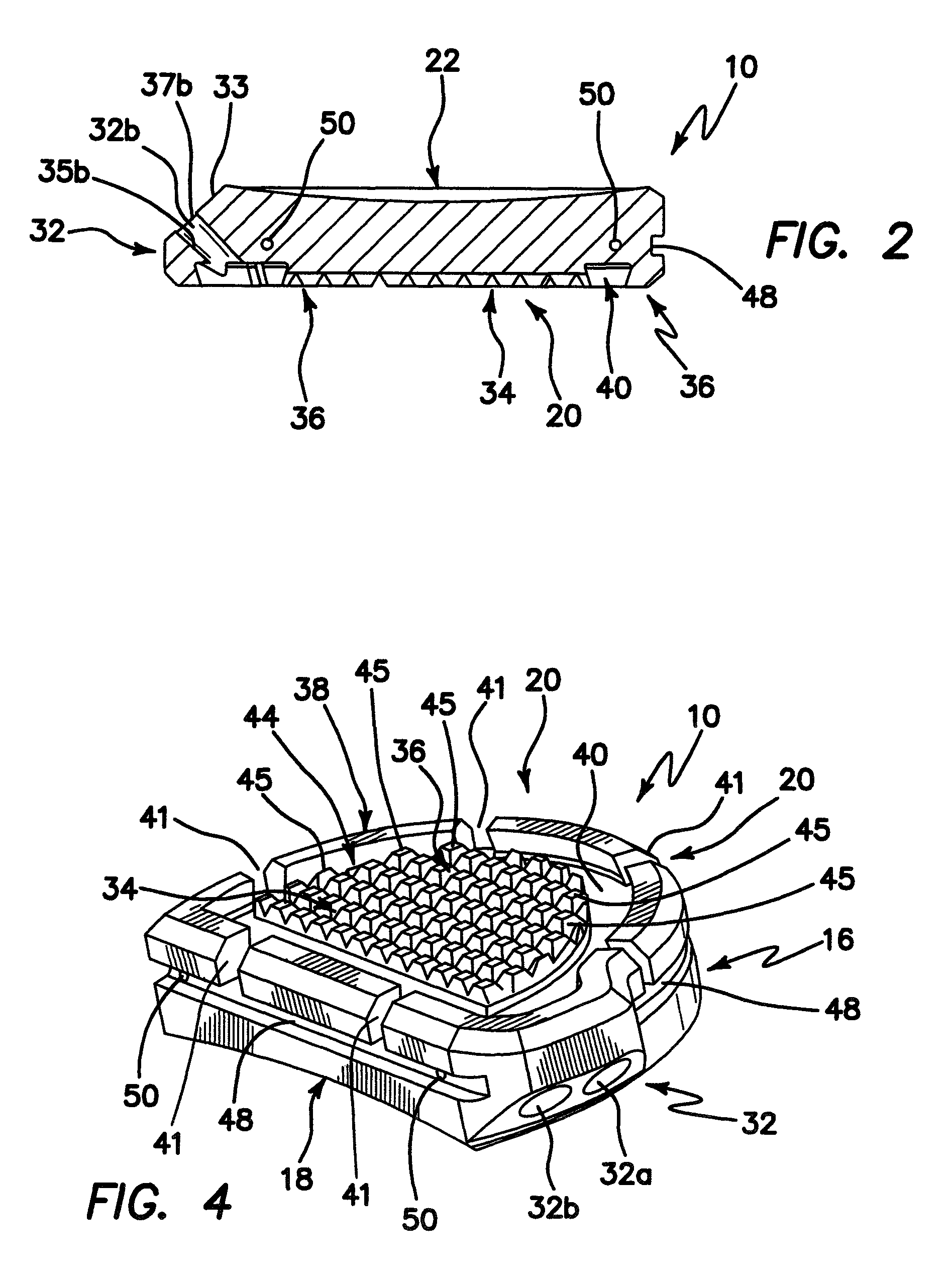
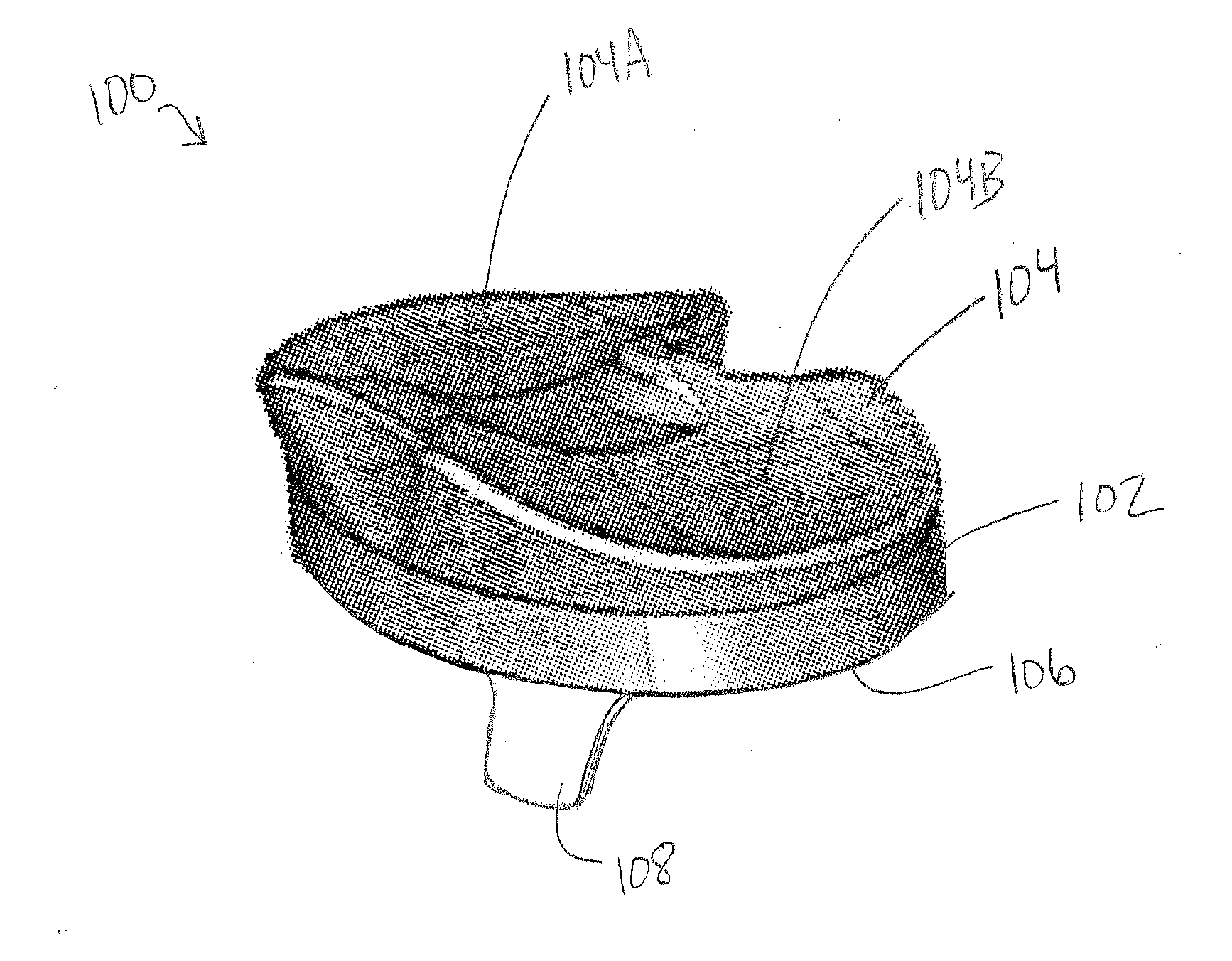
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121 results about "Knee joint replacement operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
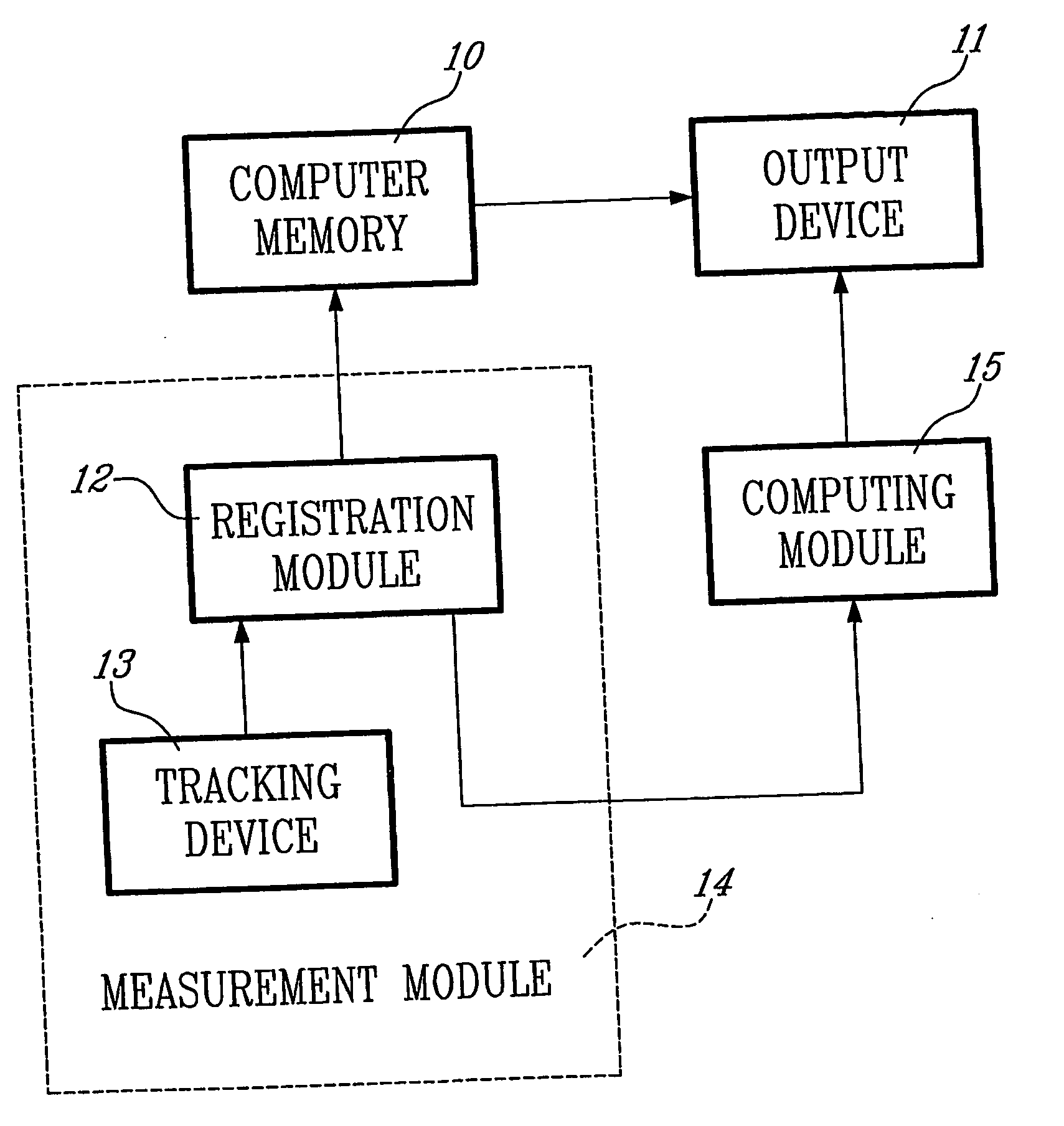
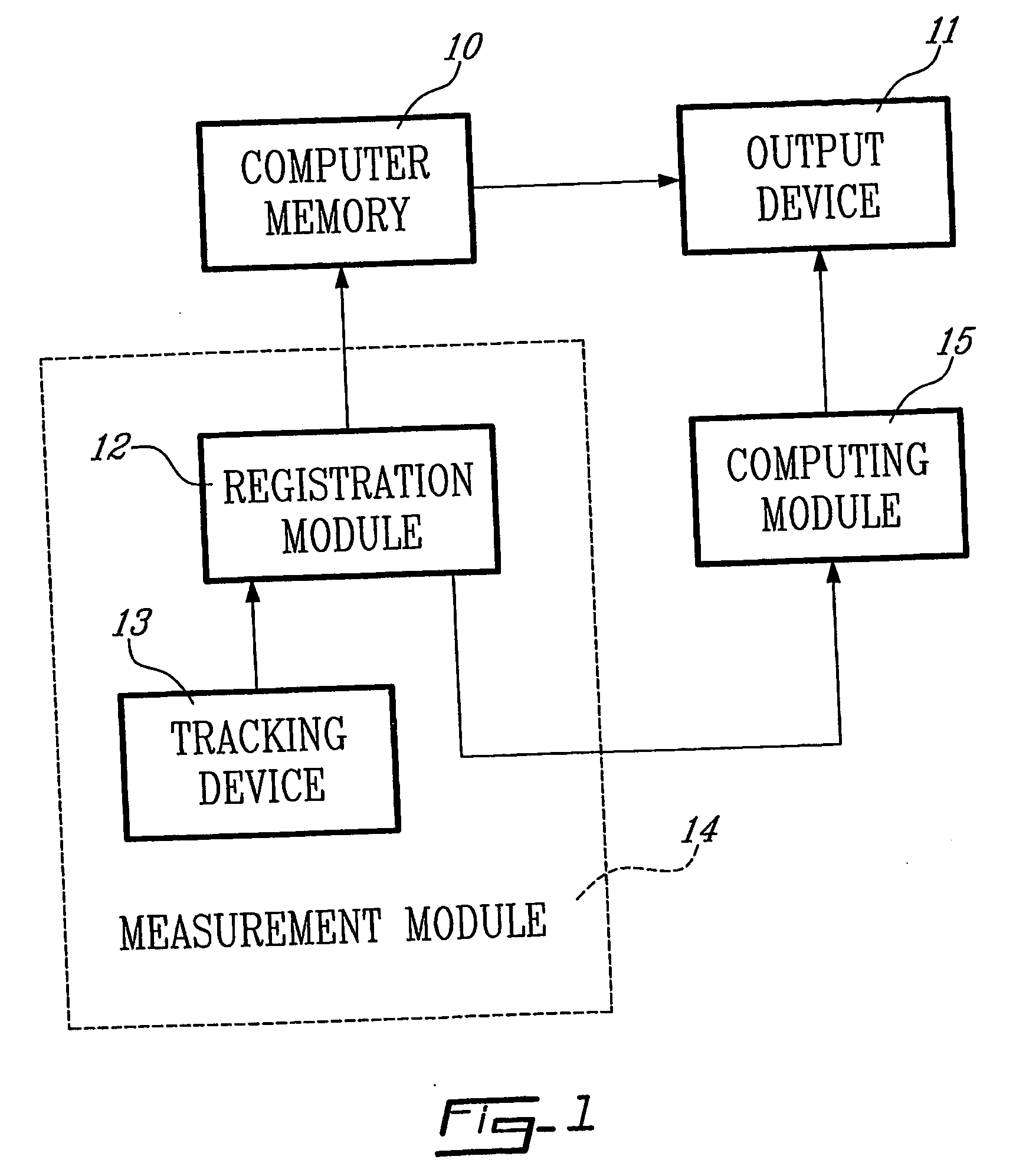
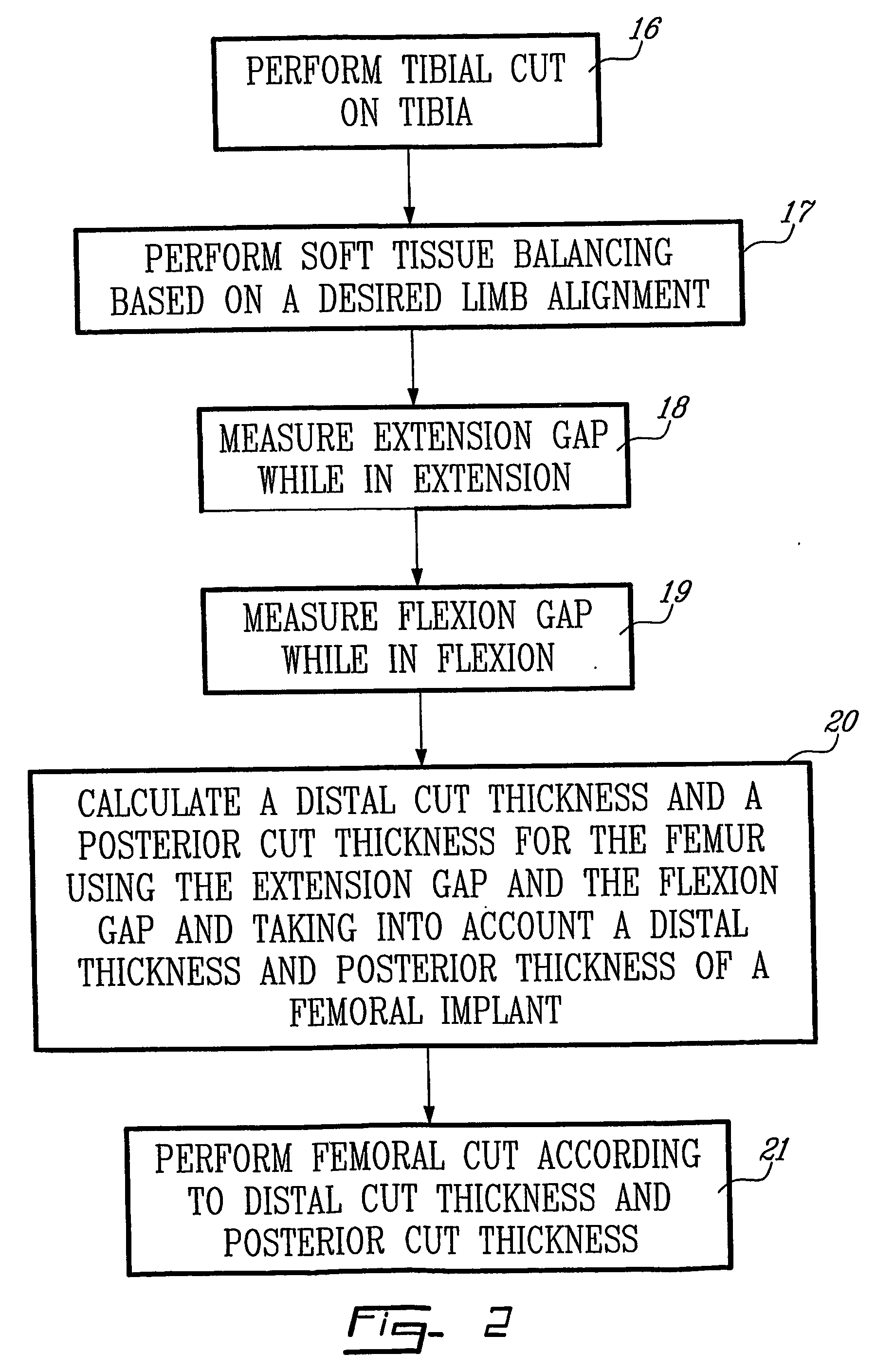
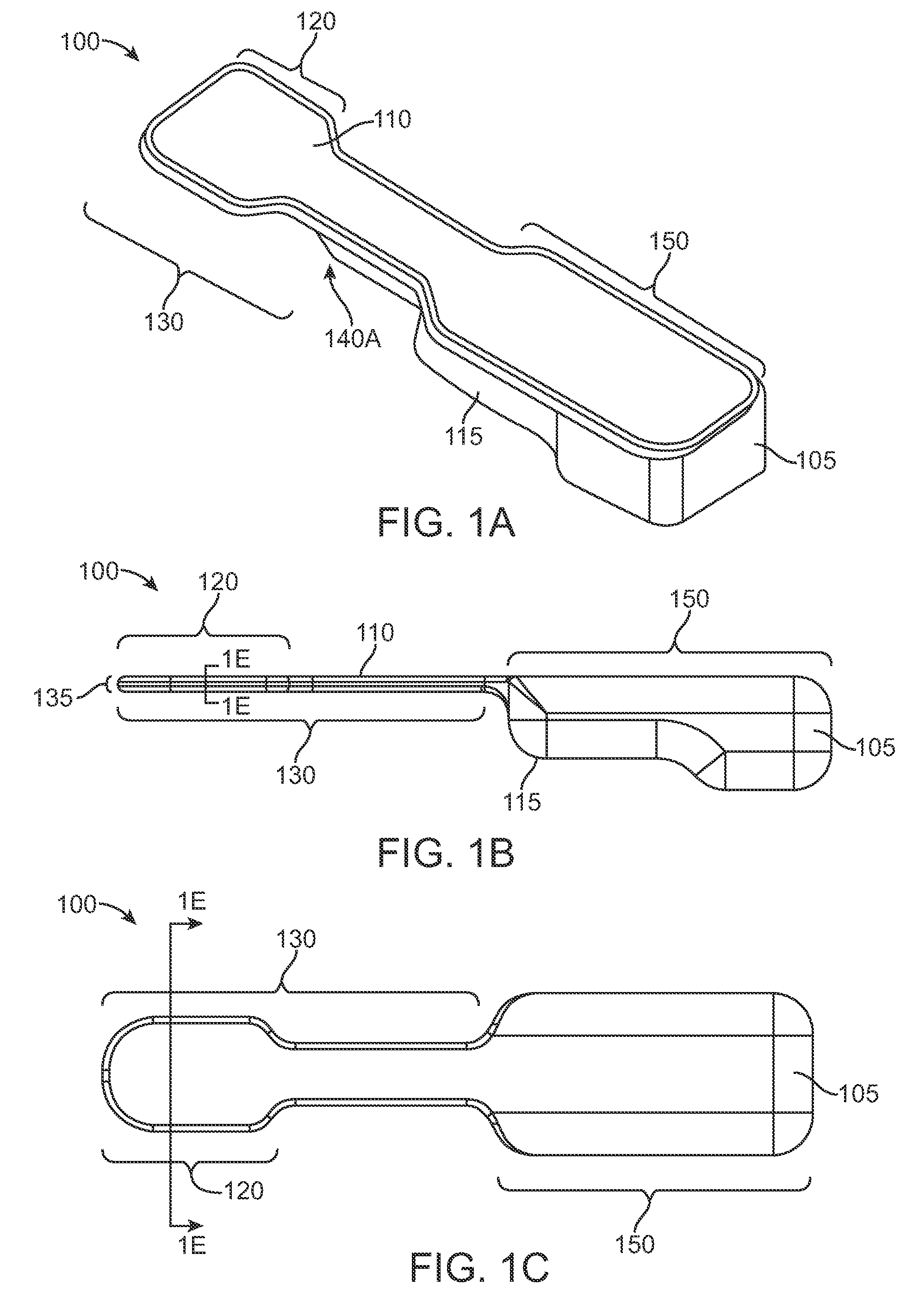
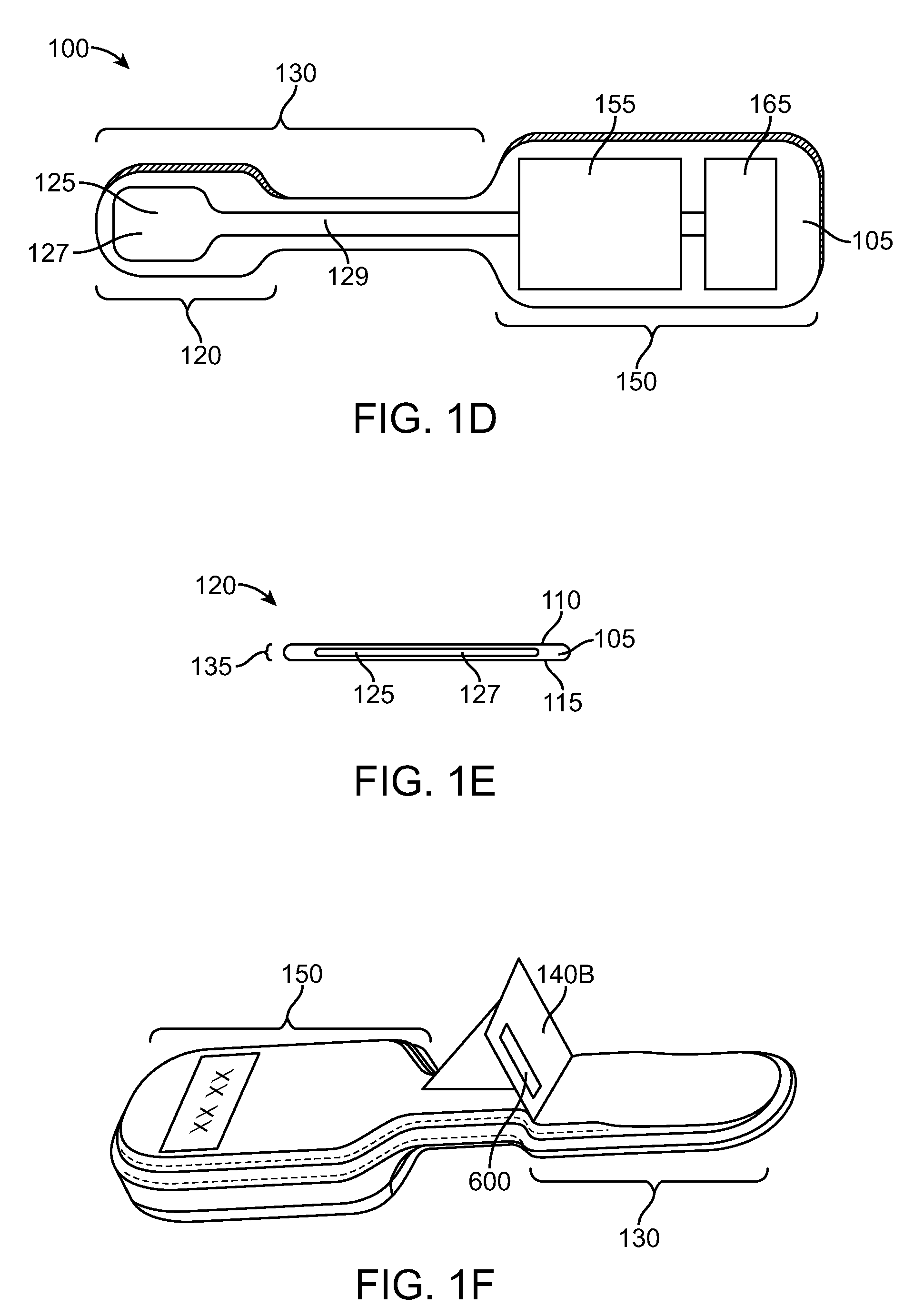
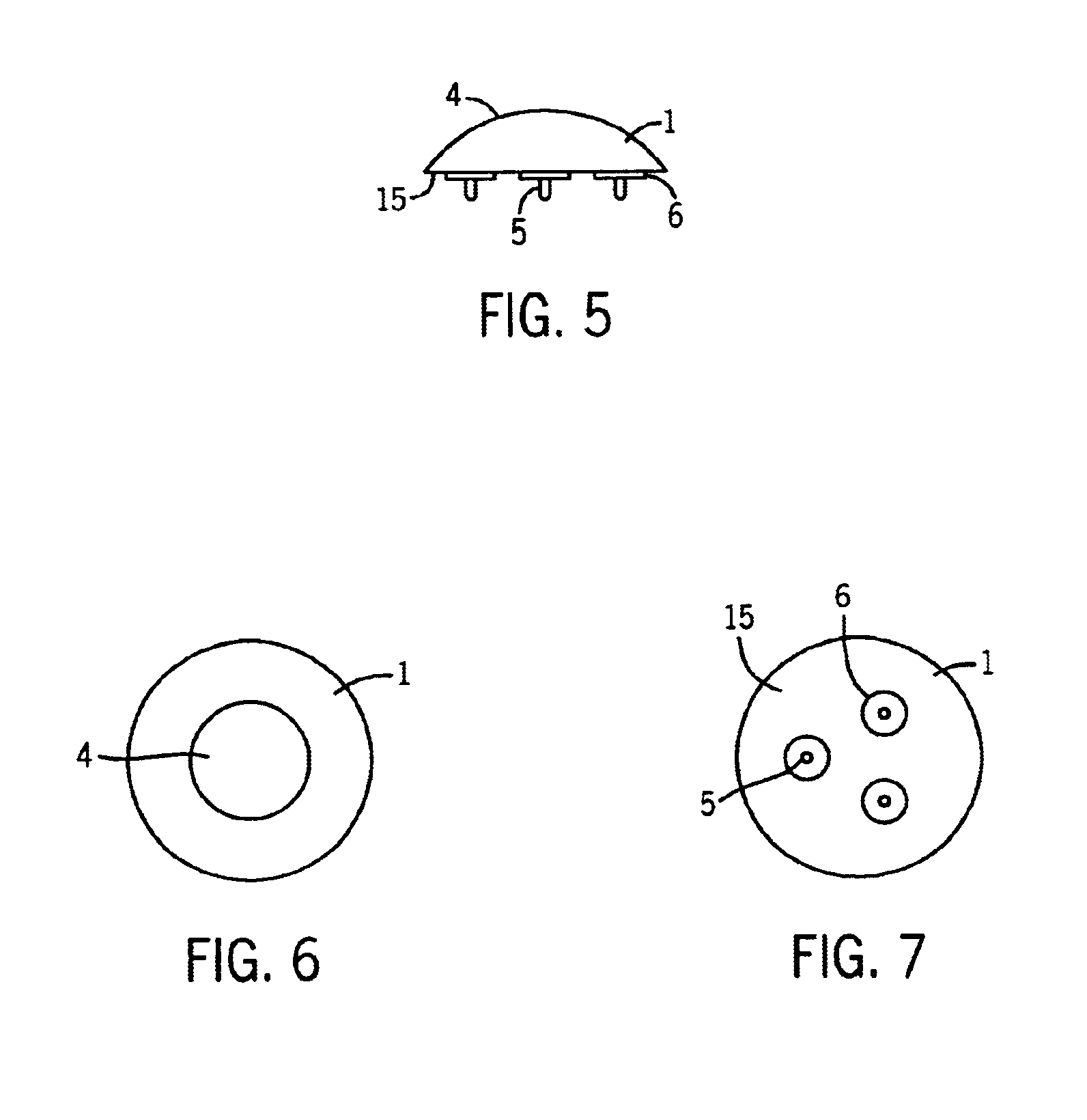
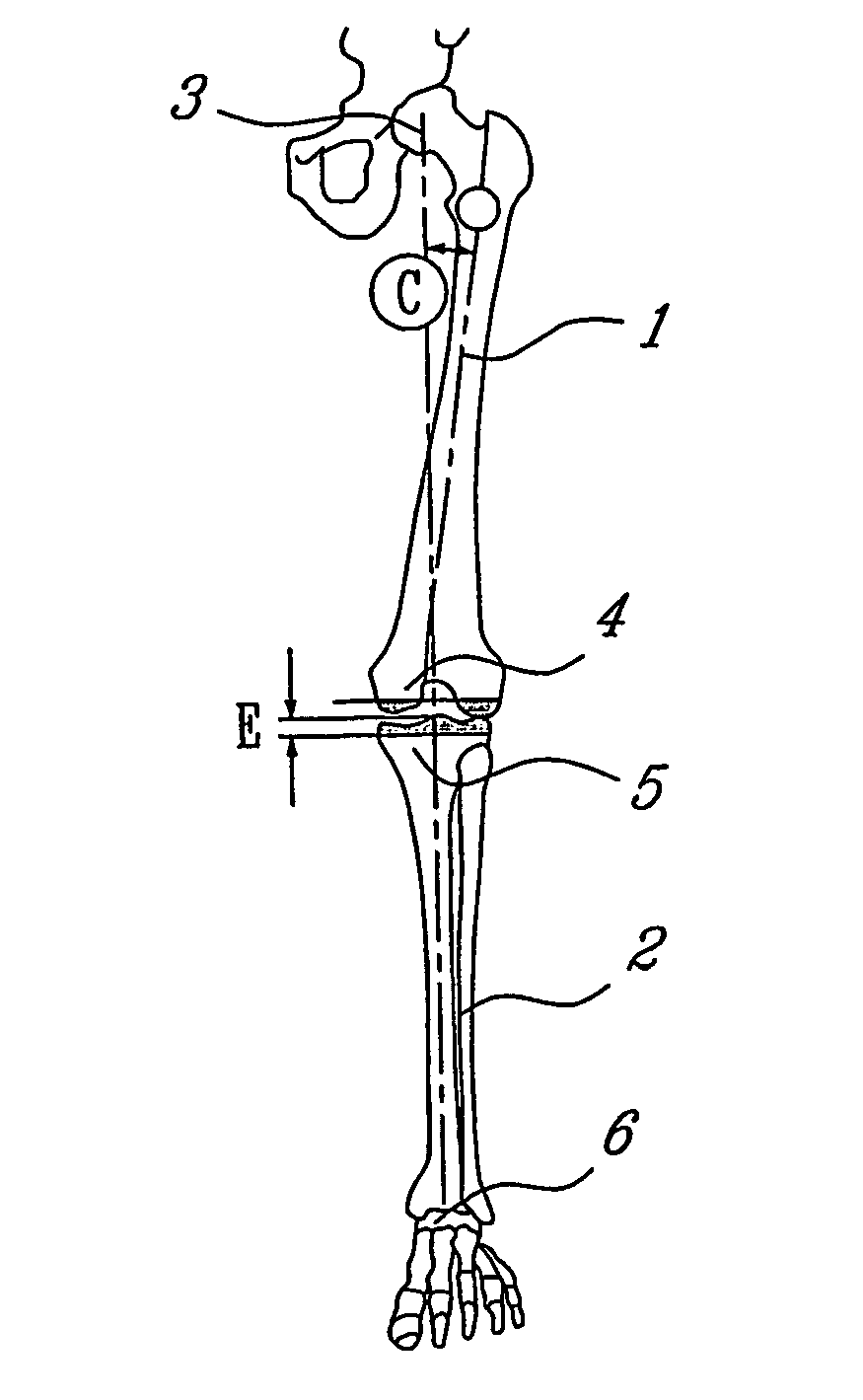
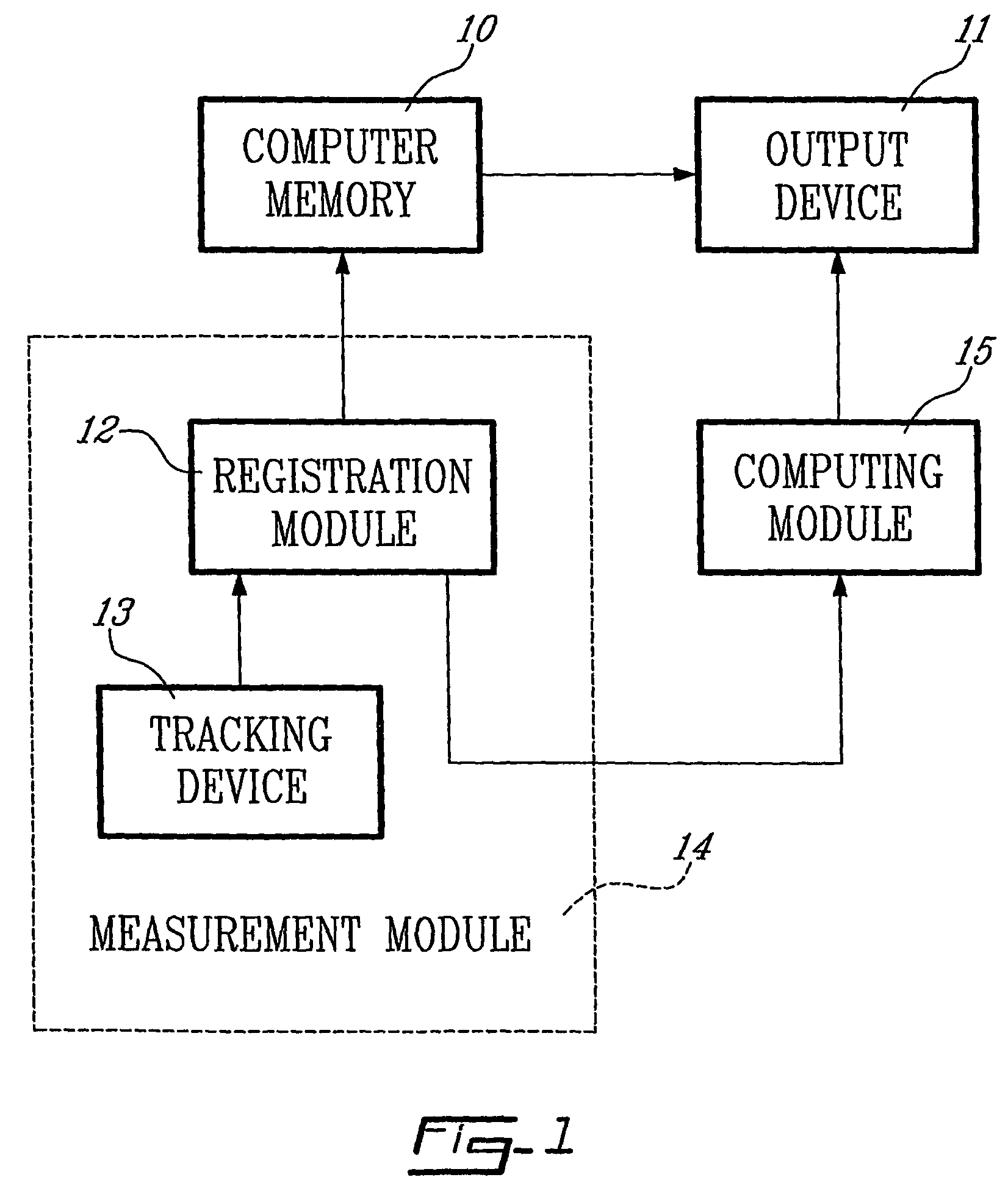
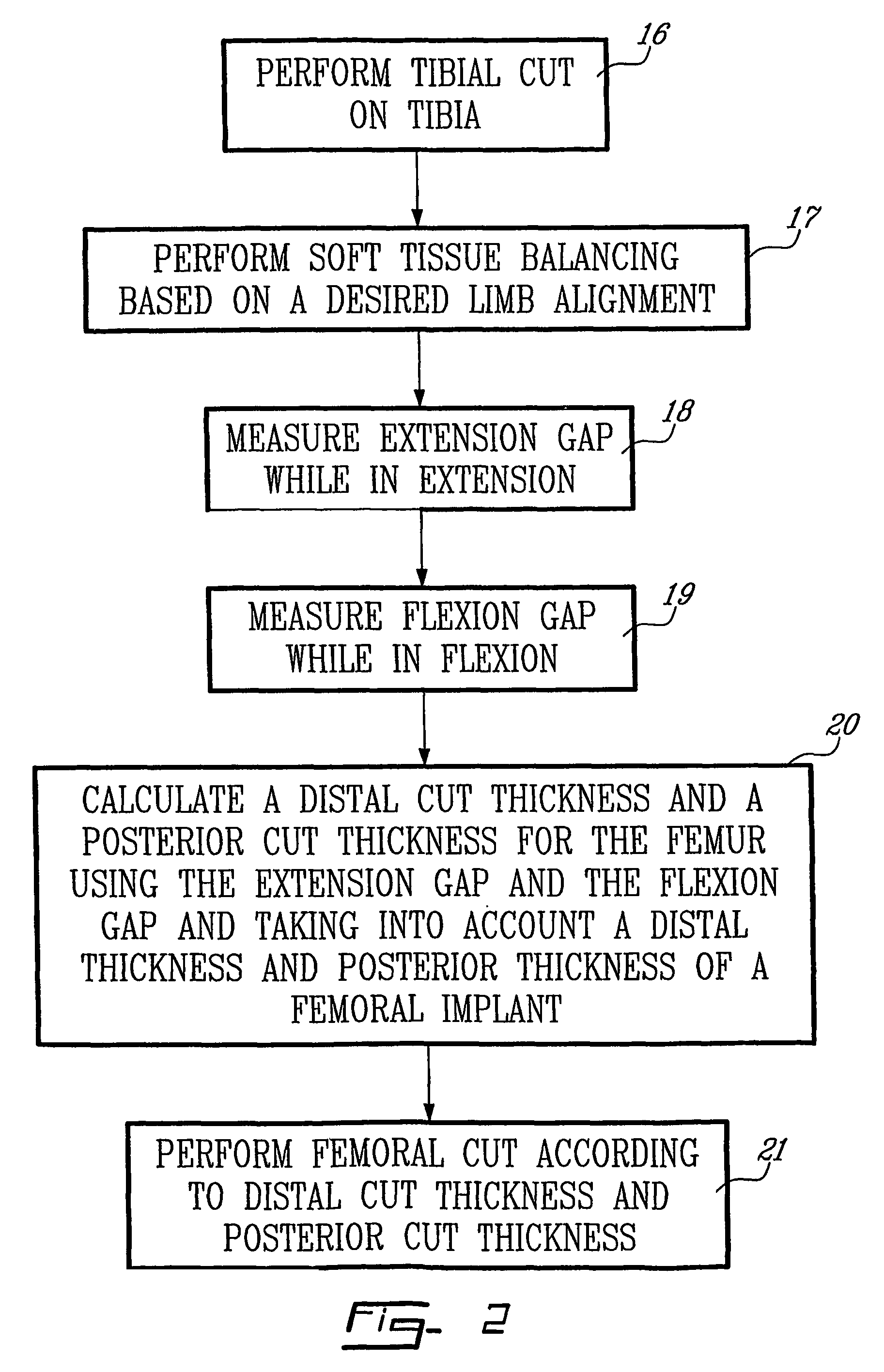
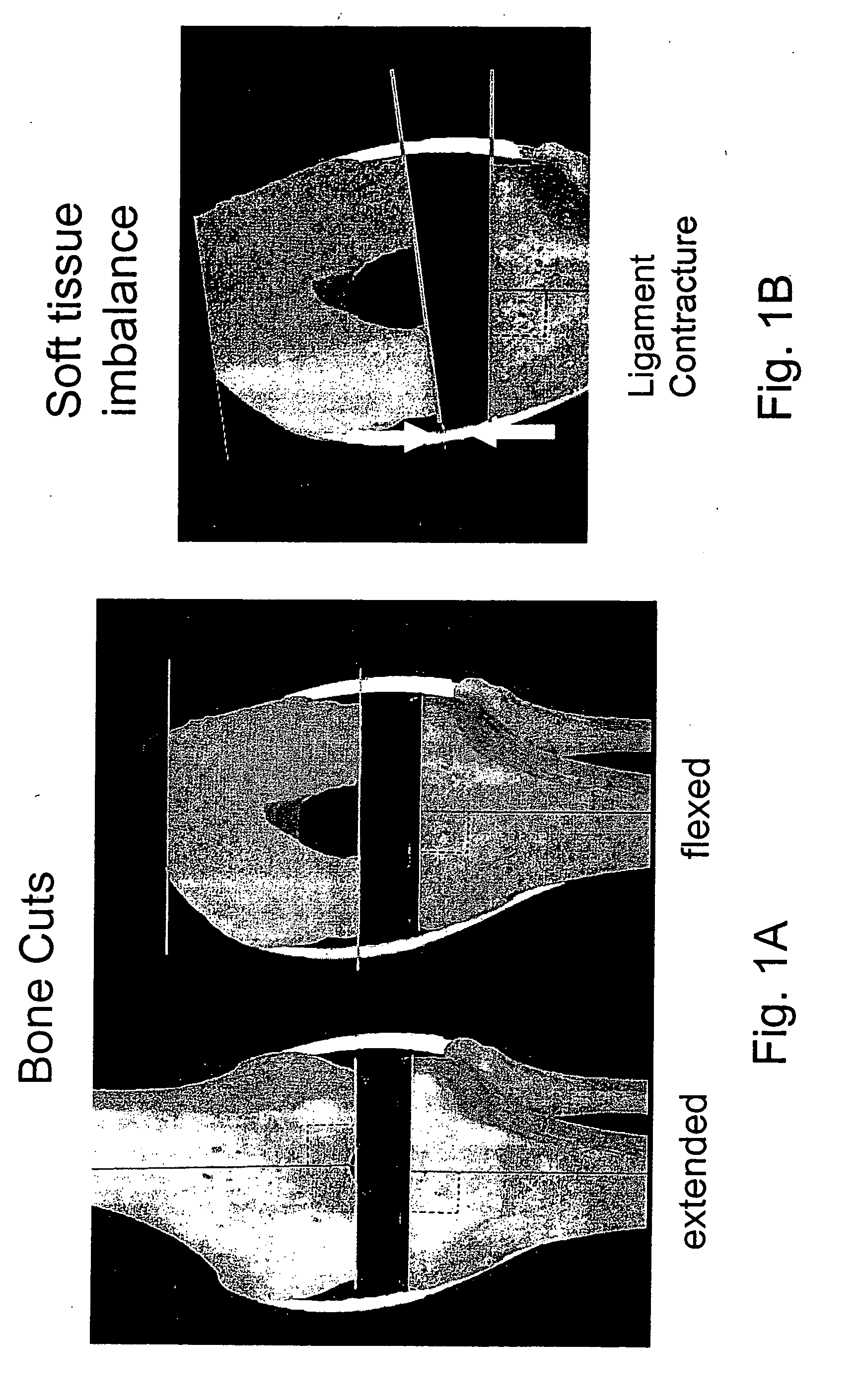
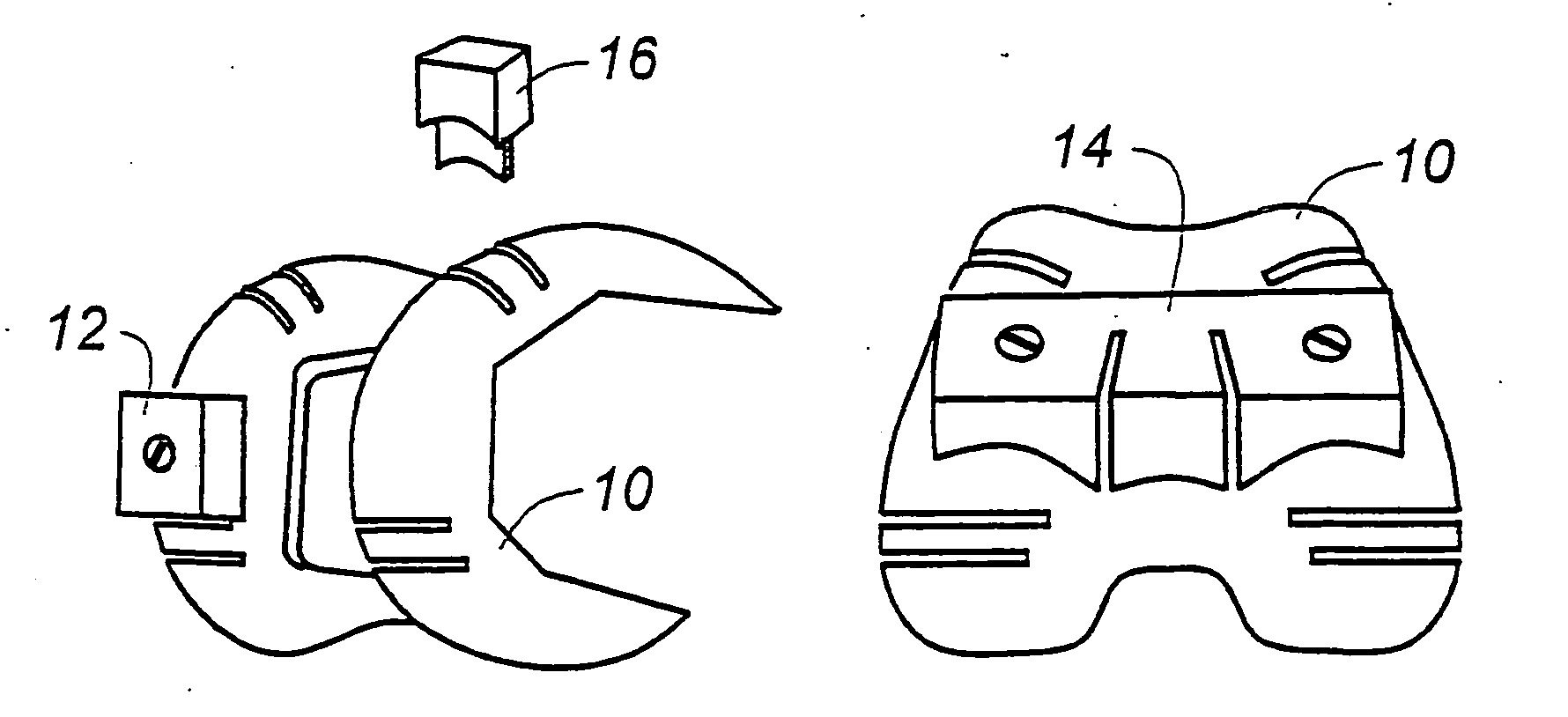
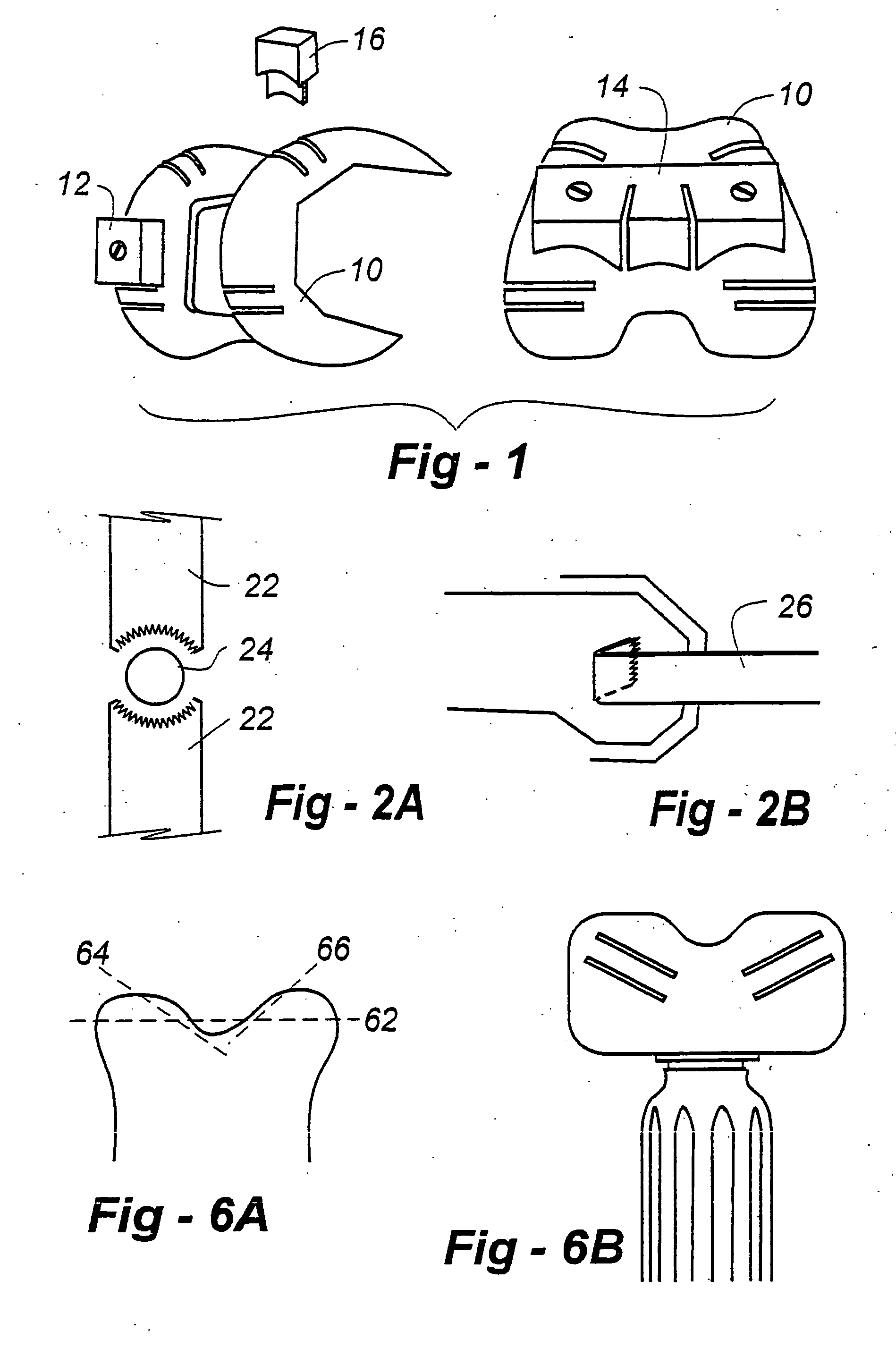
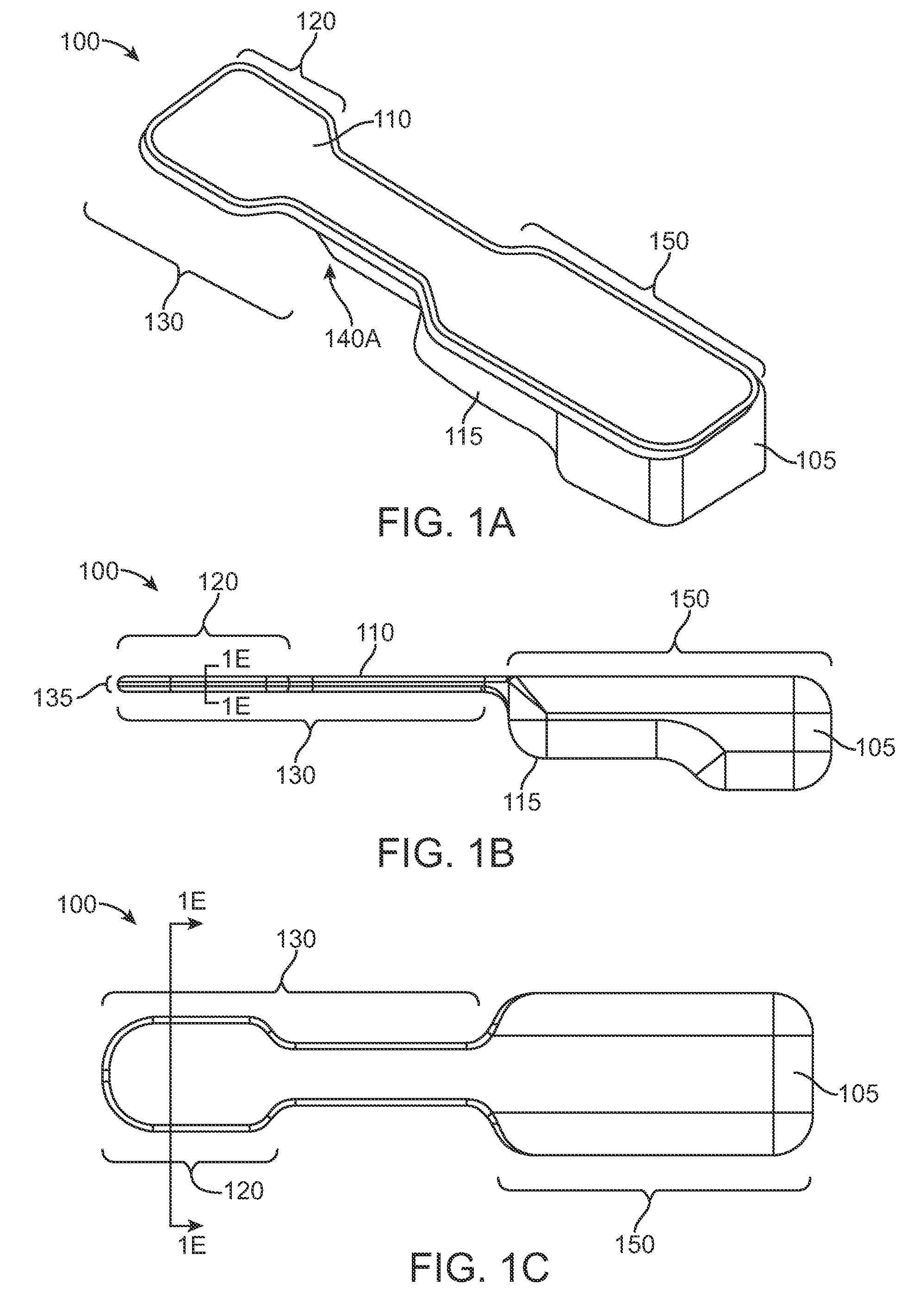
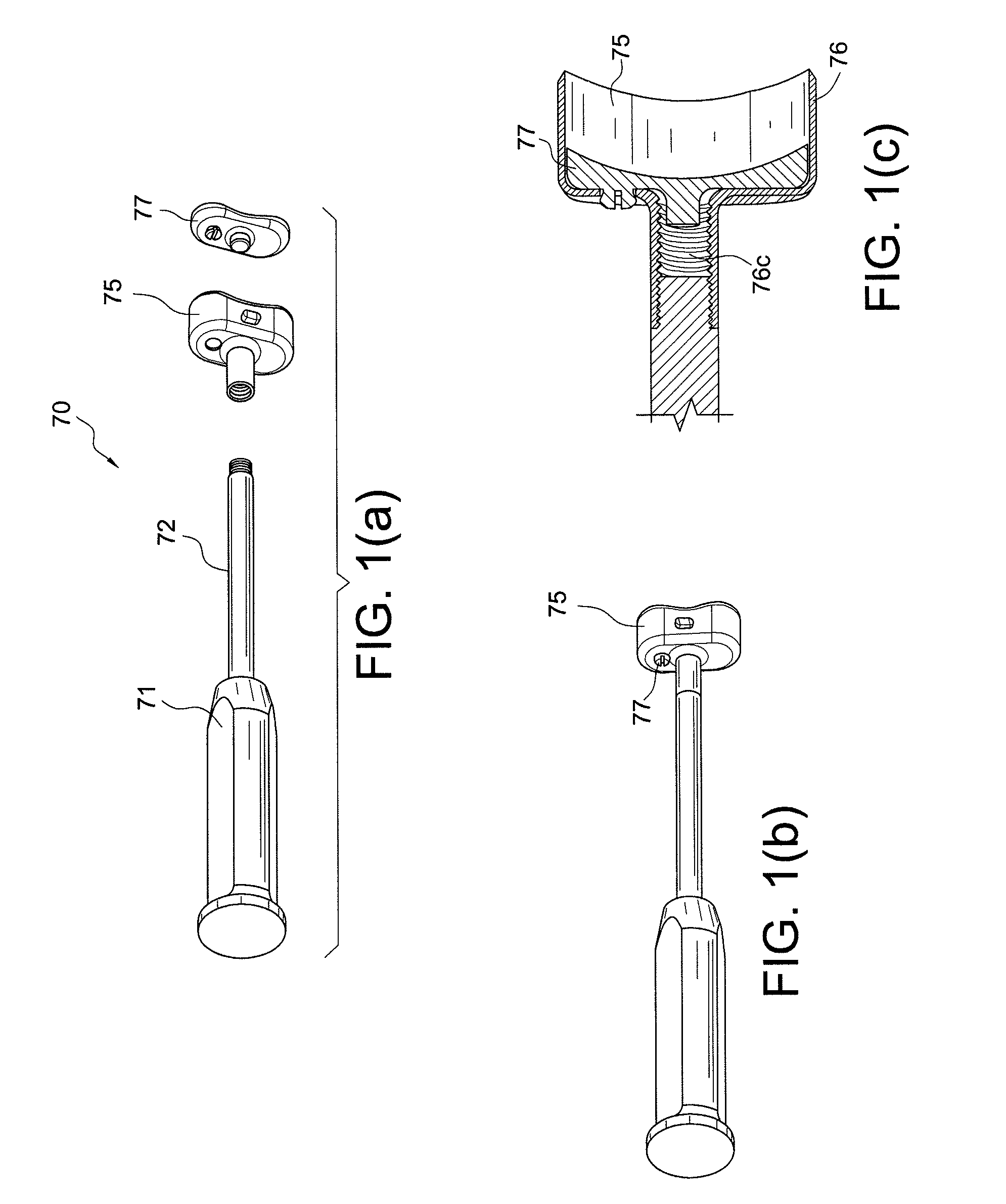
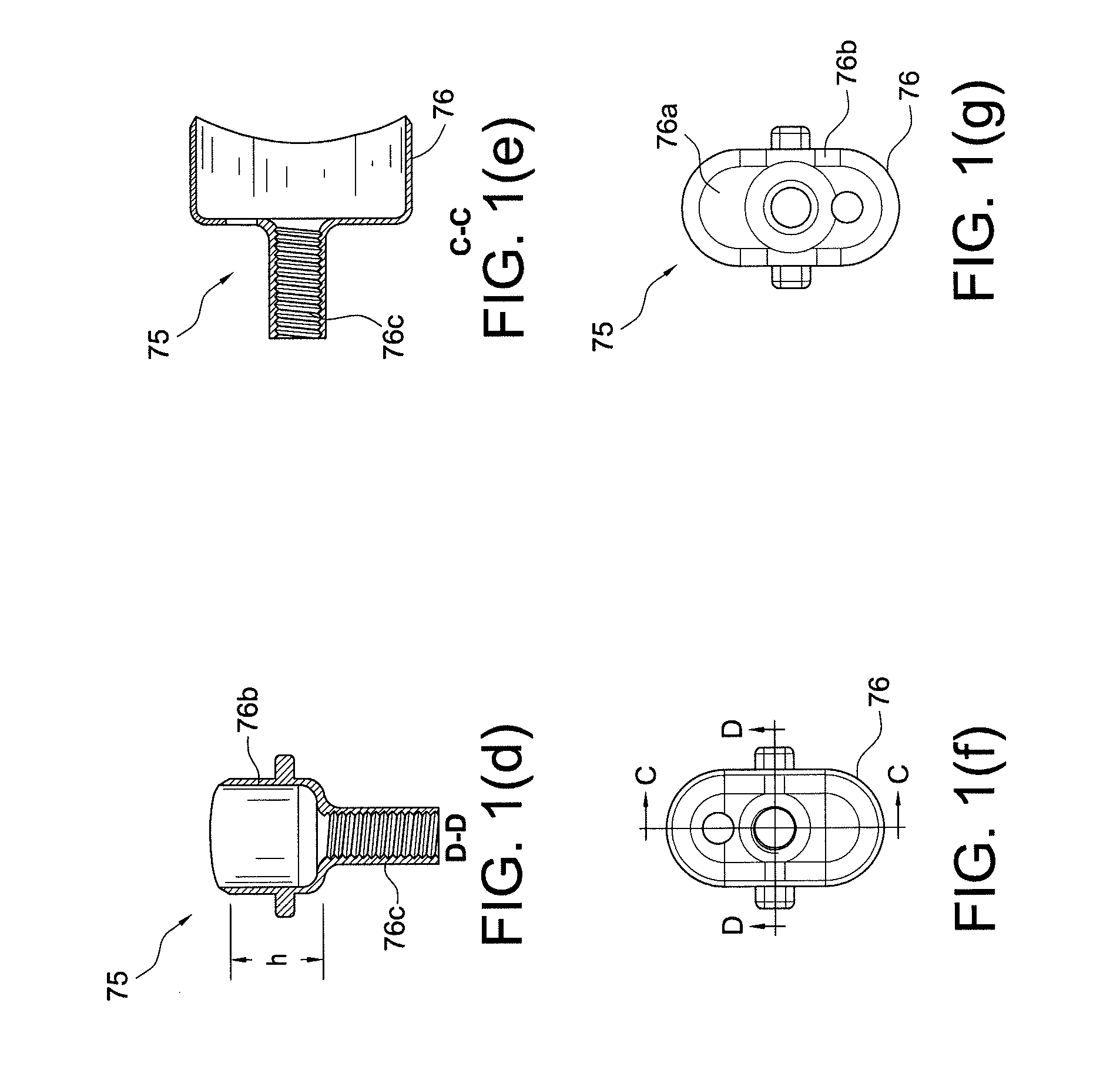
Determining femoral cuts in knee surgery
ActiveUS20060015120A1Extended service lifeEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsKnee surgeryTibia
There is provided a method and system for determining a distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness for a femur in a knee replacement operation, the method comprising: performing a tibial cut on a tibia; performing soft tissue balancing based on a desired limb alignment; measuring an extension gap between the femur and said tibial cut while in extension; measuring a flexion gap between the femur and the tibial cut while in flexion; calculating a distal cut thickness and a posterior cut thickness for the femur using the extension gap and the flexion gap and taking into account a distal thickness and posterior thickness of a femoral implant; and performing said femoral cut according to the distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
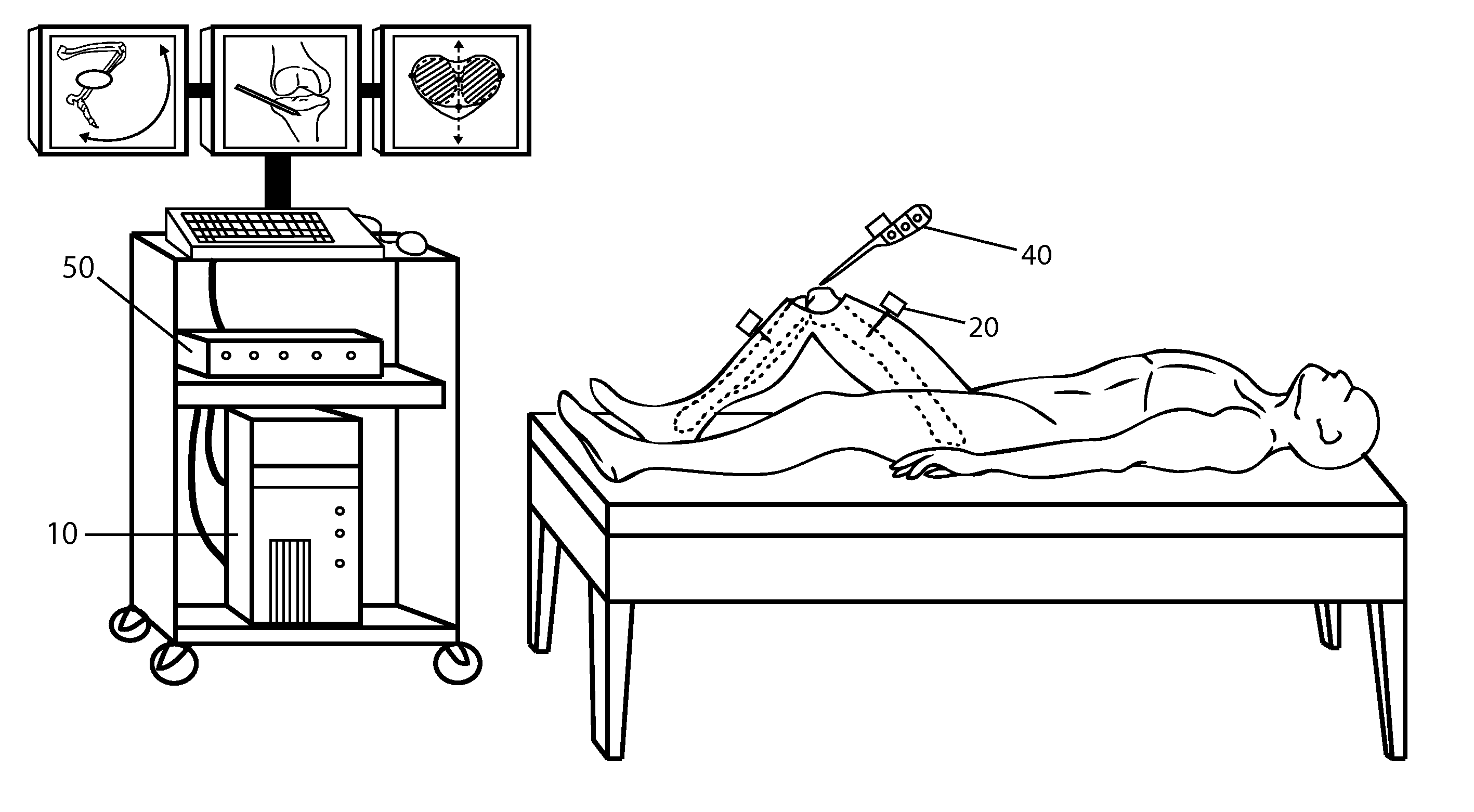
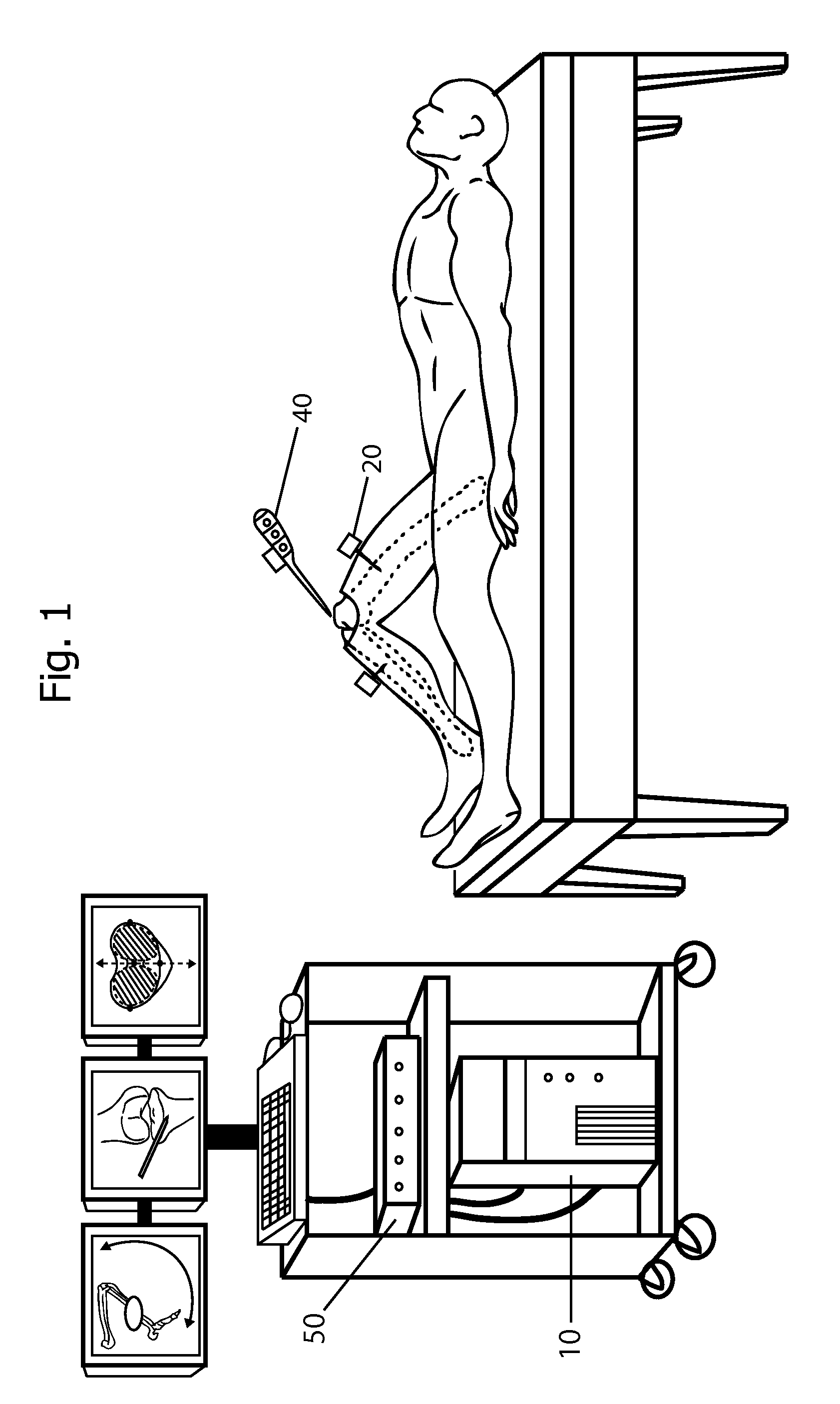
Inertial Sensor Based Surgical Navigation System for Knee Replacement Surgery
ActiveUS20110275957A1Improve accuracyGood precisionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationKnee JointNavigation system
An inertial sensor based surgical navigation system for knee replacement surgery is disclosed. Inertial sensors composed of six-degree-of-freedom inertial chips, whose measurements are processed through a series of integration, quaternion, and kalman filter algorithms, are used to track the position and orientation of bones and surgical instruments. The system registers anatomically significant geometry, calculates joint centers and the mechanical axis of the knee, develops a visualization of the lower extremity that moves in real time, assists in the intra-operative planning of surgical cuts, determines the optimal cutting planes for cut guides and the optimal prosthesis position and orientation, and finally navigates the cut guides and the prosthesis to their optimal positions and orientations using a graphical user interface.
Owner:BHANDARI SACHIN
Method for resecting the knee using a resection guide and provisional prosthetic component
InactiveUSRE39301E1Properly balanceAccurate balanceDiagnosticsJoint implantsAnterior surfaceKnee Joint
A method and apparatus for knee replacement surgery wherein a femoral provisional component is provided which corresponds to a permanent component to be implanted in a human and which includes means for establishing the correct fit and position of such a component, prior to its implantation, in relation to the soft tissues of the knee before final resection of the anterior femoral surface. The provisional component further includes cutting guide means for such anterior surface resection such that accurate cuts may be made with the provisional component in place. The method involves preparing the distal femoral surface using the femoral intramedullary canal as a constant reference point for posterior and distal cutting guides followed by locating the provisional component by means of a provisional intramedullary stem so that the relationship with the soft tissues of the knee may be accurately established.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Method of preparing bones for knee replacement surgery
InactiveUS7708741B1Promote balance between supply and demandSuture equipmentsOperating tablesTibiaDistal portion
A method is provided for performing knee replacement surgery on a leg of a patient. The method includes making a cut on a posterior portion of a patella, making a cut on a proximal portion of a tibia, and making a cut on the distal portion of the femur. The cut on the patella is performed before making the cuts on the tibia and femur.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
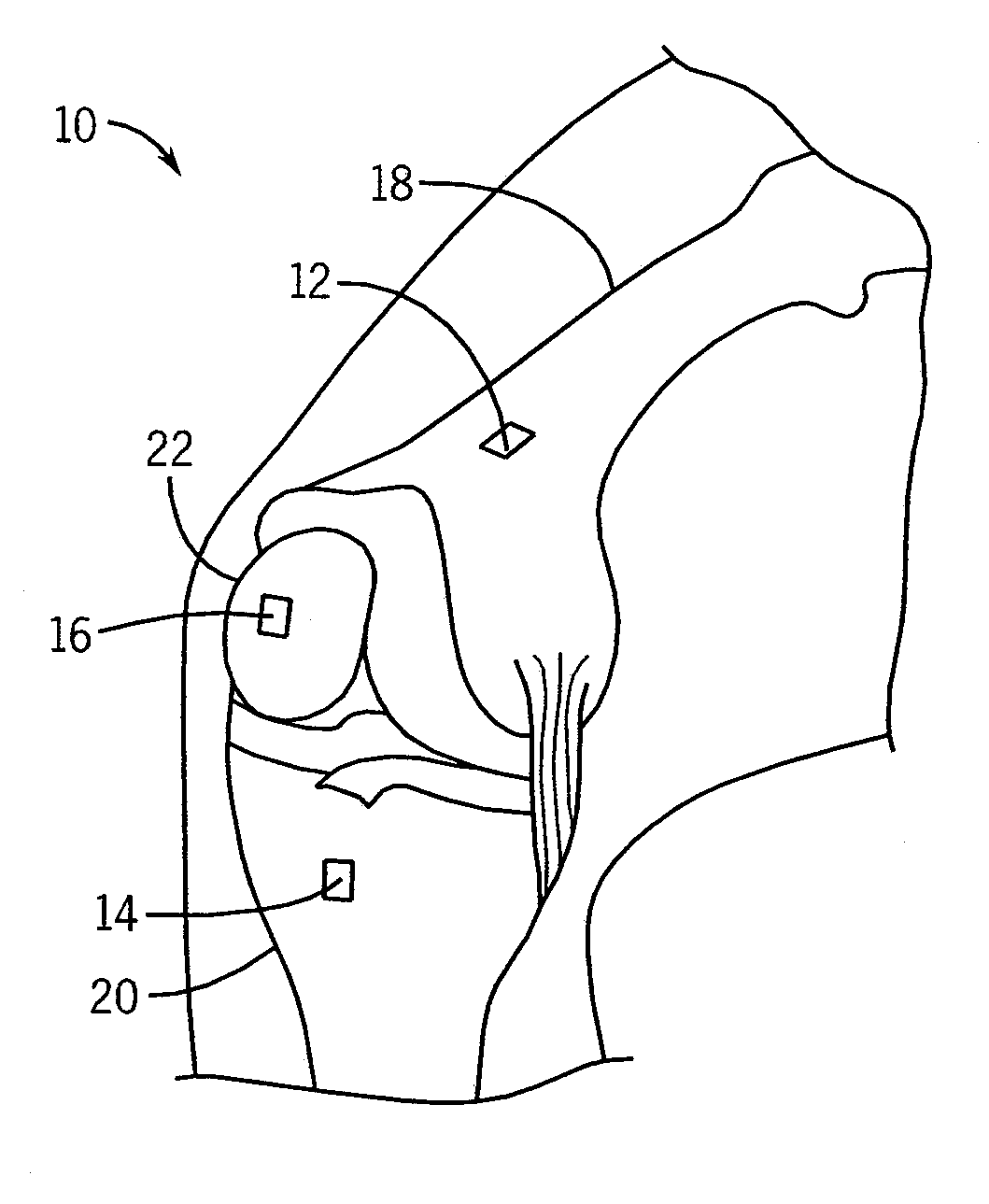
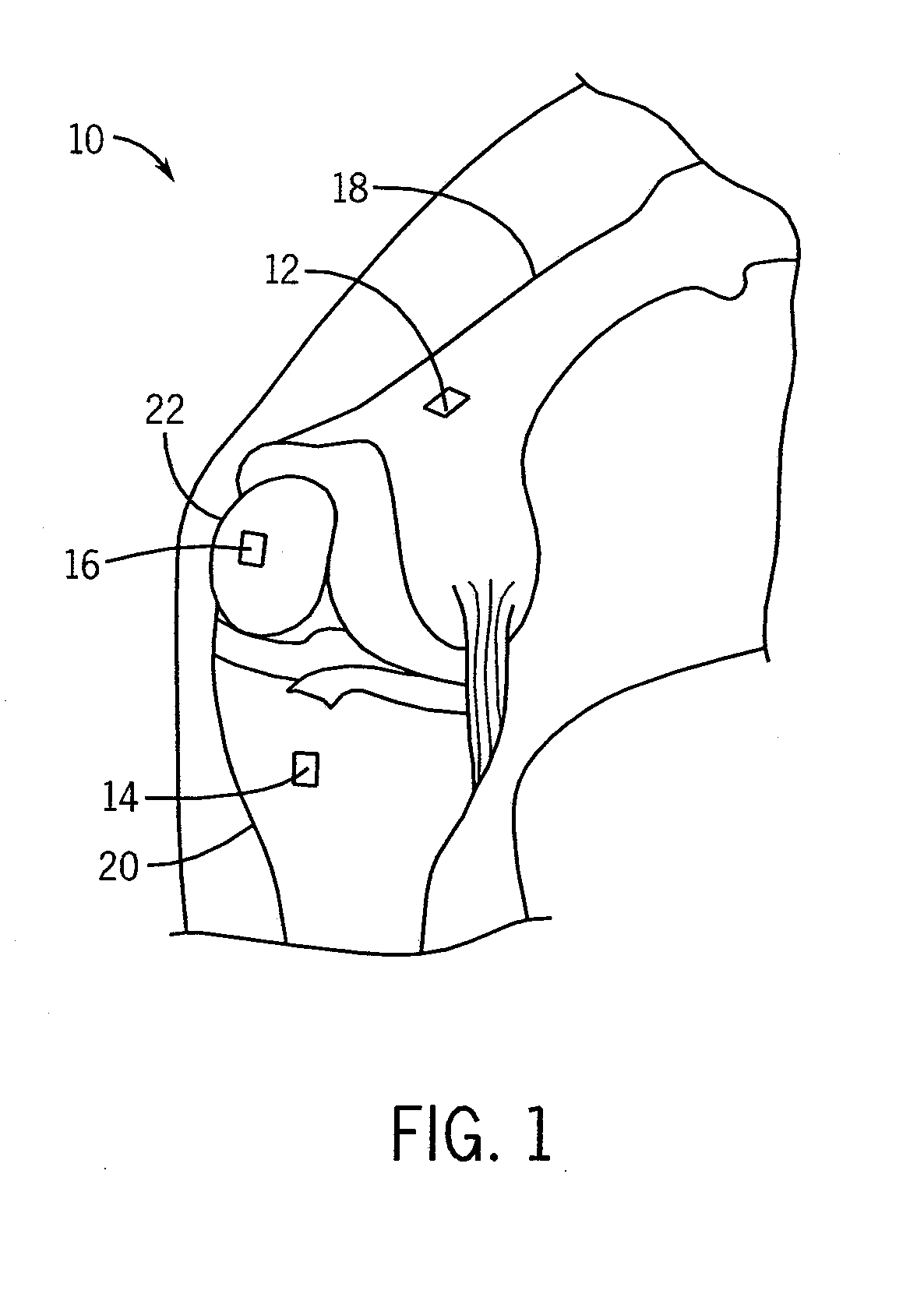
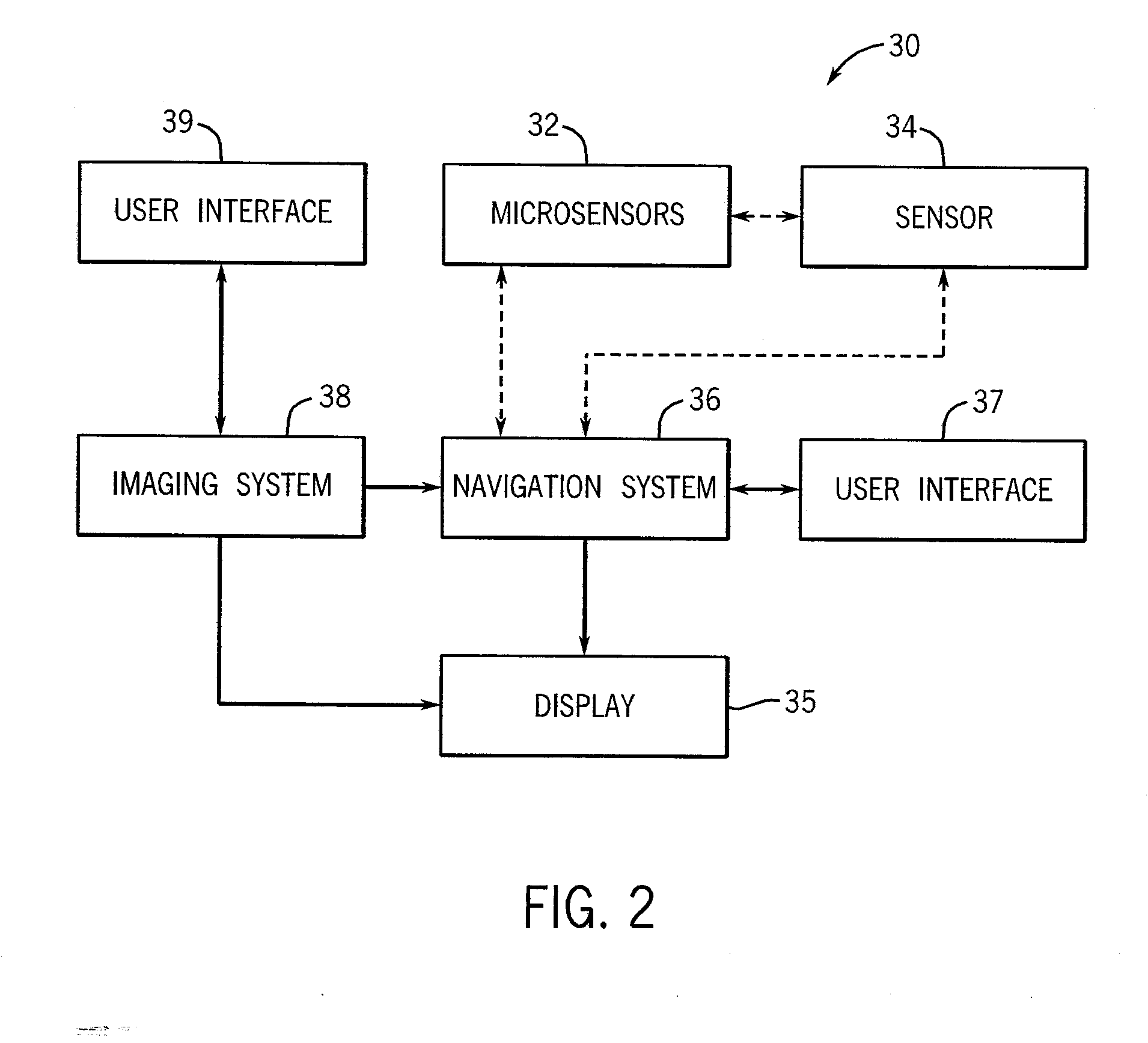
System and method for measurement of clinical parameters of the knee for use during knee replacement surgery
A system and method for measuring biomechanical parameters of a knee prior to total knee replacement (TKR) surgery includes a plurality of microsensors removably attached to the femur, tibia and patella; at least one sensor communicating with the plurality of microsensors; a navigation system coupled to the at least one sensor; an imaging system coupled to the navigation system for performing imaging of the joint; and at least one display for displaying imaging and tracking data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
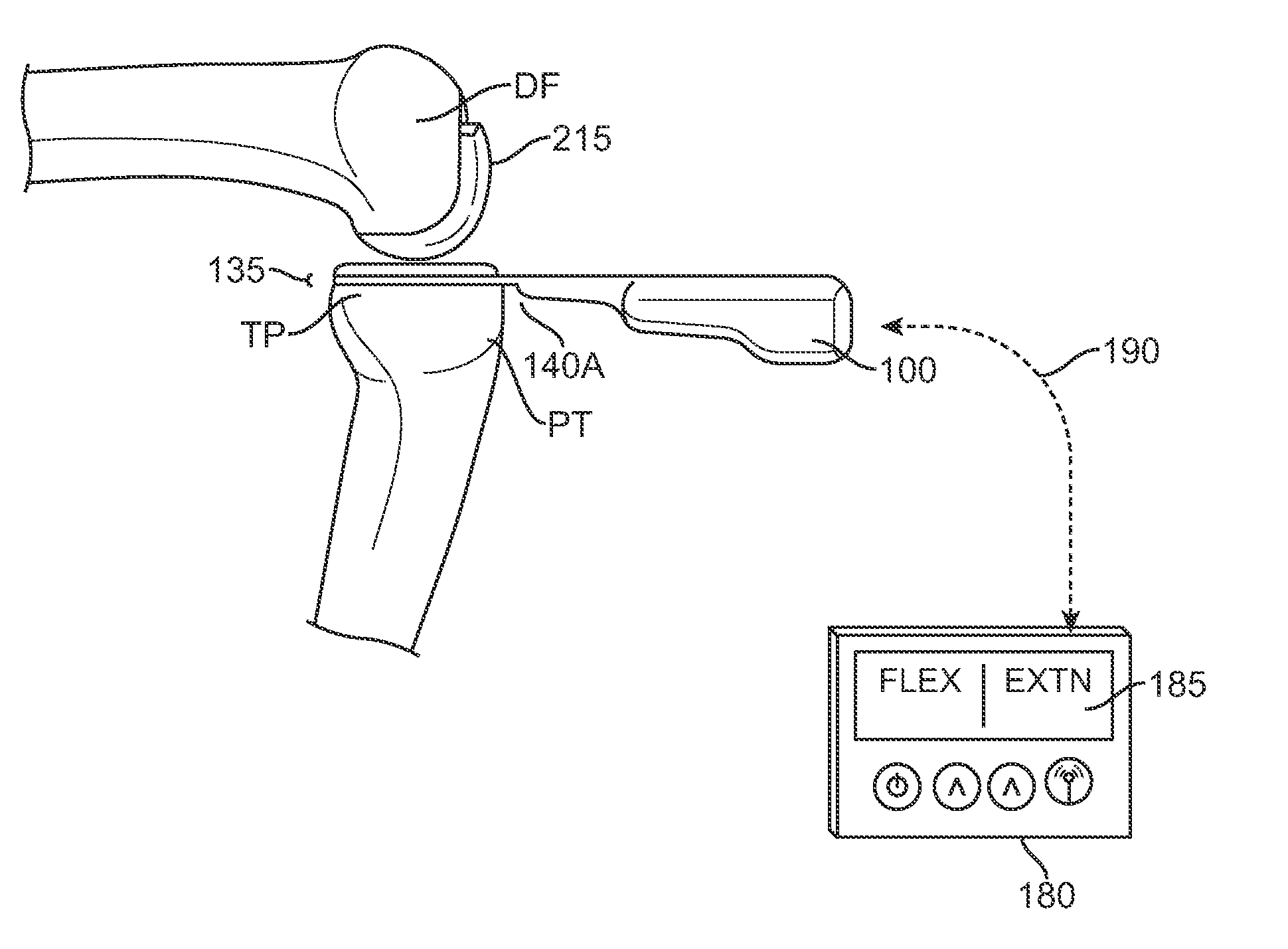
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
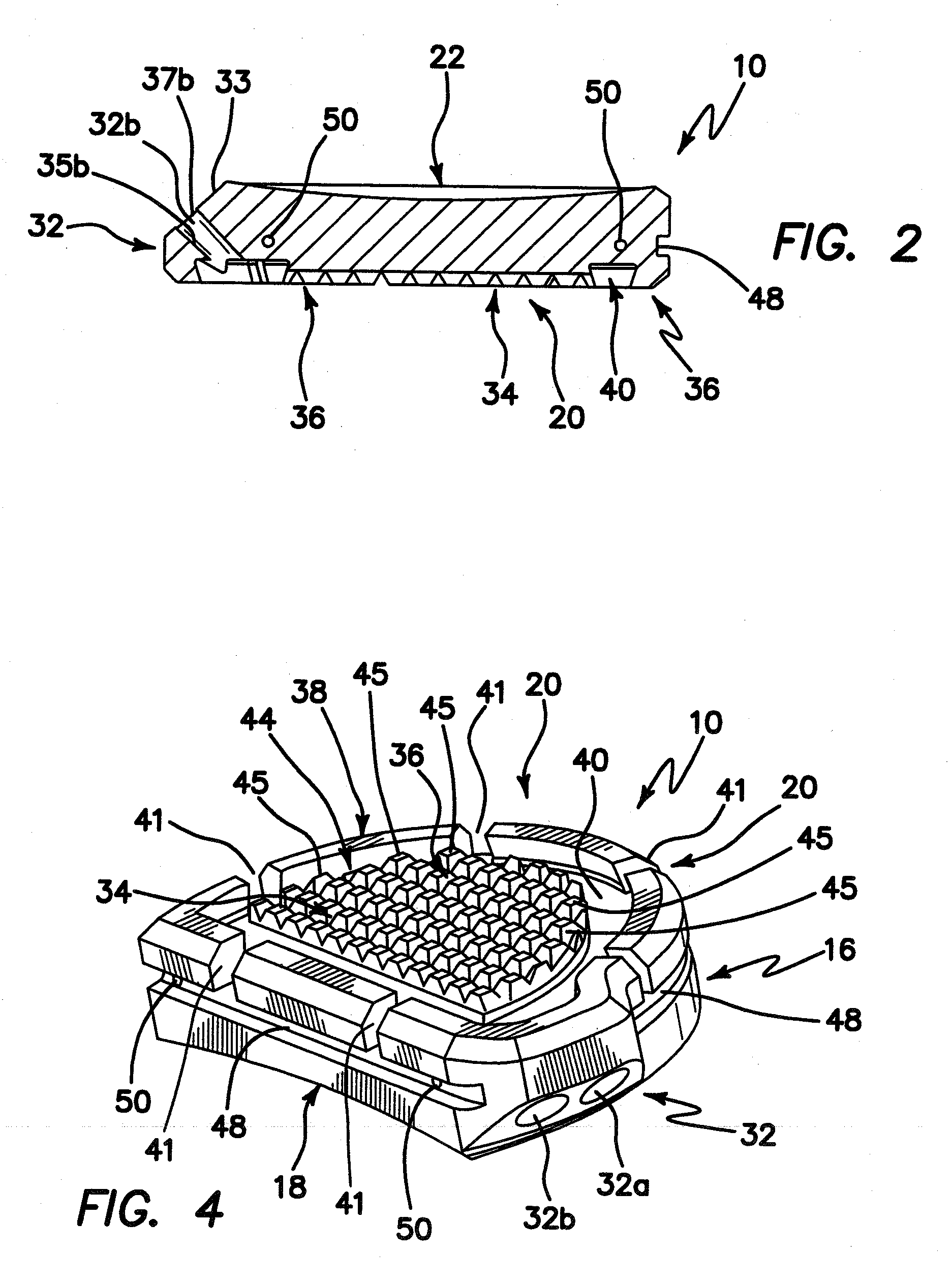
Patellar trial and drill guide for use in knee replacement surgery
InactiveUS6855150B1Shorten operation timeDecreasing potential complicationJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A patellar trial and drill guide for use during knee replacement surgery comprising an articular surface member and a fixation peg drill guide. The articular surface member is the exact geometry as the artificial patellar implant, and the drill guide aligns the holes for the fixation pegs of the artificial patellar implant. The patellar trial is placed on the resected patella in the desired position, a patellar clamp is used to temporary fix the patellar trial to the patella. The patella is then returned to its normal position and a trial reduction of the total knee replacement is completed. If the placement and / or size of the patellar trial is unacceptable, the patella is inverted, the patellar trial removed, and a different sized trial or new location is determined. The new patellar trial is secured to the resected patella, and another trial reduction of the total knee replacement is completed. This procedure can be repeated until the patellar trial is the correct size and in the proper location. If the placement of the patella is acceptable, the patella is inverted, the articular surface member removed, fixation peg holes are drilled using the fixation peg holes of the drill guide, and an artificial patellar implant is implanted on the patient's remaining patella.
Owner:LINEHAN TIMOTHY R
Determining femoral cuts in knee surgery
ActiveUS8257360B2Extended service lifeEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee surgery
There is provided a method and system for determining a distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness for a femur in a knee replacement operation, the method comprising: performing a tibial cut on a tibia; performing soft tissue balancing based on a desired limb alignment; measuring an extension gap between the femur and said tibial cut while in extension; measuring a flexion gap between the femur and the tibial cut while in flexion; calculating a distal cut thickness and a posterior cut thickness for the femur using the extension gap and the flexion gap and taking into account a distal thickness and posterior thickness of a femoral implant; and performing said femoral cut according to the distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
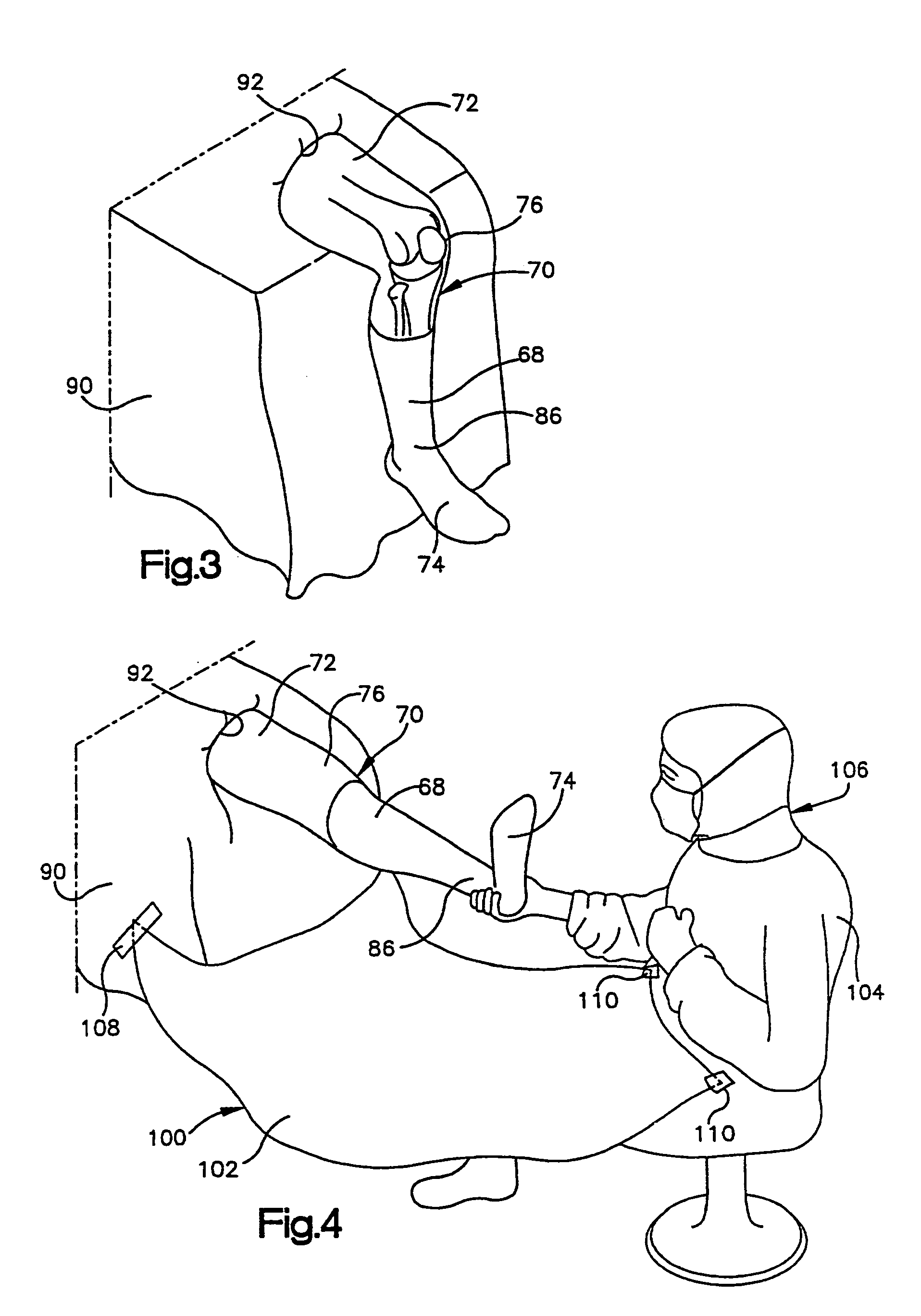
Apparatus, operating means and process
InactiveUS20050038442A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesJoint implantsSurgical operationEngineering
The invention relates to surgical instruments, a computer program element which provides control or information relating to the surgical instruments, a computer program providing the same, a computer readable medium comprising the computer program, a method for implementing a computer-aided means of guiding a surgeon through a desired surgical procedure and to a computer aided surgical procedure. In a preferred embodiment, the invention relates to instruments, a computer program element, computer programs, a computer readable medium and methods for use in knee replacement operations.
Owner:FINSBURY DEV
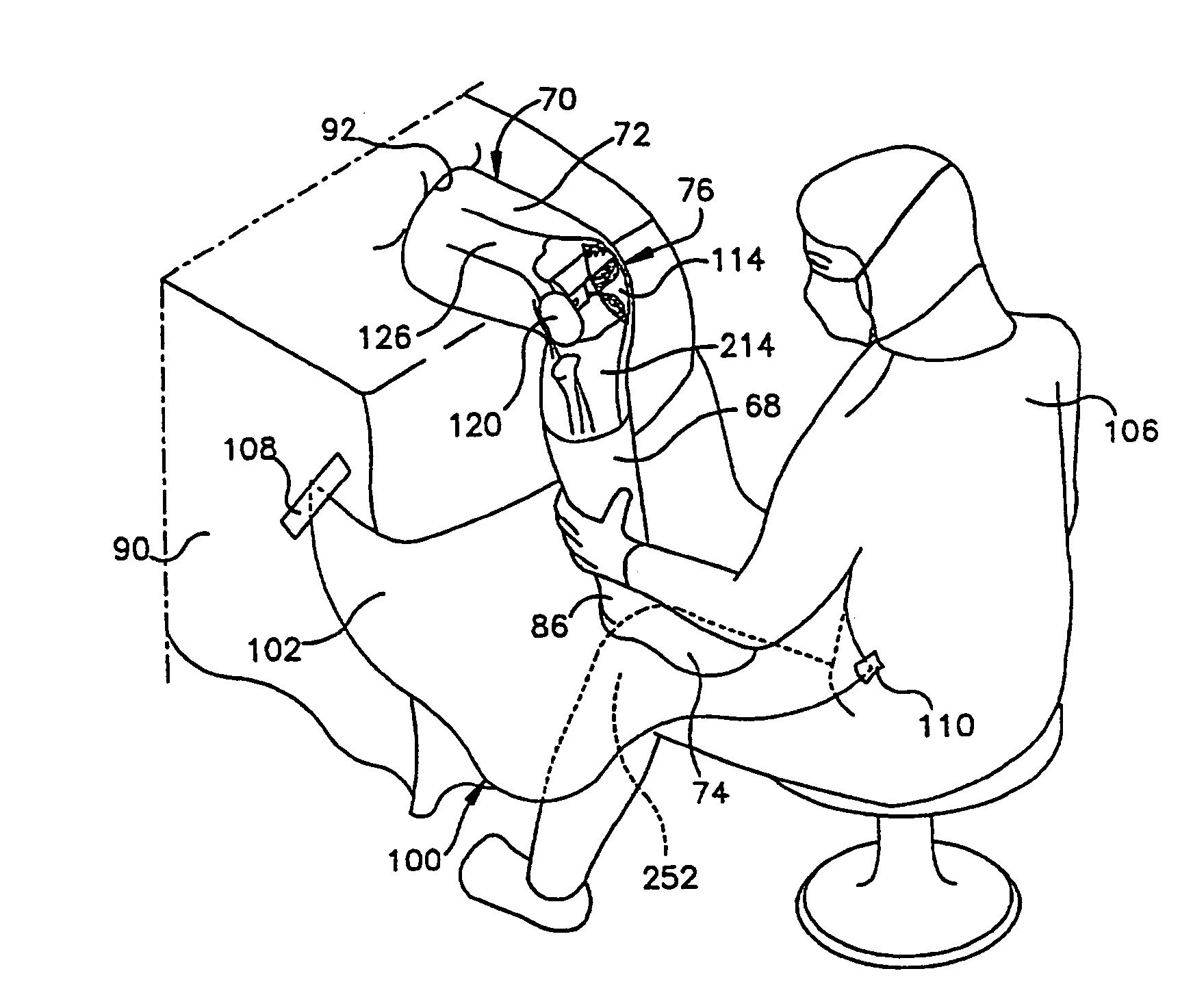
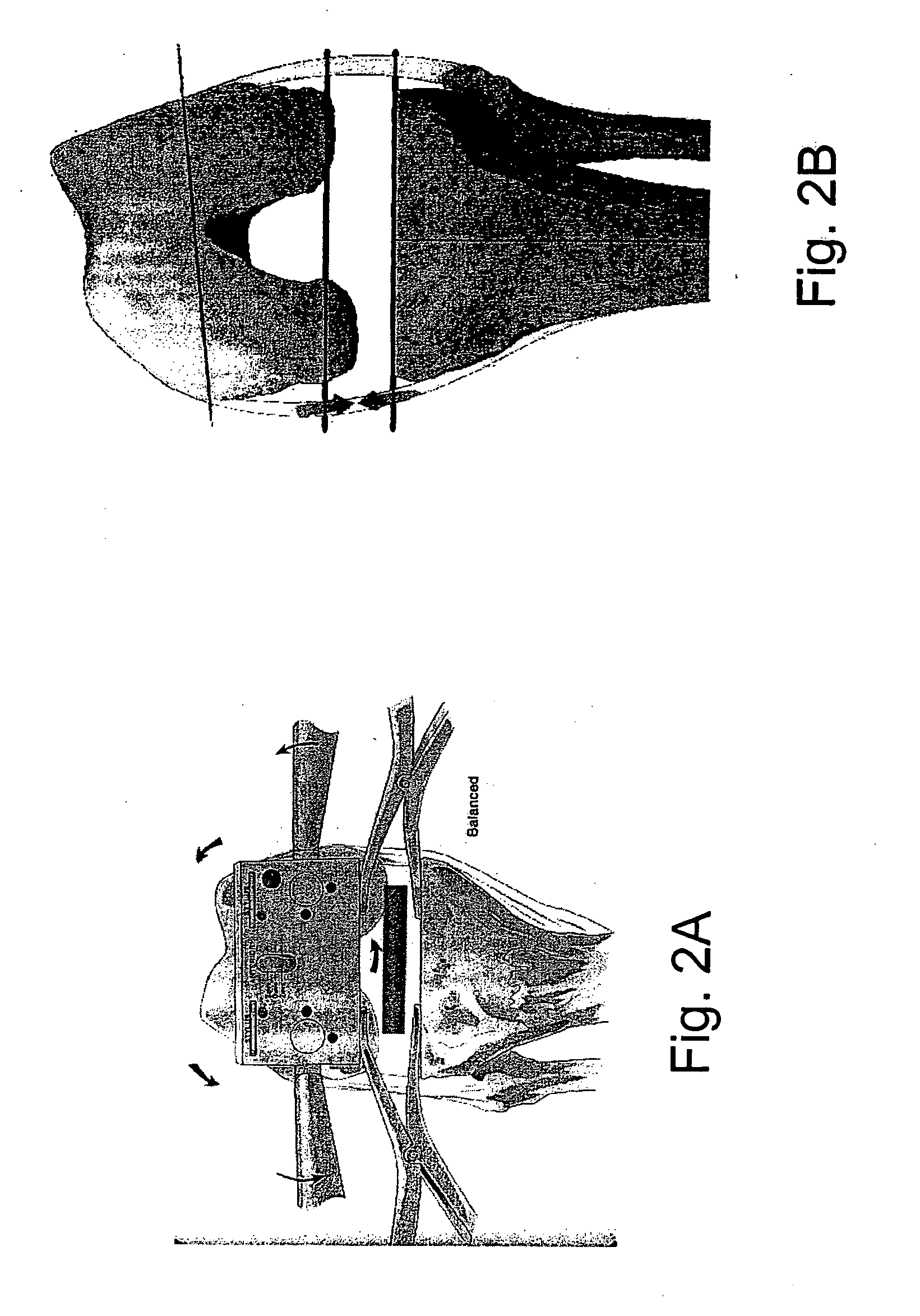
Methods and systems for intraoperative measurement of soft tissue constraints in computer aided total joint replacement surgery
InactiveUS20050119661A1Maintaining soft tissue balance of the replacement kneeDraw tensionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaMathematical model
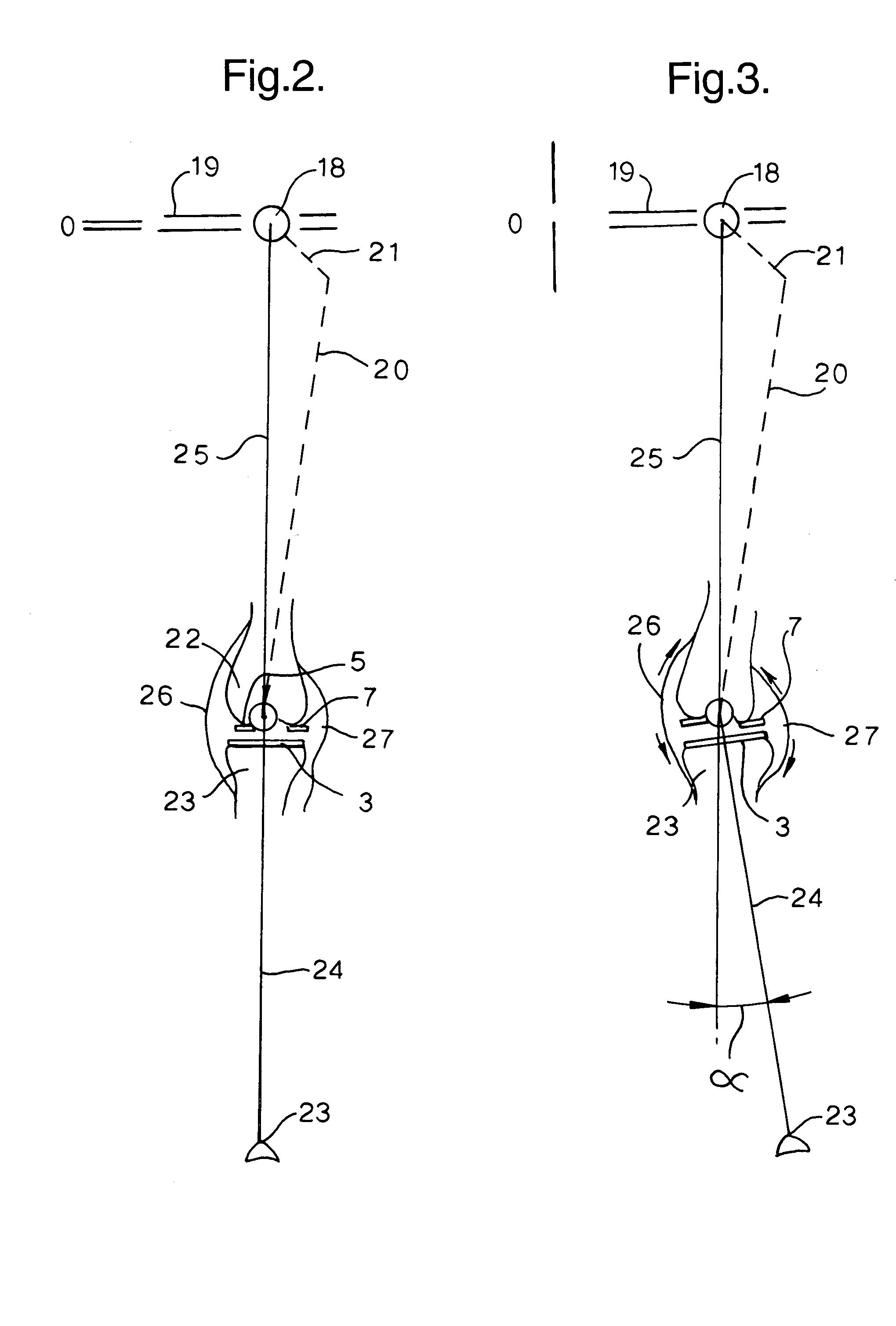
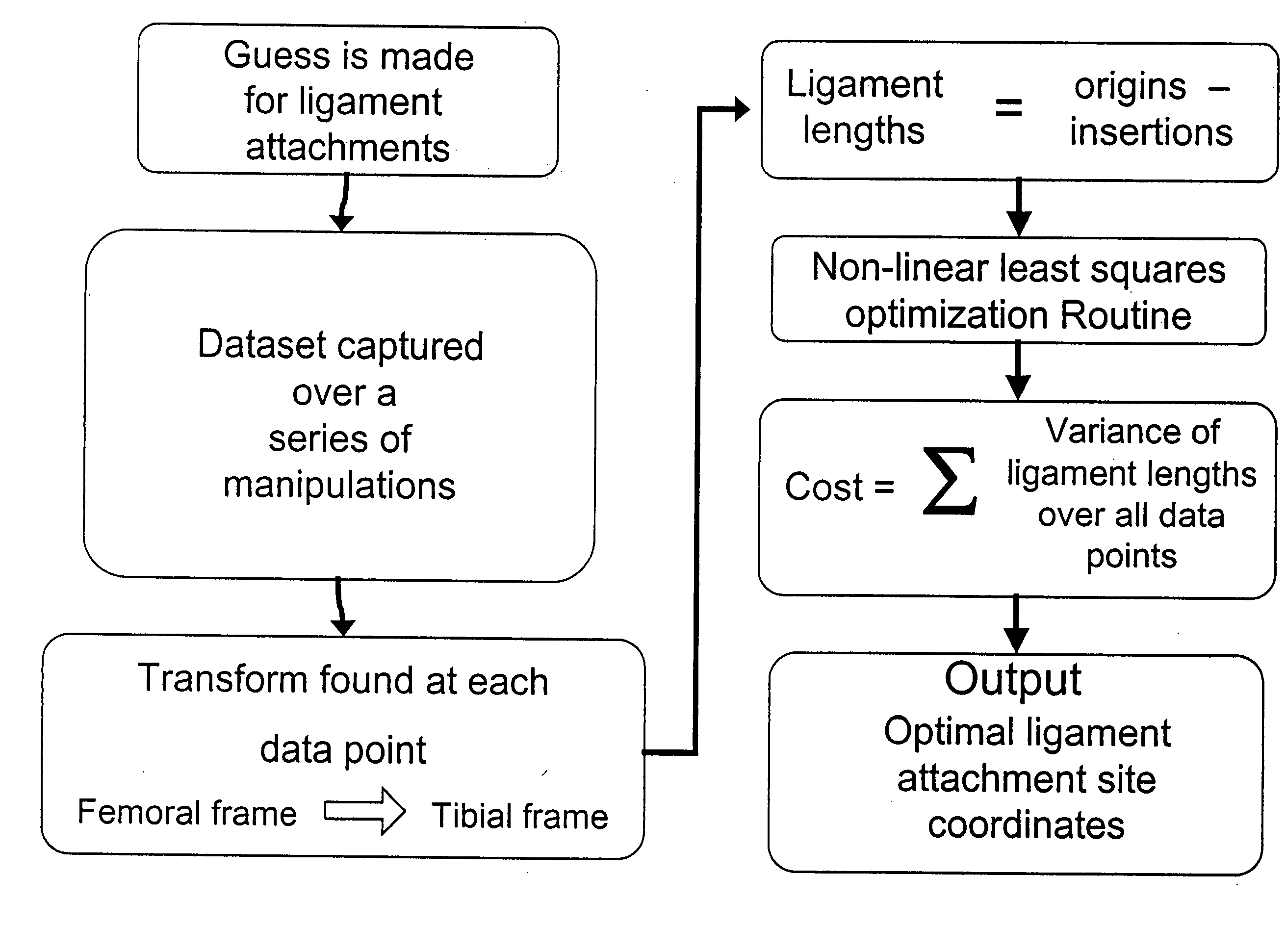
Methods and systems are described to quantitatively determine the degree of soft tissue constraints on knee ligaments and for properly determining placement parameters for prosthetic components in knee replacement surgery that will minimize strain on the ligaments. In one aspect, a passive kinetic manipulation technique is used in conjunction with a computer aided surgery (CAS) system to accurately and precisely determine the length and attachment sites of ligaments. These manipulations are performed after an initial tibial cut and prior to any other cuts or to placement of any prosthetic component. In a second aspect, a mathematical model of knee kinematics is used with the CAS system to determine optimal placement parameters for the femoral and tibial components of the prosthetic device that minimizes strain on the ligaments.
Owner:HODGSON ANTONY J +1
Joint replacement methods and apparatus
Apparatus and surgical techniques provide alternative cutting fixtures and other features to improve bone resection accuracy and joint stability. According to one embodiment, stabilizers are removably attached to a cutting guide to temporarily lengthen the surface against which a saw or other cutting device rests. Another embodiment provides differently shaped saw blades, having curved distal ends and right-angle bends applicable to box cuts of the type associated with cruciate sacrifice knee-replacement surgery. Methods are also disclosed whereby the box cuts, distal and posterior augment cuts may be approached from a distal perspective, both laterally and medially. A different embodiment provides a trial / cutting guide having flat surfaces as opposed to curved surfaces adapted for articulation within a joint. Yet a further alternative embodiment teaches a device for determining the joint line relative to a tibia using the fibula as reference.
Owner:MEDIDEA
Joint replacement methods and apparatus
Apparatus and surgical techniques provide alternative cutting fixtures and other features to improve bone resection accuracy and joint stability. According to one embodiment, stabilizers are removably attached to a cutting guide to temporarily lengthen the surface against which a saw or other cutting device rests. Another embodiment provides differently shaped saw blades, having curved distal ends and right-angle bends applicable to box cuts of the type associated with cruciate sacrifice knee-replacement surgery. Methods are also disclosed whereby the box cuts, distal and posterior augment cuts may be approached from a distal perspective, both laterally and medially. A different embodiment provides a trial / cutting guide having flat surfaces as opposed to curved surfaces adapted for articulation within a joint. Yet a further alternative embodiment teaches a device for determining the joint line relative to a tibia using the fibula as reference.
Owner:MASINI MICHAEL A
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS20100217156A1Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
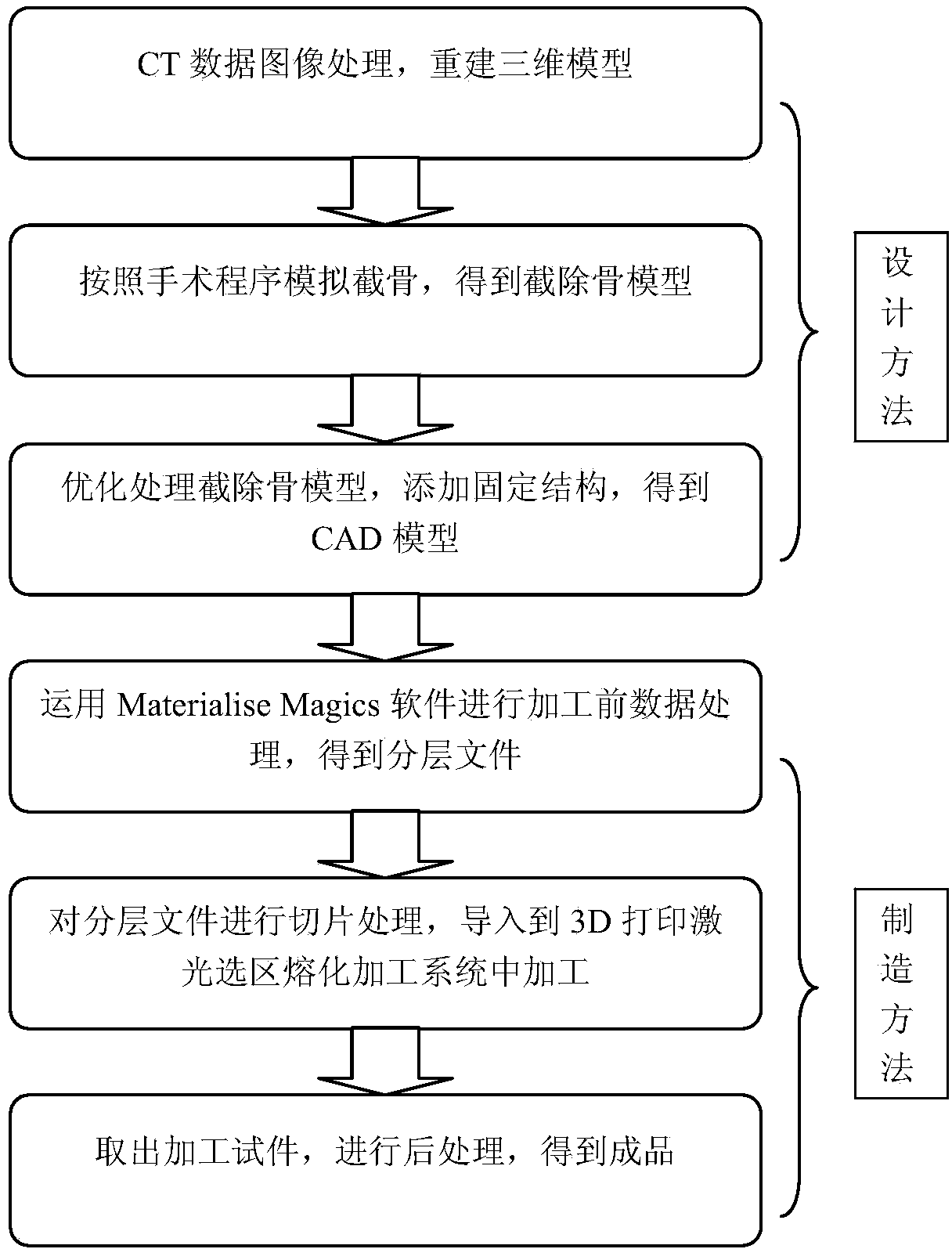
Individualized reversal design and manufacturing method for full knee joint replacing prosthesis
ActiveCN103860293AImprove matchShort processing cycleJoint implantsImage data processingTibiaMedical imaging data
The invention relates to an individualized reversal design and manufacturing method for a full knee joint replacing prosthesis. The method comprises the following steps that 1, three-dimensional digital models of the thighbone and the tibia are built on the basis of the medical image data of the knee joint of a patient; 2, virtual bone cutting software is used for respectively carrying out simulated bone cutting on the three-dimensional digital models of the thighbone and the tibia; 3, the reversal design of CAD (computer-aided design) models of a thighbone replacing prosthesis, a tibia replacing prosthesis and a tibia gasket prosthesis is carried out; 4, the full knee joint replacing prosthesis is manufactured according to the CAD models of each prosthesis through the 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that on the basis of the original bone structure of the patient, the virtual knee joint replacing operation bone cutting form is combined, the structural form of the replacing prosthesis is subjected to reversal design, the structural form consistency of the cut bone and the replacing implanted body structure is realized to the greatest degree, and the optimum matching between the prosthesis and the individual bone form is reached. In addition, the laser selective melting 3D printing technology is used for manufacturing the designed replacing prosthesis, the optimum matching between the prosthesis and the knee joint bone cutting surface is ensured on the basis of the minimum bone cutting quantity, and the effect optimization is reached.
Owner:BEIJING NATON TECH GRP CO LTD +1
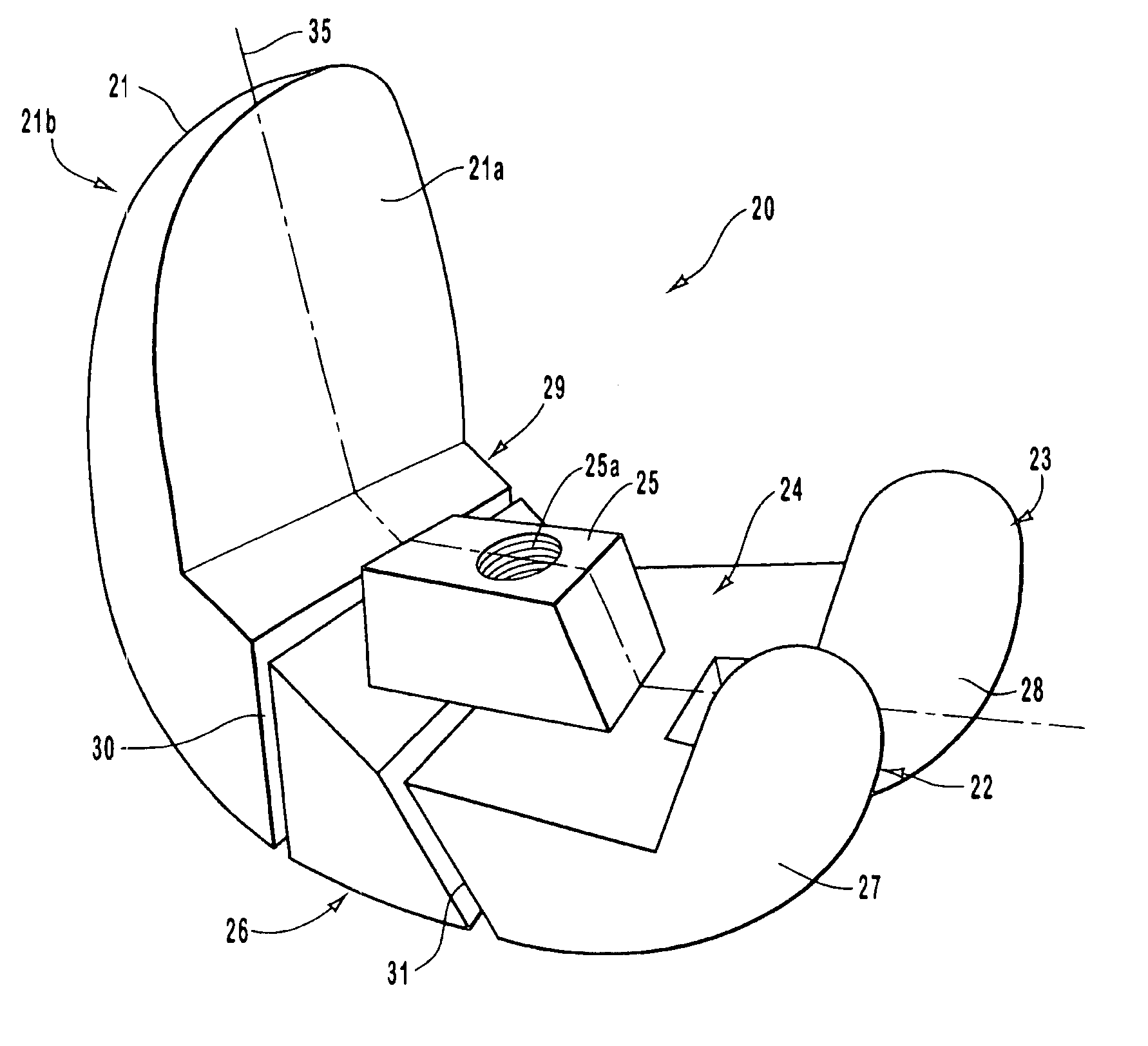
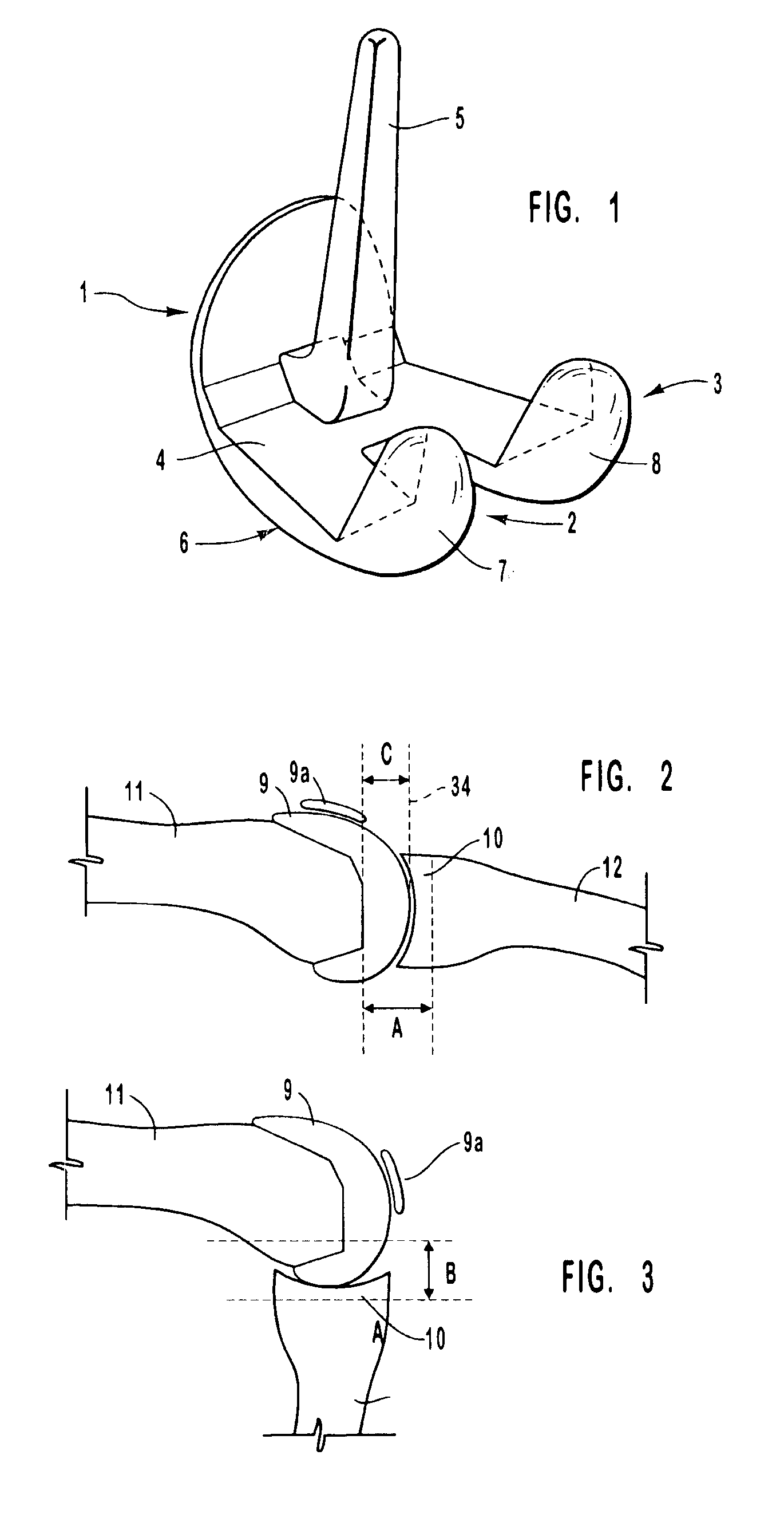
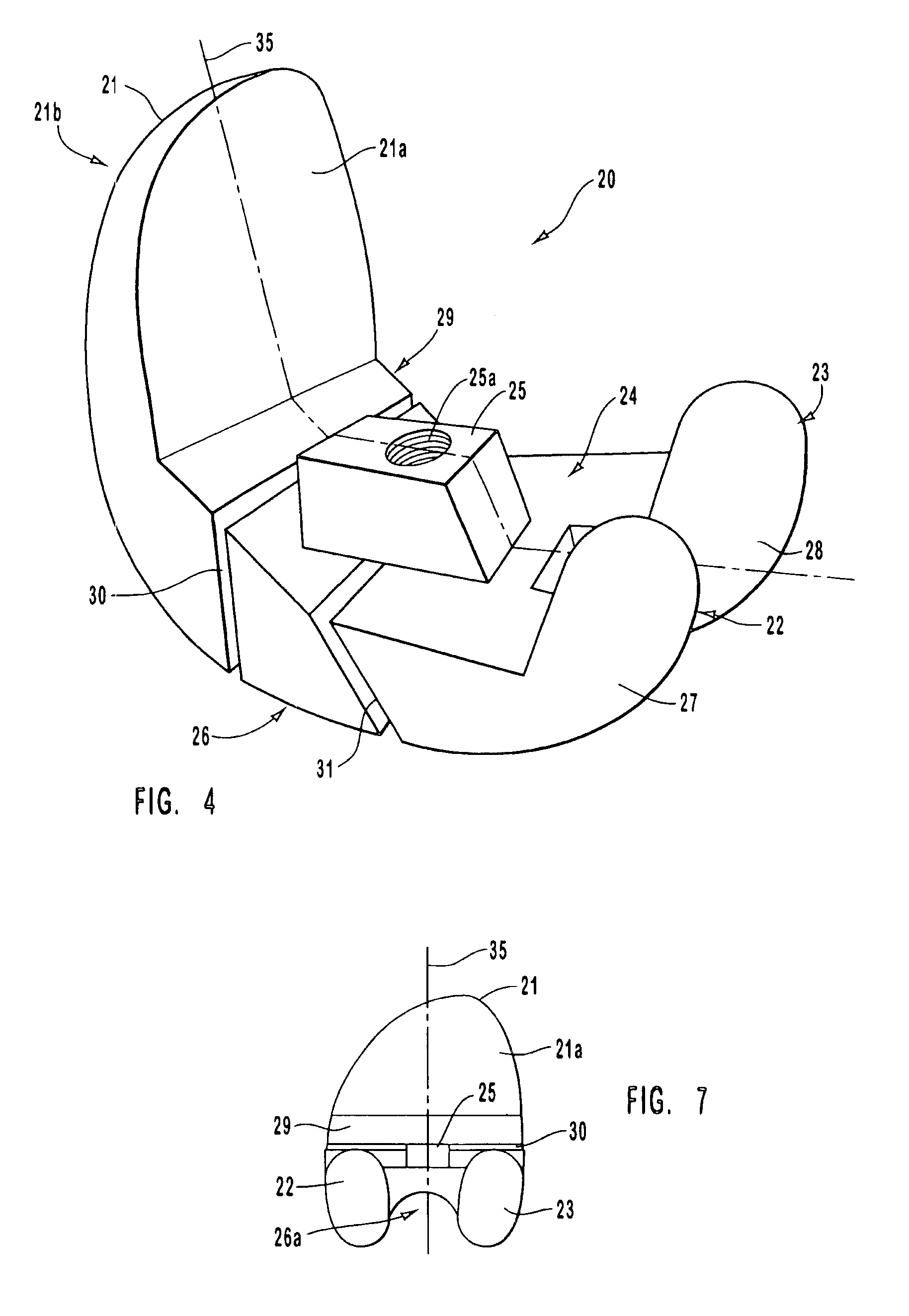
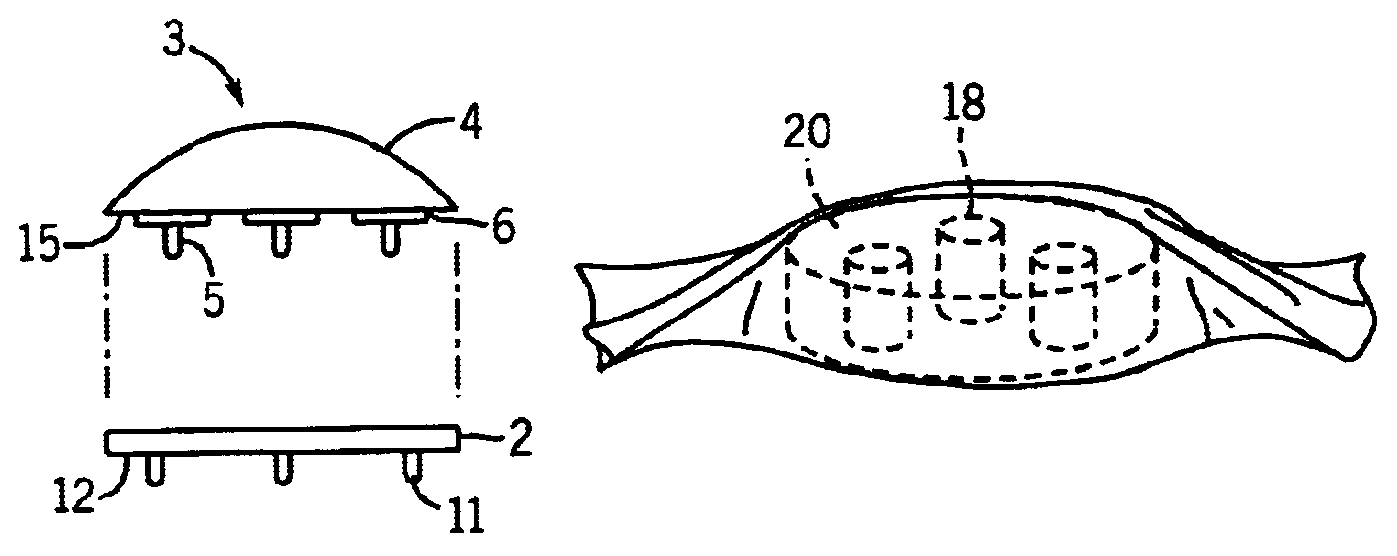
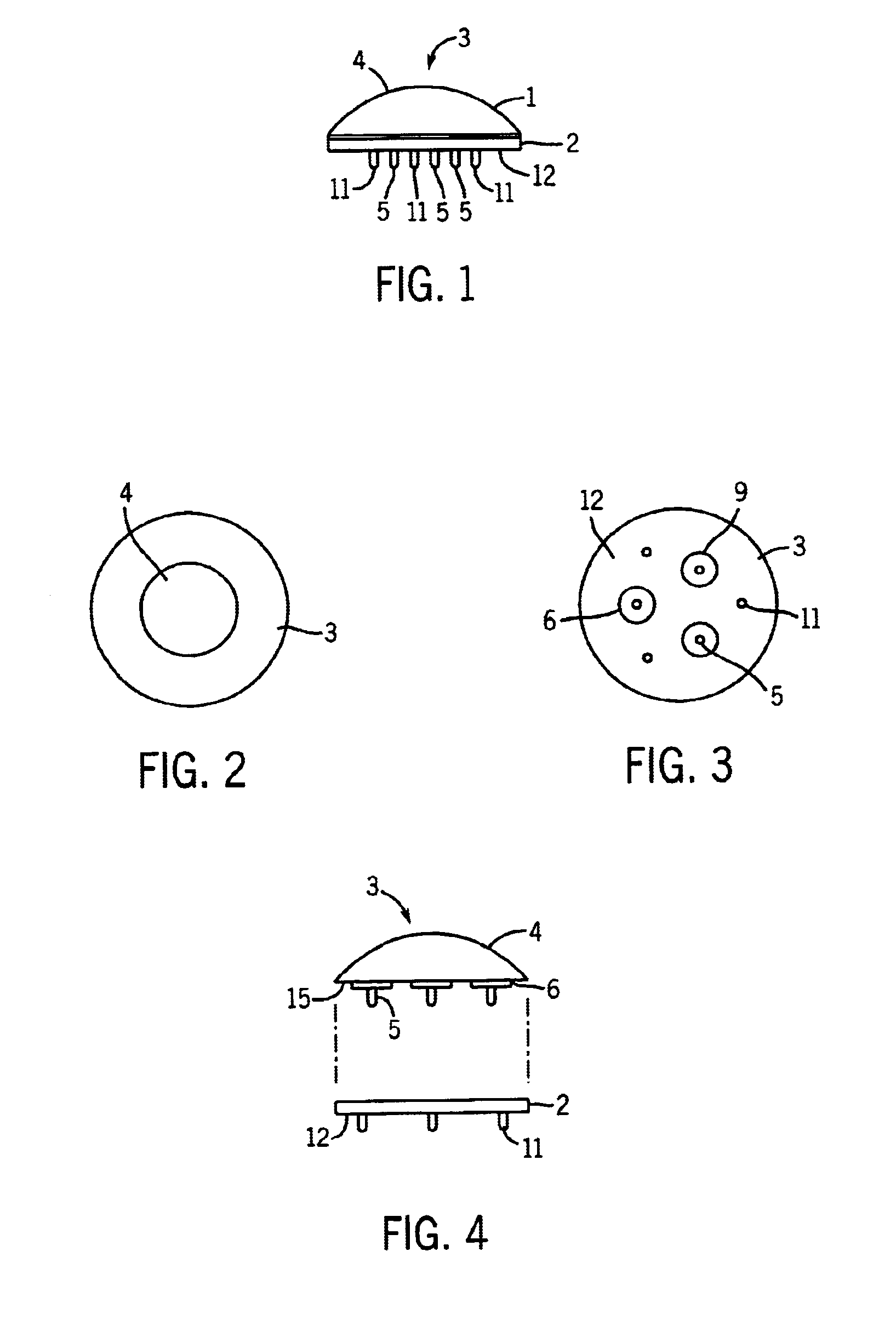
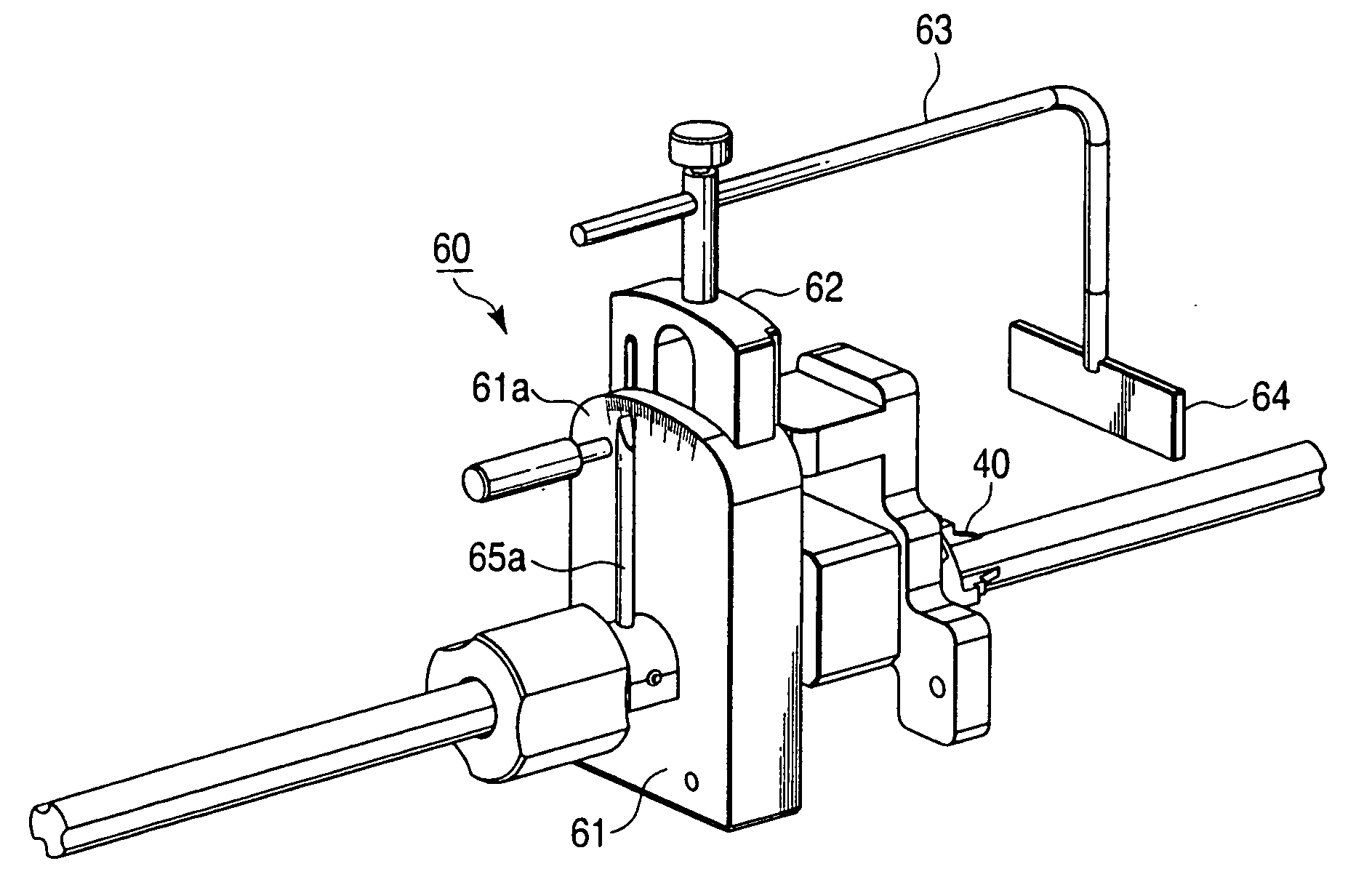
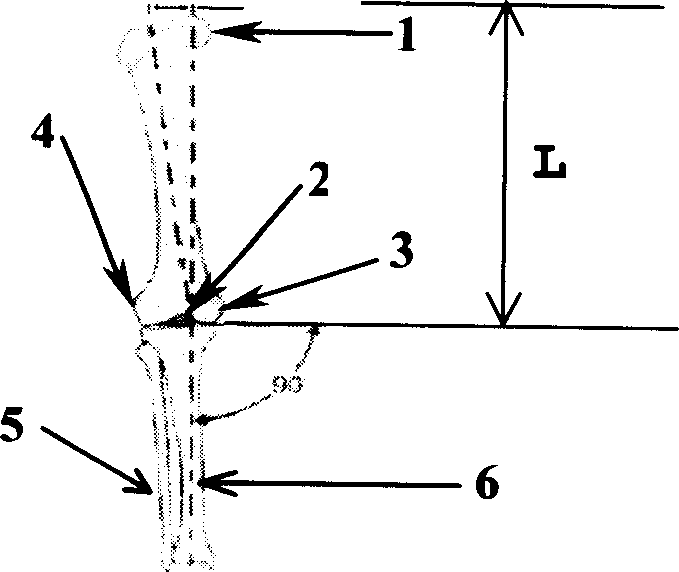
Bone Resection Jig Used in Artificial Knee Joint Replacement Surgery
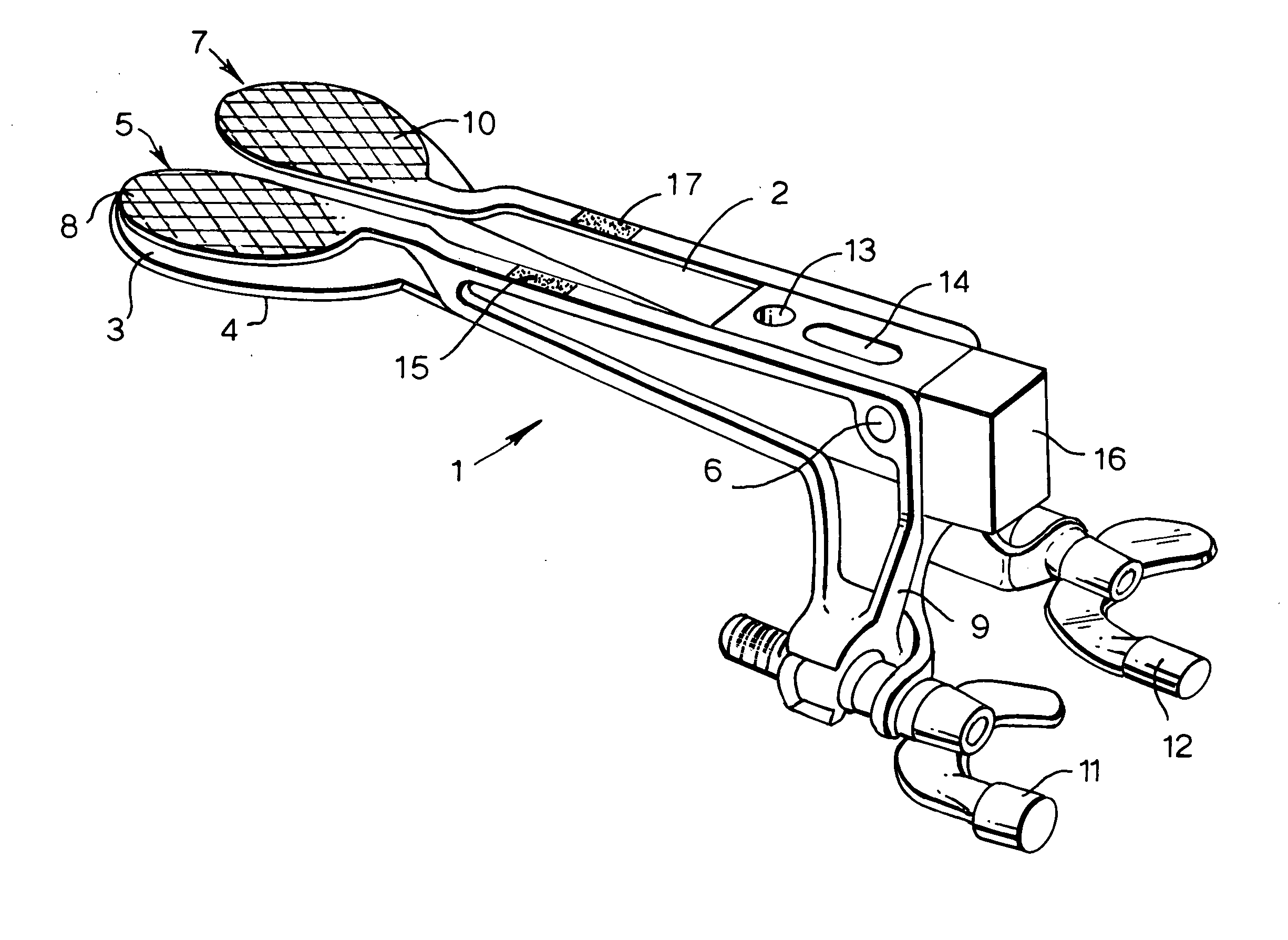
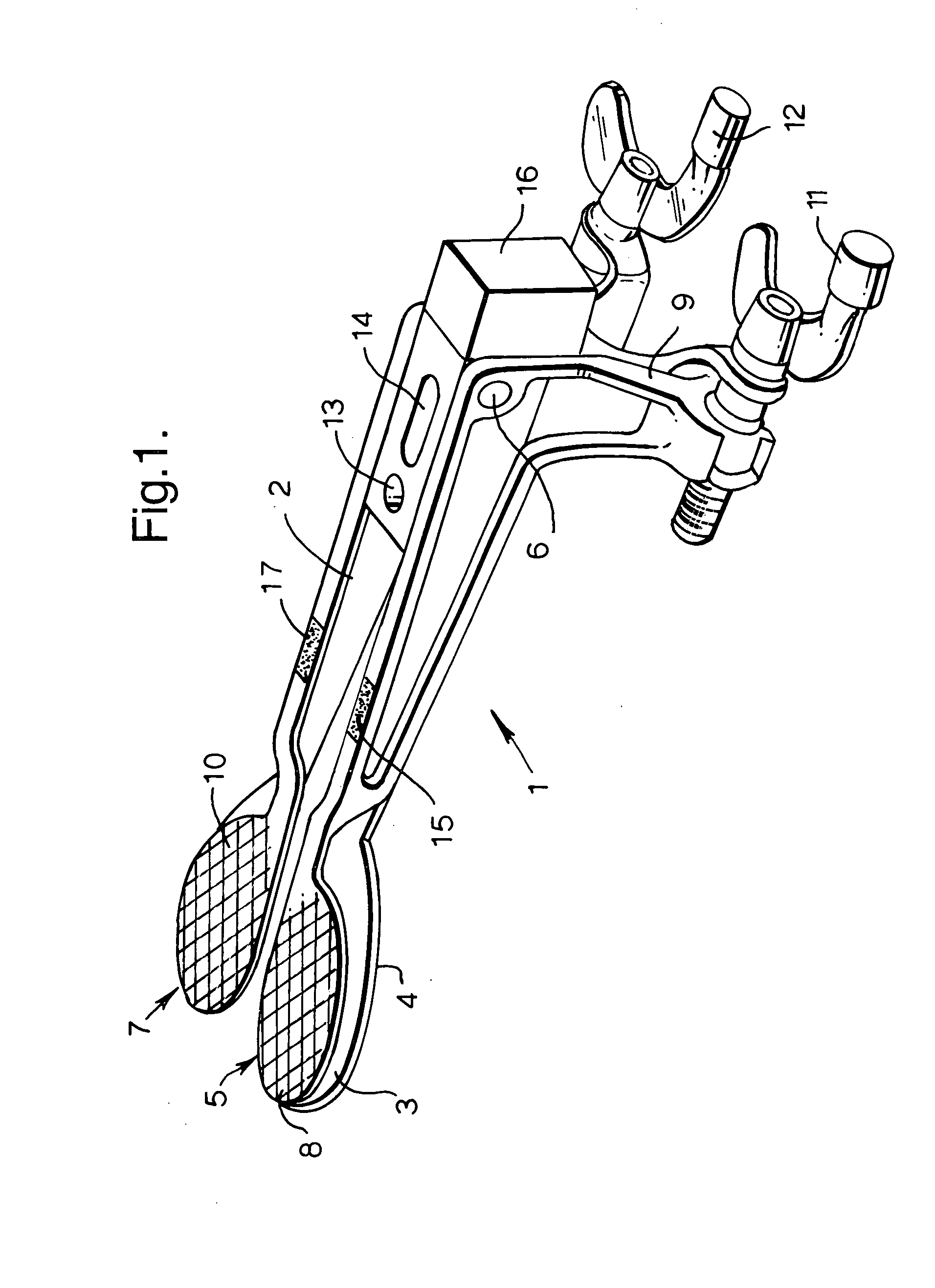
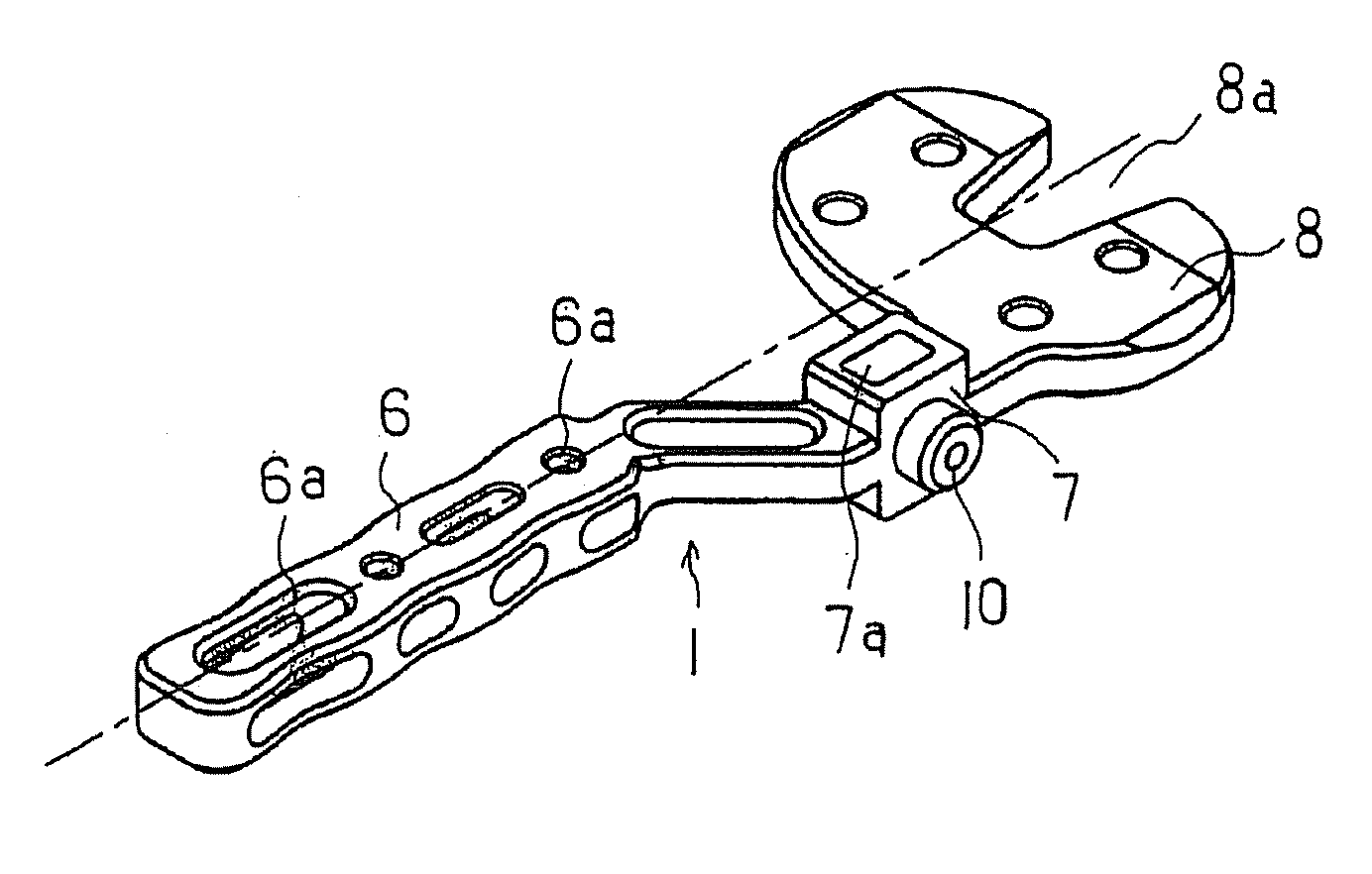
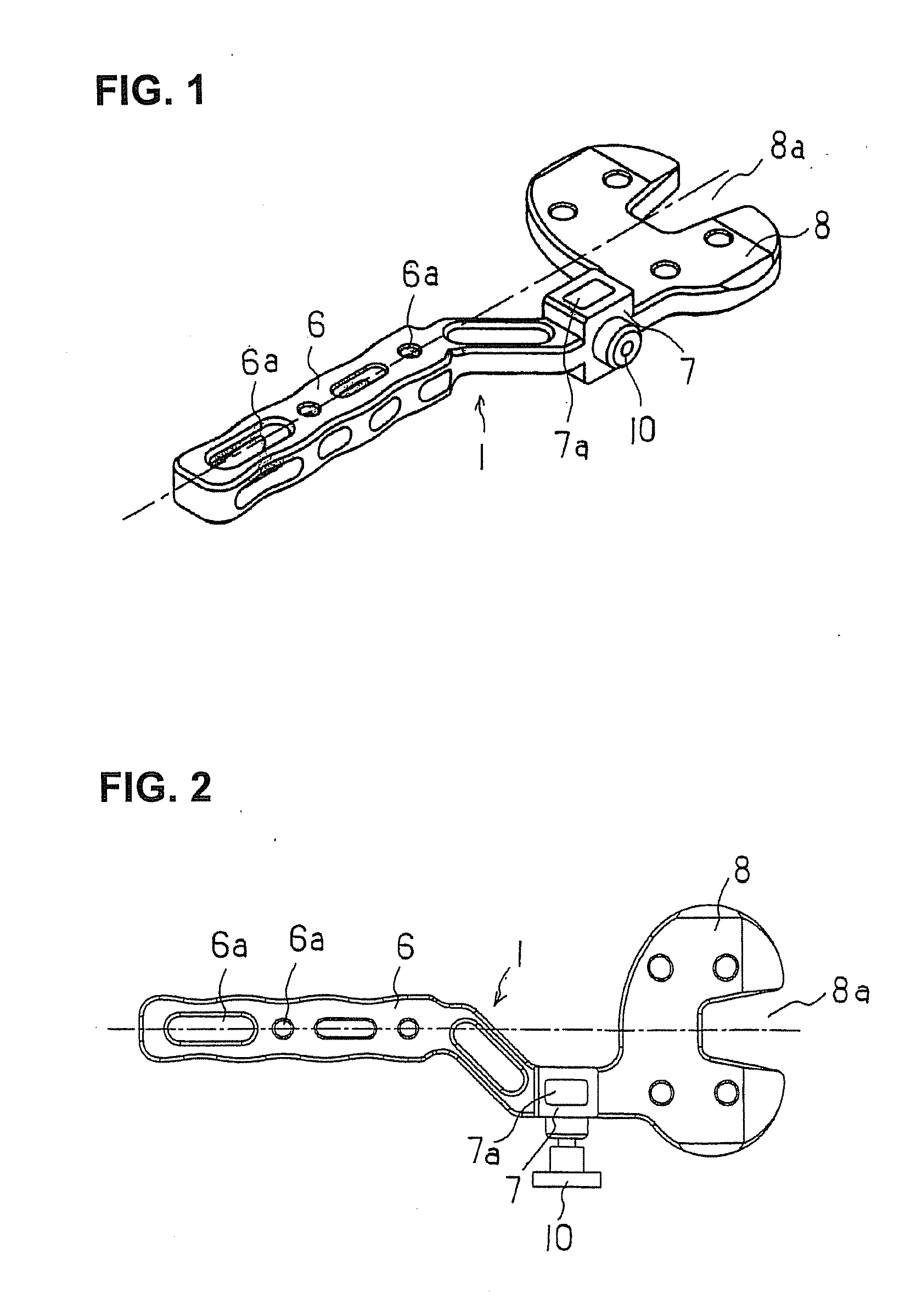
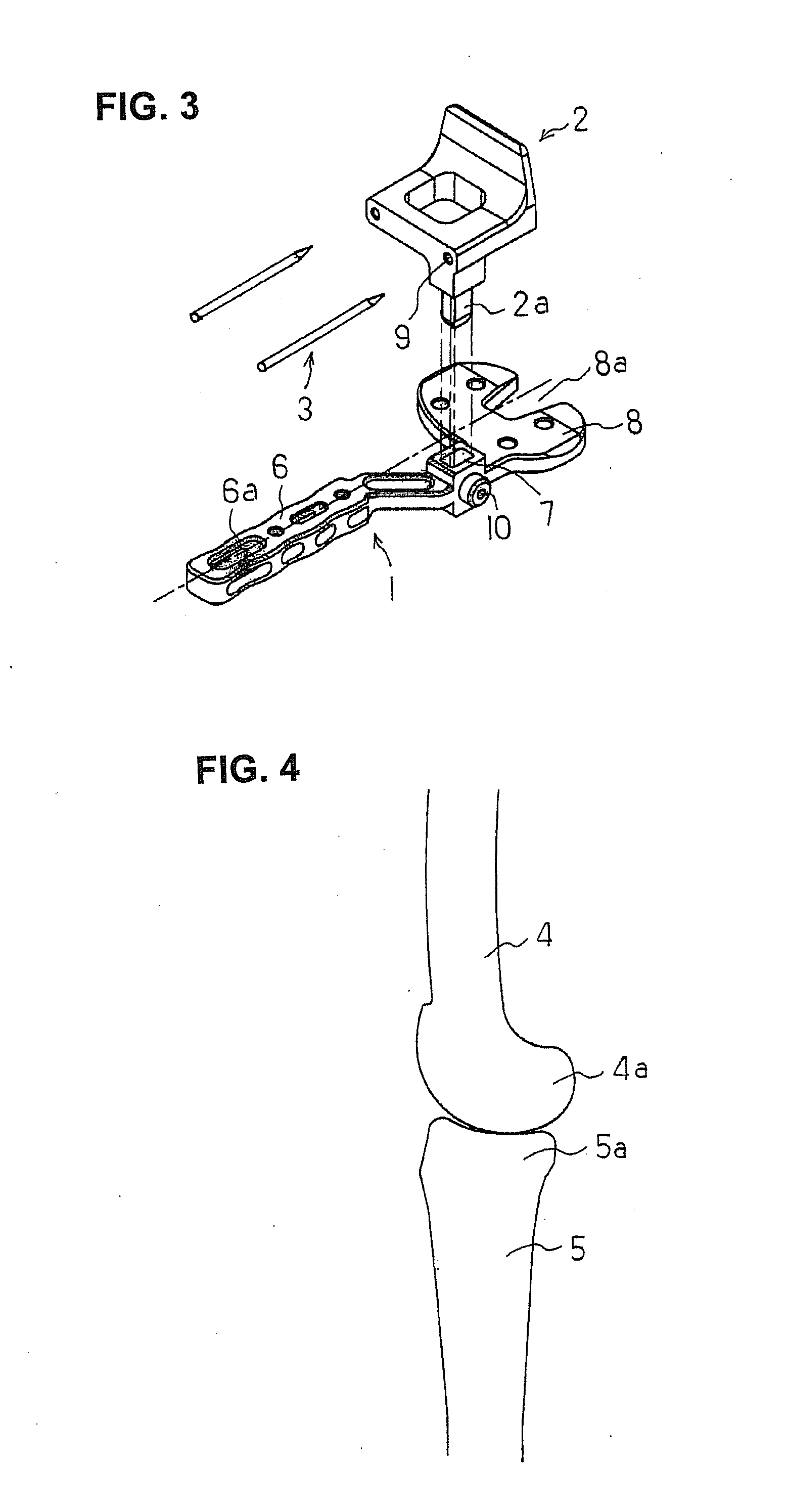
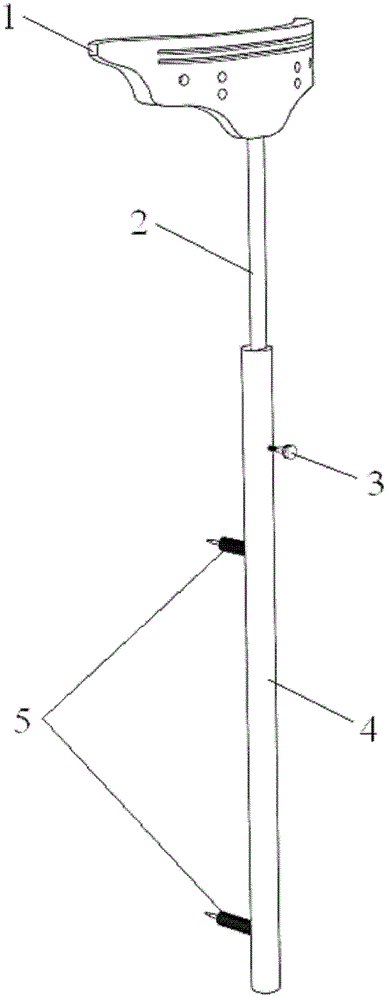
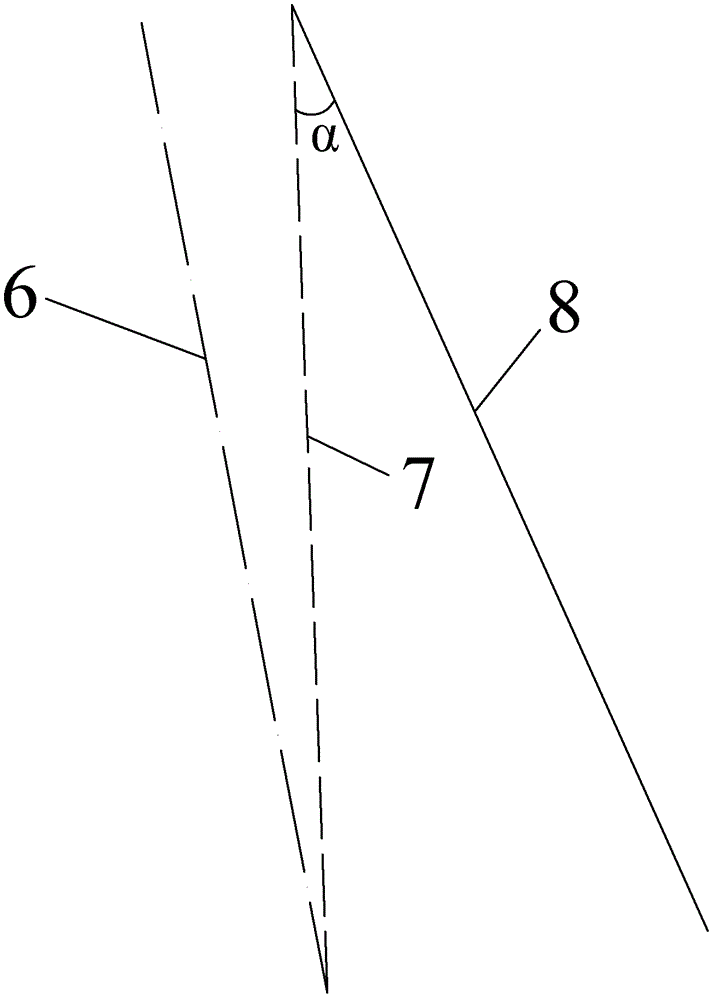
A bone resection jig that can make ligament tension equal at extension and flexion positions without any actual measurements when resecting femur and tibia during artificial knee joint replacement surgery. The bone resection jig used in artificial knee joint replacement surgery includes a spacer block (1) comprised of a grip (6), a hollow box (7) that is provided on an other end side of the grip and has a vertical hole (7a) therein, and a reference spacer part (8) that extends out from the hollow box (7) and is adapted be inserted into the resection region between femur and tibia; a reference pin guide (2) which, when the femur and tibia are in the flexion position, is inserted into the vertical hole (7a) of the hollow box, extends on the reference spacer part (8) to the other end side of the grip so as to come into contact with a resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur, and is formed with guide holes (9) for guiding reference pins (3) to be installed from a front side into the resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur; and an aiming member (12) which is, after the spacer block (1) has been removed from a space between the femur and tibia leaving the reference pins (3), brought onto the reference pins (3) by being guided thereby, the aiming member being provided with an indicator (14) that indicates a resection plane (FR) at a back of the distal end of the femur when the aiming member (12) comes into contact with the resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur.
Owner:NAKASHIMA MEDICAL +1
Methods and instruments for forming non-circular cartilage grafts
Techniques and instruments for knee replacement surgery that allow for the removal of an oval oblong-shaped allograft bone and cartilage plug from a donor distal femur. The instruments include (i) sizing guides to match the recipient's femoral size and curvature to that of a donor femur (the sizing guides also acting as a wide pin placement template for the donor distal femur); (ii) osteotomes that cut the curved and straight portions of the implant shape (these may be disposable or reusable); and (iii) templates that fit over the guide pins and have openings to allow the osteotomes to cut the donor femur plug to the correct size, shape and depth. The instruments allow for a non-circular shape to be extracted from a donor femur for use in a bone-saving osteoarthritis distal femur resurfacing procedure.
Owner:ARTHREX
Methods and instruments for forming non-circular cartilage grafts
Techniques and instruments for knee replacement surgery that allow for the removal of an oval oblong-shaped allograft bone and cartilage plug from a donor distal femur. The instruments include (i) sizing guides to match the recipient's femoral size and curvature to that of a donor femur (the sizing guides also acting as a wide pin placement template for the donor distal femur); (ii) osteotomes that cut the curved and straight portions of the implant shape (these may be disposable or reusable); and (iii) templates that fit over the guide pins and have openings to allow the osteotomes to cut the donor femur plug to the correct size, shape and depth. The instruments allow for a non-circular shape to be extracted from a donor femur for use in a bone-saving osteoarthritis distal femur resurfacing procedure.
Owner:ARTHREX
Tibial Prosthesis
InactiveUS20090228112A1Reduces surgical traumaEasy maintenanceJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaKnee Joint
The present invention relates to a tibial prosthesis useful in knee replacement surgeries. The prosthesis includes one or more cement introduction ports which may be used to deliver and control delivery of bone cement to a prosthesis-bone interface after the prosthesis has been positioned on a resurfaced area of a tibia bone. The prosthesis is suitable for implantation using arthroscopic as well as open surgical procedures. The prosthesis may be used as a unicondylar implant in either compartment of the knee or in both compartments of the knee.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Apparatus for preoperative planning of artificial knee joint replacement operation and jig for supporting operation
InactiveUS20110009868A1Precise positioningAccurate angleImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTibiaTomographic image
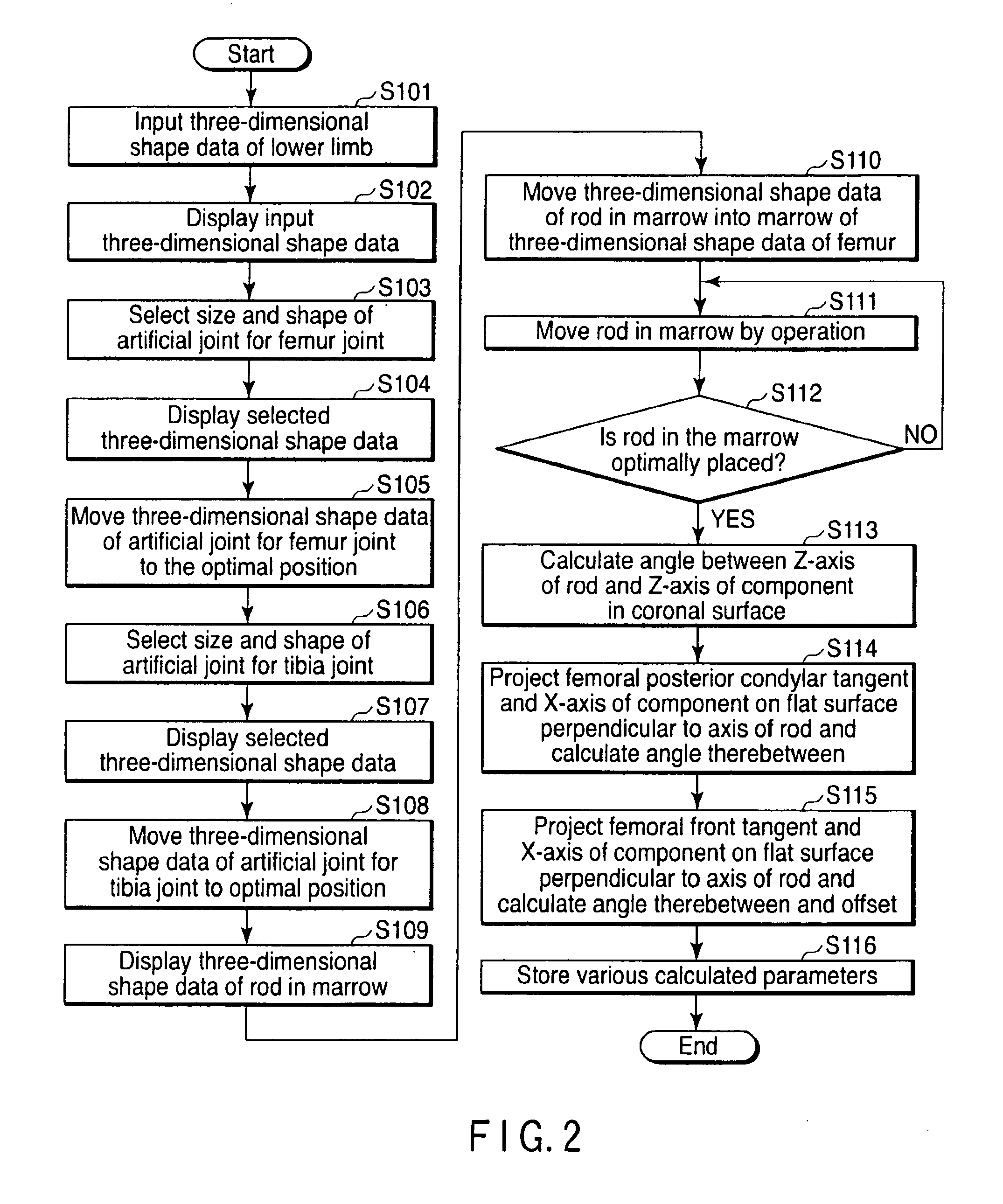
Steps S101 and S102 of displaying images which input two-dimensional tomographic images of the lower limb including the knee joint and displays three-dimensional images of the femur and the tibia including the knee joint from the image input, steps S103 to S105 and S106 to S108 of determining artificial joint which determine the artificial joint to be replaced from the three-dimensional images of each knee joint of the femur and tibia, and steps S113 and S114 of parameter determination which determine various parameters used in an artificial knee joint replacement operation using an alignment rod in the marrow to be inserted into the femur based on the artificial joint and reference points of the knee joint determined in steps S103 to S105 of determining femur side artificial joint are performed by a computer.
Owner:LEXI CO LTD
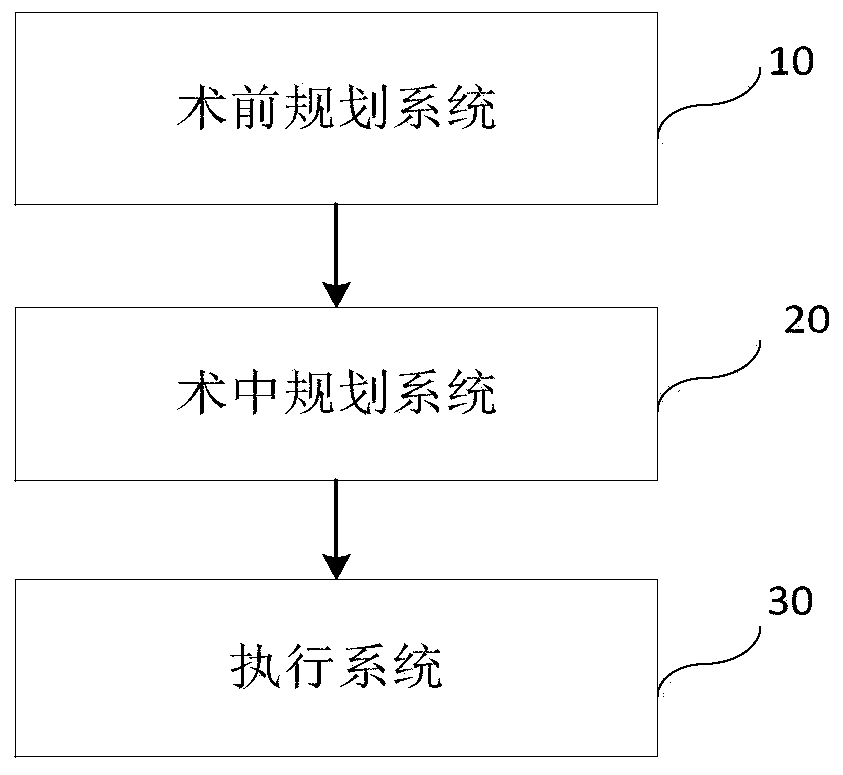
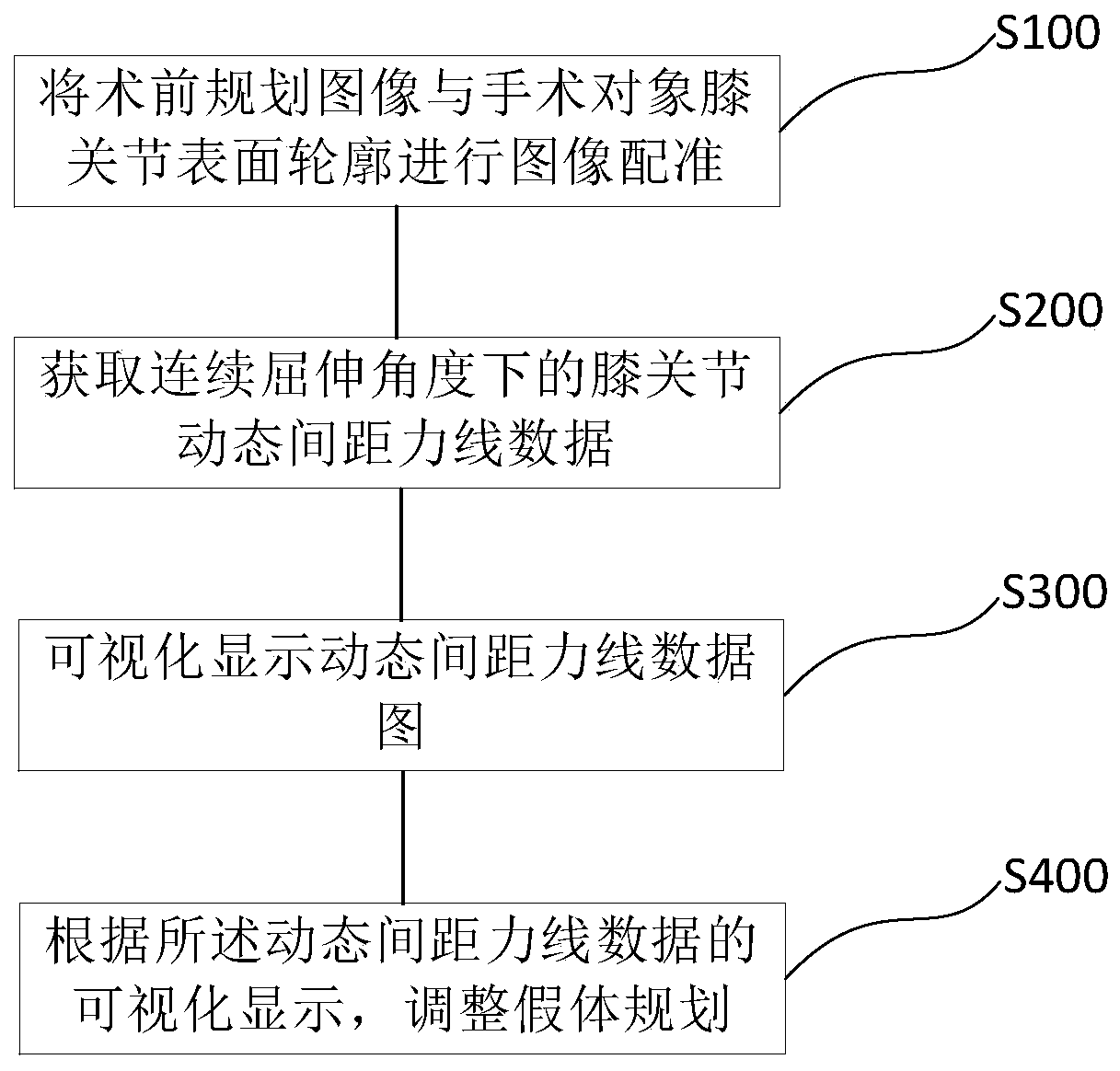
Total knee arthroplasty robot auxiliary system, control method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111345895AHigh precisionPromote reconstructionSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceData graphTotal knee replacement
The invention provides a total knee arthroplasty robot auxiliary system, a control method, electronic equipment, and a computer-readable medium. The auxiliary system comprises a pre-operative planningsystem, an intraoperative planning system and an execution system, wherein the pre-operative planning system is used for formulating pre-operative planning, wherein the pre-operative planning data comprises a knee image; the intraoperative planning system is used for formulating intraoperative planning, wherein the knee image in the pre-operative plan and a knee surface profile determined in theoperation of a patient are subjected to image registration; knee dynamic spacing force line data at a continuous flexion angle is acquired; visual displaying of a dynamic spacing force line data graphis performed; prosthesis planning is adjusted according to the visual display of the dynamic spacing force line data graph to obtain intraoperative planning; and the execution system is used for guiding an osteotomy guide mounted at the operating end of a mechanical arm of the surgical robot to be located in a predetermined position in the planning, wherein the osteotomy guide is used for positioning an osteotomy saw.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
Full digital total knee arthroplasty robot system and its simulated surgical method
ActiveCN109925055AFamiliar with operabilityFamiliar with the methodCosmonautic condition simulationsSurgical navigation systemsSimulationActuator
The invention relates to a full digital total knee arthroplasty robot system and its simulated surgical method. According to the full digital total knee arthroplasty robot system and a working methodthereof, the system comprises a control computer and a robot, an end effector is mounted on the robot, the end effector operates according to an instruction of the robot, and the control computer controls an action of the robot; and the system further comprises a structured light navigator, a dynamic reference, and a fixing device; the structured light navigator is mounted adjacent to a surgical bed, the fixing device is mounted on the surgical bed, the dynamic reference is mounted on the fixing device, and the structured light navigator is capable of capturing the motion locus of the dynamicreference.
Owner:BEIJING HURWA ROBOT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Augmented reality navigation method for minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty and system thereof
ActiveCN110353806ARealize semi-automatic calibrationAugmented reality navigationSurgical navigation systemsTibiaVirtual space
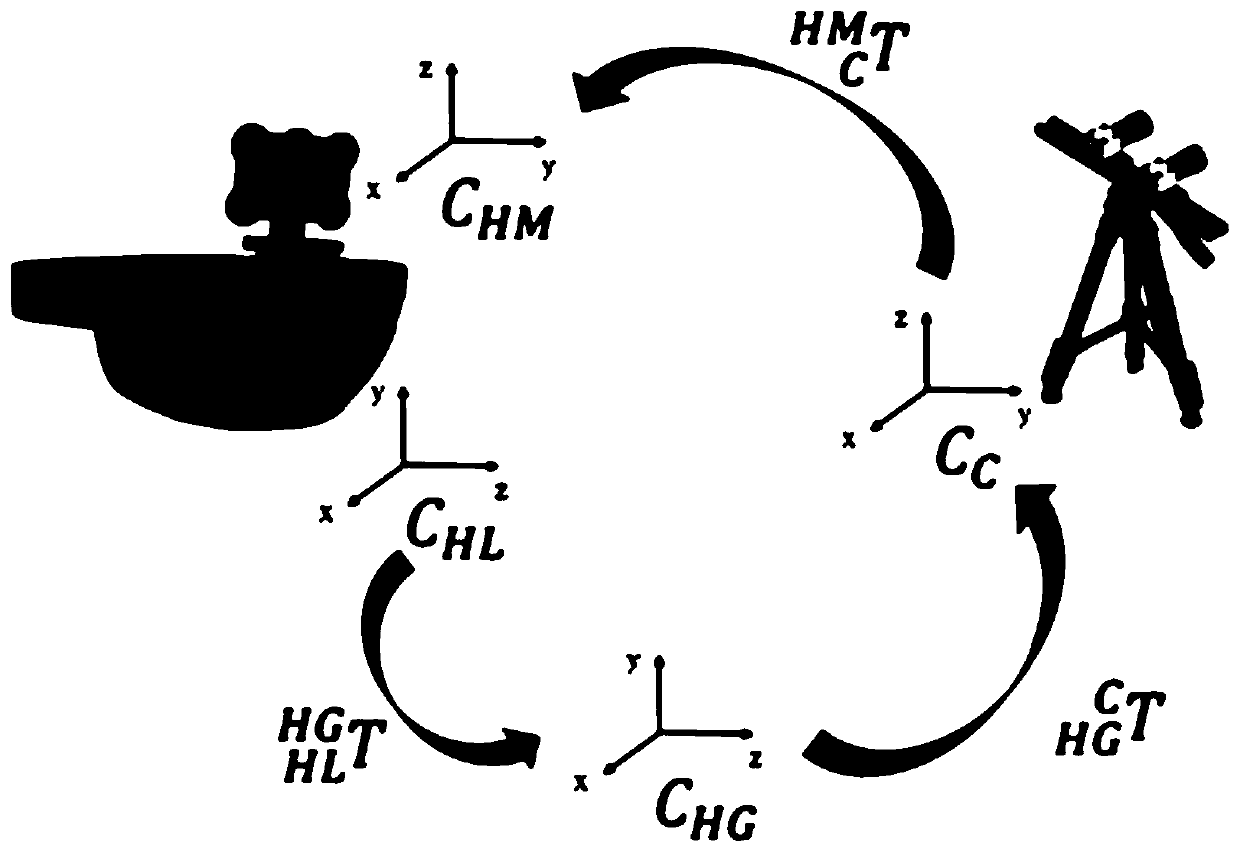
The invention discloses an augmented reality navigation method and a system for minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty. The method includes: obtaining a first relationship between a world coordinate system of a HoloLens application program corresponding to a virtual space and a coordinate system of a real scene; matching the knee point cloud and the preset three-dimensional model point cloud according to spatial alternation during operation to obtain a second relationship between a preoperative medical image space coordinate system and a binocular camera coordinate system; and superimposing virtual femur, tibia model and corresponding surgical guide model under Hollens field of vision according to the first relationship and the second relationship so as to realize augmented reality navigation. The method can help realize semi-automatic calibration of Hollens virtual space coordinate system, and combines the image registration technology to accurately superimpose the virtual knee anatomical model and the virtual surgical guide model to a corresponding real affected part location, thus providing doctors with intuitive and accurate intraoperative images guide.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Tibia osteotomy positioning device
The invention discloses a tibia osteotomy positioning device which is used for artificial total knee prosthesis replacement operation. The tibia osteotomy positioning device comprises an osteotomy plate and a positioning rod, the osteotomy plate is fixed at the top end of the positioning rod, and contact screws which are used for being nailed into tibia ridge front edge bone cortex for positioning are arranged on the positioning rod. The device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the positioning is accurate, the operation and the usage are convenient, during knee prosthesis replacement, inside and outside turning, rotation and hypsokinesis can be excellently controlled to perform a marrow outside positioning tibia osteotomy in tibia osteotomy operation, and the defects that tibia osteotomy positioning devices in prior art are inaccurate in alignment, complicated in operation, and unstable caused by human factors and the like are overcome. The two contact screws are nailed into the tibia ridge for fixture, so that the upper end of a positioning device is not required to be in contact with a tibial platform, and the osteotomy plane is determined mainly according to the tibia ridge.
Owner:GUANGDONG STABLE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
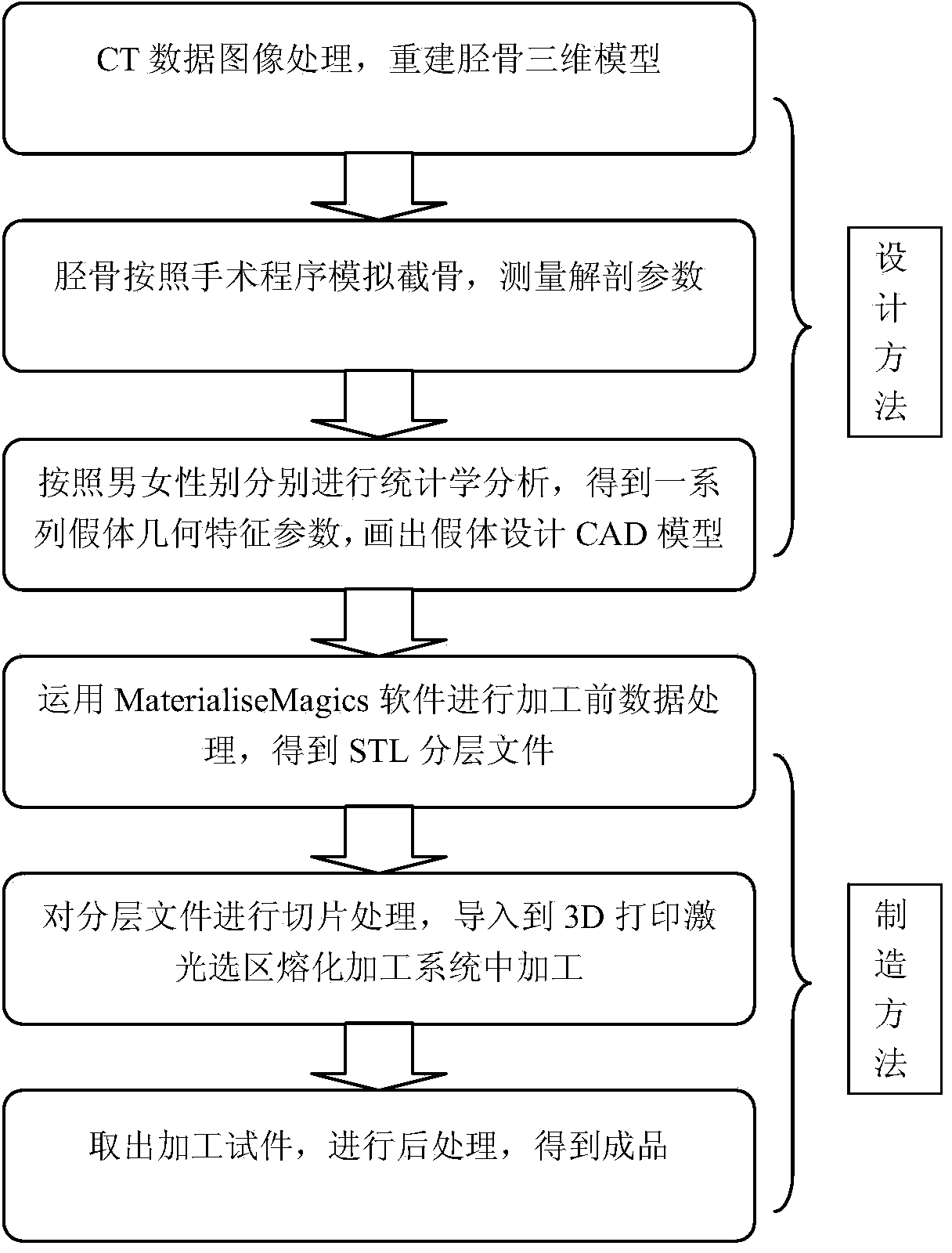
Digital design and manufacturing method for knee joint tibia prosthesis
InactiveCN103860295AIncrease coverageImprove yieldJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaMedical imaging data
The invention relates to a digital design and manufacturing method for a knee joint tibia prosthesis. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a knee joint tibia three-dimensional digital model according to medical image data based on the knee joint tibia of healthy people; (2), performing digital simulation of tibia rear end osteotomy according to a knee joint arthroplasty surgery scheme and measuring the design-related geometric parameter of the tibia prosthesis; (3), obtaining the geometric shape parameters of the tibia prosthesises of different genders and models according to the statistical analysis, and drawing the tibia prosthesis design model; (4) manufacturing the knee joint tibia prosthesis according to the tibia prosthesis design model through a 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology. According to the digital design and manufacturing method for the knee joint tibia prosthesis, the tibia prosthesises of different genders and models can be obtained, the prosthesises can be matched with the anatomic form features of different knee joint tibia skeletons of male and female in China, and the coverage rate between the prosthesises and the osteotomy section of the knee joint tibia and the good rate of surgeries are improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL +1
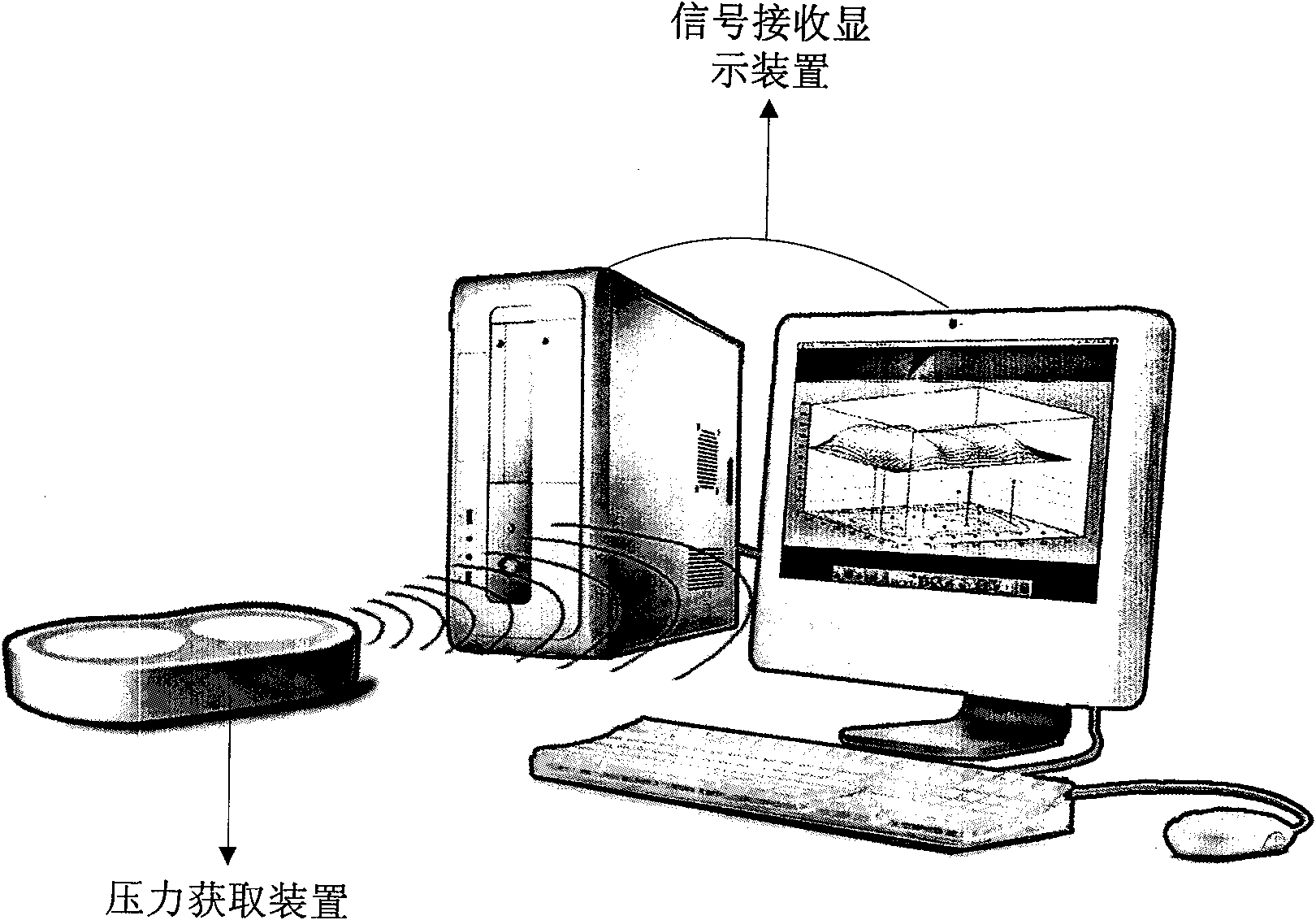
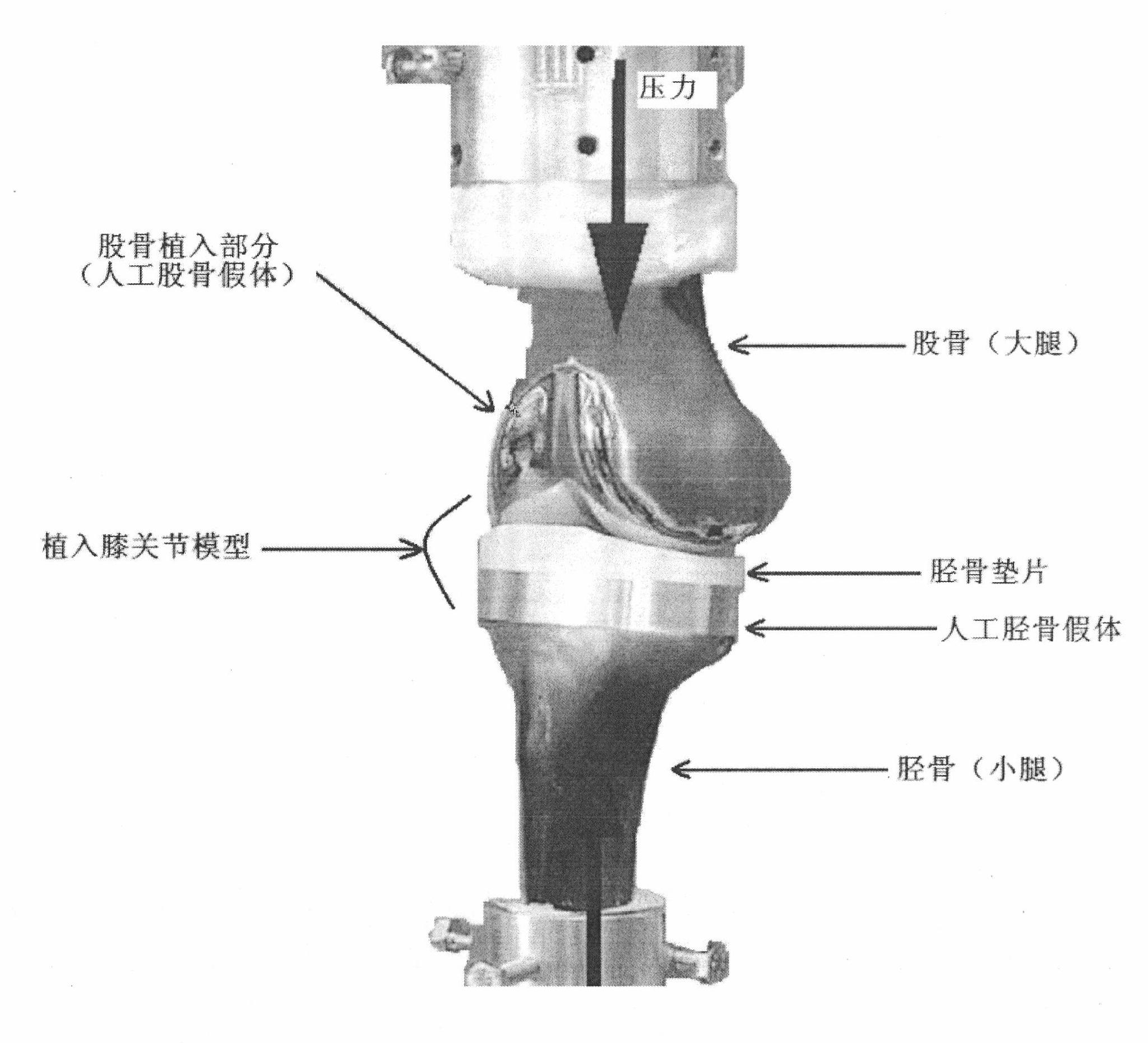
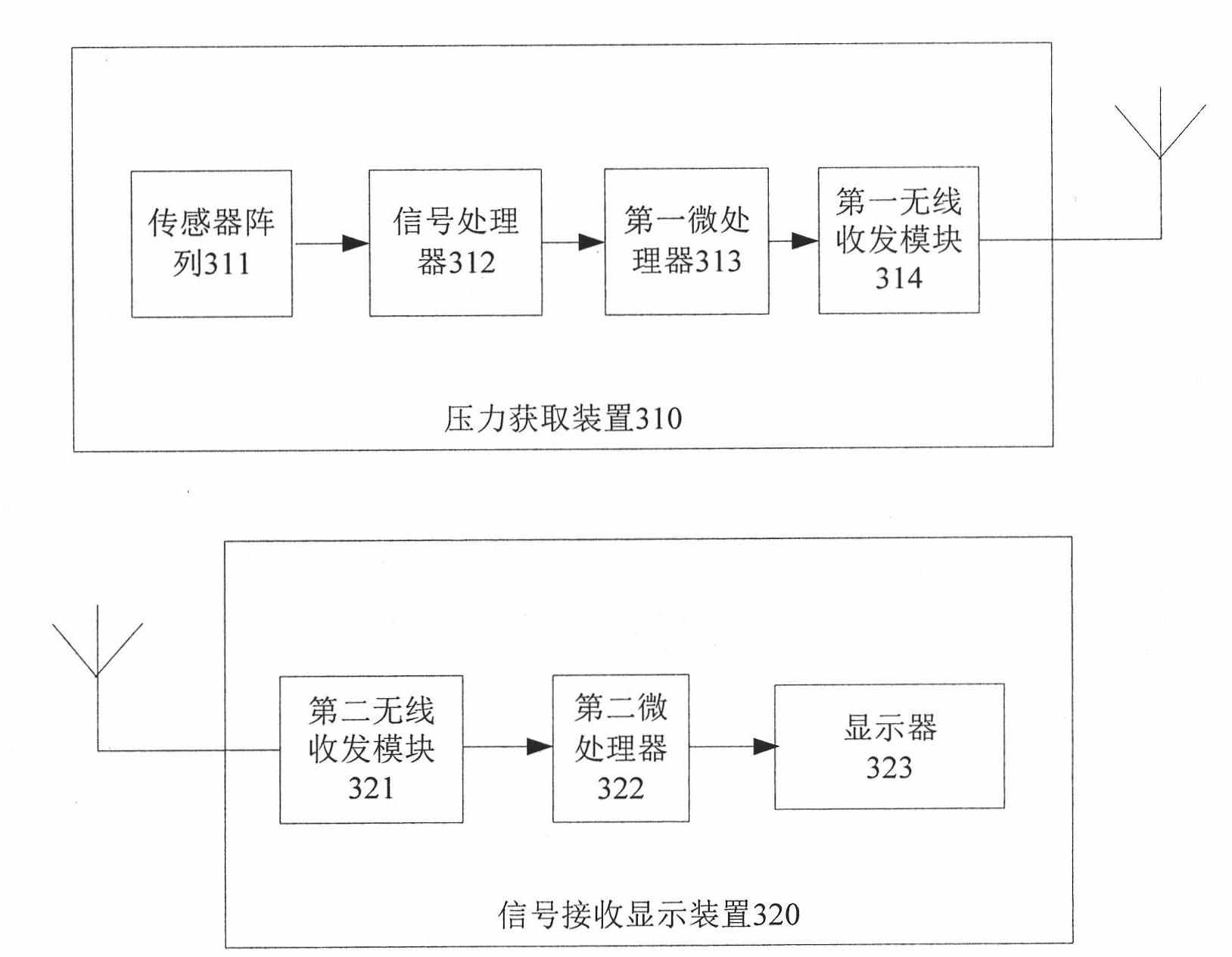
Total knee replacement pressure balance measuring system
ActiveCN101884542AGuaranteed accuracyImprove rationalityMuscle exercising devicesTibiaStress conditions
The invention relates to a total knee replacement pressure balance measuring system, which comprises a pressure acquiring device and a signal receiving and displaying device. The shape and dimension of the pressure acquiring device are the same as those of a tibia gasket in artificial knee prosthesis, and the pressure acquiring device is arranged at the knee joint of a patient during the operation so as to acquire a pressure signal and transmit the pressure signal to the signal receiving and displaying device. The signal receiving and displaying device performs force processing on the received pressure signal and displays the pressure distribution condition in a form of a three-dimensional pressure diagram so as to provide the stress condition at the tibia gasket of the artificial knee joint for a doctor in real time. The pressure acquiring device is arranged at the knee joint of the patient during the operation so as to acquire the pressure signal and is taken out after the pressure is balanced, and a proper tibia gasket is put at the knee joint of the patient. The total knee replacement pressure balance measuring system can be widely applied to the total knee replacement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Thigh-bone positioning method for full knee-joint replacement operation by robot
InactiveCN1488321AMeet the precision requirementsThe principle is simpleDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryThighSimulation
The invention provides a thighbone positioning method of robot full-knee joint replacement. First, abstract the problem to determine the center of thighbone into a geometric model to find the sphere center according to the known point on the sphere, combine three arbitrary points according to the collected spacing-socket central data of the thighbone, determine the coordinate information of the thighbone center by numerical calculation, then build the thighbone reference frame, then make the vectors on coordinate axes of three thighbone reference frame in the robot reference frame and ones on three coordinate axes of the robot reference frame compose a one-to-one relationship, and thus, find and build the corresponding relationship of the robot and thighbone reference frames, which accurately positions the thighbone.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Tibial prosthesis
The present invention relates to a tibial prosthesis useful in knee replacement surgeries. The prosthesis includes one or more cement introduction ports which may be used to deliver and control delivery of bone cement to a prosthesis-bone interface after the prosthesis has been positioned on a resurfaced area of a tibia bone. The prosthesis is suitable for implantation using arthroscopic as well as open surgical procedures. The prosthesis may be used as a unicondylar implant in either compartment of the knee or in both compartments of the knee.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Low stress all poly tibial component
A tibial component for use in conjunction with a knee replacement surgery. An inferior surface of the tibial component may be concave to thereby improve bonding between the tibial component and a tibia. The tibial component may produce low stress in the cement mantle during in-vivo loading. A stem extending from the inferior surface of the tibial component may include an anterior curvature to facilitate the use of minimally evasive surgical techniques. The stem may further include medial-lateral wing portions with a posterior curvature to provide improved support.
Owner:KEGGI JOHN +4
Apparatus for preoperative planning of artificial knee joint replacement operation and jig for supporting operation
InactiveUS20120172882A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionTibiaPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Steps S101 and S102 of displaying images which input two-dimensional tomographic images of the lower limb including the knee joint and displays three-dimensional images of the femur and the tibia including the knee joint from the image input, steps S103 to S105 and S106 to S108 of determining artificial joint which determine the artificial joint to be replaced from the three-dimensional images of each knee joint of the femur and tibia, and steps S113 and S114 of parameter determination which determine various parameters used in an artificial knee joint replacement operation using an alignment rod in the marrow to be inserted into the femur based on the artificial joint and reference points of the knee joint determined in steps S103 to S105 of determining femur side artificial joint are performed by a computer.
Owner:LEXI CO LTD
Tibia osteotomy positioning device for knee joint replacement surgery
The invention discloses a tibia osteotomy positioning device for a knee joint replacement surgery. The tibia osteotomy positioning device comprises an osteotomy unit, a backward inclination angle adjuster and a first toe and second toe aligner, wherein an arc-shaped contact surface is arranged at the inner side of the osteotomy unit; an osteotomy groove penetrating through the osteotomy unit is arranged at the outer side of the osteotomy unit; a plurality of first positioning holes and a plurality of second positioning holes are respectively arranged at the upper end and the lower end of the osteotomy groove; the number of the first positioning holes is larger than the number of the second positioning holes; and fixators used for fixing the osteotomy unit to the outer surface of the tibiaare detachably arranged in the first positioning holes and the second positioning holes. When the fixators penetrates through the first positioning holes and the second positioning holes to fix the osteotomy unit on the tibia, a majority of the fixators are nailed into the bone of the spinous process of the tibia located above the osteotomy groove, while the bone of the spinous process of the tibia located above the osteotomy groove is cut off in a surgery, so the injury of the fixators to the tibia can be greatly reduced; postoperative pain is reduced; and the postoperative recovery effect ofa patient is improved.
Owner:邬黎平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com