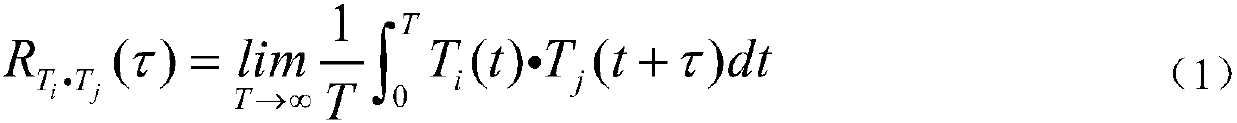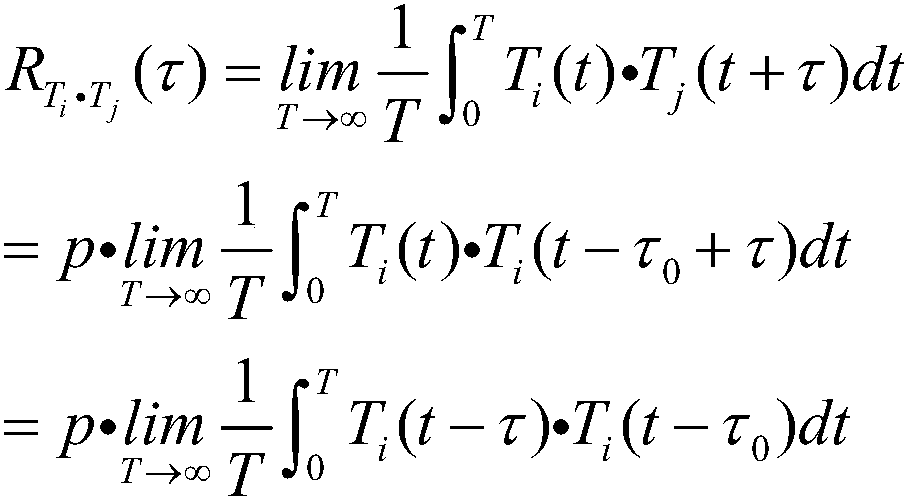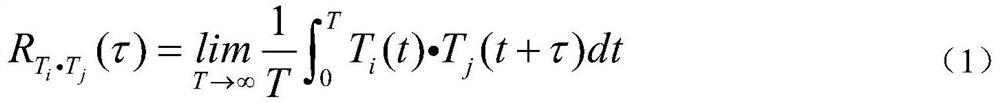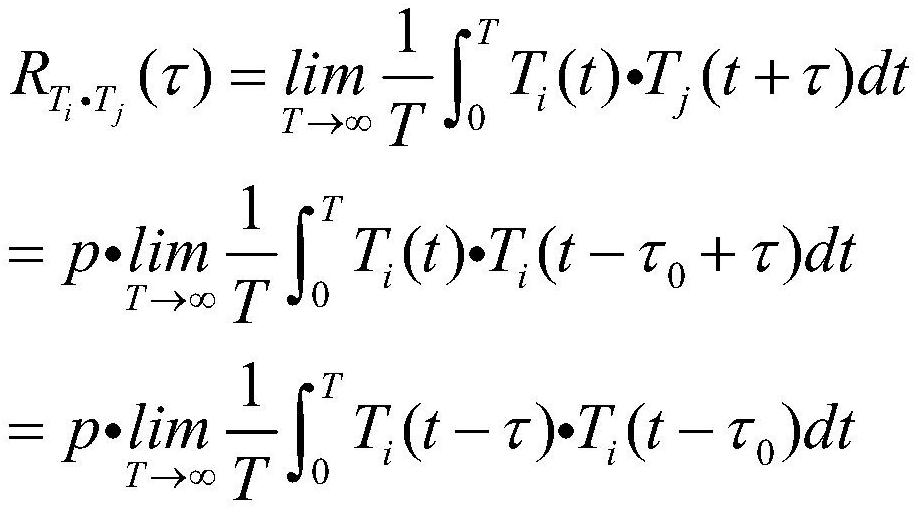Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Cerebrospinal fluid shunt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
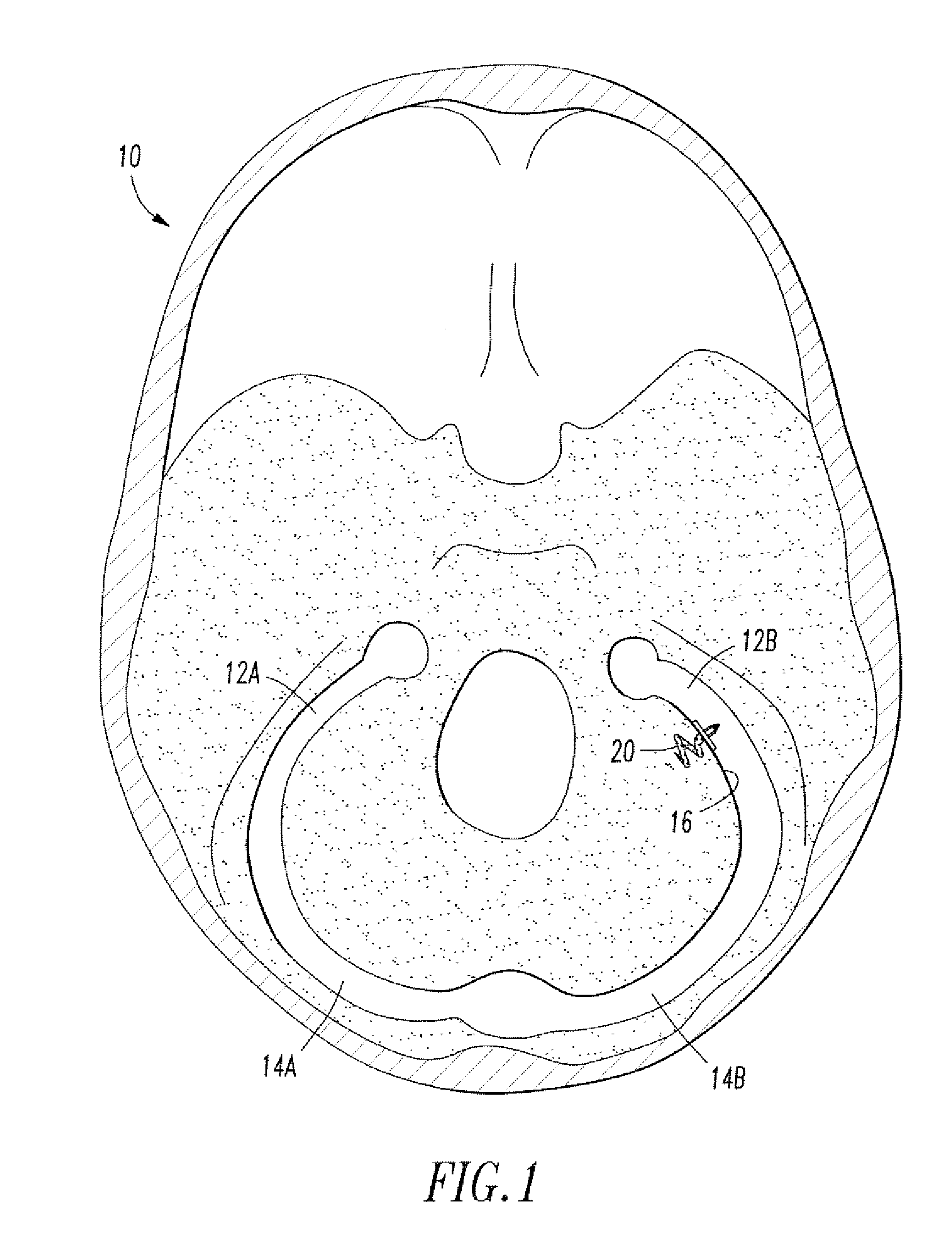
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt is a type of cerebral shunt used to alleviate the buildup of excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) on the brain.
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
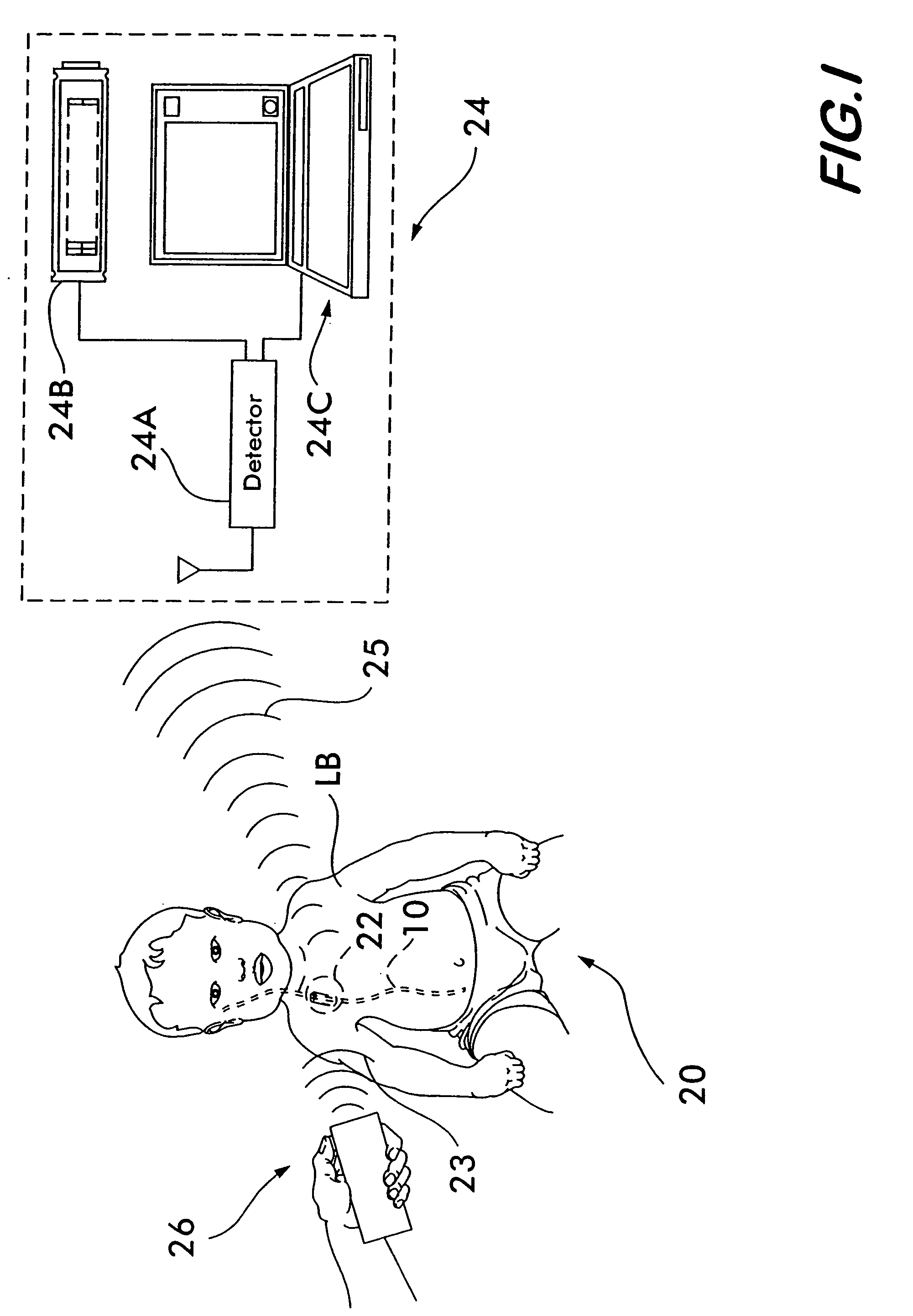
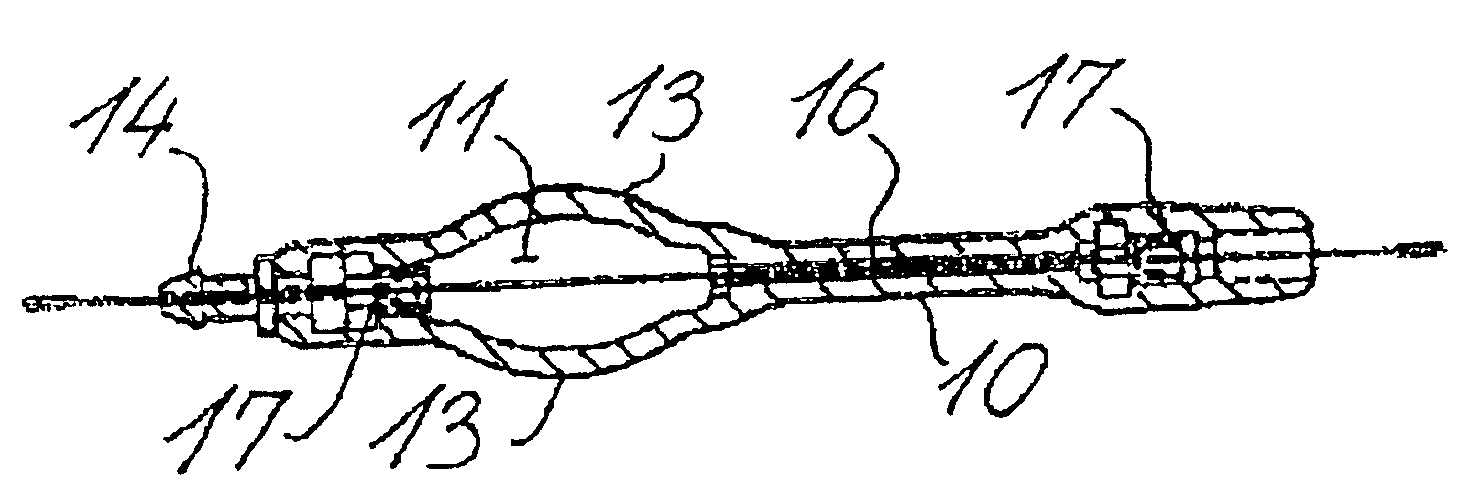
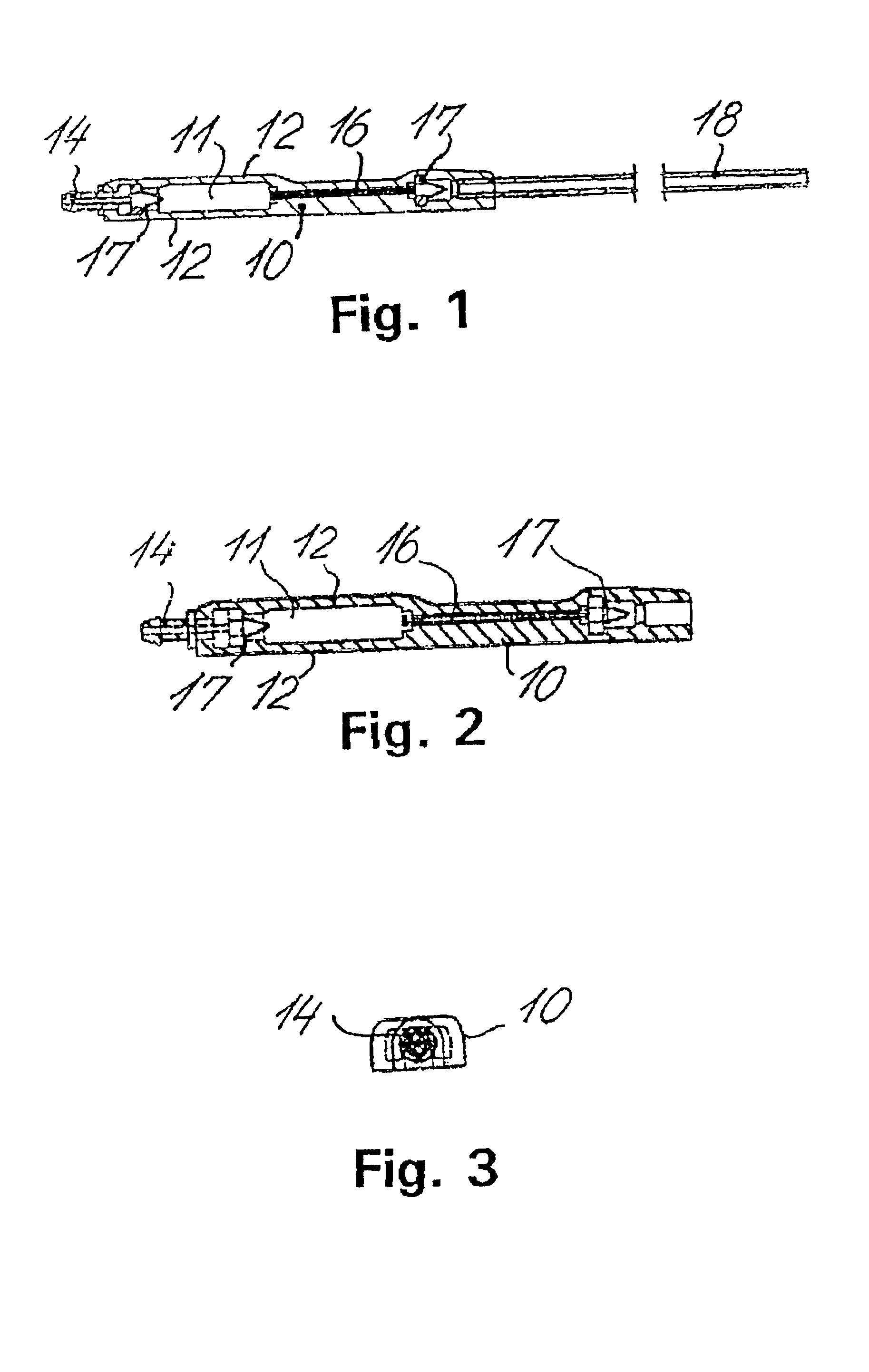
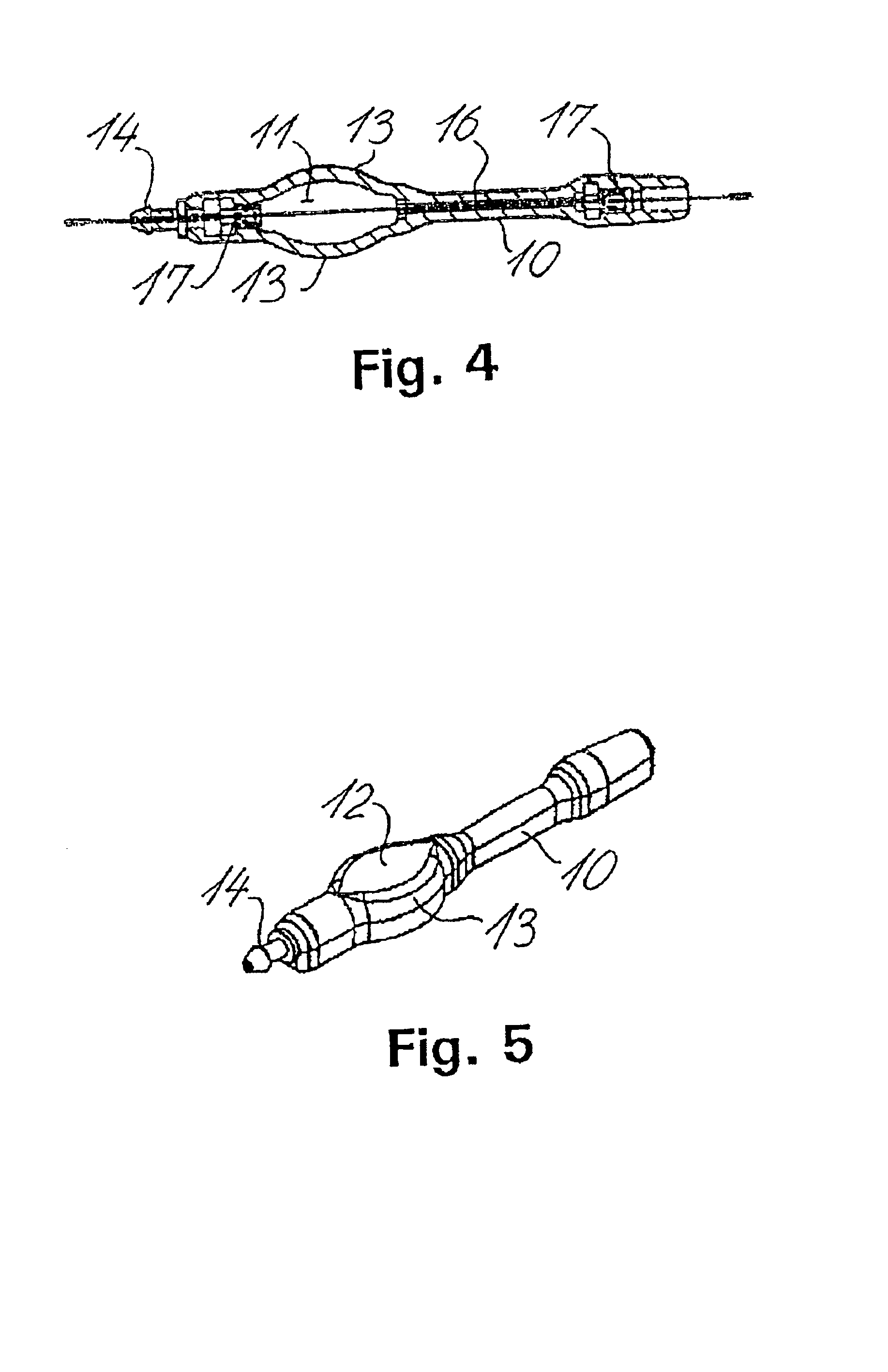
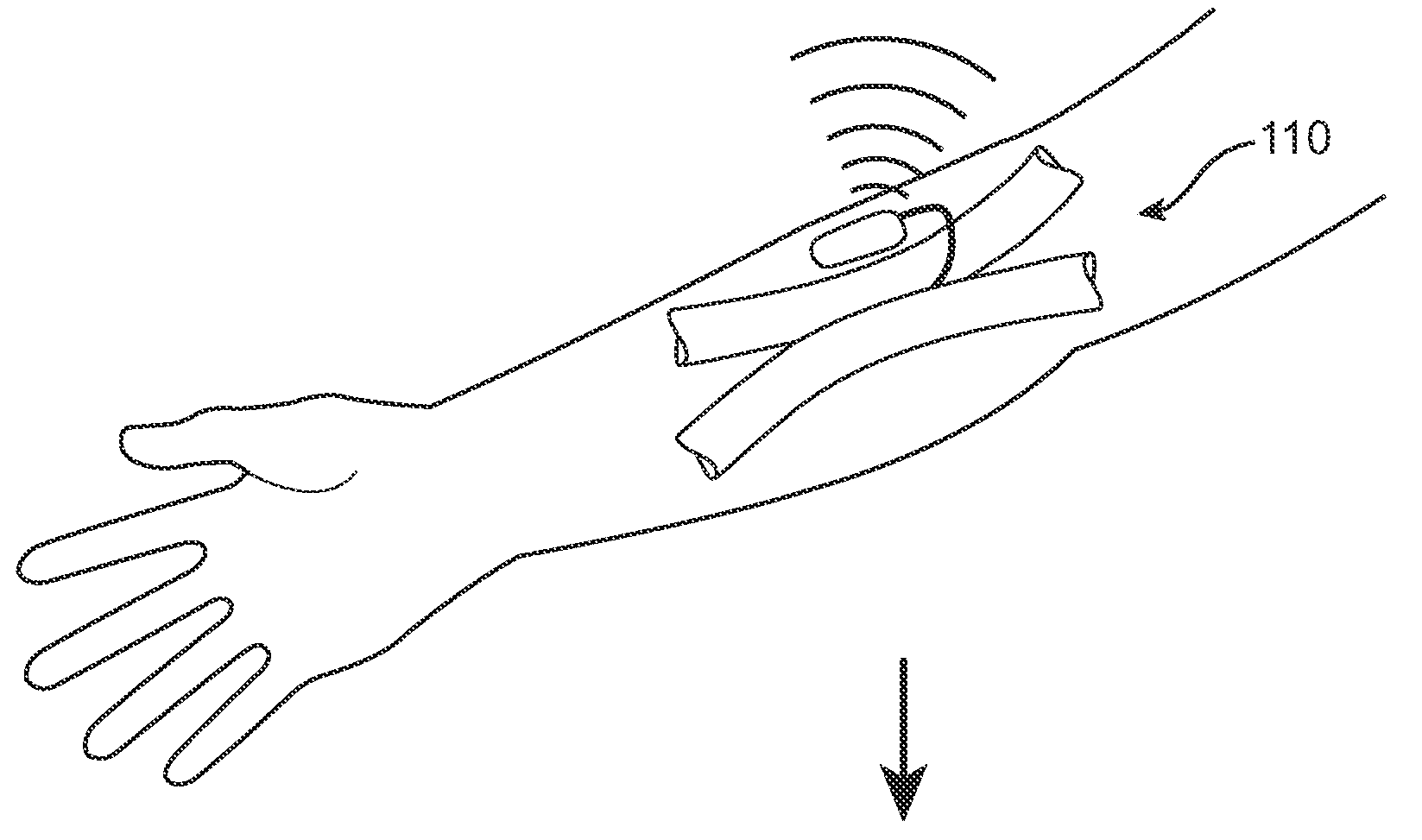
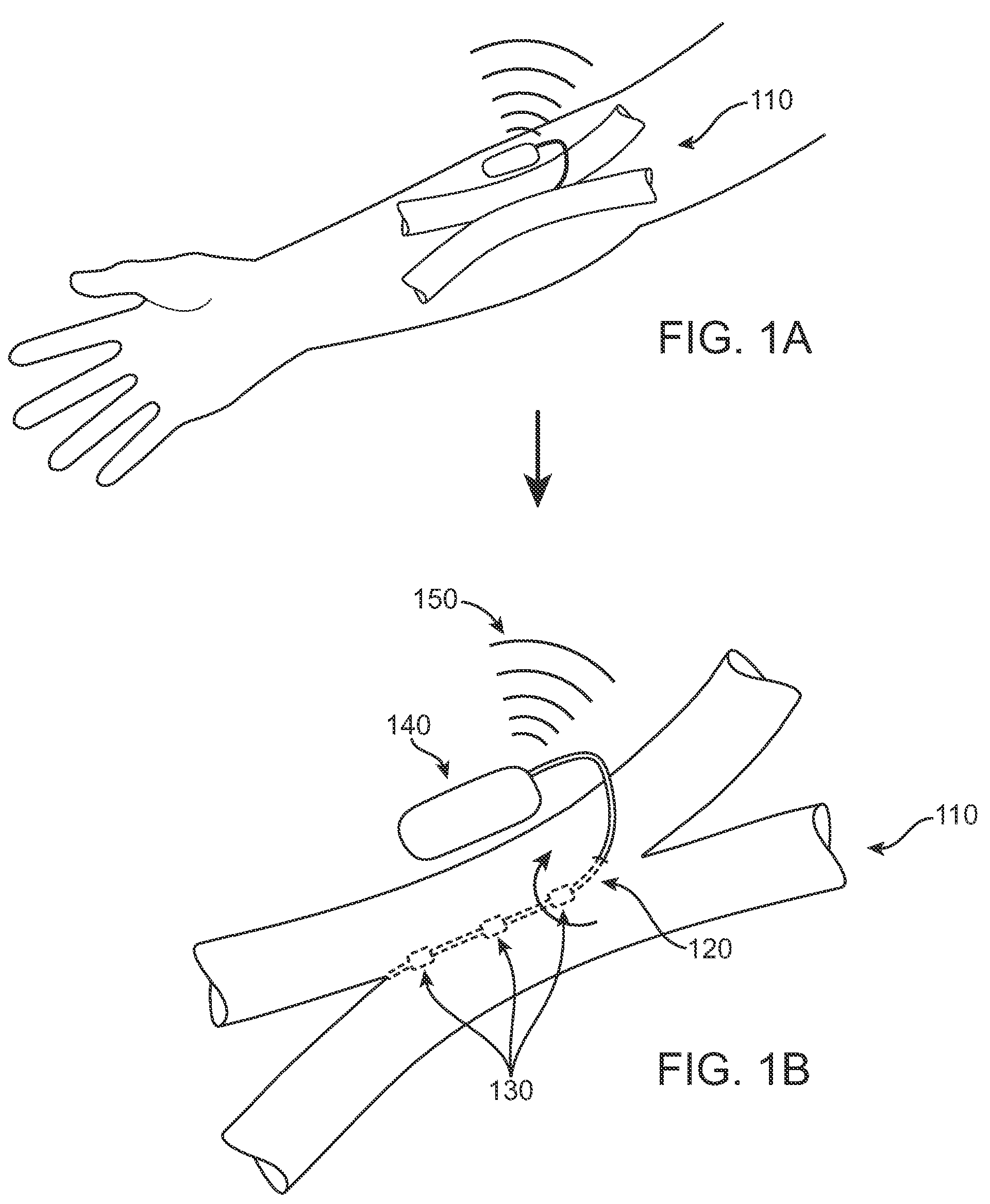
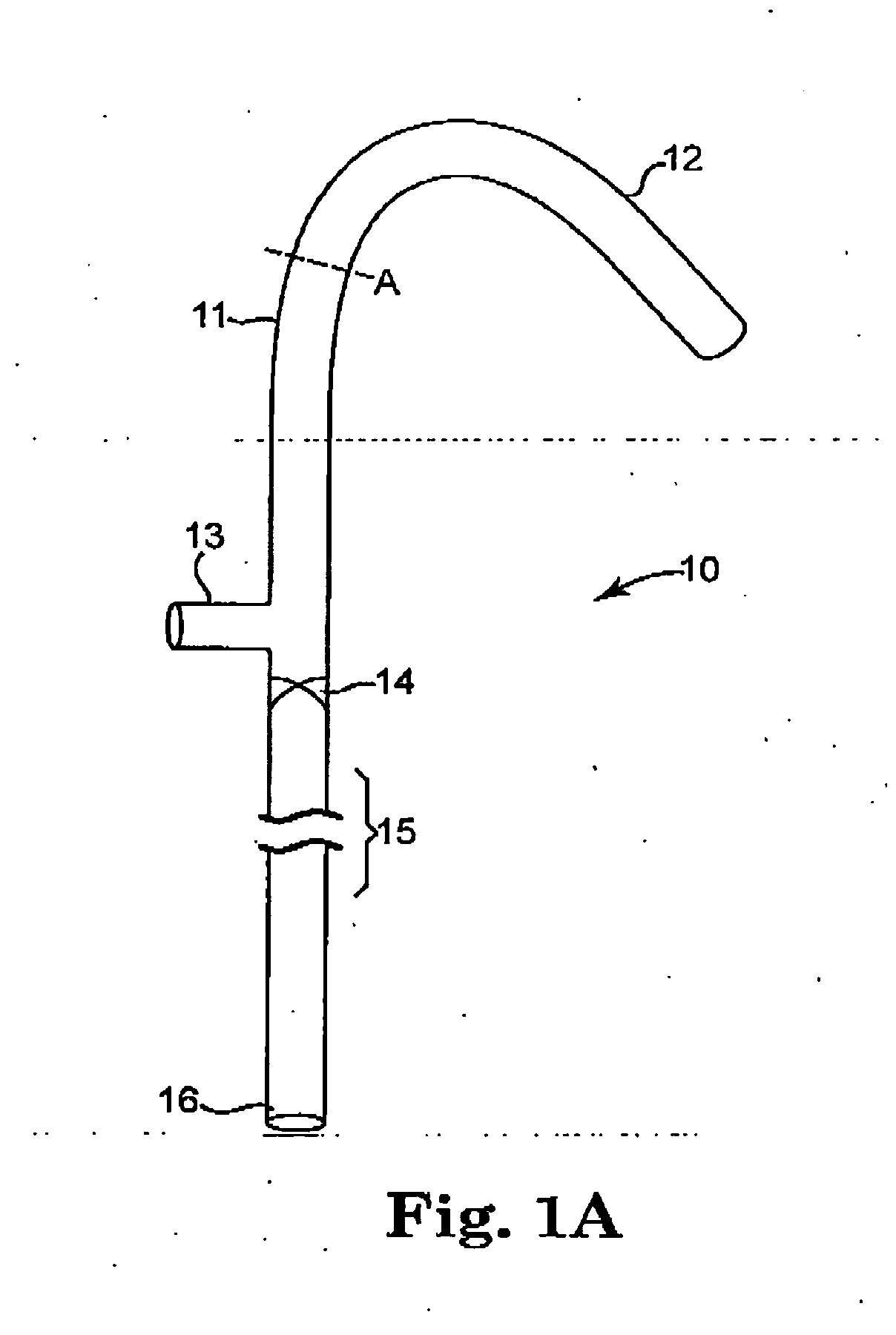
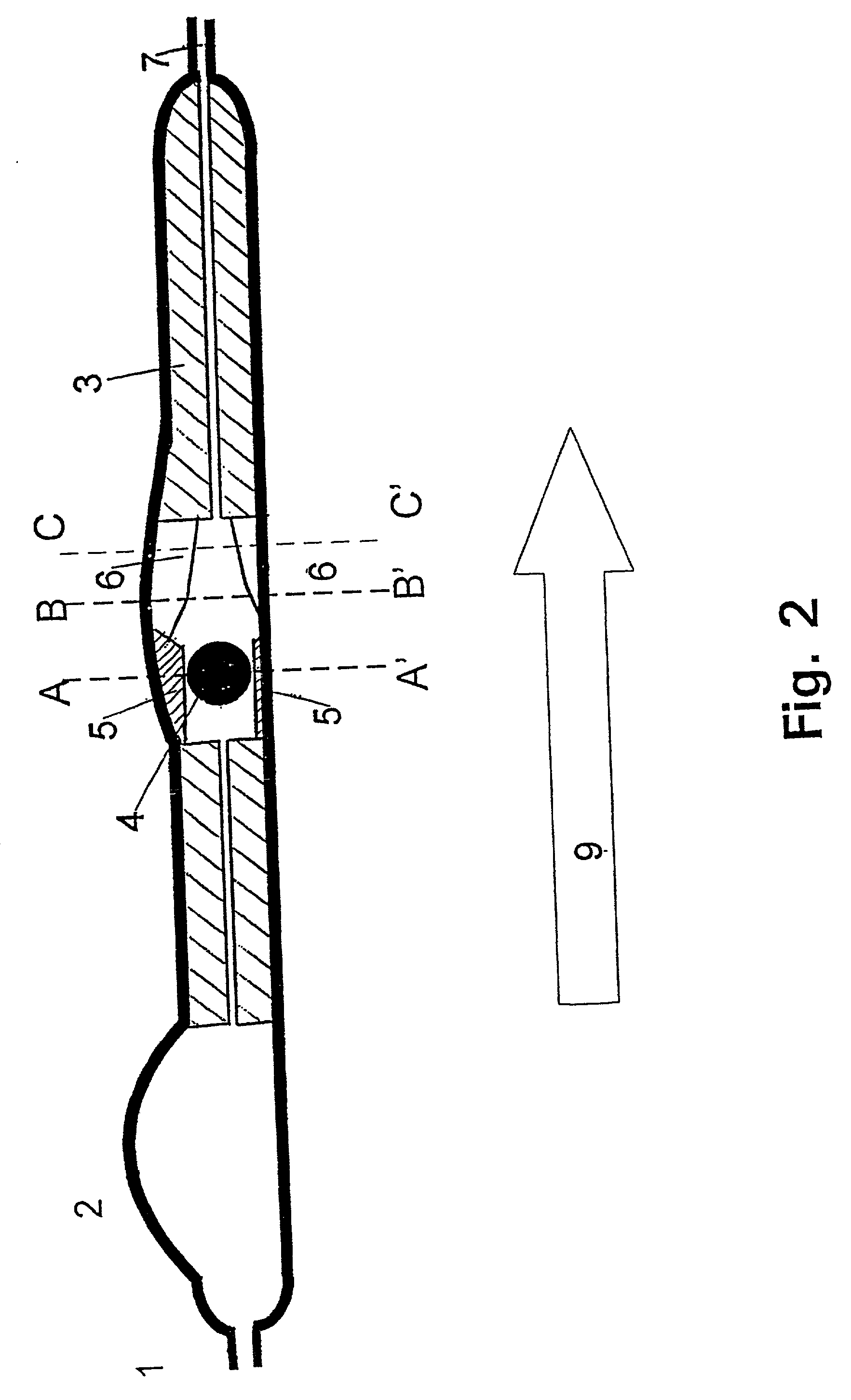
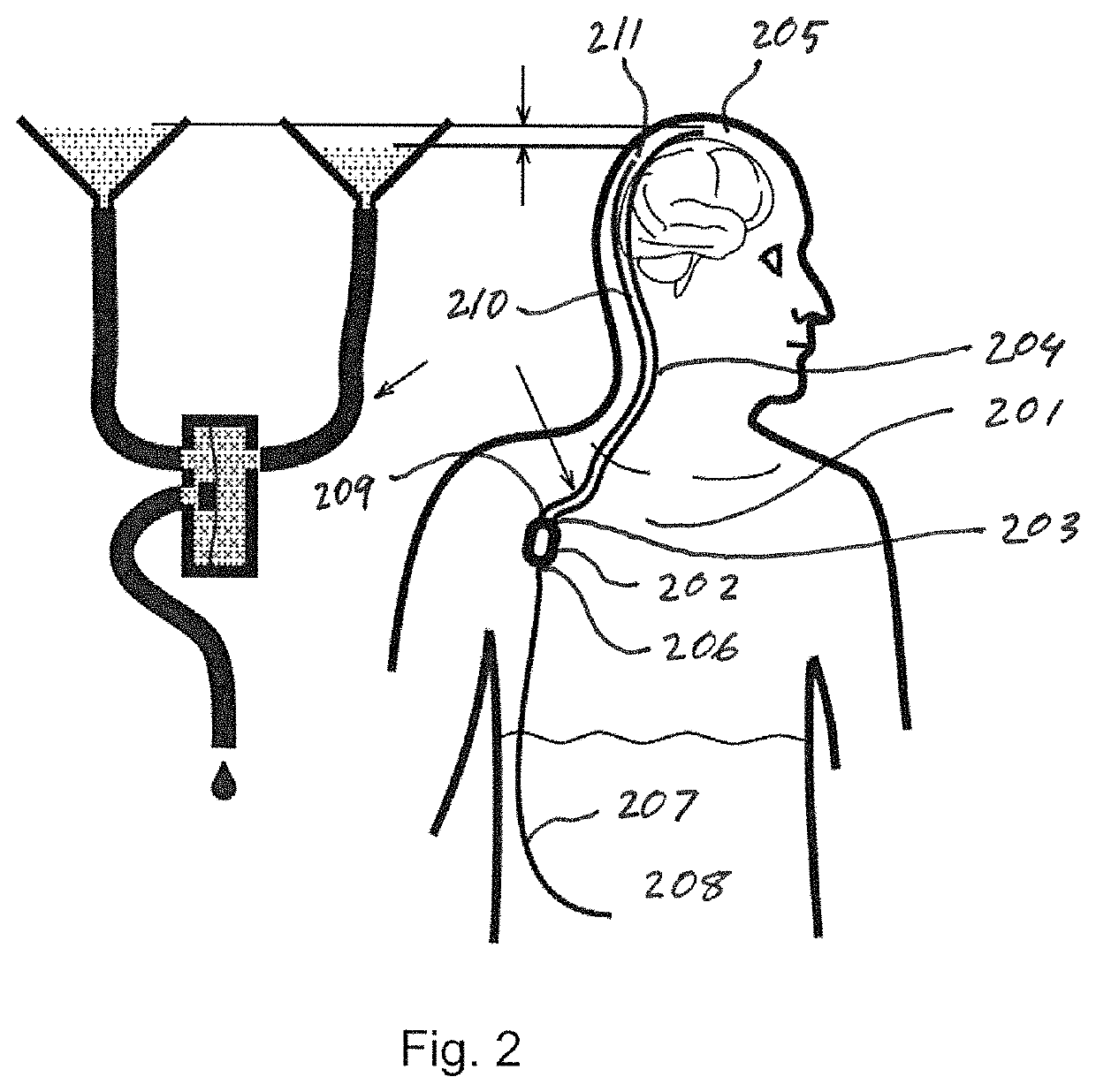
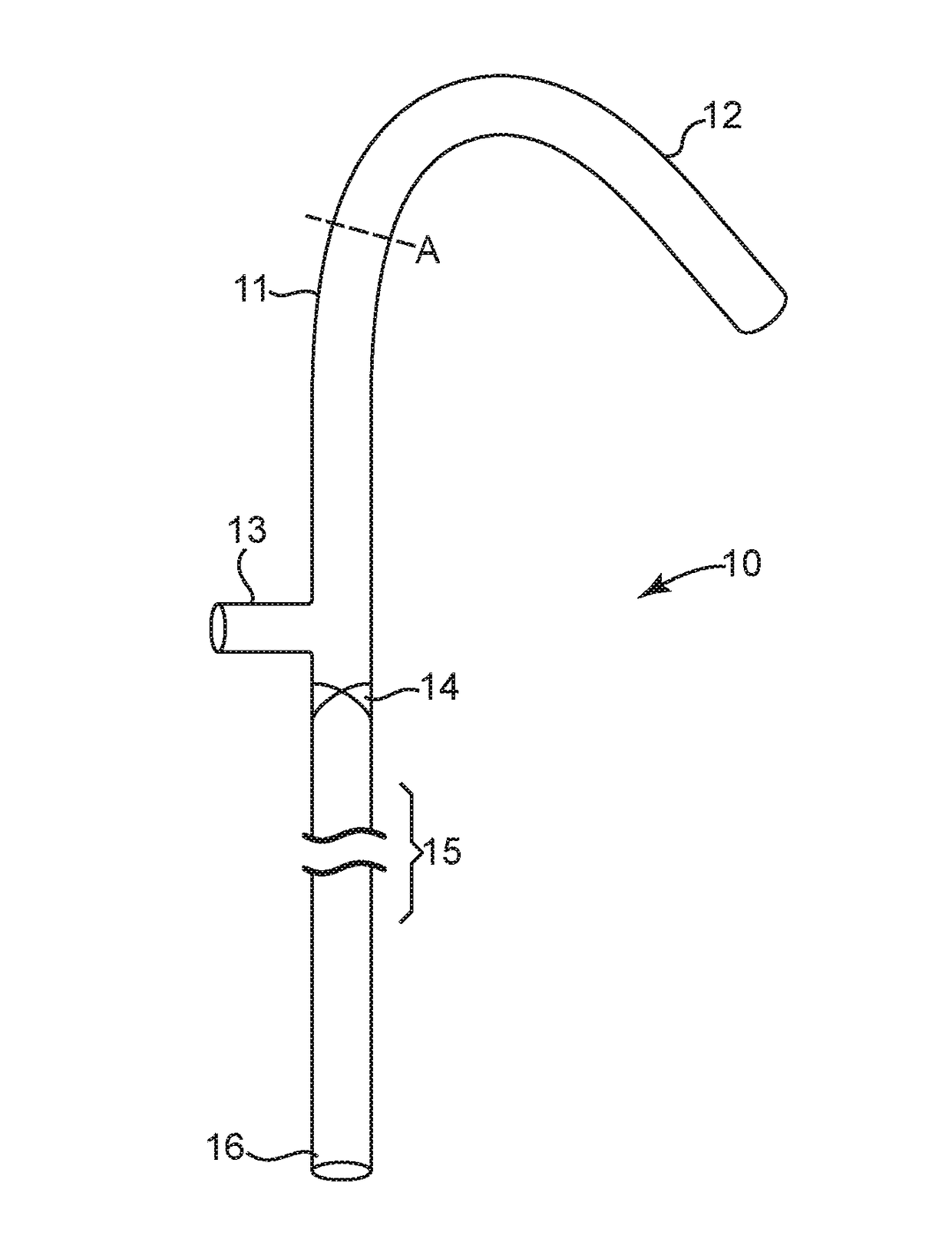
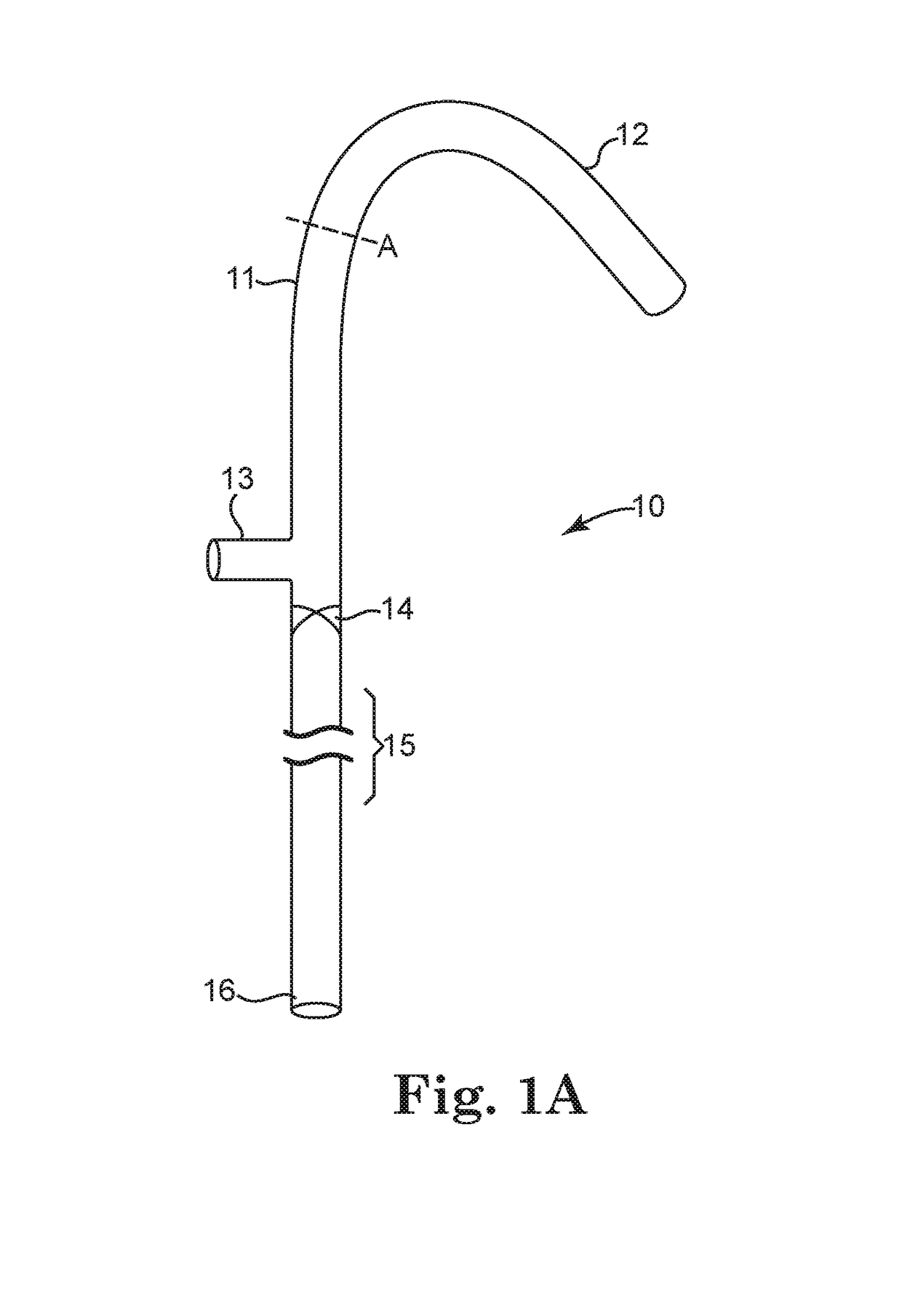
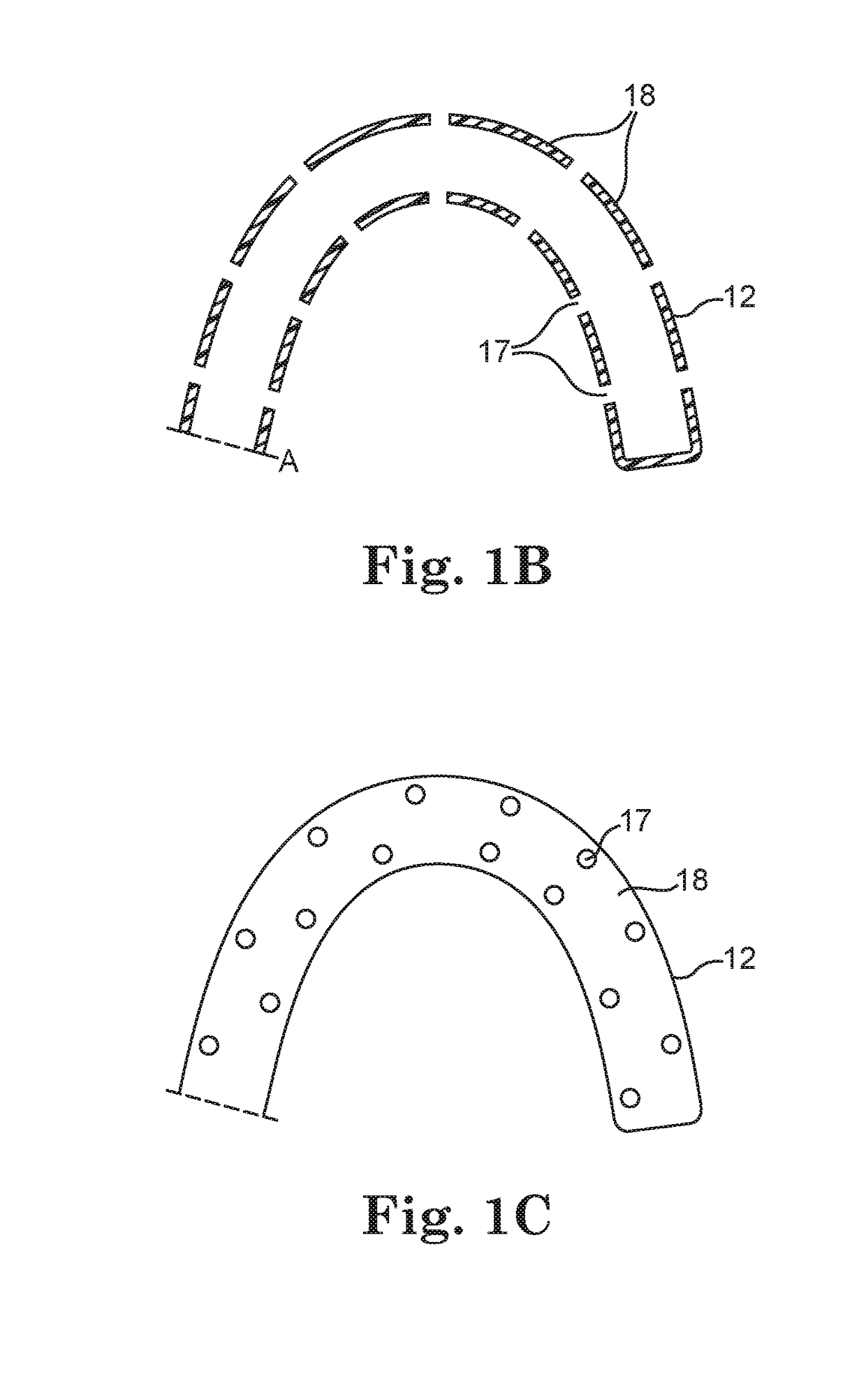
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricular catheter for insertion into the brain ventricle so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle. The system also comprises a sinus sagittalis catheter for insertion into the sinus sagittalis for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into sinus sagittalis. A shunt main body is connected at one end thereof to the brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to the sinus sagittalis catheter. The shunt main body can provide fluidic communication between the brain ventricle catheter and the sinus sagittalis catheter. The system further comprises a tubular flow passage restricting member defined within the shunt main body. The tubular flow passage restricting member defines a resistance to flow of 8-12 mm Hg / ml / min.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
System and method for measuring flow in implanted cerebrospinal fluid shunts
InactiveUS20050204811A1Volume/mass flow by thermal effectsWound drainsFlow diverterCerebrospinal fluid shunt
A system and method for a thermal convection flow detection in a cerebrospinal fluid shunt that uses very little power for extended operation and for providing flow data to a remotely-located device.
Owner:NEFF INDIVIDUAL JANINE +1
Shunt system with coating and flow restricting component exerting a passive and essentially constant resistance to outflow
InactiveUS20070112291A1Reduce as muchReduce infectionWound drainsFlow monitorsCsf shuntBrain Ventricle
The present invention relates to an improved cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprising a coating covering at least part of the system and a flow restricting component exerting a passive and essentially constant resistance to flow. The present invention also relates to methods for implanting different catheters of a cerebrospinal fluid shunt system into a brain ventricle and the sinus system, respectively, of an individual. The present invention further relates to methods for shunting cerebrospinal fluid from a brain ventricle to the sinus system of an individual.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
Fluid shunt system and a method for the treatment of hydrocephalus
InactiveUS6905474B2Lower resistanceInhibit posture changesWound drainsMedical devicesFlow diverterBrain Ventricle
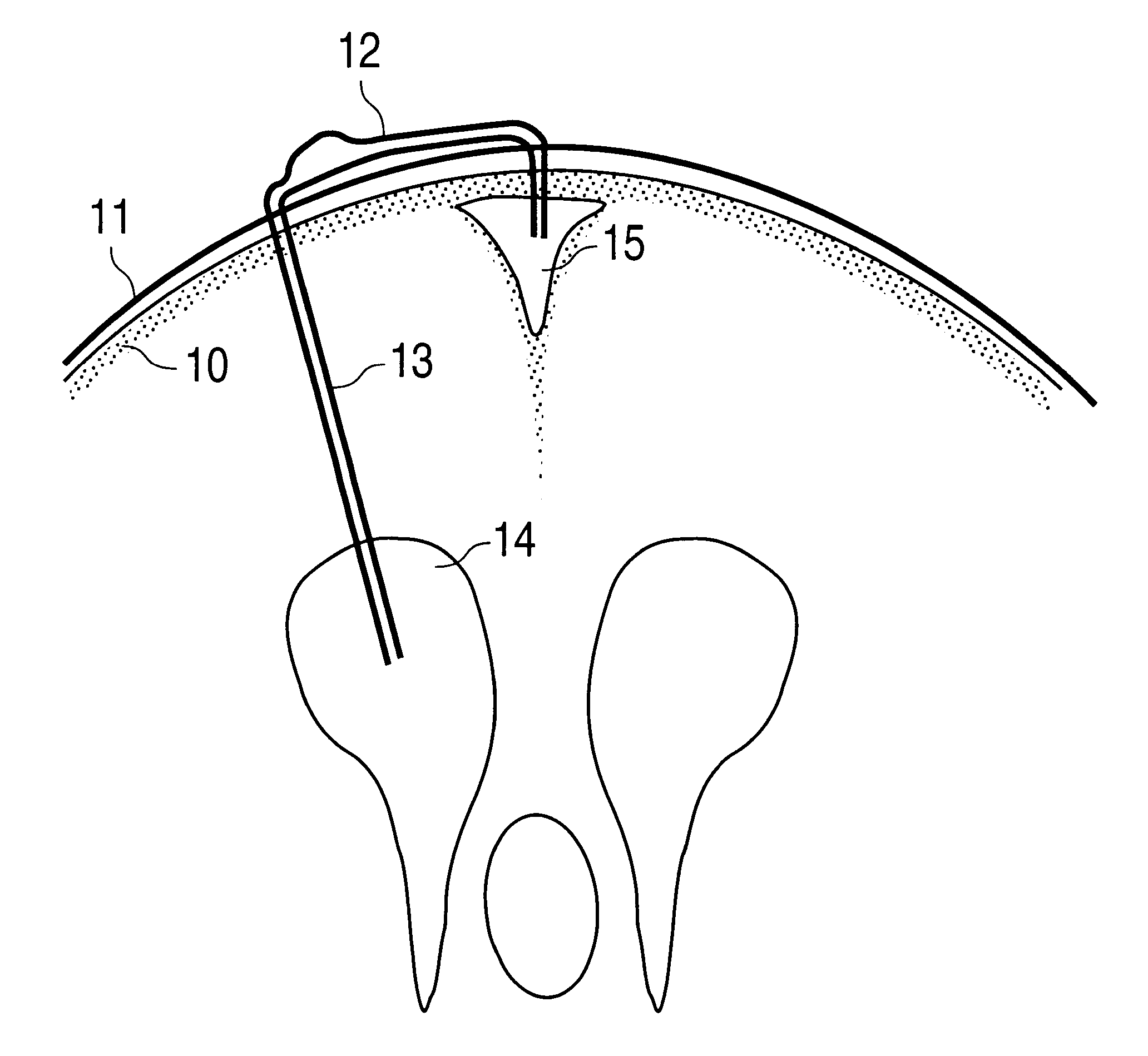
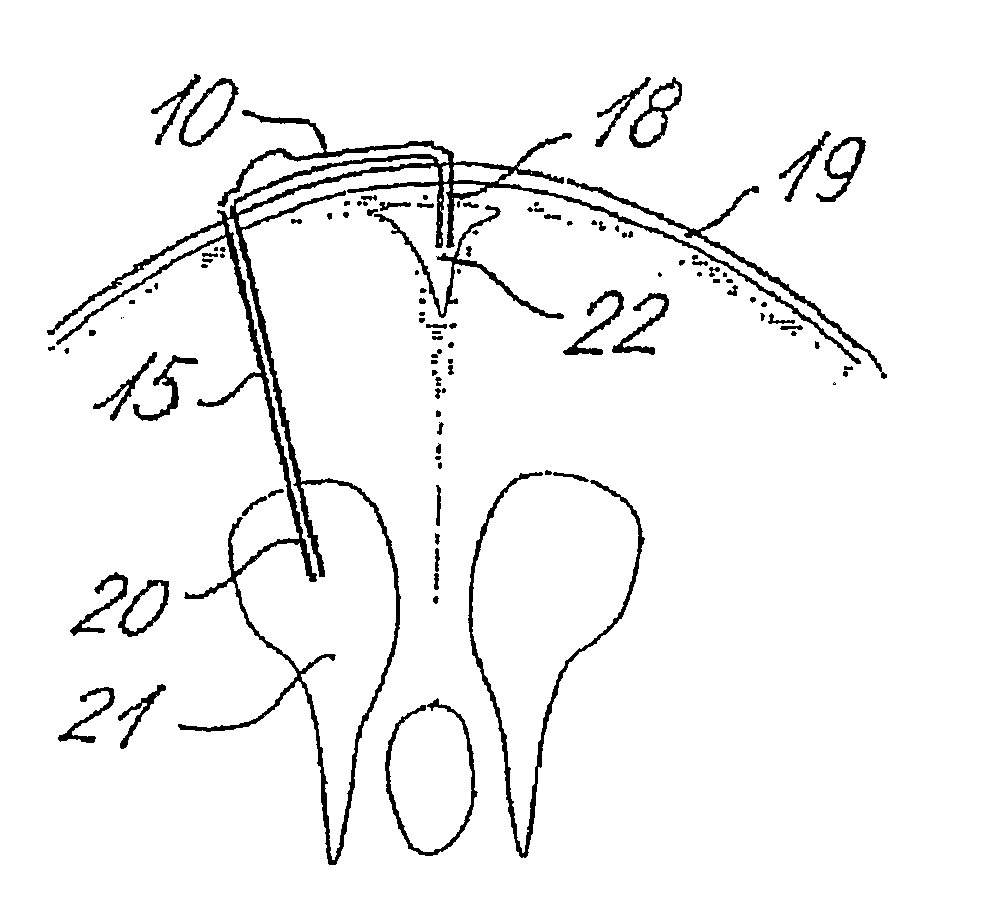
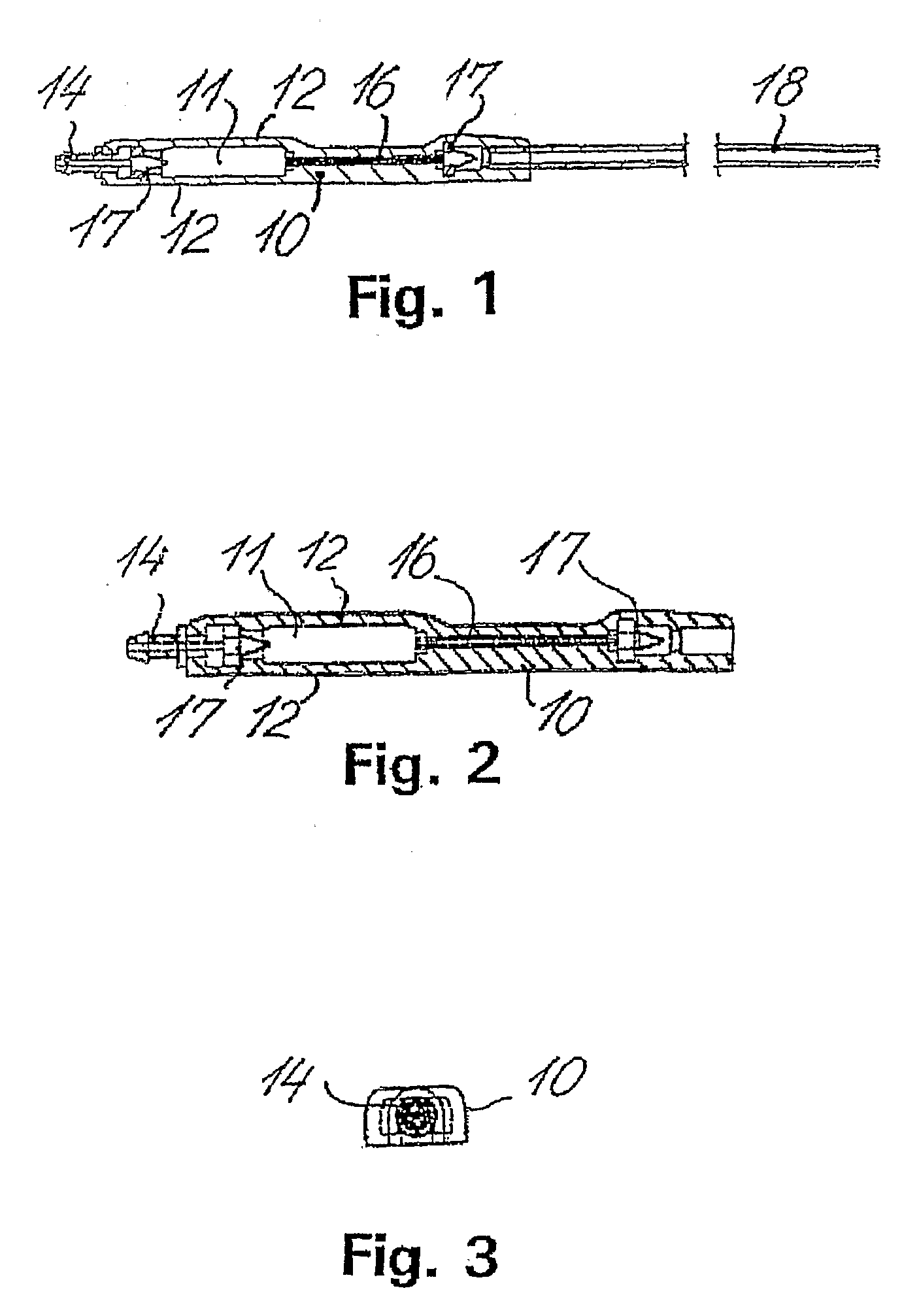
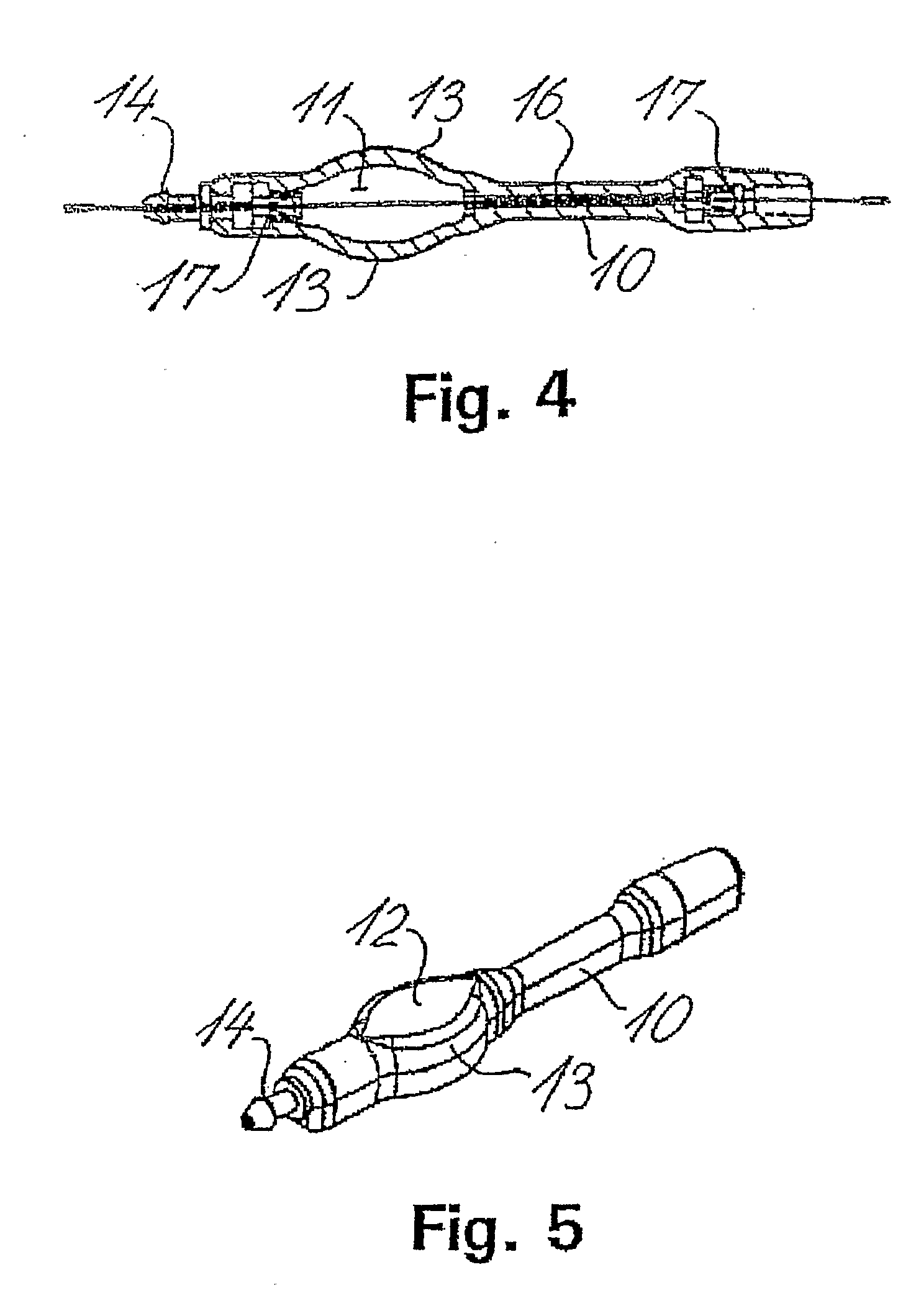
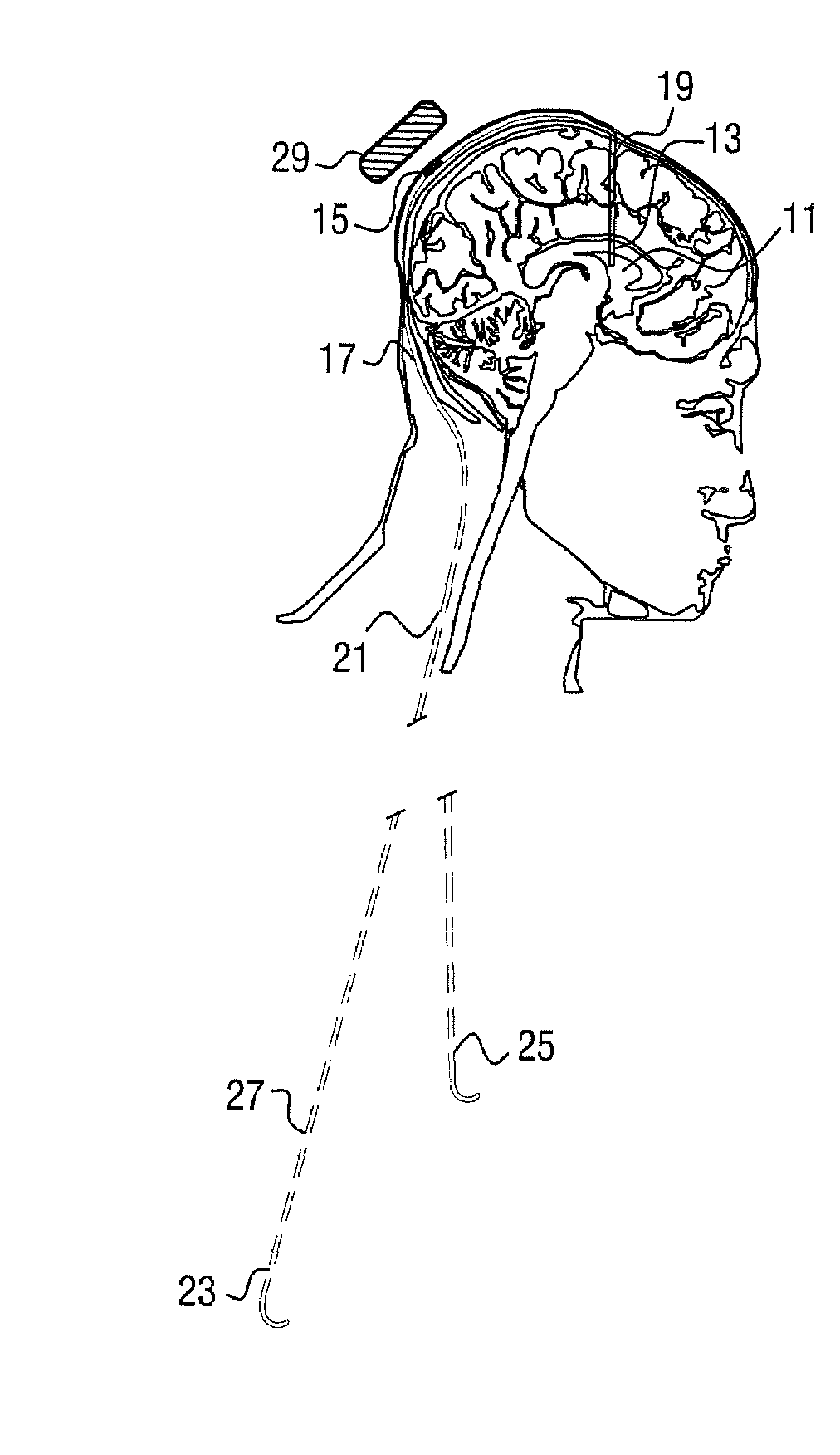
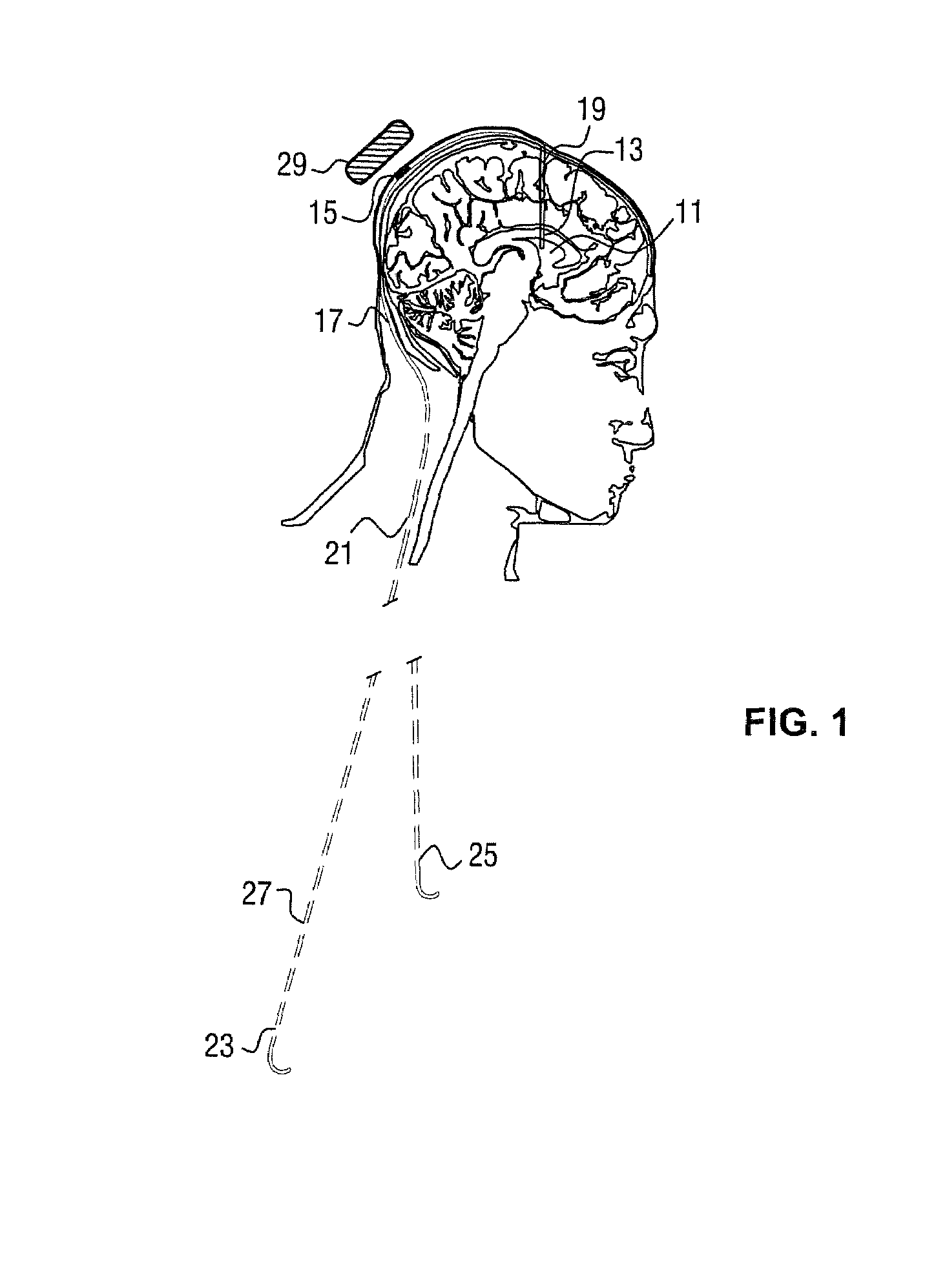
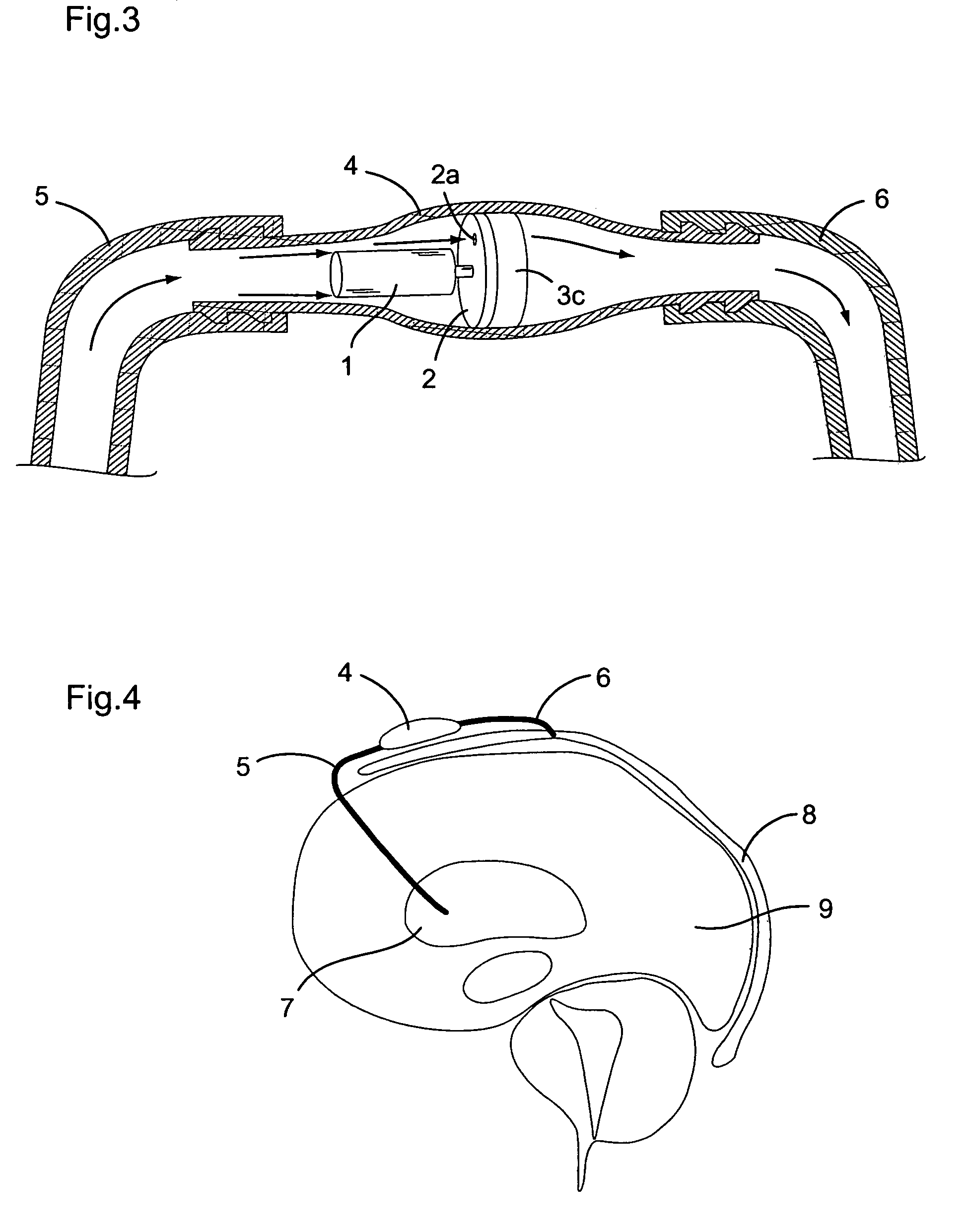
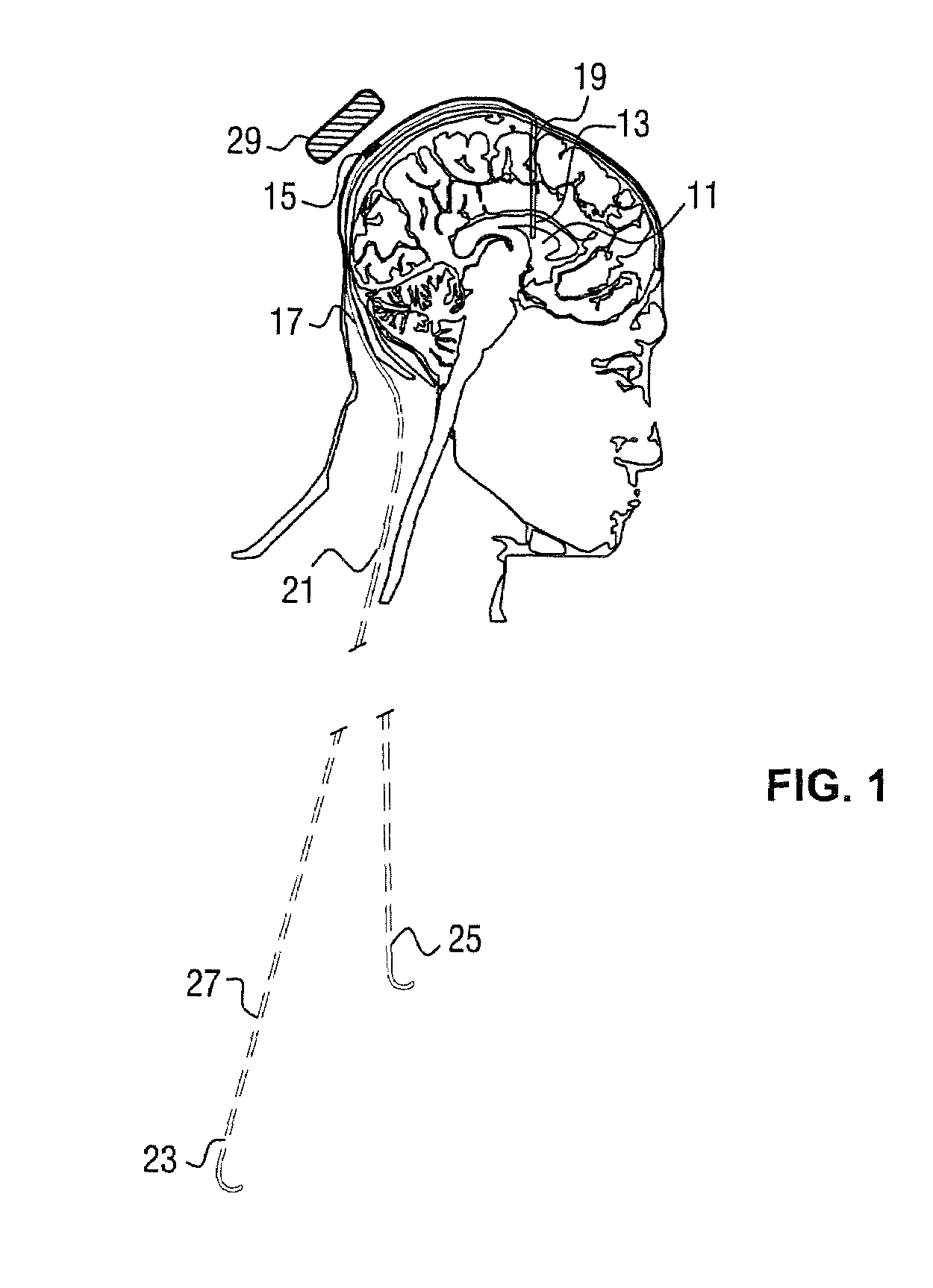
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricle catheter (15) to insert into the brain ventricle (21) so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle, a sinus catheter (18) to insert into the sinus sagittalis system (22) for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into the sinus sagittalis system, a shunt body member (10) connected at one end thereof to said brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to said sinus catheter system to provide fluidic communication between said brain ventricle catheter (15) and said sinus catheter (18), and a flow restriction (16) defined within the shunt body member (10) to maintain a resistance to fluid flow of the shunt system of less than 8 mm Hg / ml / min, such as 2-7 or 4-6 and preferably about 5 mm Hg / ml / min. When the shunt system is implanted the shunt body member (10) is placed subcutaneously on top of the calvarium of a patient, behind the coronal suture on one of side of the sagittal suture. One end of each of the catheters (15, 18) is then connected to a respective end of the shunt body member (10), and a second end of each catheter is inserted in the right ventricle (21) and in the sinus sagittalis system (22), respectively, via holes bored in the scull (19).
Owner:CSF DYNAMICS
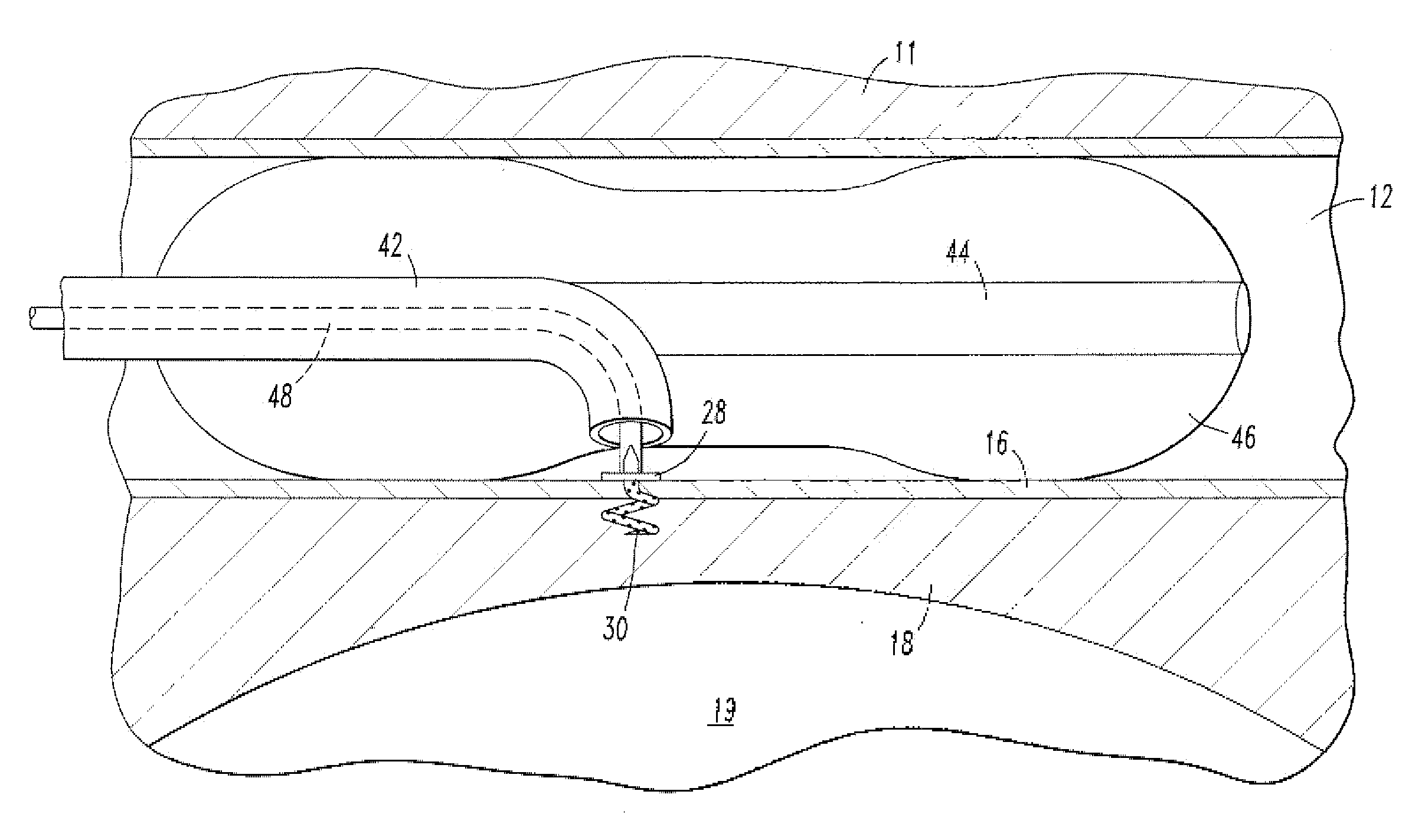
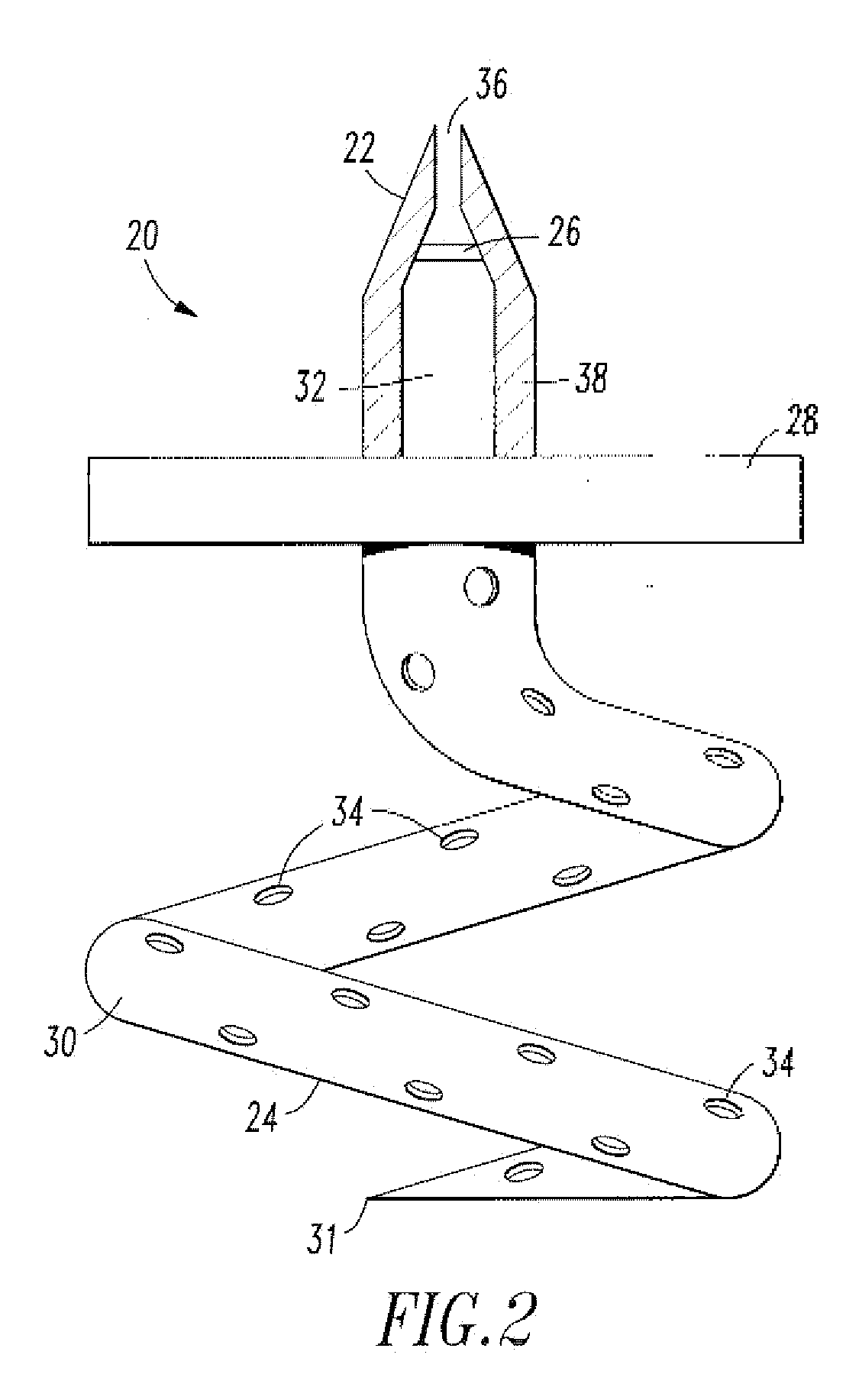
Endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20100191168A1More physiologic drainageWound drainsMedical devicesShunt DeviceSubarachnoid space
An implantable shunt device for draining cerebrospinal fluid from a patient's subarachnoid space. The device includes a shunt having opposed first and second ends. A one-way valve is located at the first end of the shunt. A helical tip is disposed at the second end. The helical tip is constructed to penetrate a sinus wall of the patient. Upon implantation, a hollow passageway extends between the helical tip and one-way valve such that fluid can be drained through the helical tip and out through the valve. The endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt of the present invention can be placed into a patient percutaneously via a catheter inserted into the venous system of the body through a needle hole, without the need for open surgery and the skin incisions required with current shunt devices. The device also allows for more physiologic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid since the device is shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the same cerebral venous system that occurs naturally in normal people.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
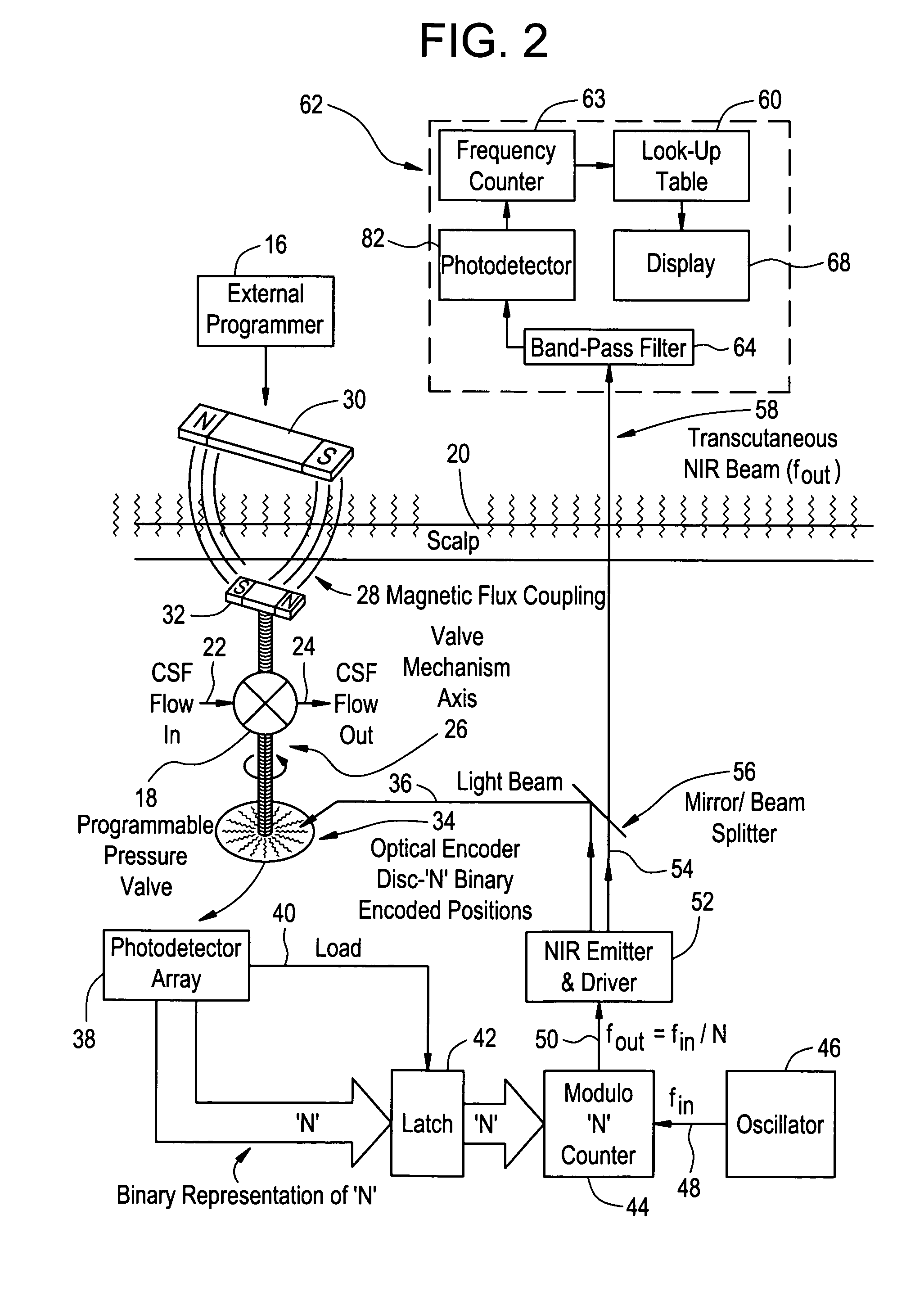
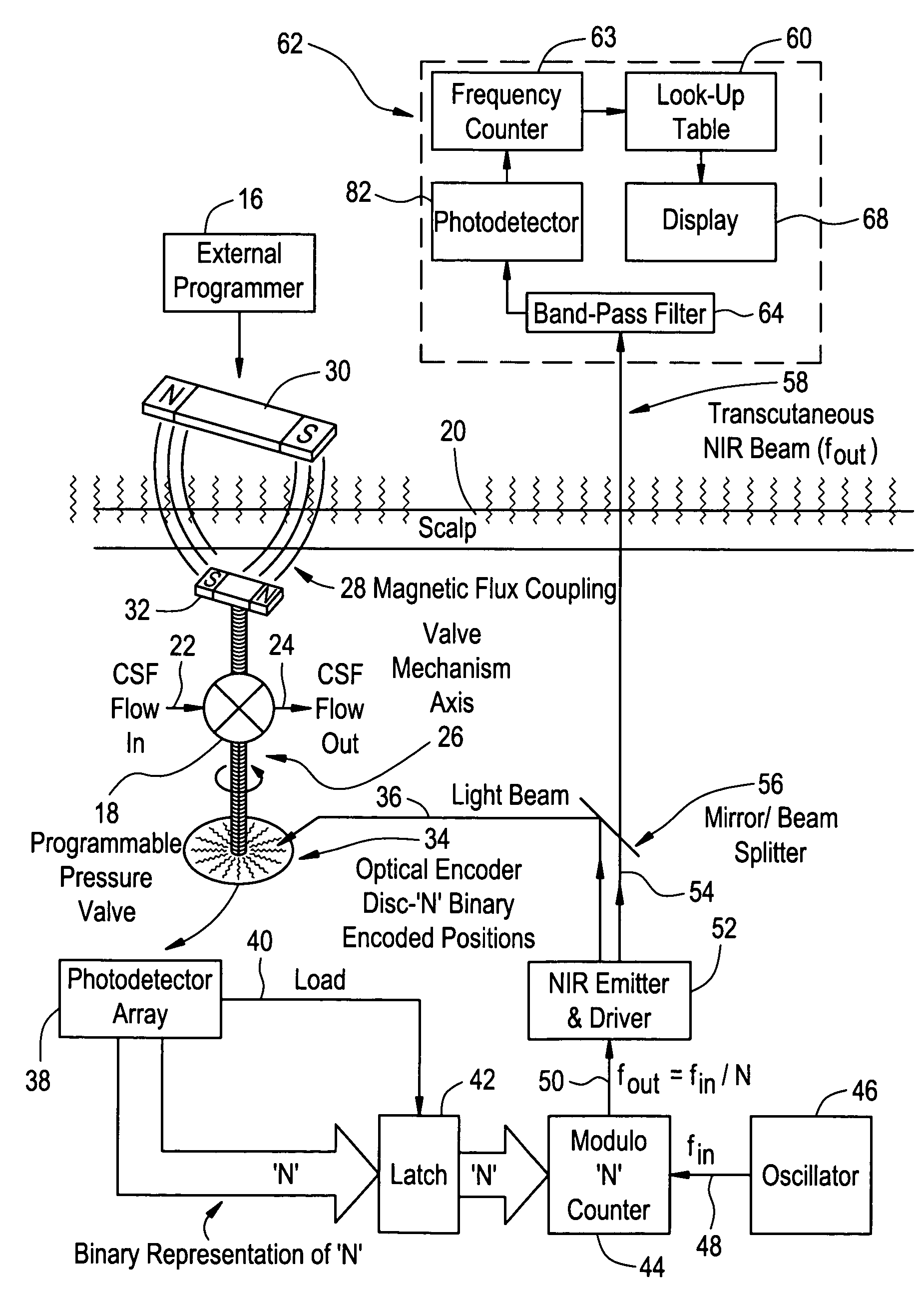
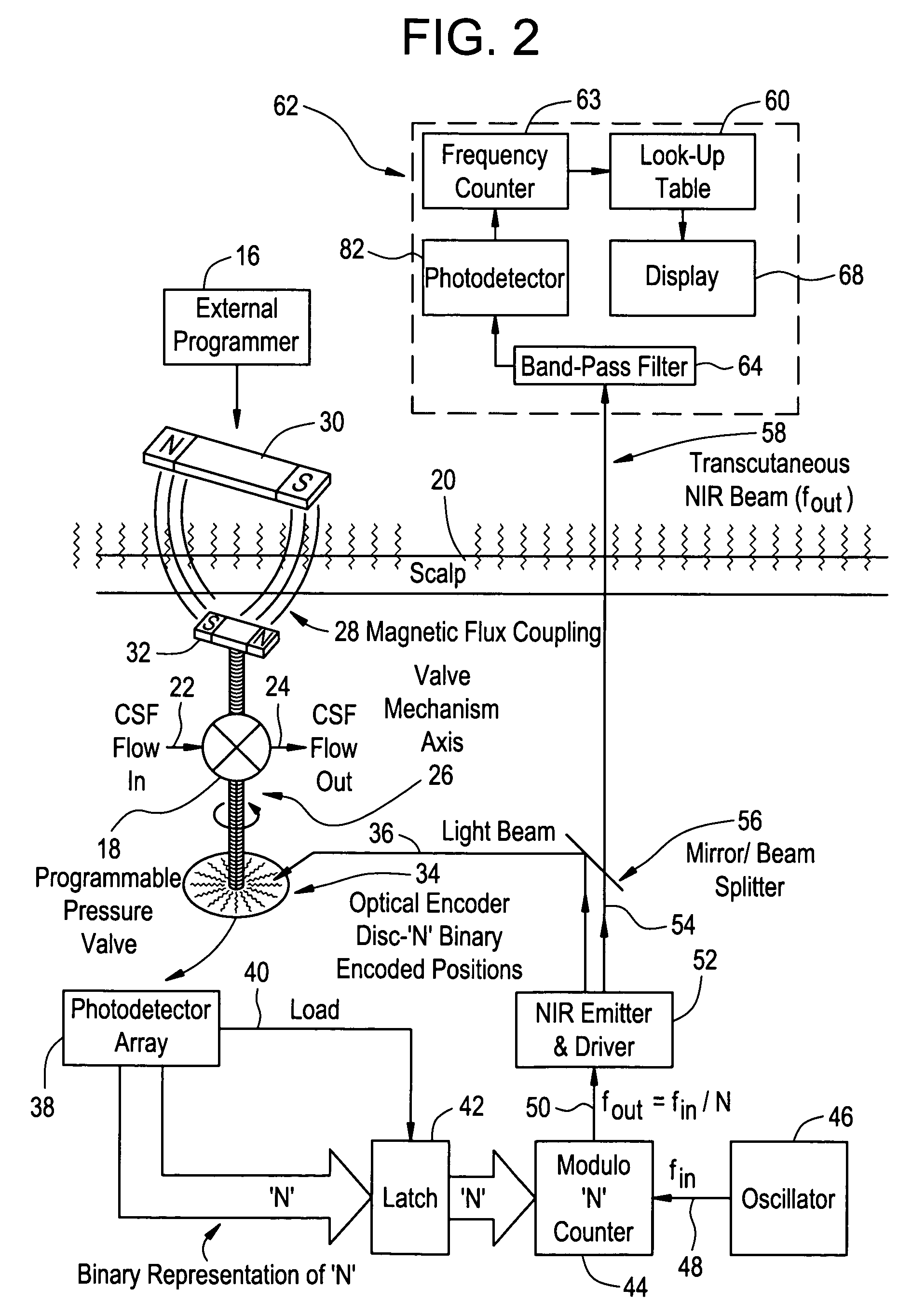
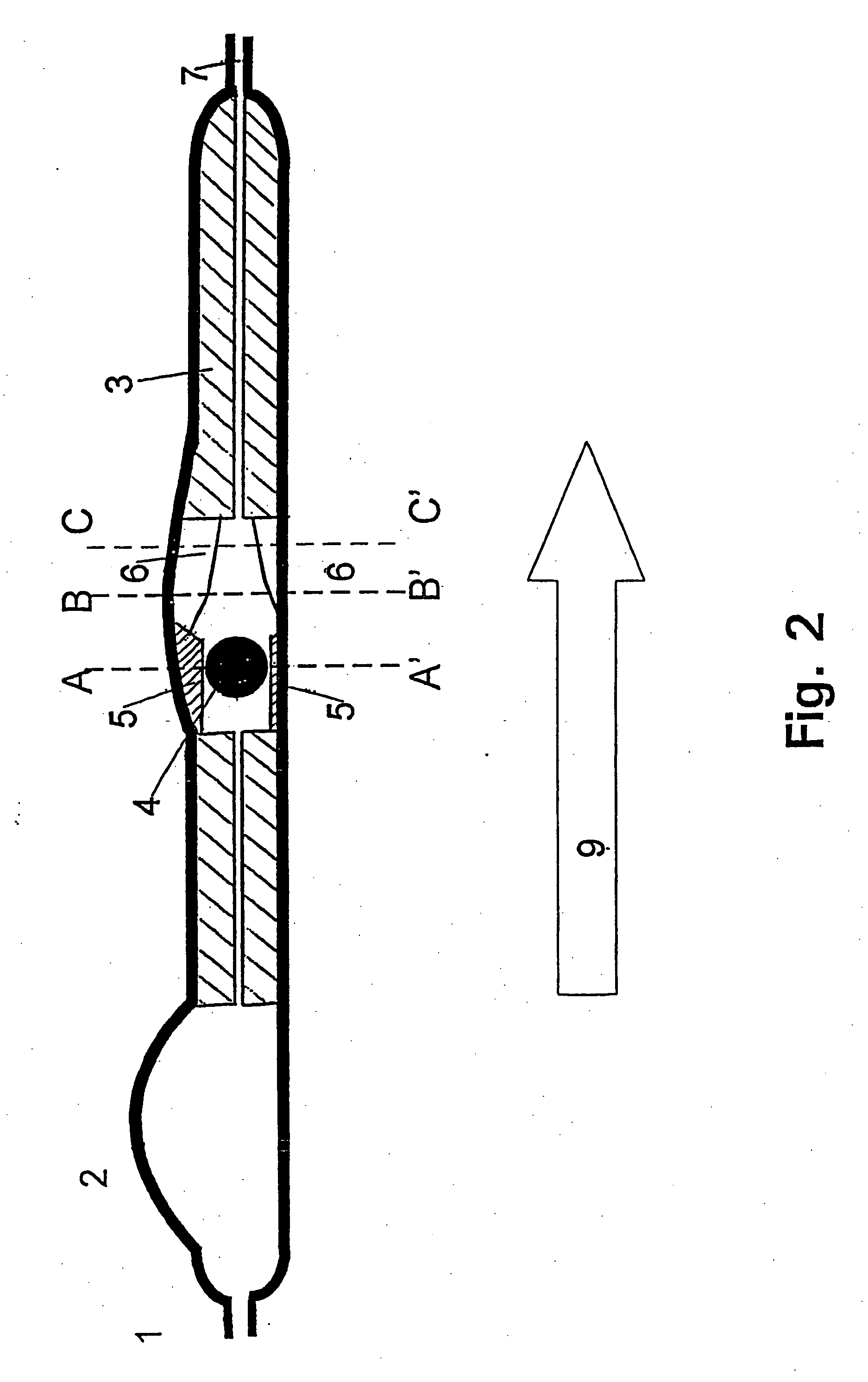
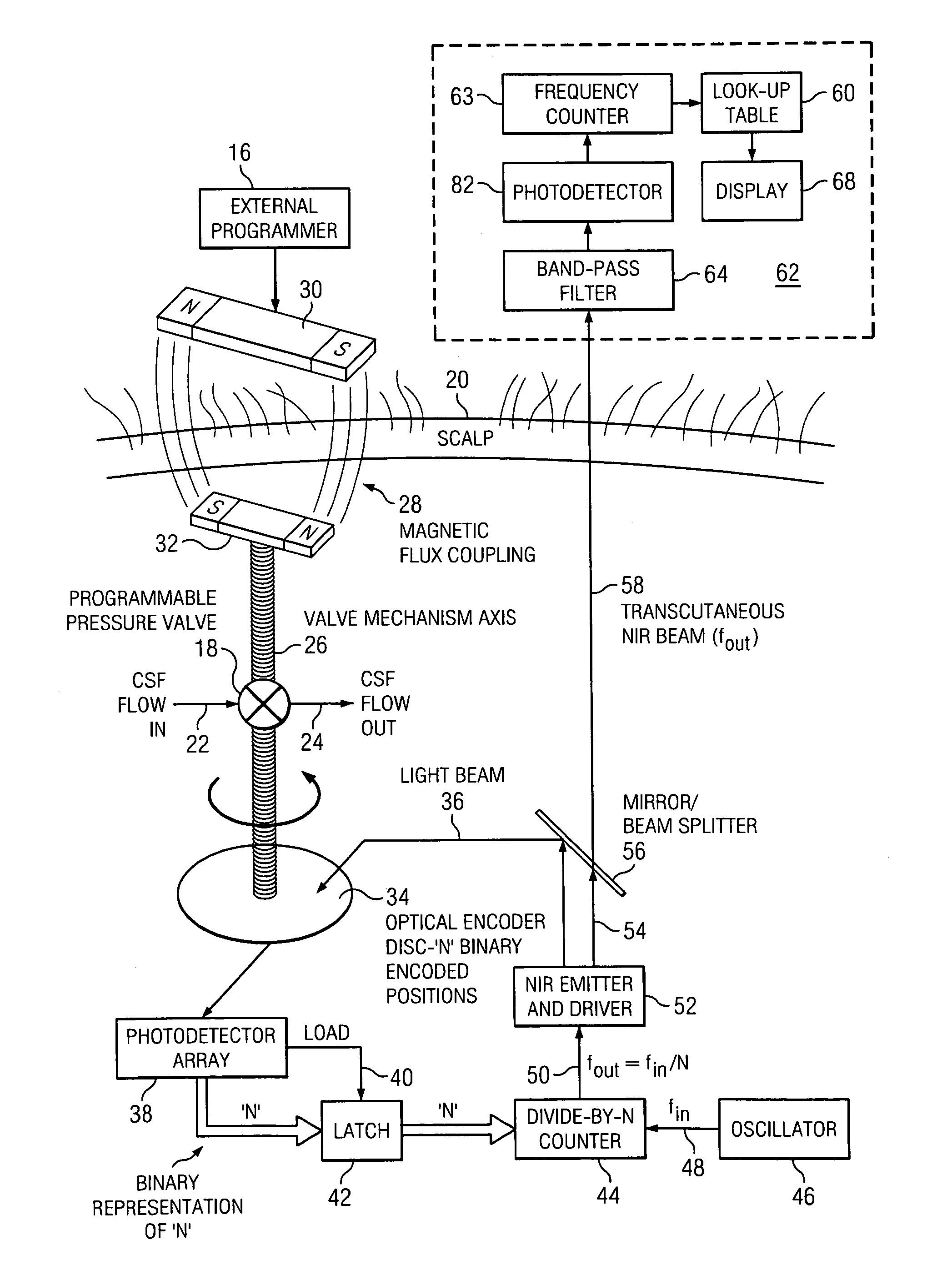
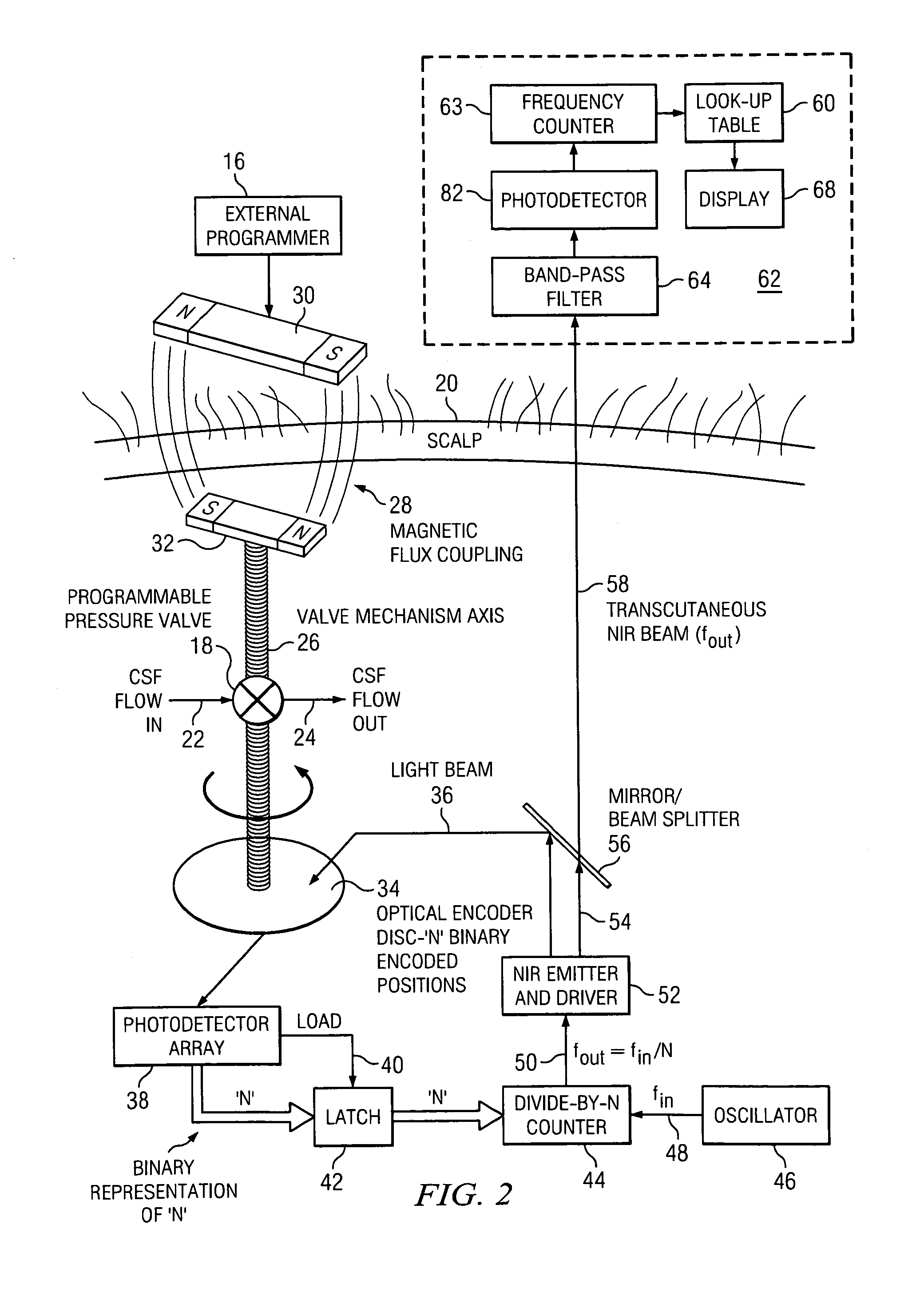
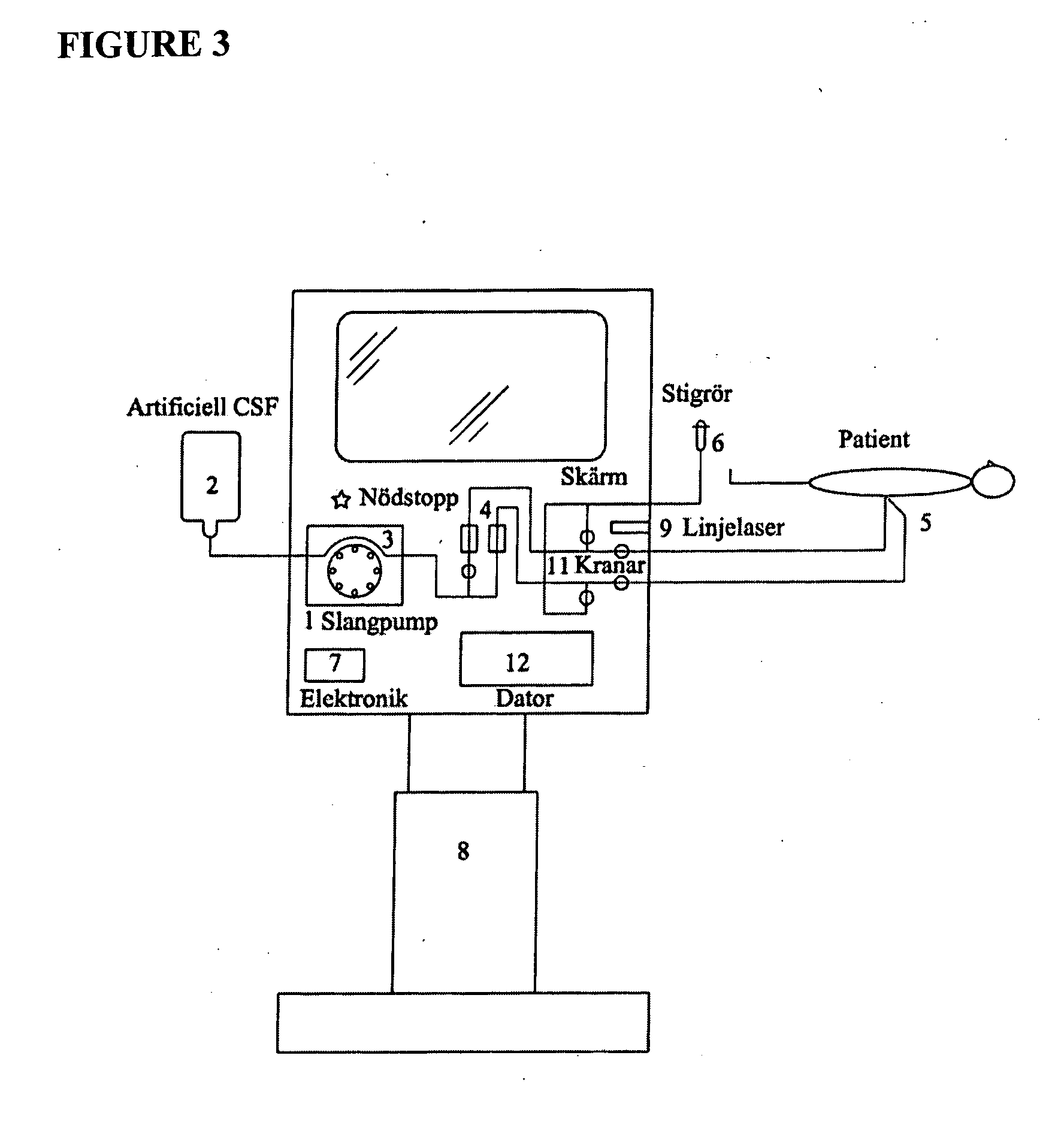
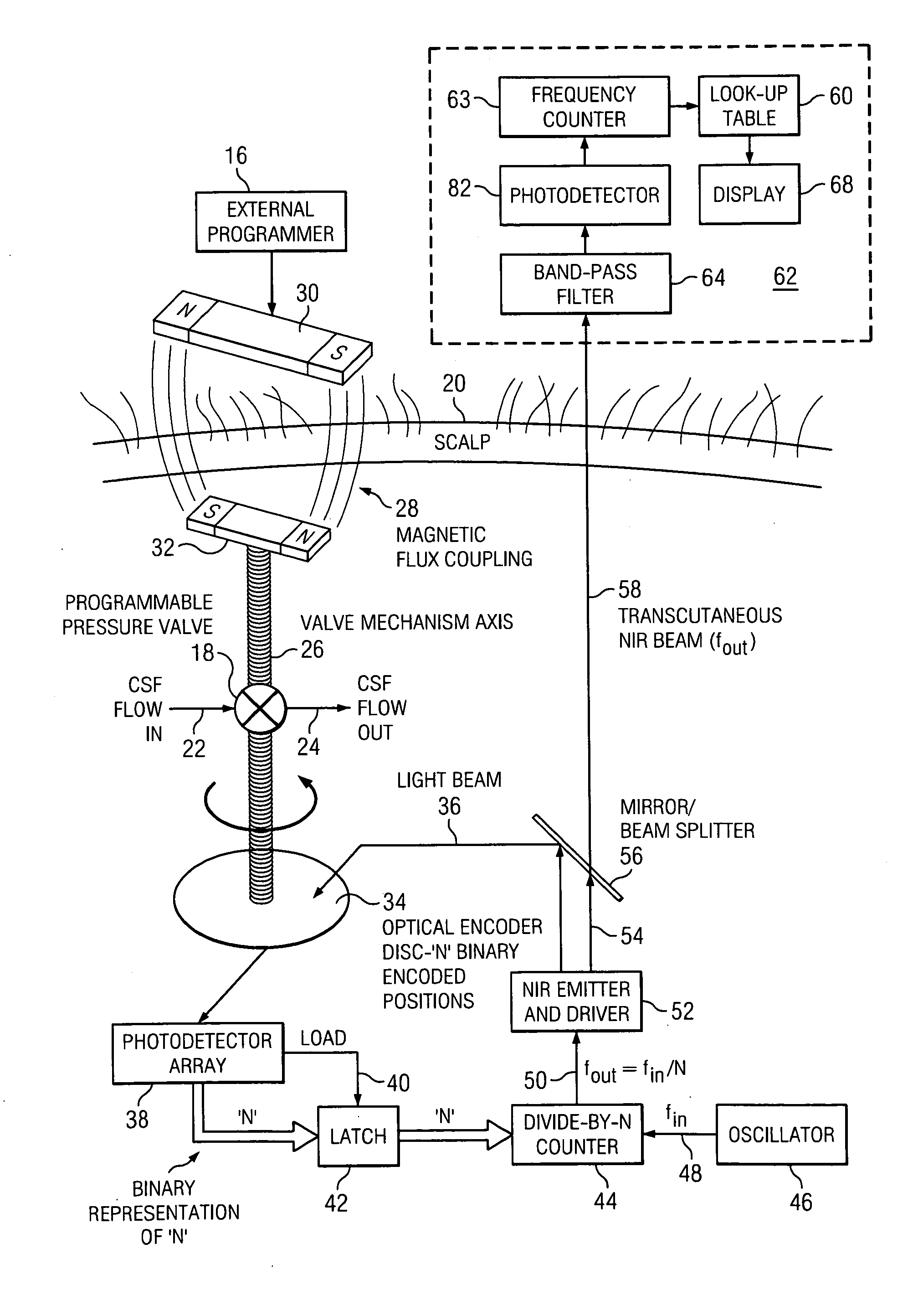
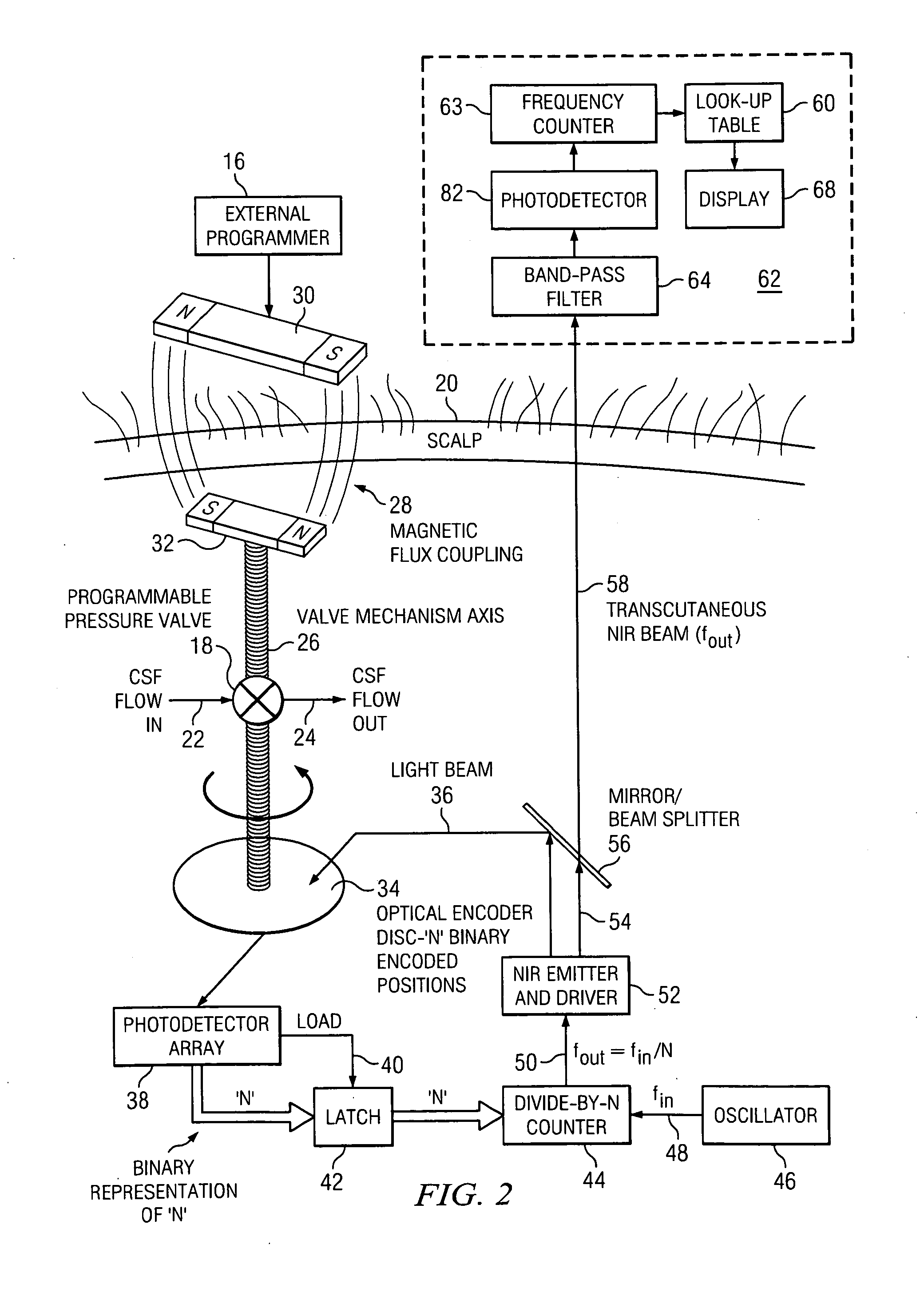
Transcutaneous telemetry of cerebrospinal fluid shunt programmable-valve pressure using near-infrared (NIR) light
InactiveUS20050187509A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsInfraredAbdominal cavity
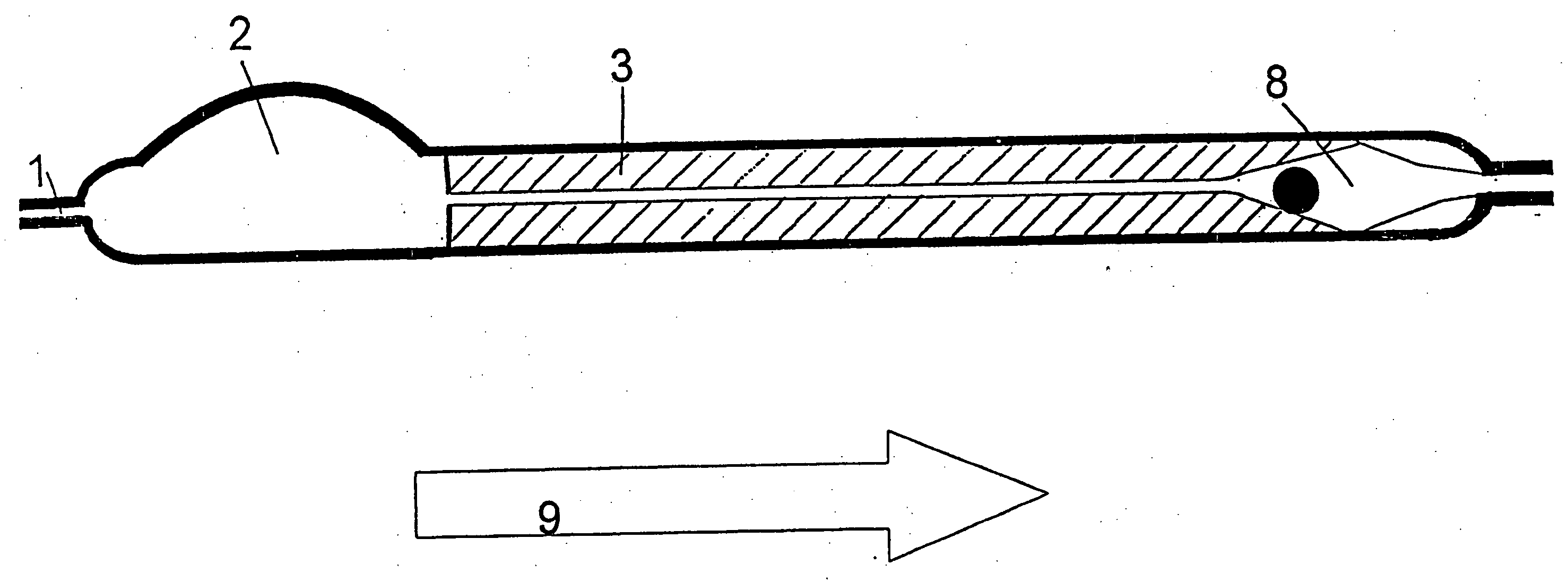
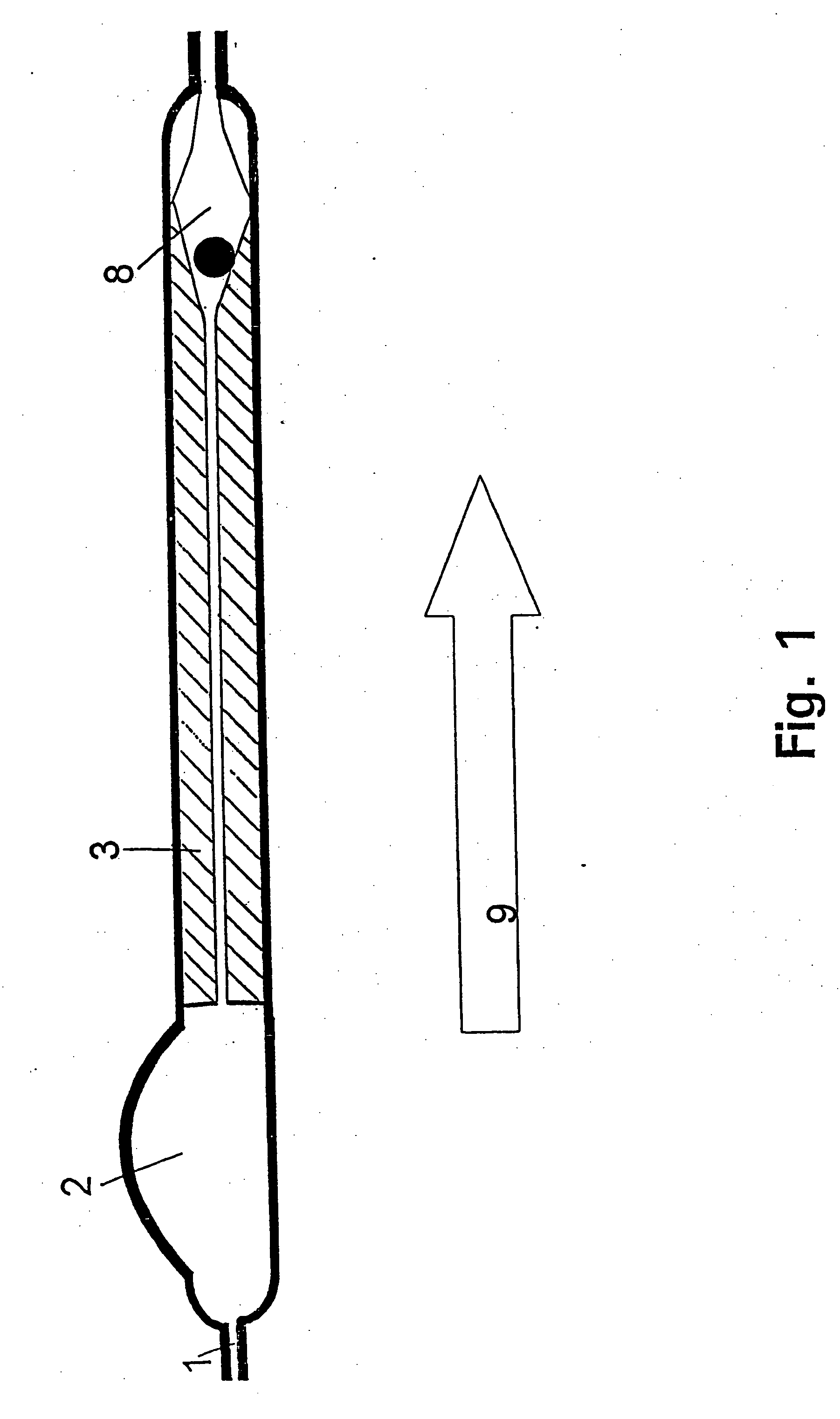
An improvement for a programmable valve system of the type which is implanted in a medical patient and used to divert cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from an intraventricular space of the patient to a terminus such as the patient peritoneal cavity. Such system includes means for establishing a flow path for the CSF to the terminus, which flow path includes a normally closed valve and means for adjusting the opening pressure of the valve in order to regulate the quantity of CSF diverted. The improvement enables an operator to be apprised of the actual opening pressure setting of the valve. A sensor is implantable at the patient and responds to the actual opening pressure setting, by generating an NIR telemetry signal indicative of the actual setting. This signal is transcutaneously transmitted through the skin of the patient to an external point. The telemetry signal is processed to produce observer intelligible data indicating the opening pressure setting of the valve.
Owner:WOLF ERICH W
Implantable anti-clogging device for maintenance of cerebrospinal fluid shunt patency
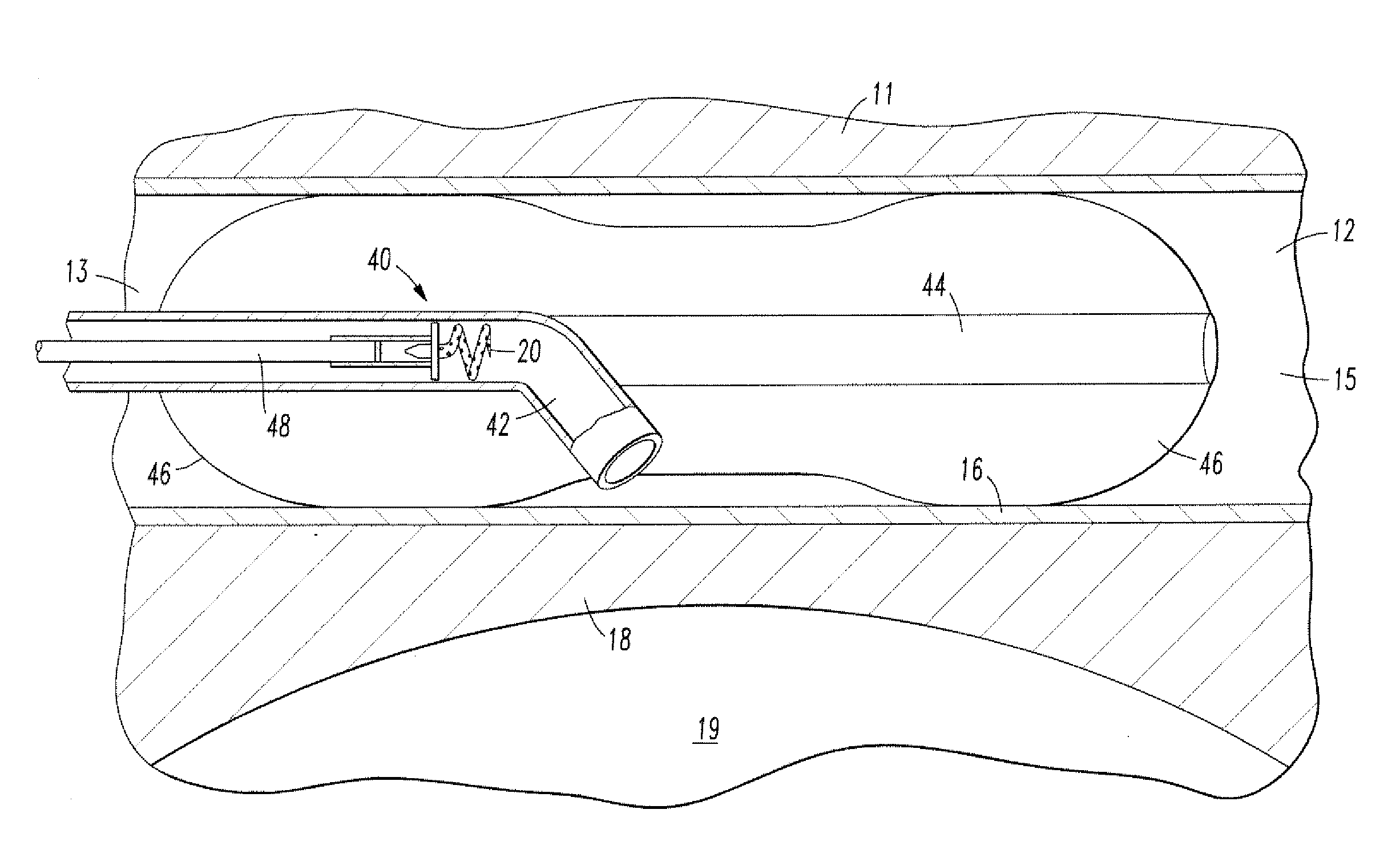
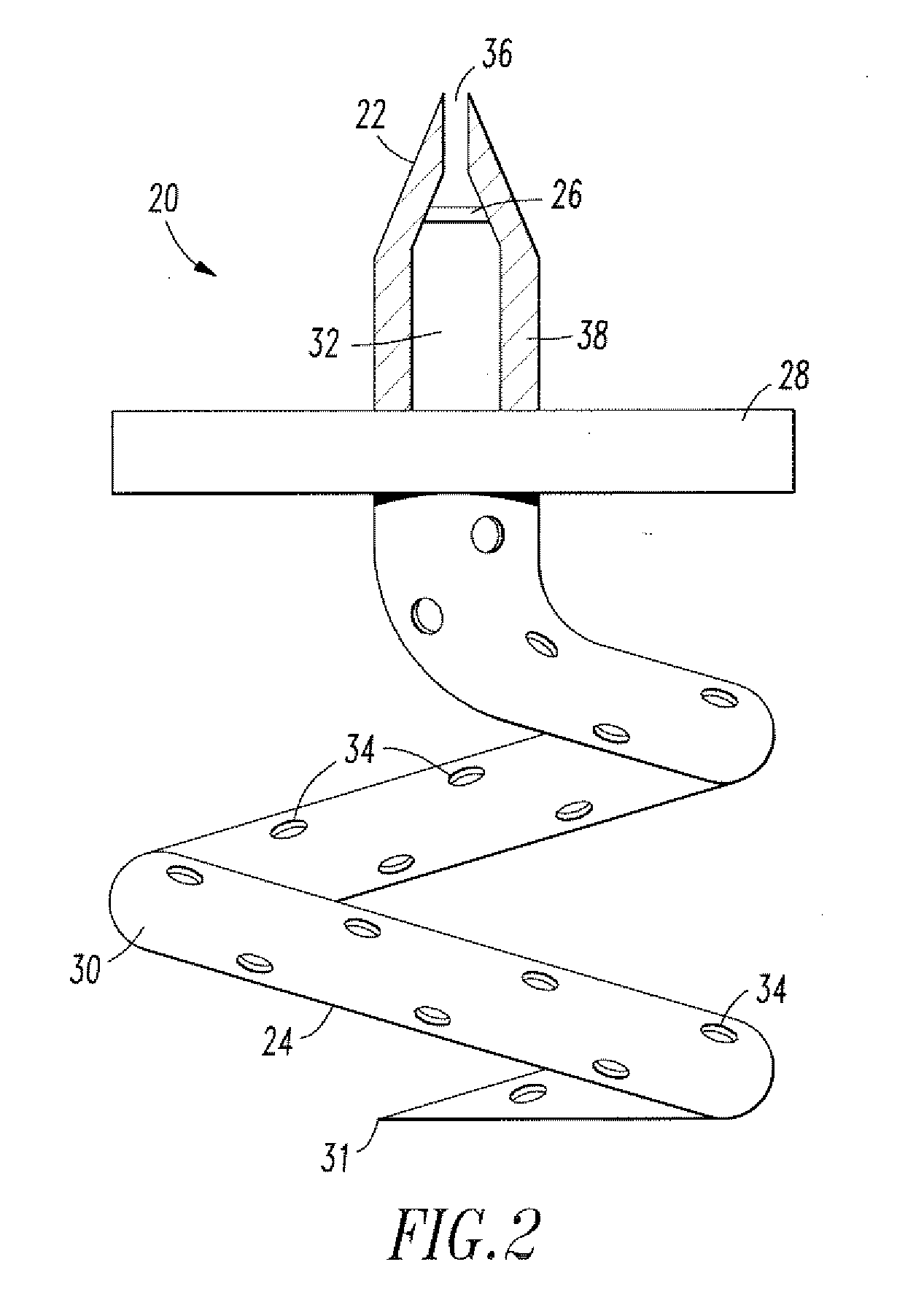
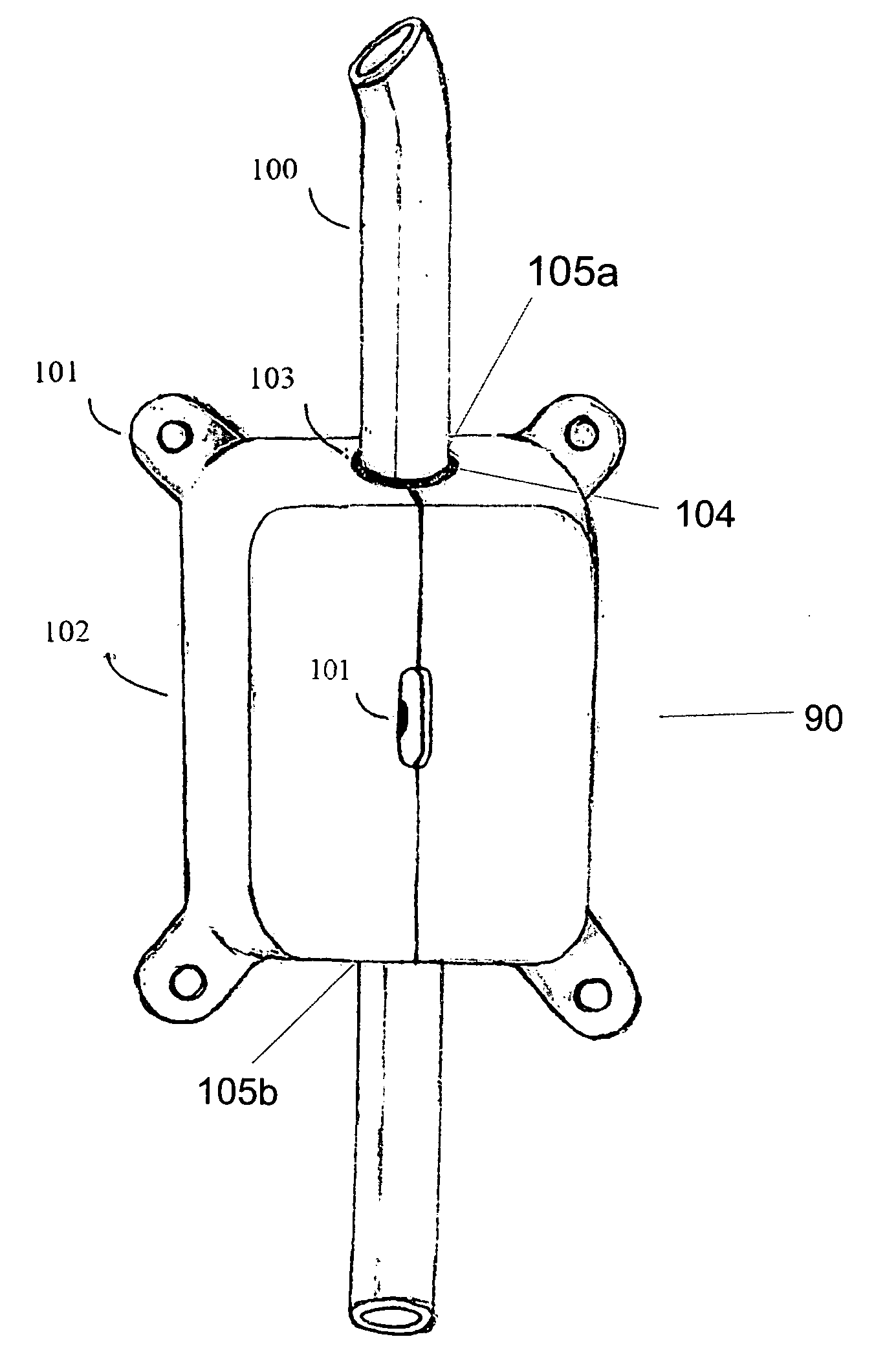
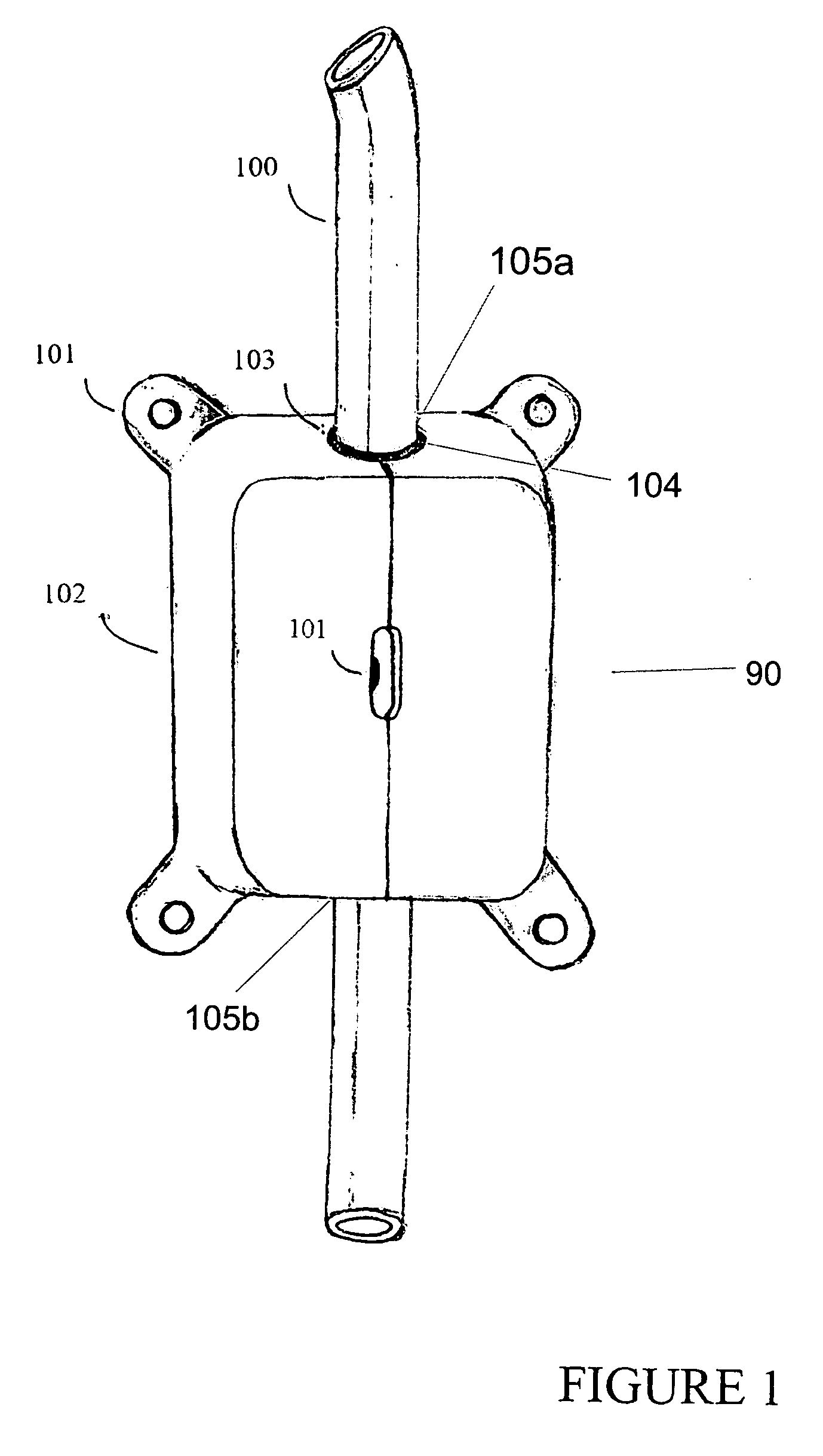
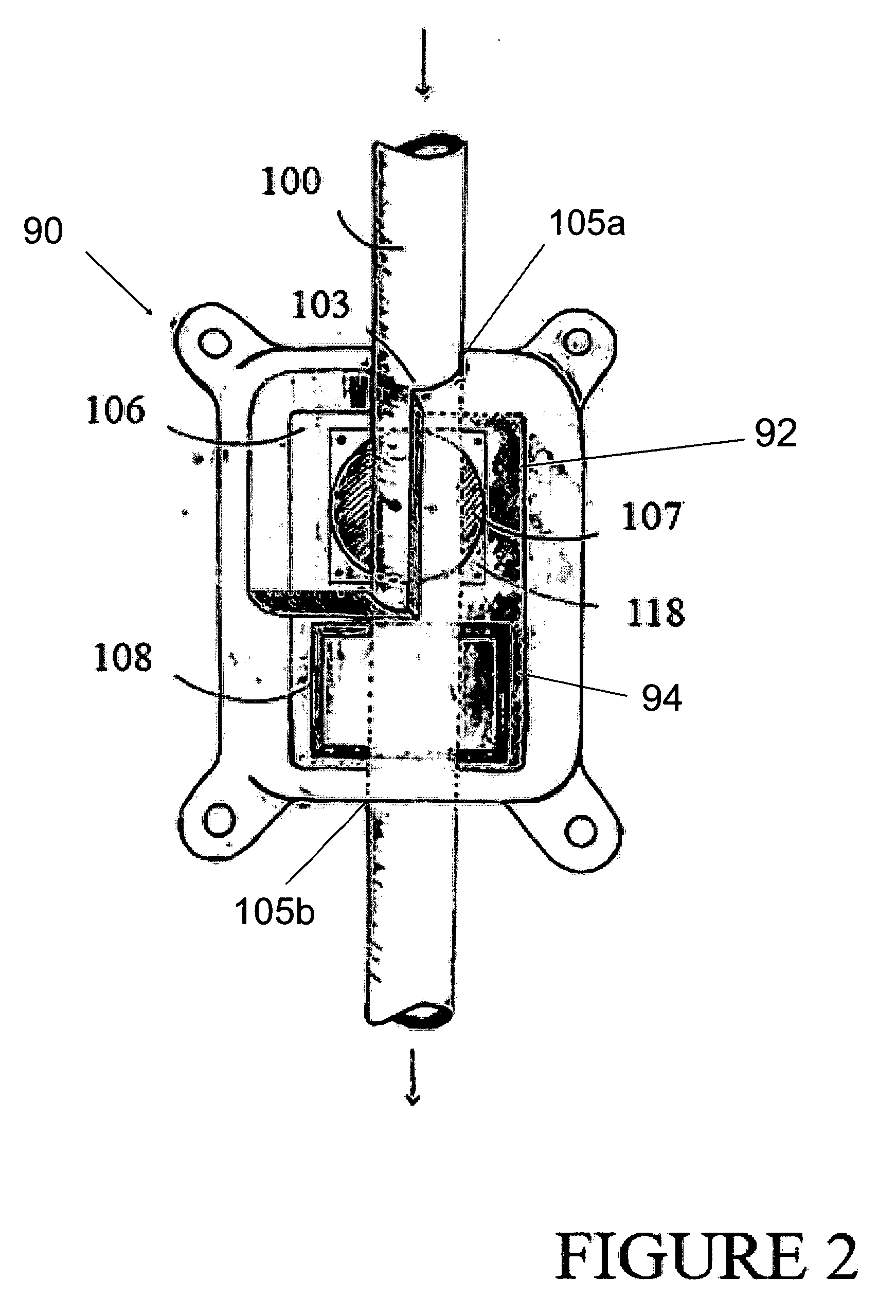
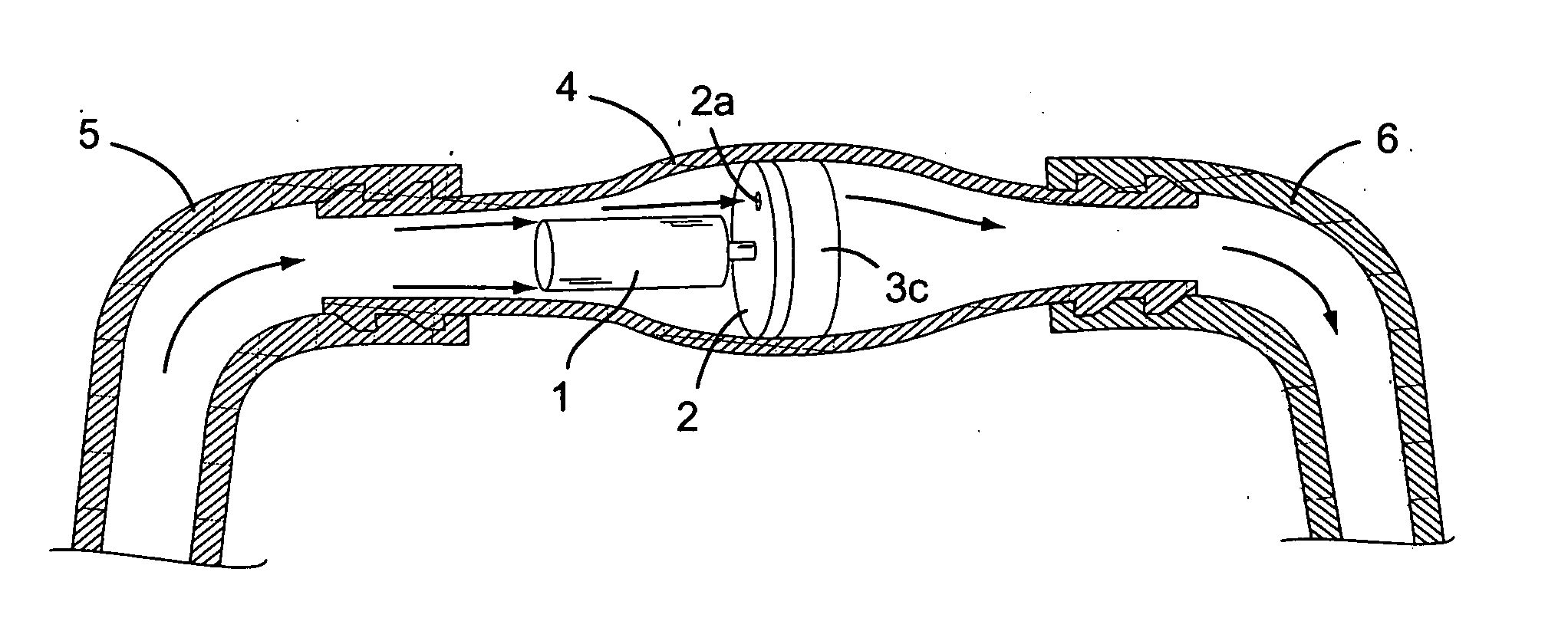
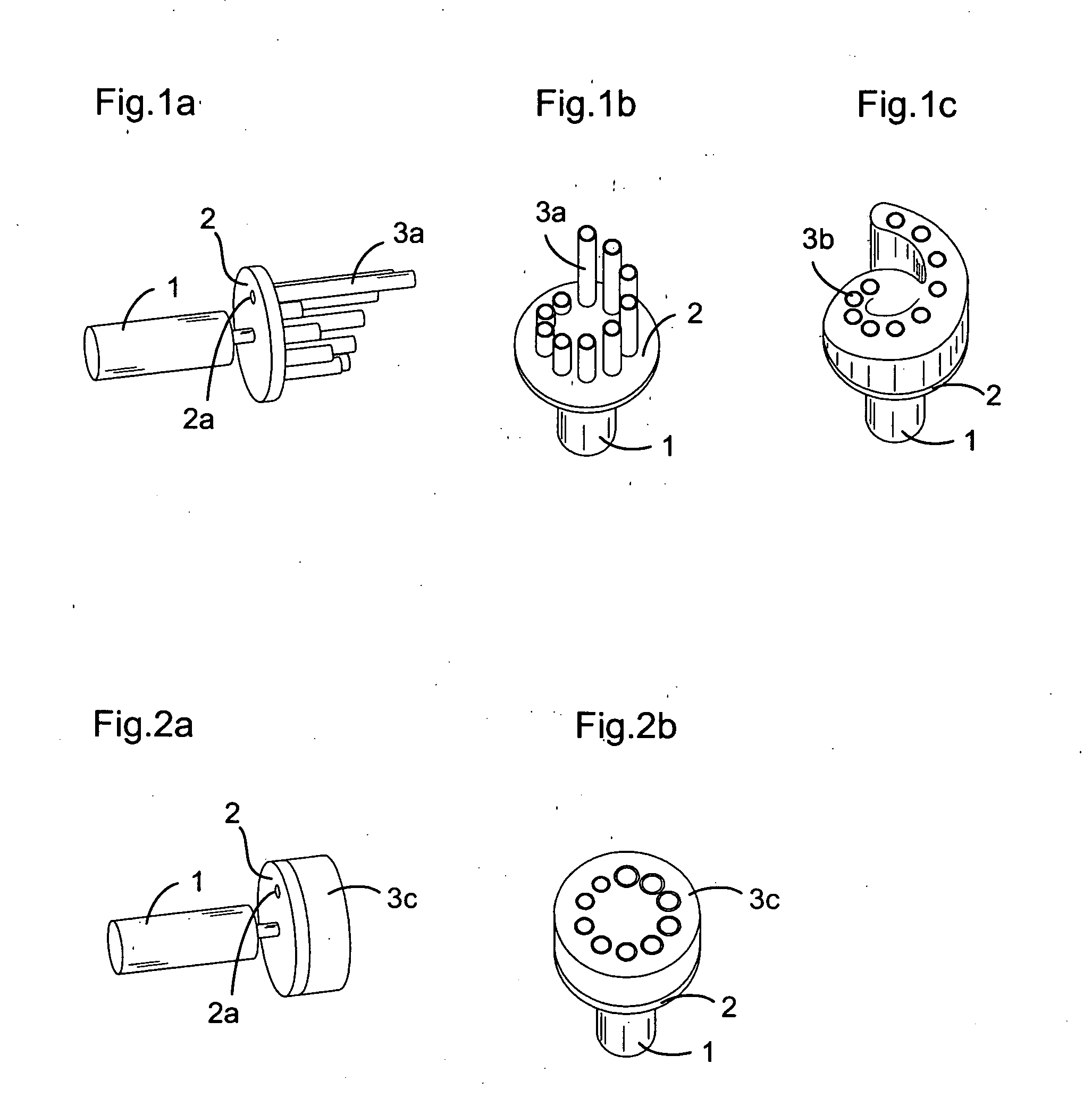
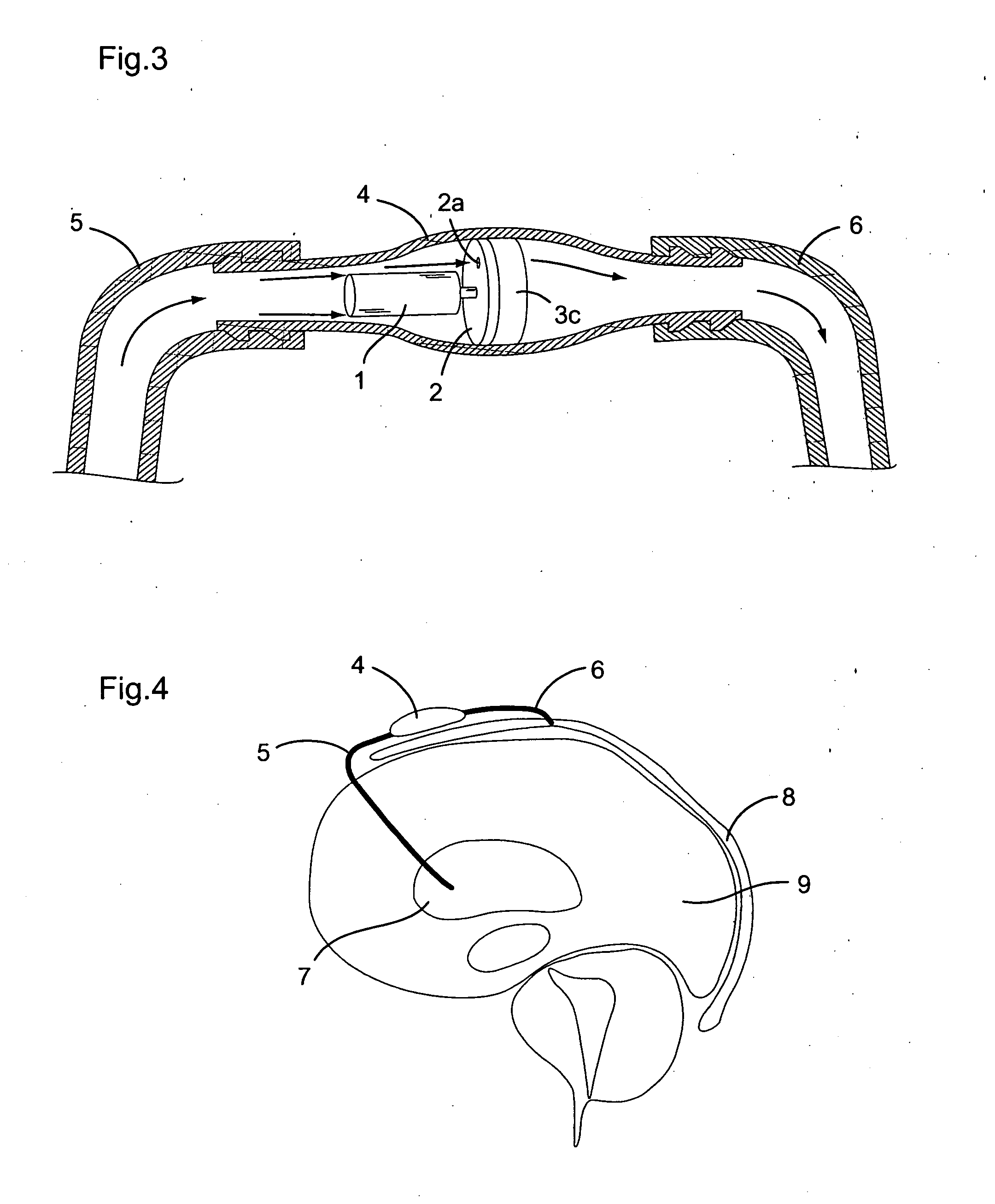
Cerebrospinal fluid shunts (implantable devices for diversion of excess fluid from the brain to other body cavities) used to treat hydrocephalus often malfunction. A common etiology of shunt malfunction is obstruction of the distal catheter tip by accumulating particulate matter such as fat or proteinaceous debris. The proposed implantable device maintains the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt with mechanical energy which serves to “scrub” the catheter lumen of particulate debris. The proposed device accomplishes this by housing a source of mechanical energy which is coupled to the external aspect of the catheter, itself traversing through a bore in the device. The energy source secondarily induces a waveform in the cerebrospinal fluid flowing through the catheter. The fluid waveform exerts shearing forces on the catheter wall and serves to disrupt the formation and accumulation of debris that potentially could occlude the shunt catheter, thereby maintaining patency of the shunt.
Owner:OSBORN BRETT +1
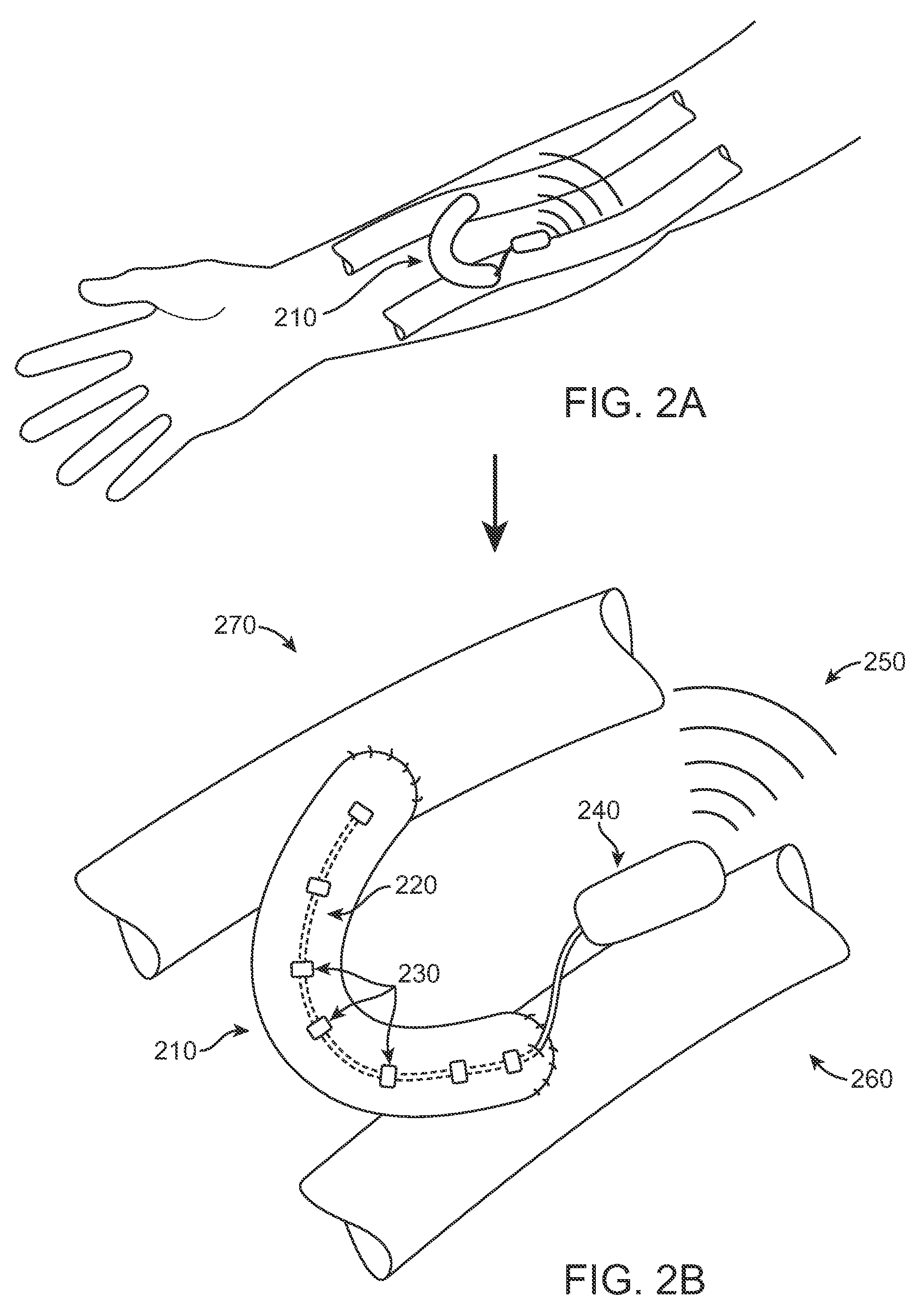
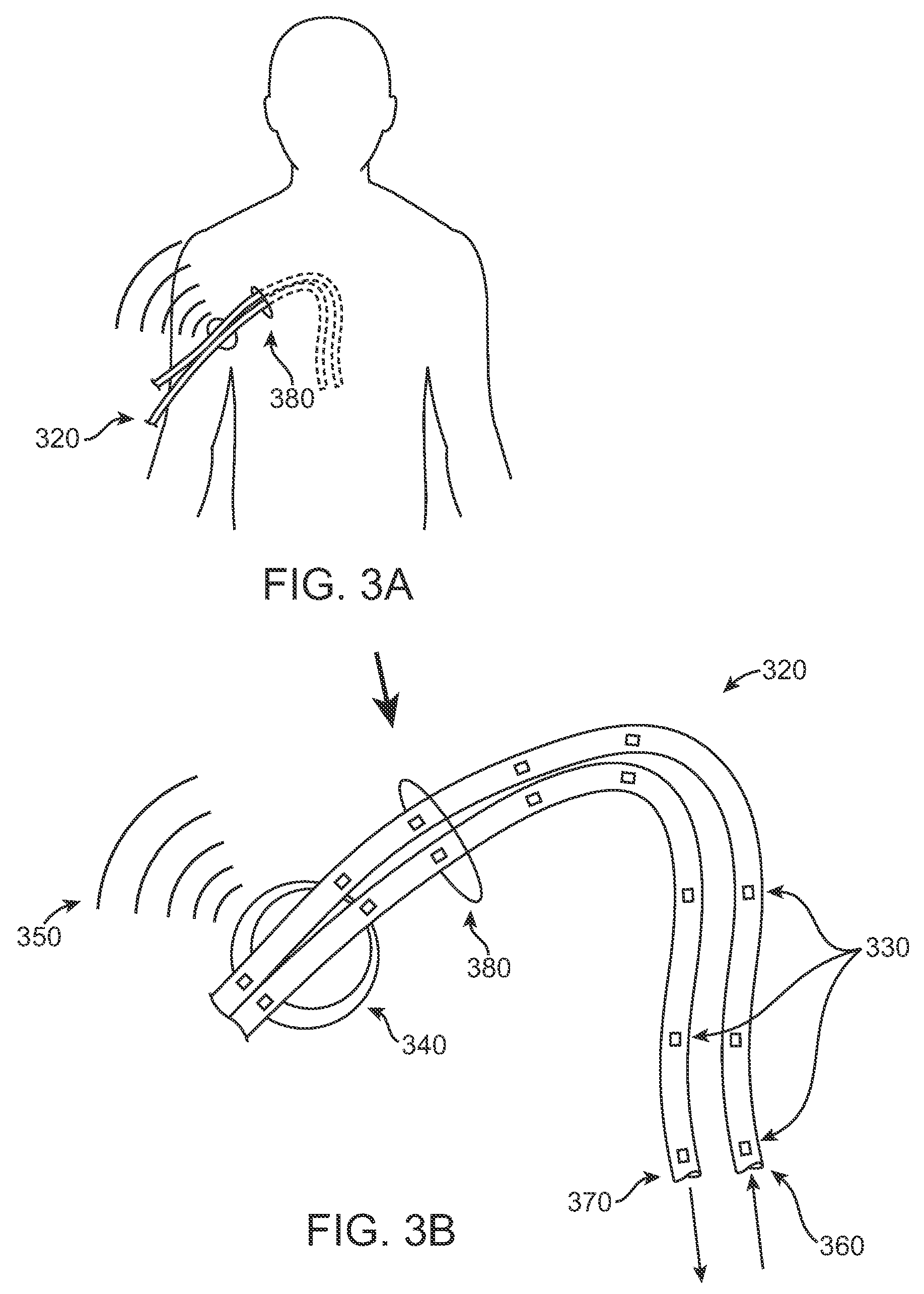
Body-associated fluid transport structure evaluation devices
Implantable devices for evaluating body-associated fluid transport structures and methods for using the same are provided. In some instances, the implantable devices include an elongated structure with at least one hermetically sealed integrated circuit sensor stably associated therewith and a transmitter. The devices find use in a variety of different applications, including monitoring the function of various types of body-associated fluid transport structures, such as arteriovenous fistulae, vascular grafts, catheters, cerebrospinal fluid shunts, and implantable central venous access devices.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt having long term Anti-occlusion agent delivery
The invention includes a shunt for at least partial implantation into a patient that includes an elongated conduit having at least one lumen therethrough, that includes a proximal end for receipt of bodily fluids for flow through the shunt and a distal end for discharge of the bodily fluids from the shunt, and a long term source of at least one occlusion resistant agent, wherein said at least a portion of the at least one occlusion resistant agent can permeate through at least a portion of the elongated conduit. The invention also includes kits and systems.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
Owner:SINU SHUNT
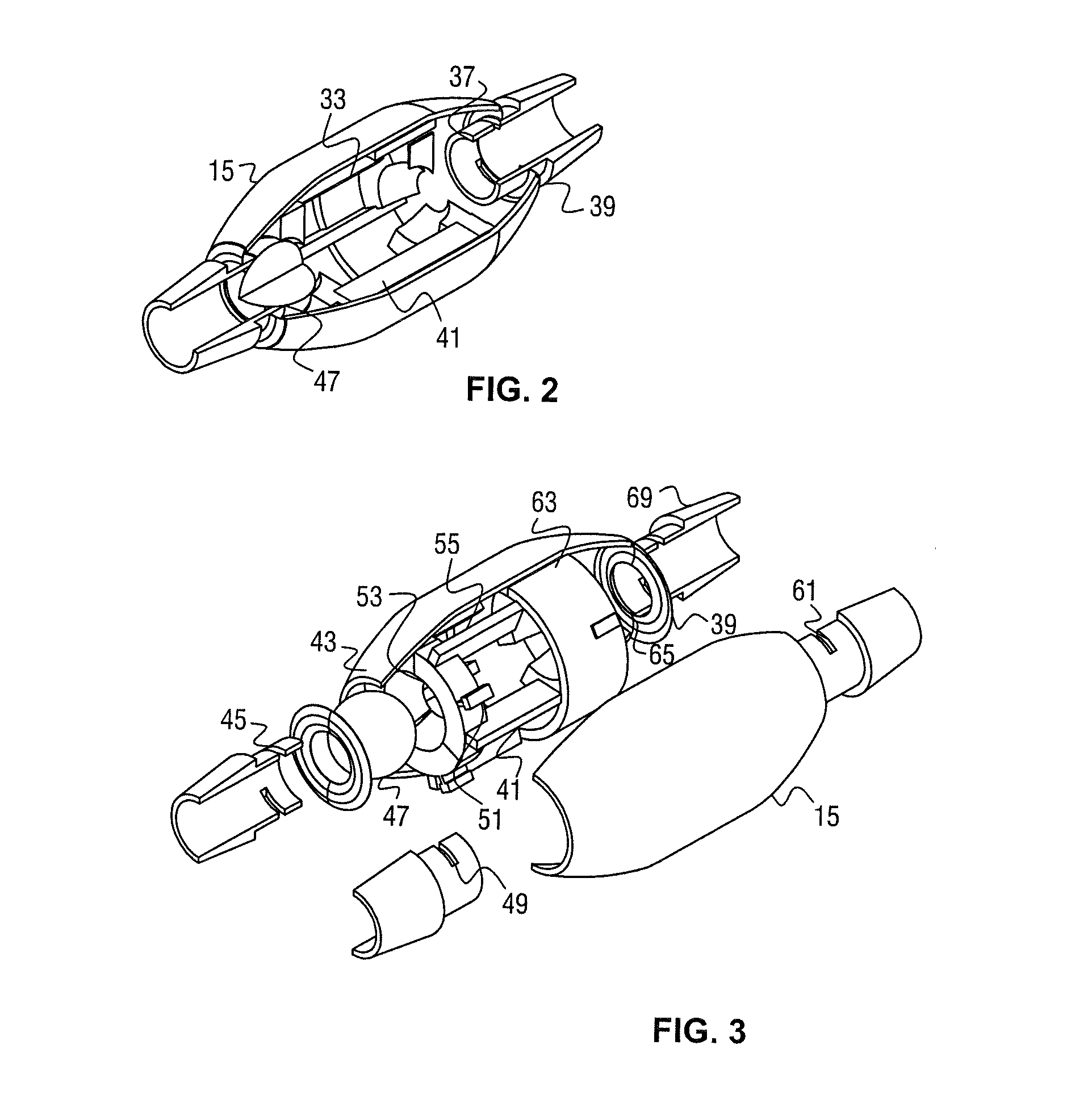
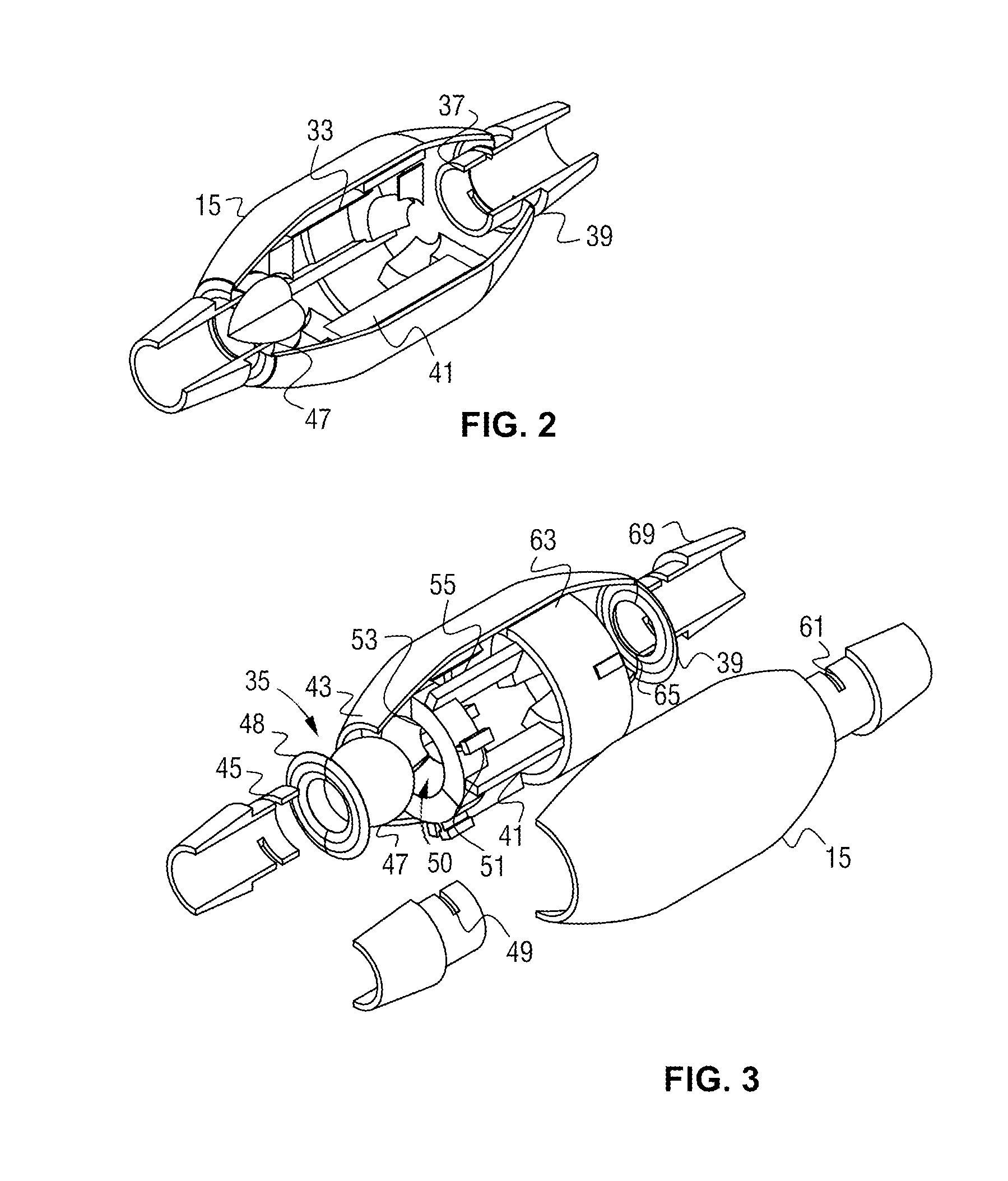
Adjustable resistance valve for a cerebrospinal fluid shunt system
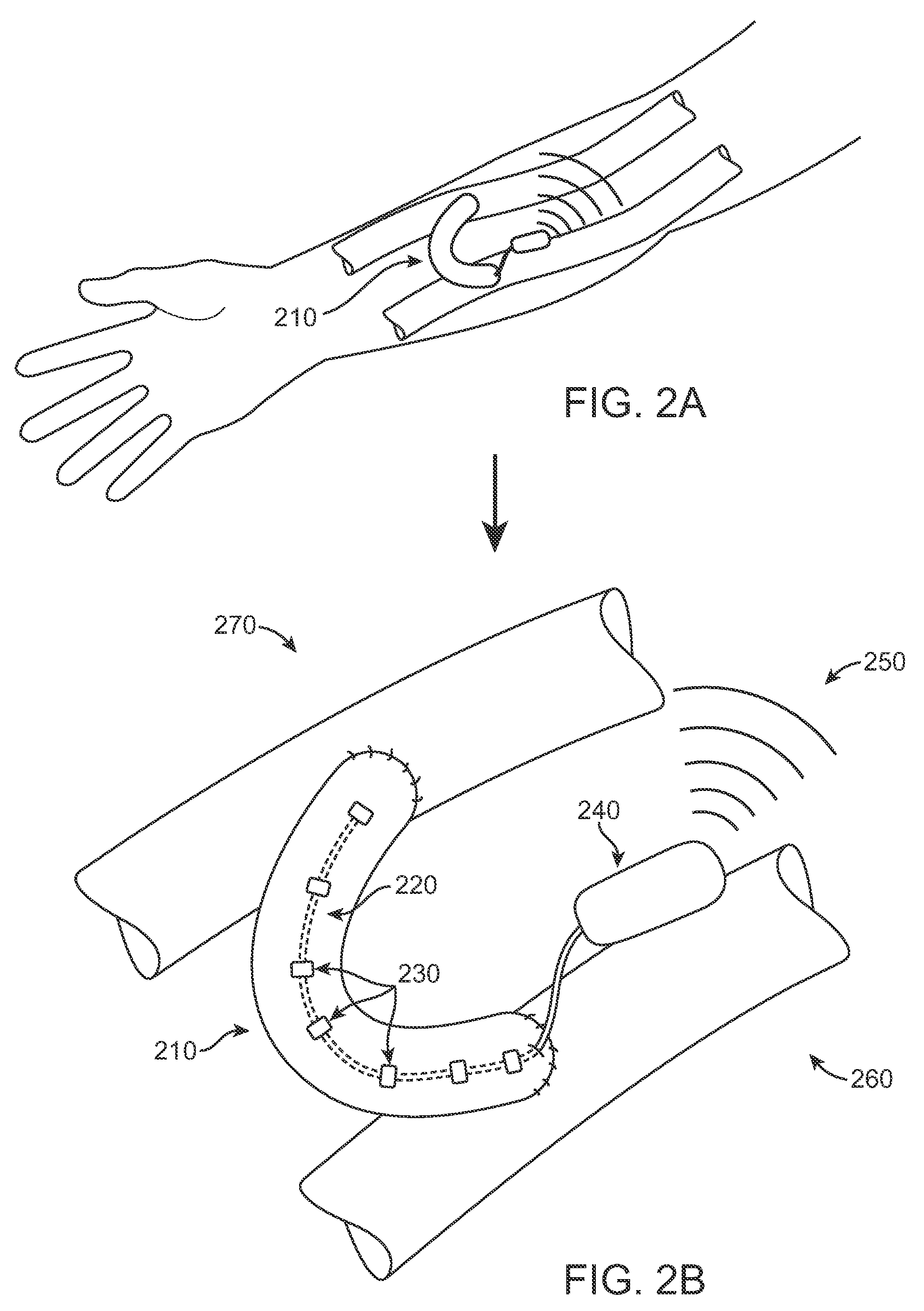
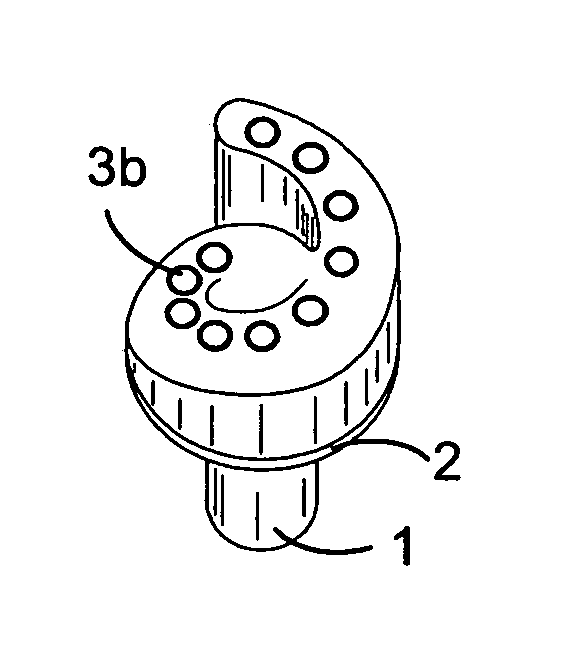
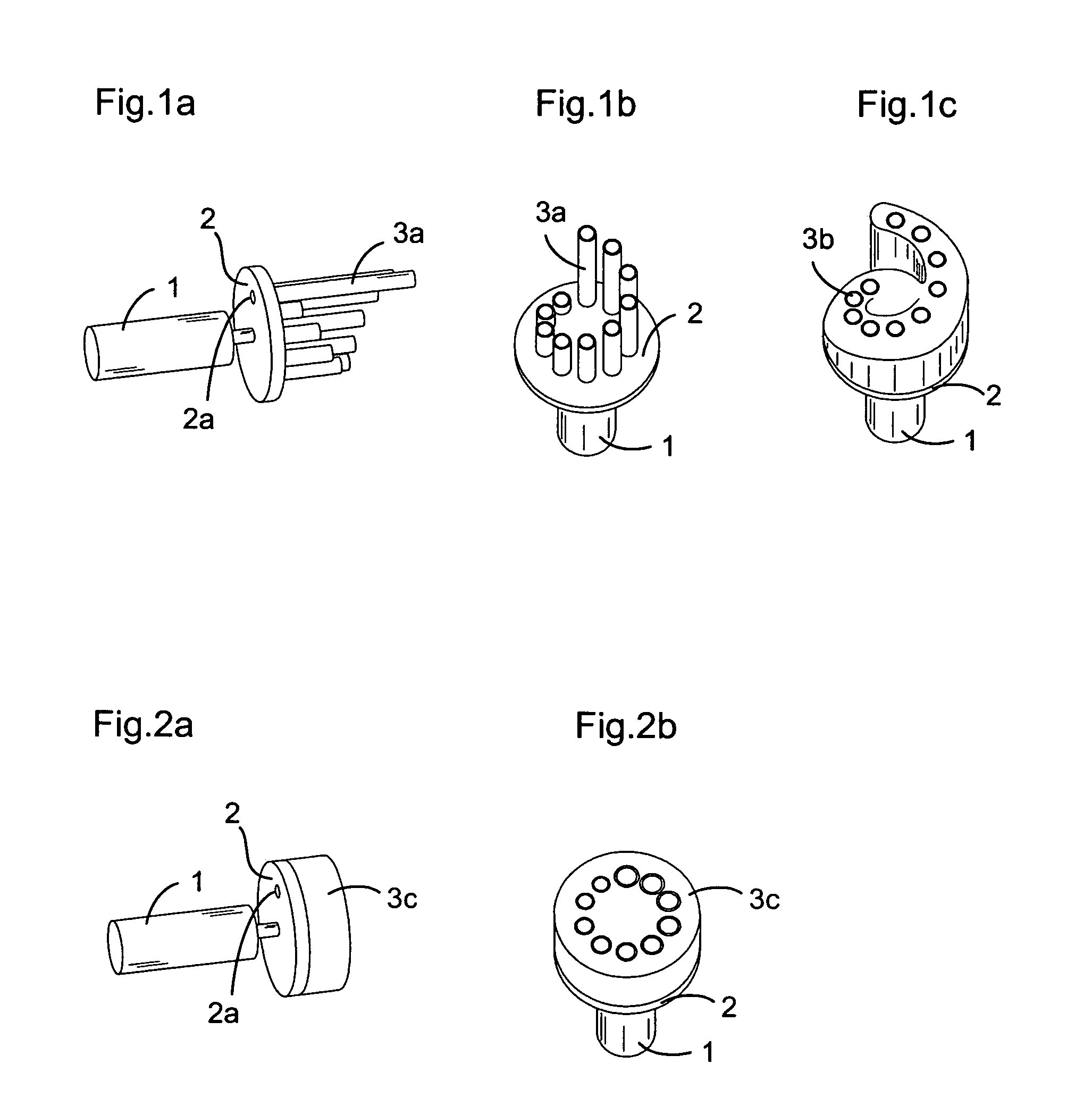
An adjustable resistance valve for a cerebrospinal fluid shunt system includes an actuator for allowing the selection of the resistance to flow of the valve, a device for selecting at least one passage traversing across the valve, and a resistance system. The resistance system includes a set of passages each defining a different resistance to flow. The passages are disposed in a circle facing the selecting device such as to guide the flow of the cerebrospinal fluid traversing the passage of the selecting device through the selected passage of the resistance system. The actuator enables one to change the relative position of the selecting device with respect to the resistance system by a rotational movement to select the desired resistance of the valve.
Owner:MEDOSA
Transcutaneous telemetry of cerebrospinal fluid shunt programmable-valve pressure using near-infrared (NIR) light
InactiveUS7485105B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsInfraredEmergency medicine
An improvement for a programmable valve system of the type which is implanted in a medical patient and used to divert cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from an intraventricular space of the patient to a terminus such as the patient peritoneal cavity. Such system includes means for establishing a flow path for the CSF to the terminus, which flow path includes a normally closed valve and means for adjusting the opening pressure of the valve in order to regulate the quantity of CSF diverted. The improvement enables an operator to be apprised of the actual opening pressure setting of the valve. A sensor is implantable at the patient and responds to the actual opening pressure setting, by generating an NIR telemetry signal indicative of the actual setting. This signal is transcutaneously transmitted through the skin of the patient to an external point. The telemetry signal is processed to produce observer intelligible data indicating the opening pressure setting of the valve.
Owner:WOLF ERICH W
Electroactive polymer actuated cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20080125690A1Reduce in quantityAvoid possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesInternal pressureVentricular catheters
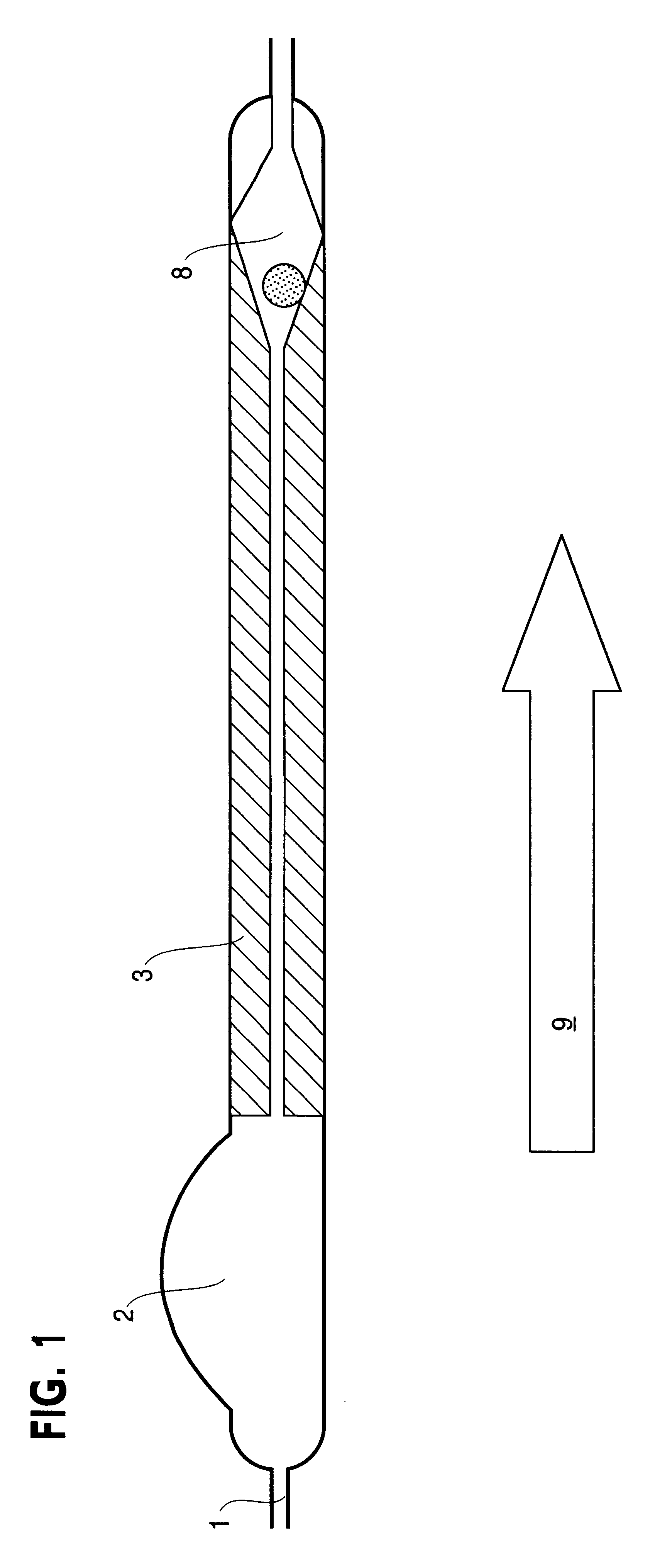
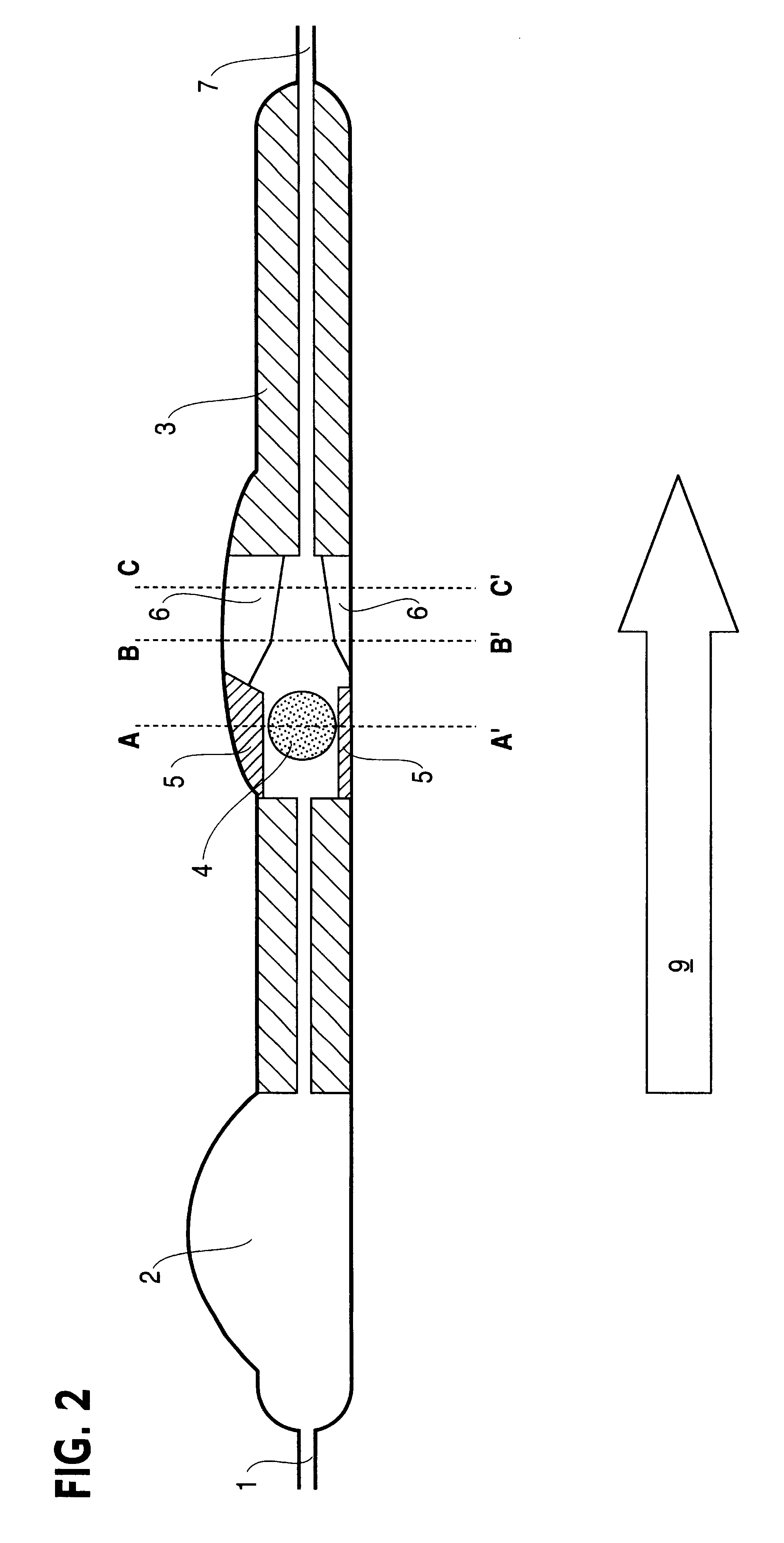
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt comprises a ventricular catheter and an electroactive polymer actuated valve for regulating the drainage rate of CSF from the brain ventricle of a patient. The shunt system also comprises a distal catheter for discharge of the CSF to a separate location in the patient's body such as the peritoneal cavity or atrium of the heart. The electroactive polymer actuated valve regulates the flow rate of CSF through a predetermined threshold pressure, which can be adjusted and programmed externally from the patient's body by means of an external control unit signal, as well as through a signal indicated by an internal sensor or an electroactive polymer transducer. The sensor also communicates a signal to the external control unit for indicating the internal pressure at a single location or multiple locations throughout the fully implanted shunt assembly.
Owner:ANITEAL LAB
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
InactiveUS20050085764A1Avoid complicationsWound drainsIntravenous devicesVentricular cathetersCsf shunt
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricular catheter for insertion into the brain ventricle so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle. The system also comprises a sinus sagittalis catheter for insertion into the sinus sagittalis for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into sinus sagittalis. A shunt main body is connected at one end thereof to the brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to the sinus sagittalis catheter. The shunt main body can provide fluidic communication between the brain ventricle catheter and the sinus sagittalis catheter. The system further comprises a tubular flow passage restricting member defined within the shunt main body. The tubular flow passage restricting member defines a resistance to flow of 8-12 mm Hg / ml / min.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
Transcutaneous telemetry of cerebrospinal fluid shunt programmable-valve pressure using near-infrared (NIR) light
Owner:WOLF II ERICH W
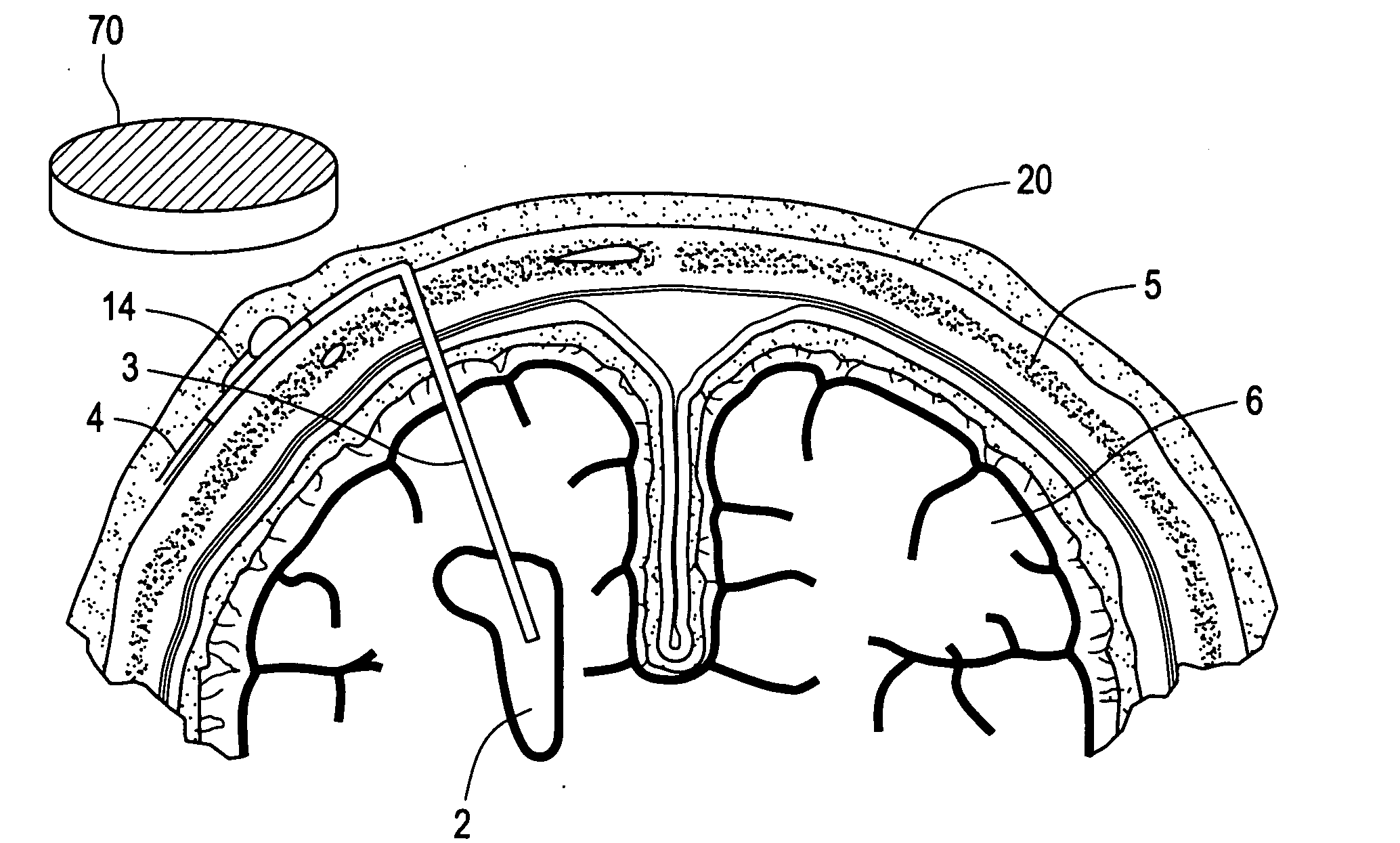
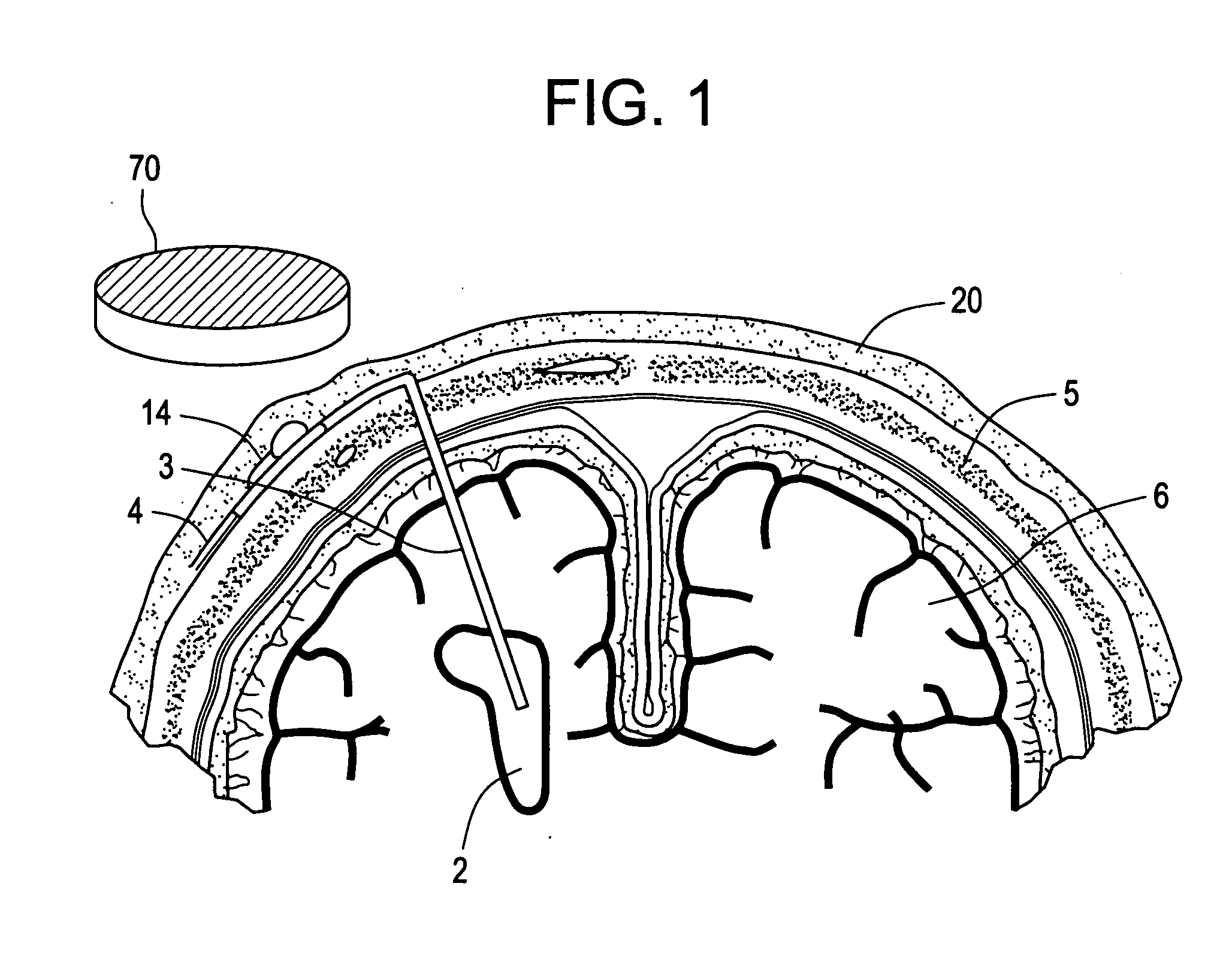
Tissue Engineered Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt
This invention relates to cerebrospinal fluid shunts, and a method of treating shunt catheters, whereby the interior lumen of a shunt catheter, comprised of a biocompatible matrix, is seeded with cells for placement within cerebrospinal fluid pathways of the central nervous system. The seeded cells have at least one of the following characteristics: (1) they are of a polarized ependymal epithelial phenotype with tight junctional complexes and apical cilia directed toward the lumen of the catheter; (2) they maintain stem / progenitor characteristics and are capable of neurogenesis; (3) they maintain stem / progenitor characteristics and are capable of gliogenesis.
Owner:AGATHOS HLDG
Tissue engineered cerebrospinal fluid shunt
Owner:AGATHOS HLDG
Body-associated fluid transport structure evaluation devices
Implantable devices for evaluating body-associated fluid transport structures and methods for using the same are provided. In some instances, the implantable devices include an elongated structure with at least one hermetically sealed integrated circuit sensor stably associated therewith and a transmitter. The devices find use in a variety of different applications, including monitoring the function of various types of body-associated fluid transport structures, such as arteriovenous fistulae, vascular grafts, catheters, cerebrospinal fluid shunts, and implantable central venous access devices.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
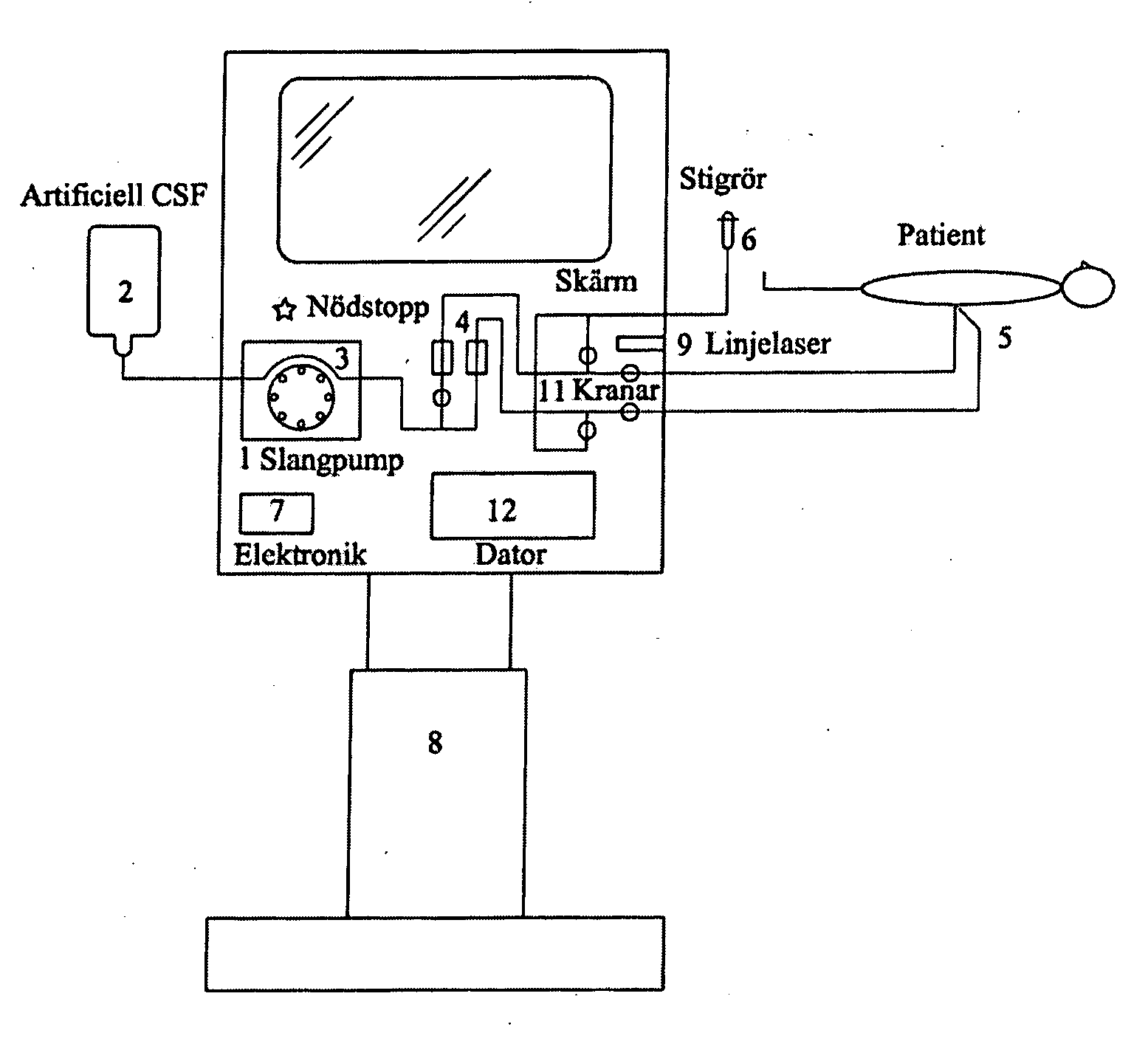
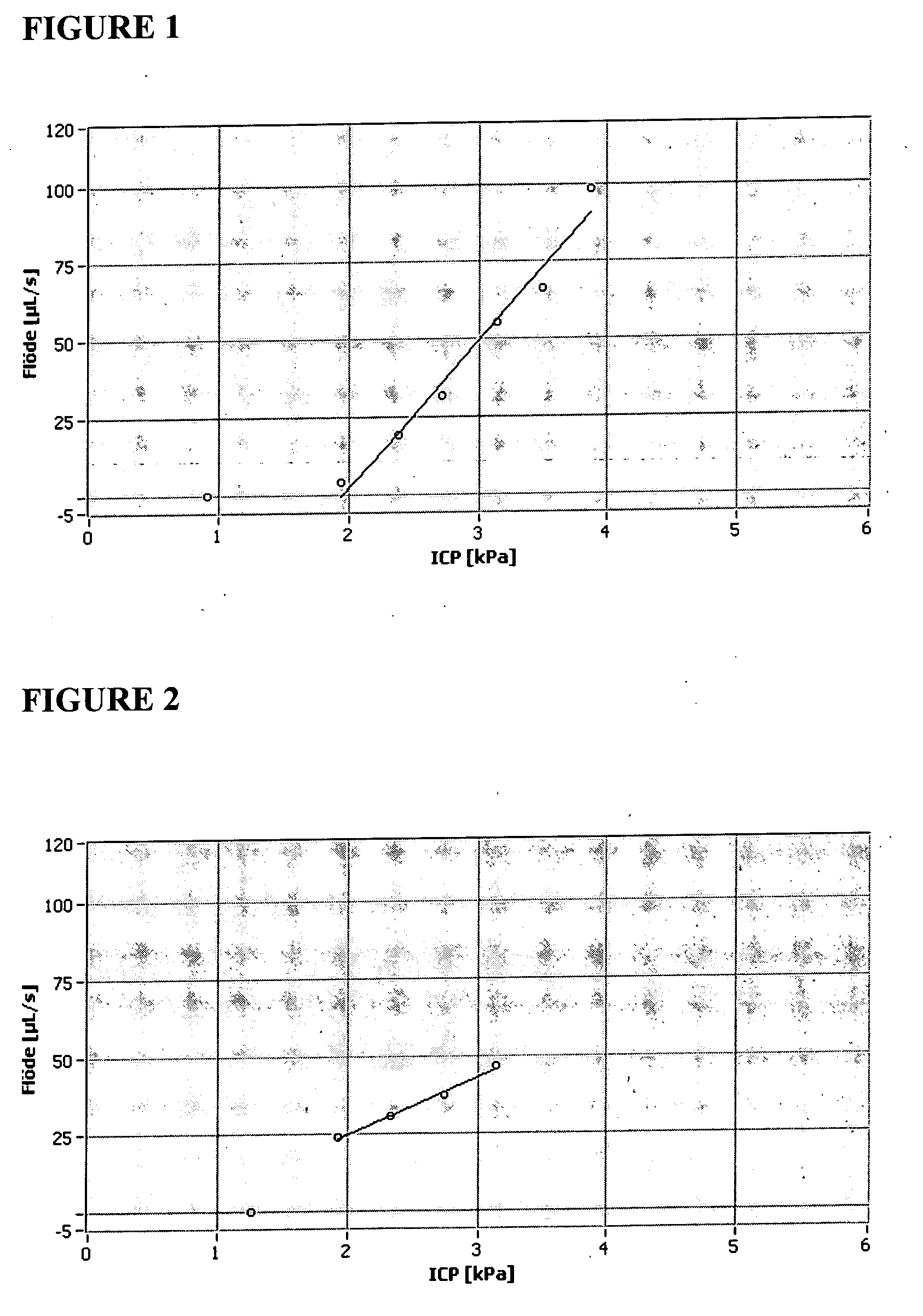
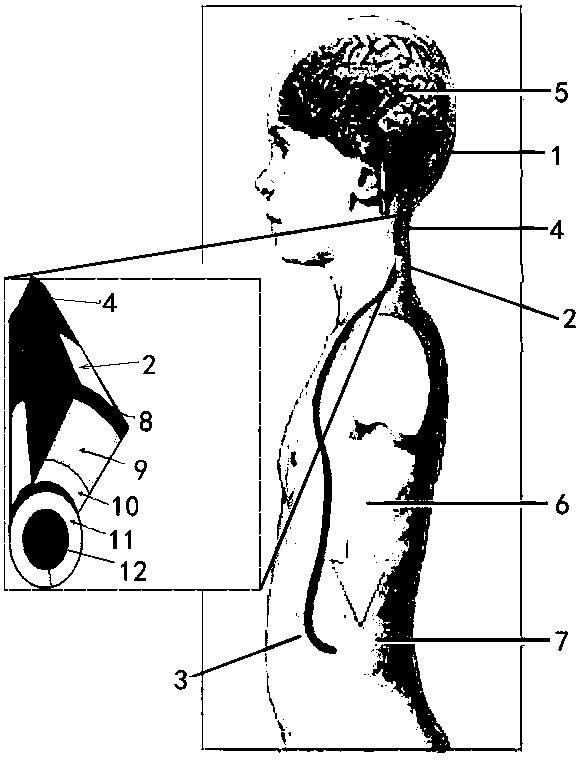
Optimization of hydrocephalus shunt settings
A method is described for using a postoperative CSF dynamical examination to determine the CSF dynamical state of the patient and the dynamical state of the CSF shunt in conjunction therewith.
Owner:LIKVOR
Transcutaneous telemetry of cerebrospinal fluid shunt programmable-valve pressure using near-infrared (NIR) light
An improvement for a programmable valve system of the type implanted in a patient and used to divert cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from an intraventricular space to a terminus such as the peritoneal cavity. Such system includes means for establishing a flow path for the CSF to the terminus, which flow path includes a normally closed valve and means for adjusting the opening pressure of the valve in order to regulate the quantity of CSF diverted. The improvement enables an operator to be apprised of the actual opening pressure setting of the valve. A sensor is implantable at the patient and responds to the actual opening pressure setting, by generating an NIR telemetry signal indicative of the actual setting. This signal is transcutaneously transmitted through the skin of the patient to an external point. The telemetry signal is processed to produce observer intelligible data indicating the opening pressure setting of the valve.
Owner:WOLF II ERICH W
Endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt
An implantable shunt device for draining cerebrospinal fluid from a patient's subarachnoid space. The device includes a shunt having opposed first and second ends. A one-way valve is located at the first end of the shunt. A helical tip is disposed at the second end. The helical tip is constructed to penetrate a sinus wall of the patient. Upon implantation, a hollow passageway extends between the helical tip and one-way valve such that fluid can be drained through the helical tip and out through the valve. The endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt of the present invention can be placed into a patient percutaneously via a catheter inserted into the venous system of the body through a needle hole, without the need for open surgery and the skin incisions required with current shunt devices. The device also allows for more physiologic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid since the device is shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the same cerebral venous system that occurs naturally in normal people.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Electroactive polymer actuated cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS8211051B2Reduce in quantityAvoid possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesCerebrospinal fluid shuntCerebral ventricle
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt comprises a ventricular catheter and an electroactive polymer actuated valve for regulating the drainage rate of CSF from the brain ventricle of a patient. The shunt system also comprises a distal catheter for discharge of the CSF to a separate location in the patient's body such as the peritoneal cavity or atrium of the heart. The electroactive polymer actuated valve regulates the flow rate of CSF through a predetermined threshold pressure, which can be adjusted and programmed externally from the patient's body by means of an external control unit signal, as well as through a signal indicated by an internal sensor or an electroactive polymer transducer. The sensor also communicates a signal to the external control unit for indicating the internal pressure at a single location or multiple locations throughout the fully implanted shunt assembly.
Owner:ANITEAL LAB
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system and method
InactiveCN107822594ARealize detectionImprove efficiencyMedical simulationMedical imagingExcitation signalCerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea
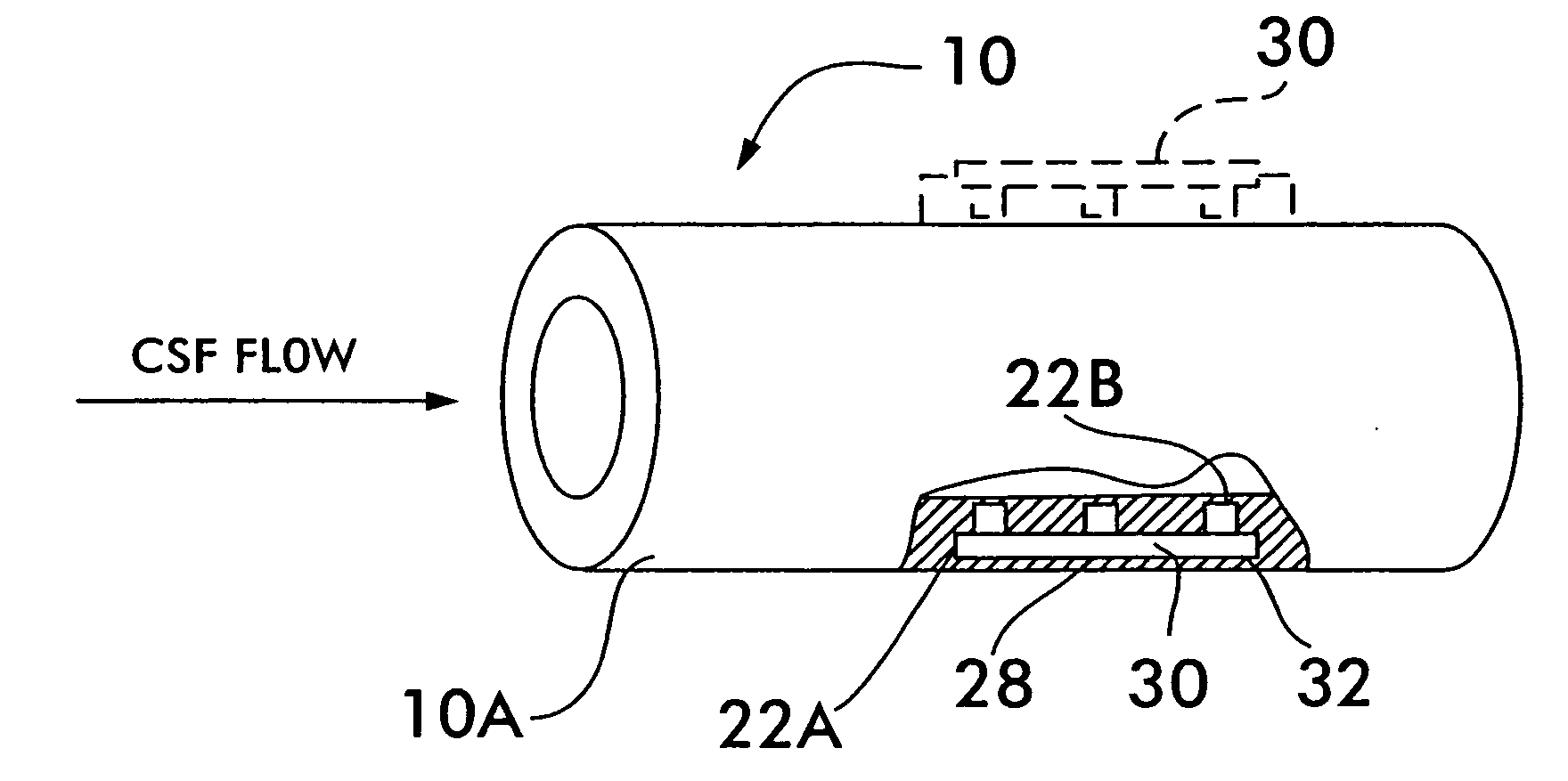
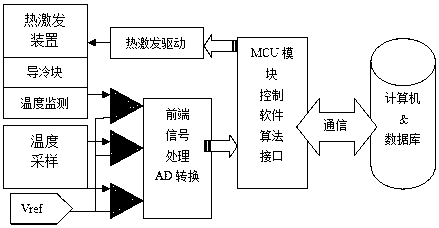
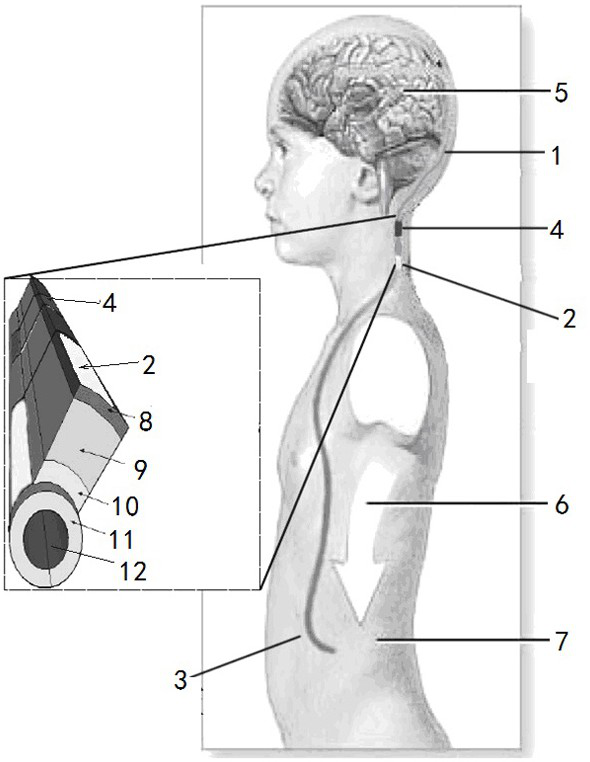
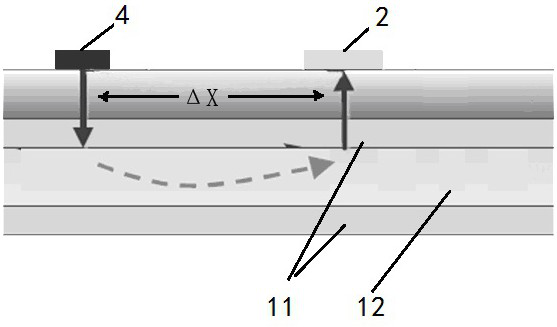
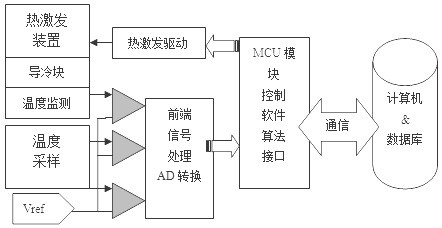
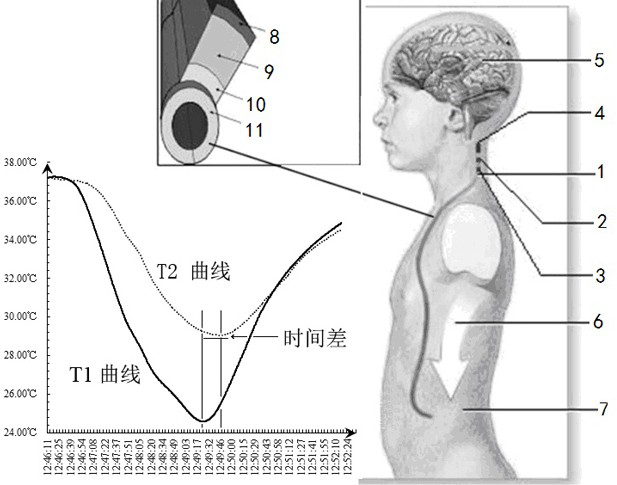
The invention relates to a cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system and method. The cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system comprises a MCU module, a computer connected to the MCU module, a signal processing module and a thermal excitation driving module, the thermal excitation driving module is further connected with a thermal conduction device through a cooling module, and the signal processing module is further connected with a signal acquisition module; the MCU module controls the operation of the cooling module through the thermal excitation driving module, and a thermal excitation signal is transmitted through the thermal conduction device so as to change the temperature of the cerebrospinal fluid at a thermal excitation point; and the signal acquisition module collects a cerebrospinal fluid temperature signal at a sampling point, and the signal processing module performs signal preprocessing and A / D conversion and transmits the processed signal to the MCU module for calculating the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow and uploading the calculated data to the computer. The cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system is applied to the thermal conduction technologyto detect the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow for the first time and can simulate the detection of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow of patients under any condition. Compared with the existing X-CT and MRI equipment, the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system has high efficiency and no radiation, and saves money. In addition, the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system only needsto adopt one sampling point to achieve the detection of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection computing method
InactiveCN107713987AImprove efficiencySave moneyVolume/mass flow measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringTime functionCerebrospinal fluid shunt
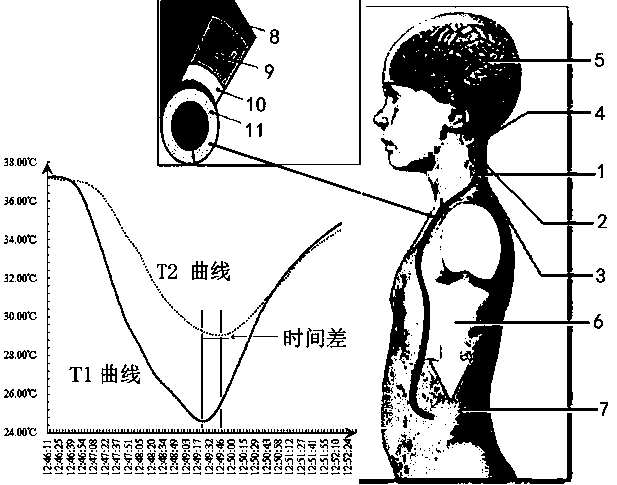
The invention relates to a cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection computing method. According to the method, since waveforms, which are formed by time sequence signal functions and time of samplingsignals when cerebrospinal fluid which carries a same exciting source signal flows into any two sampling points, are similar, and subsequently, a time-function relation of the any two sampling pointsis established, so that by calculating the maximum value of the time functions, a time difference of the any two sampling points can be obtained, and subsequently, the flow velocity and the flow rat of the cerebrospinal fluid can be obtained. The computing method provided by the invention, in comparison with existing CT and MRI detection, can improve efficiency, save money and avoid radiation; andthe computing method, in comparison with such existing computing methods as calculating extreme values in a curve, a heat conduction equation and the like, can improve the convergence and robustnessof a numerical solution, so that patient's cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection under any conditions can be satisfied.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
System and method for detecting cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow
InactiveCN107822594BRealize detectionImprove efficiencyMedical simulationMedical imagingCerebrospinal fluid shuntAv conduction
The invention relates to a cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system and method. The cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system comprises a MCU module, a computer connected to the MCU module, a signal processing module and a thermal excitation driving module, the thermal excitation driving module is further connected with a thermal conduction device through a cooling module, and the signal processing module is further connected with a signal acquisition module; the MCU module controls the operation of the cooling module through the thermal excitation driving module, and a thermal excitation signal is transmitted through the thermal conduction device so as to change the temperature of the cerebrospinal fluid at a thermal excitation point; and the signal acquisition module collects a cerebrospinal fluid temperature signal at a sampling point, and the signal processing module performs signal preprocessing and A / D conversion and transmits the processed signal to the MCU module for calculating the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow and uploading the calculated data to the computer. The cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system is applied to the thermal conduction technologyto detect the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow for the first time and can simulate the detection of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow of patients under any condition. Compared with the existing X-CT and MRI equipment, the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system has high efficiency and no radiation, and saves money. In addition, the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection system only needsto adopt one sampling point to achieve the detection of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt for treatment of hydrocephalus
The disclosure relates to a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt for treatment of hydrocephalus, comprising a valve having an inlet port and an outlet port, which ports are for draining CSF, and a control port for regulating the drainage of CSF through the valve according to a hydrostatic pressure provided to the control port, which hydrostatic pressure is dependent on the body position of the patient. The disclosure further relates to a method for treatment of hydrocephalus comprising regulating drainage of CSF based on a hydrostatic pressure that is dependent on the body position of the patient.
Owner:ROXHED NICLAS +4
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection method
InactiveCN107713987BImprove efficiencySave moneyVolume/mass flow measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyCsf shunt
The invention relates to a cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection computing method. According to the method, since waveforms, which are formed by time sequence signal functions and time of samplingsignals when cerebrospinal fluid which carries a same exciting source signal flows into any two sampling points, are similar, and subsequently, a time-function relation of the any two sampling pointsis established, so that by calculating the maximum value of the time functions, a time difference of the any two sampling points can be obtained, and subsequently, the flow velocity and the flow rat of the cerebrospinal fluid can be obtained. The computing method provided by the invention, in comparison with existing CT and MRI detection, can improve efficiency, save money and avoid radiation; andthe computing method, in comparison with such existing computing methods as calculating extreme values in a curve, a heat conduction equation and the like, can improve the convergence and robustnessof a numerical solution, so that patient's cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow detection under any conditions can be satisfied.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
Cerebrospinal fluid flow diverter
Owner:HAUGHTON VICTOR M
Cerebrospinal fluid shunt having long term Anti-occlusion agent delivery
The invention includes a shunt for at least partial implantation into a patient that includes an elongated conduit having at least one lumen therethrough, that includes a proximal end for receipt of bodily fluids for flow through the shunt and a distal end for discharge of the bodily fluids from the shunt, and a long term source of at least one occlusion resistant agent, wherein said at least a portion of the at least one occlusion resistant agent can permeate through at least a portion of the elongated conduit. The invention also includes kits and systems.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com