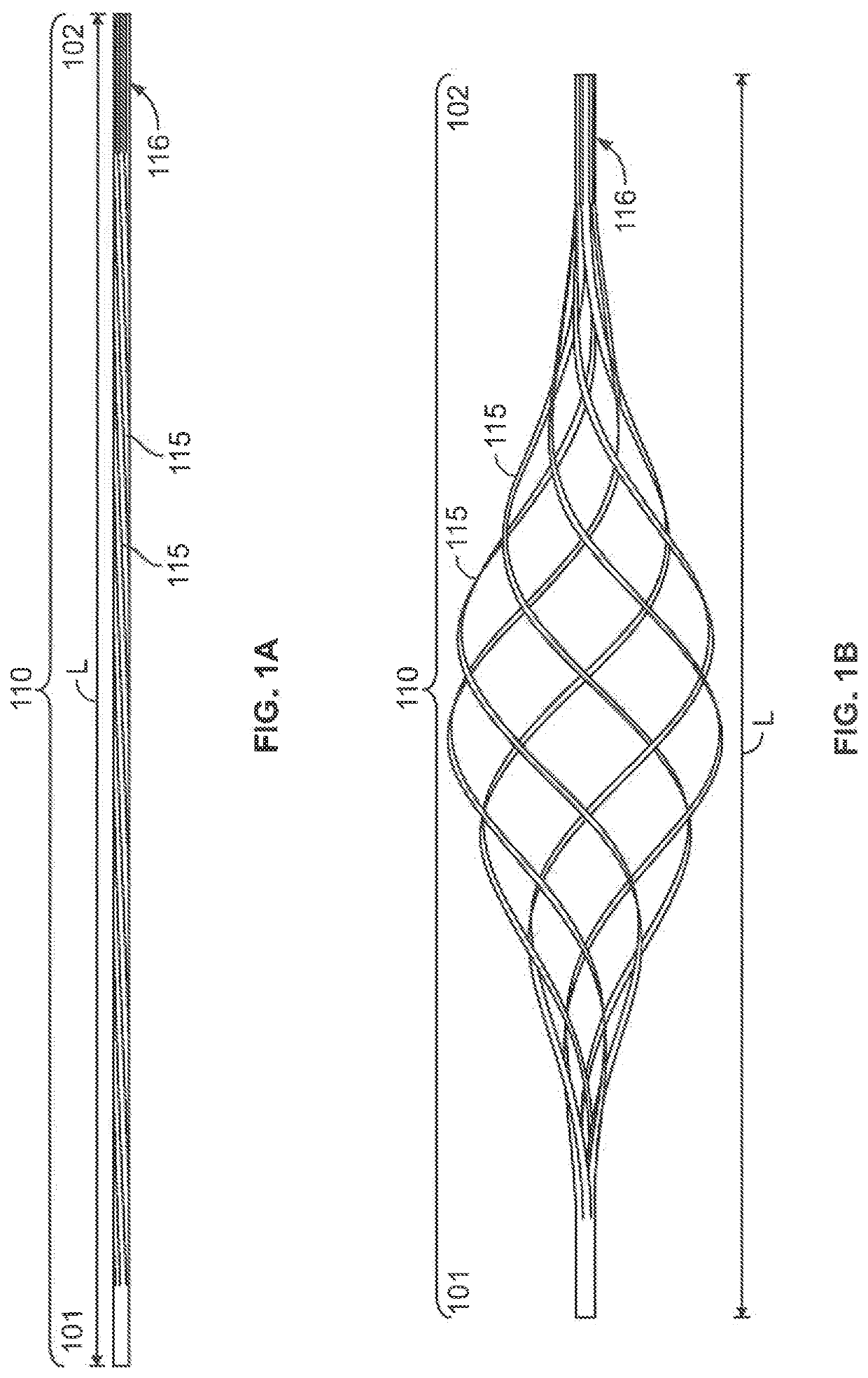
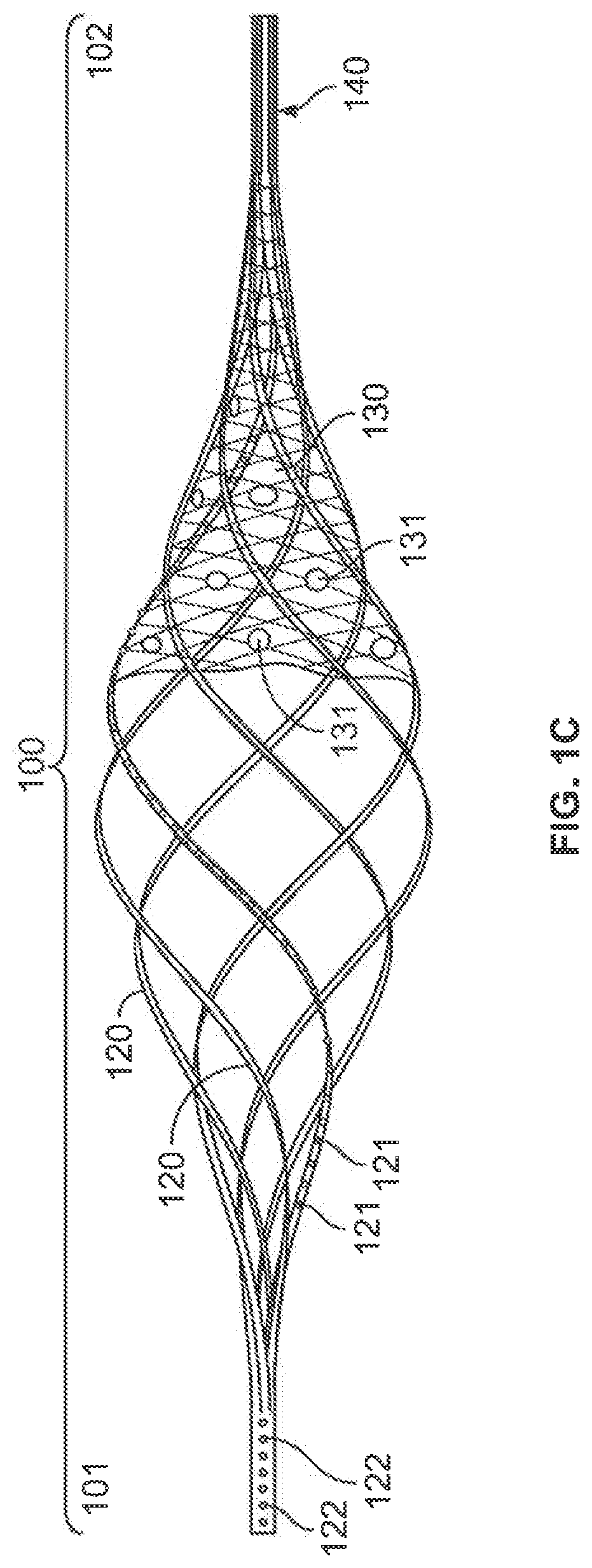
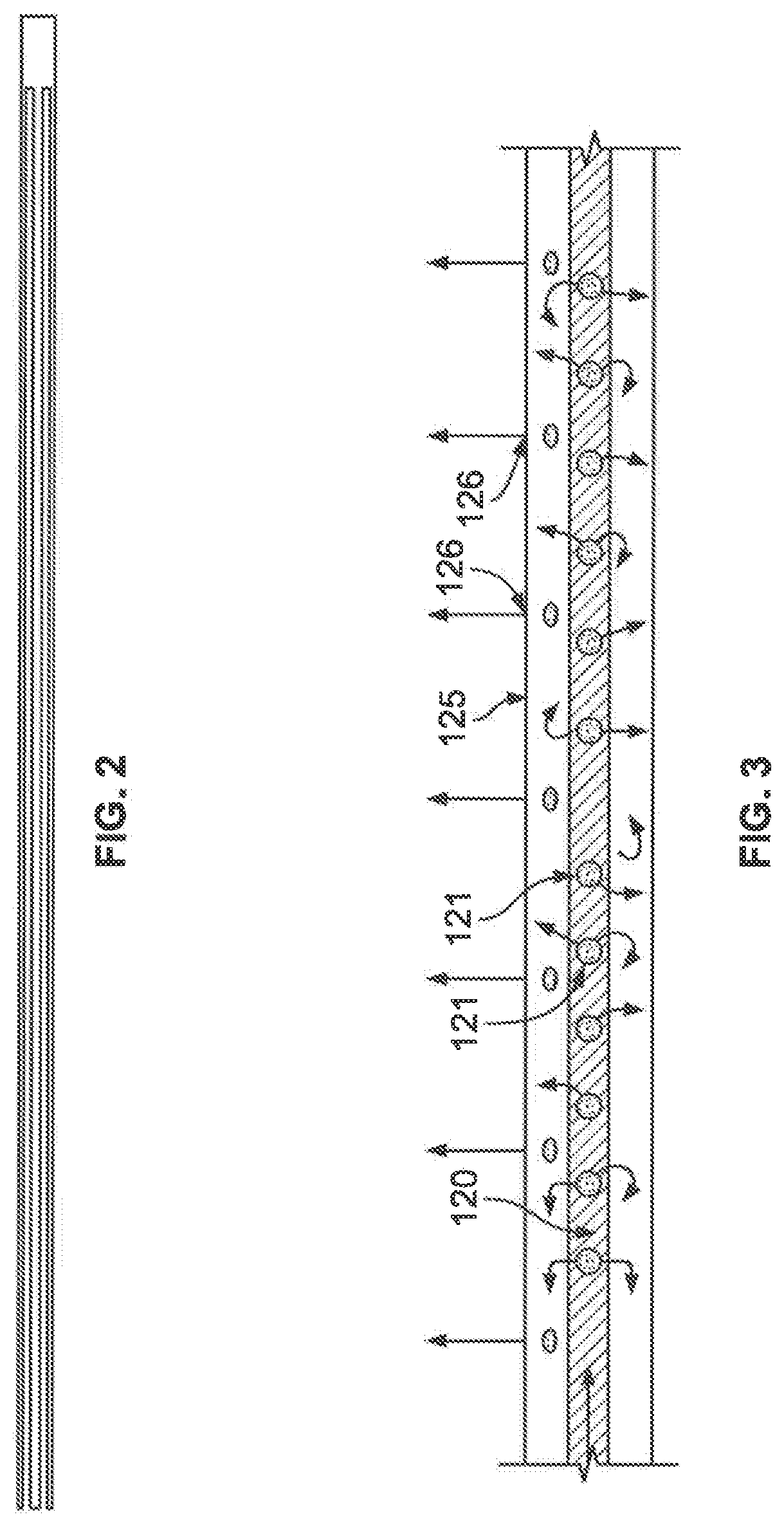
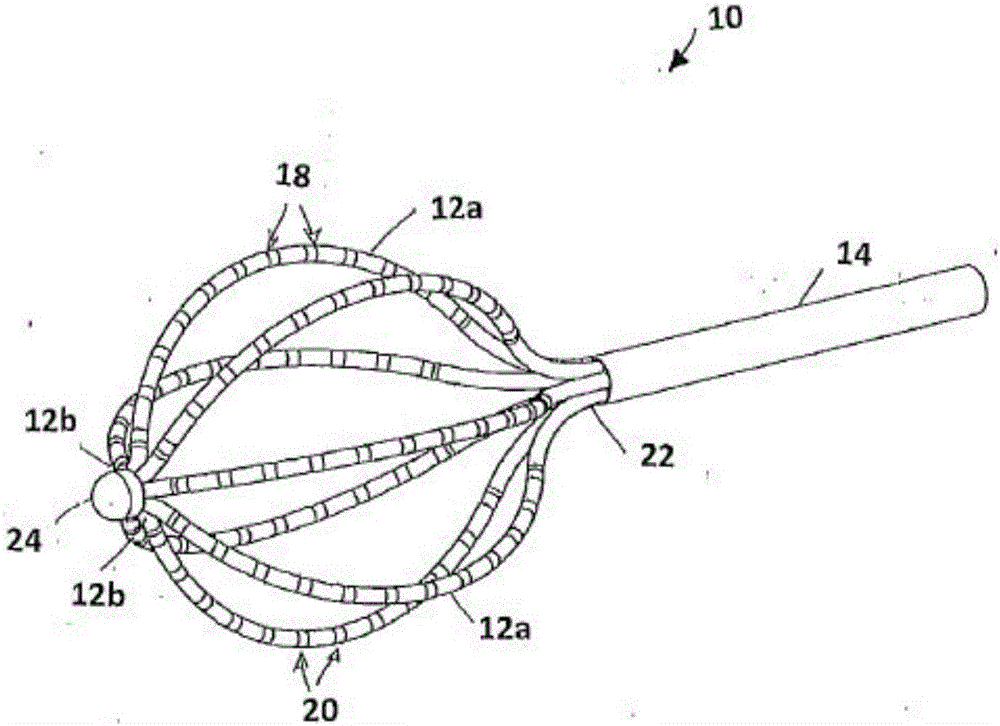
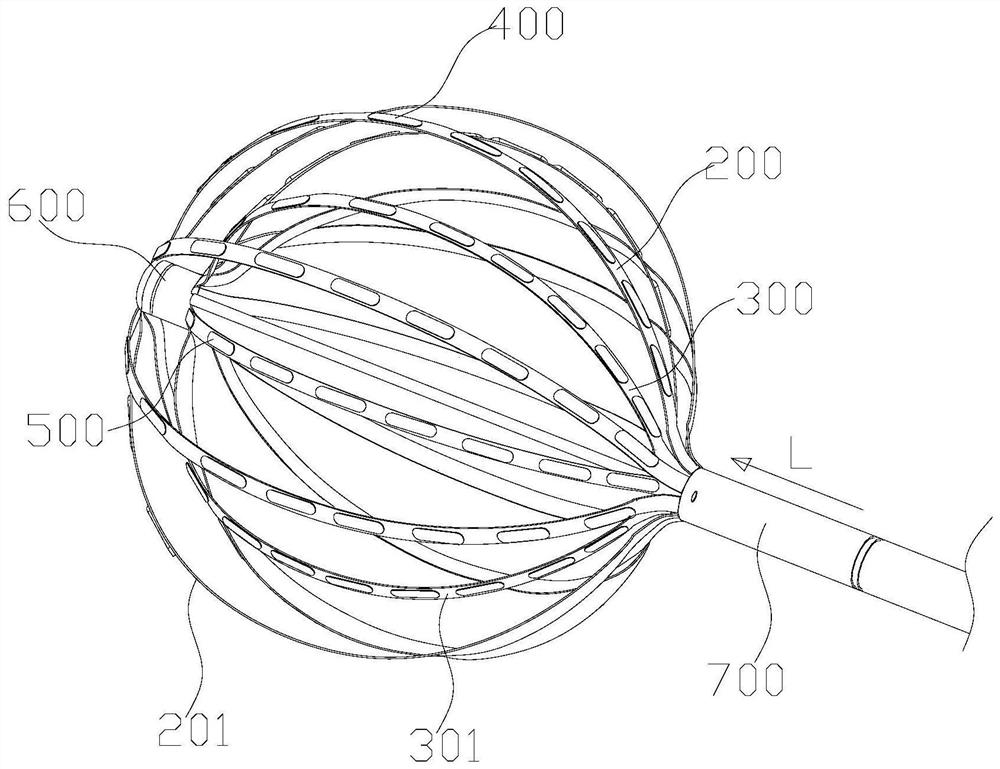
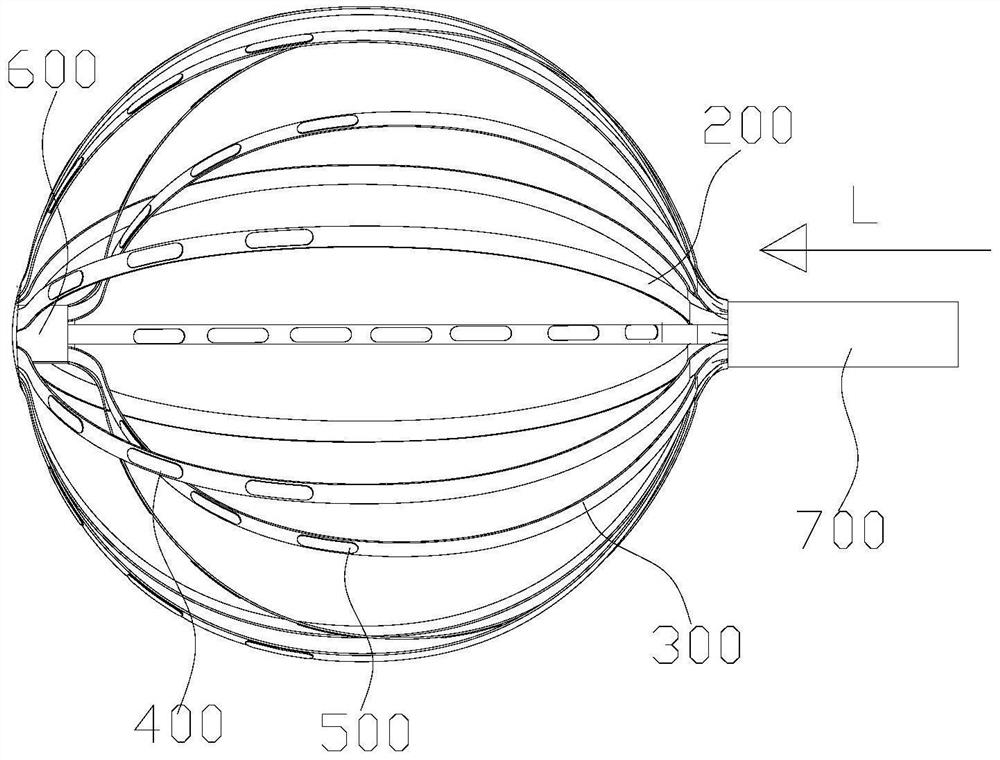
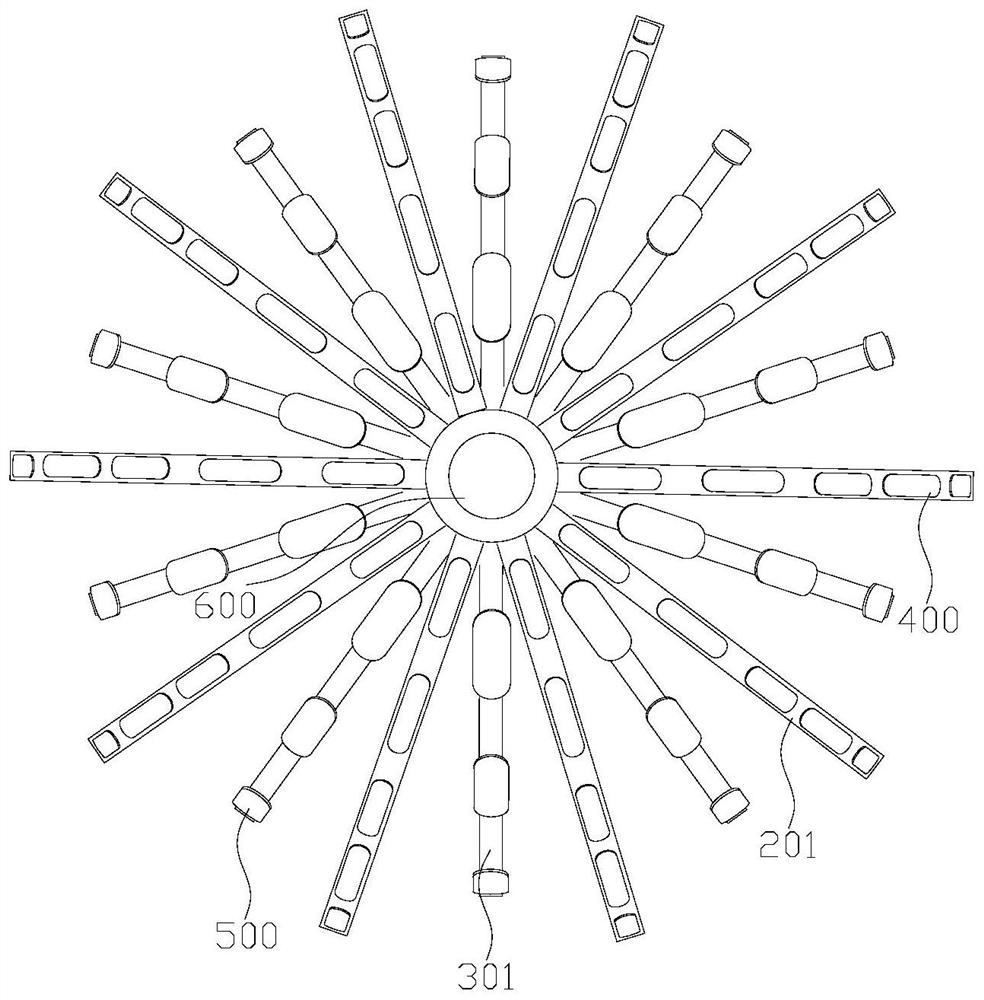
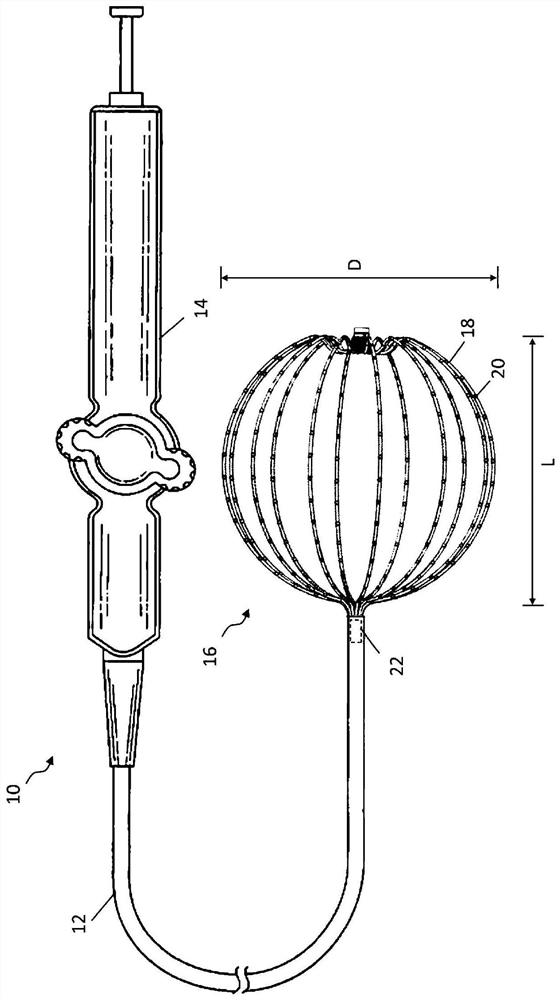
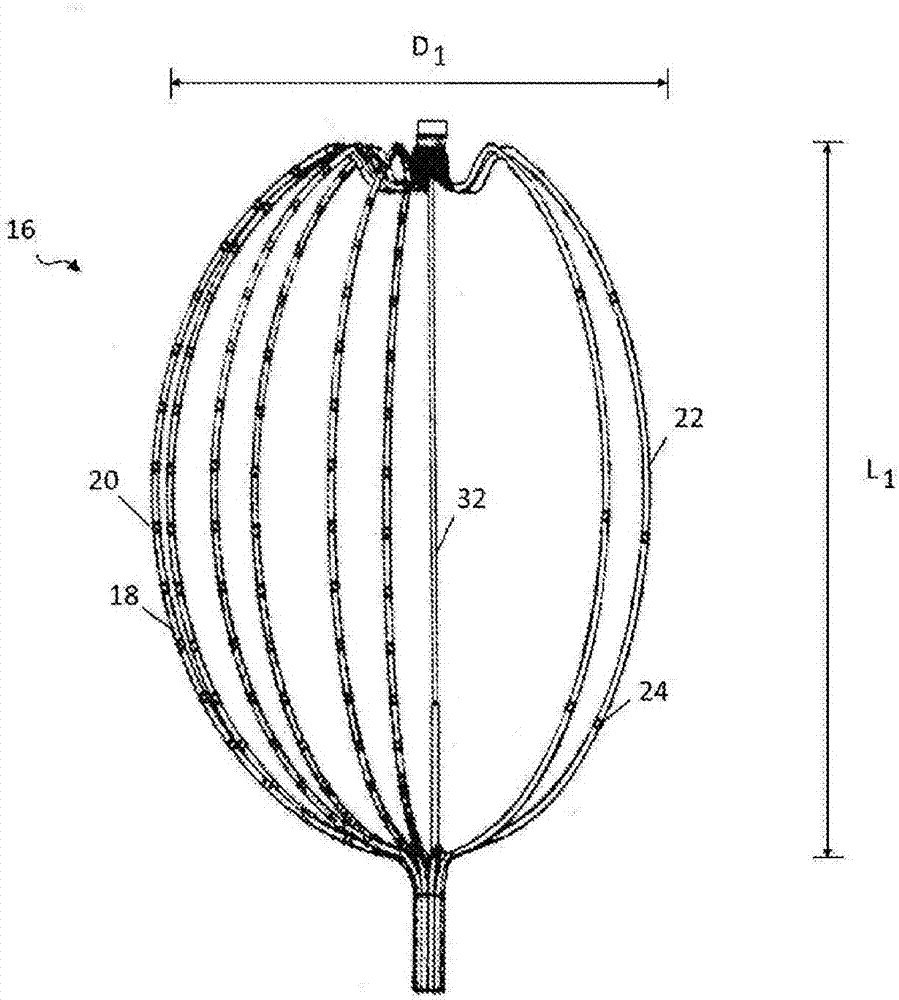
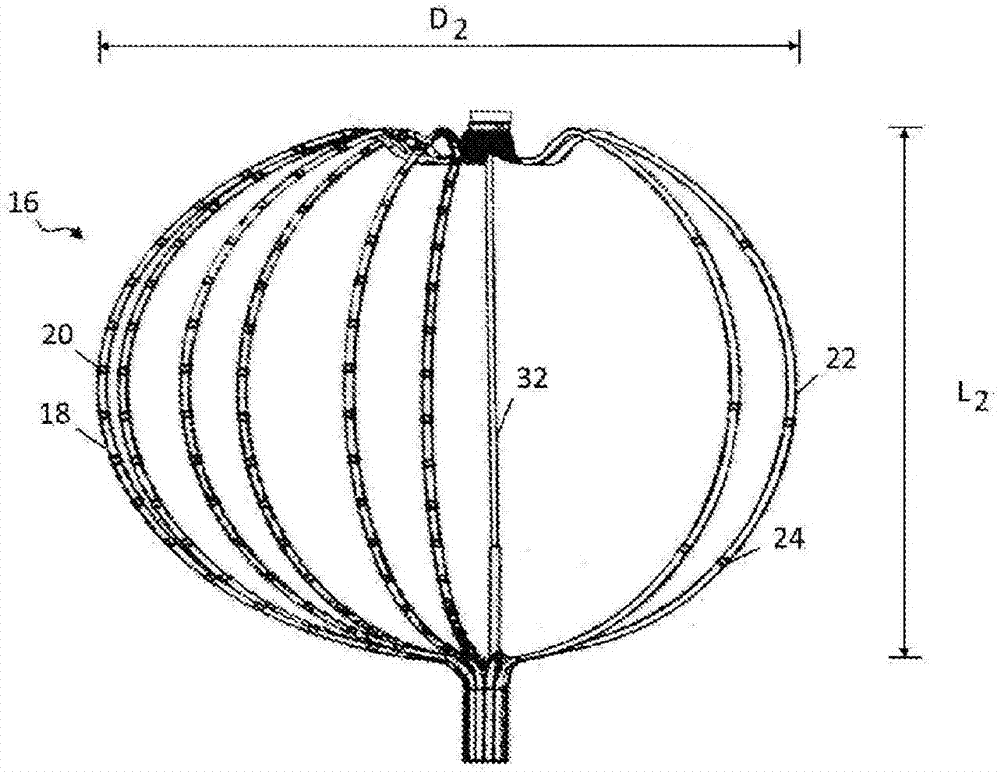
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Basket catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
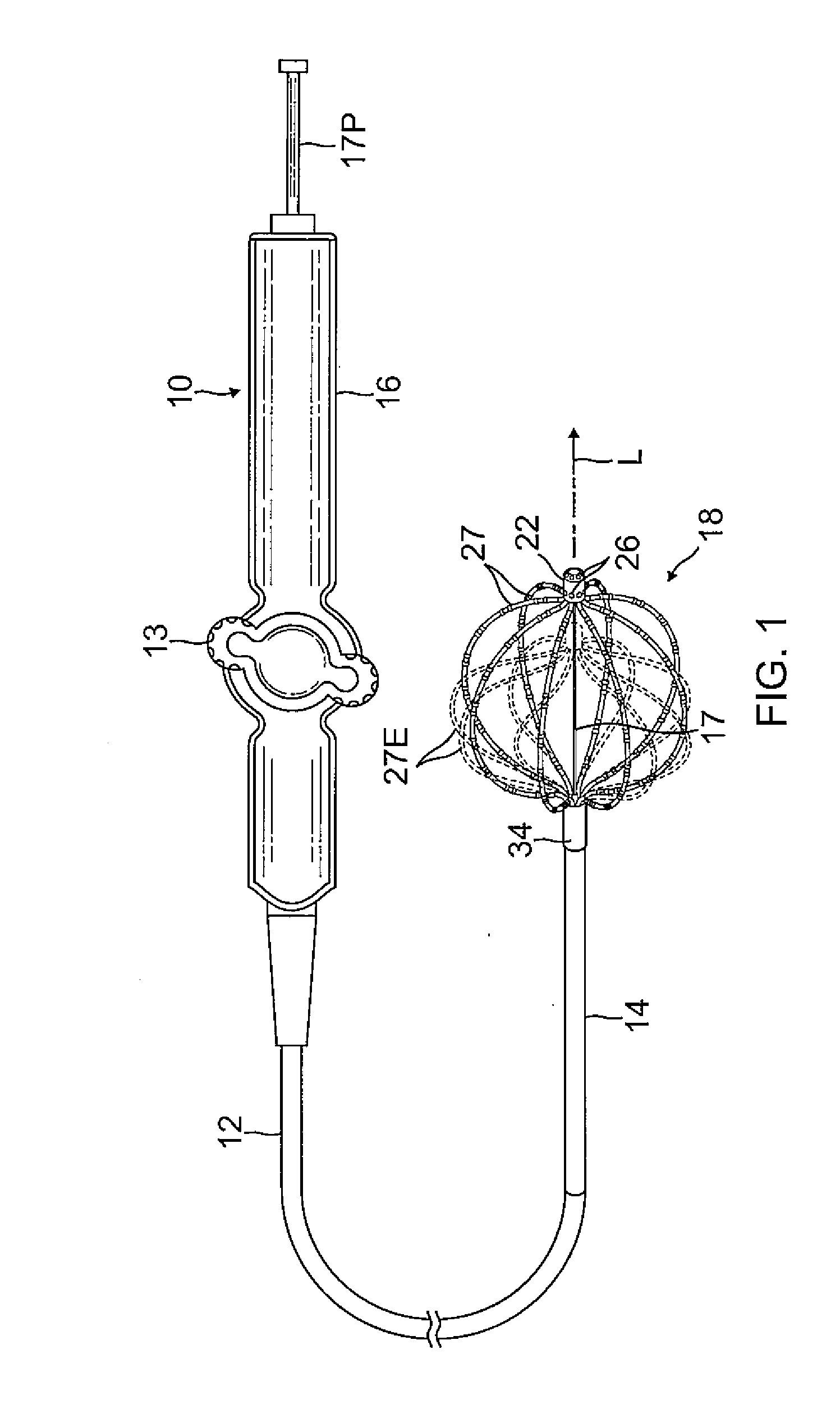
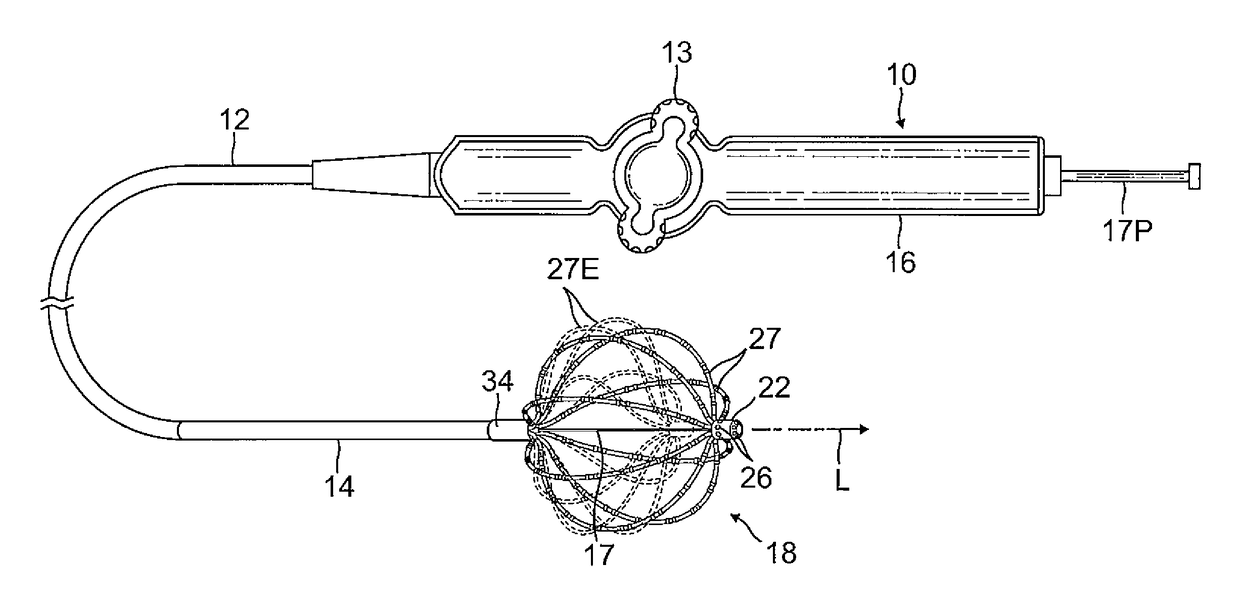
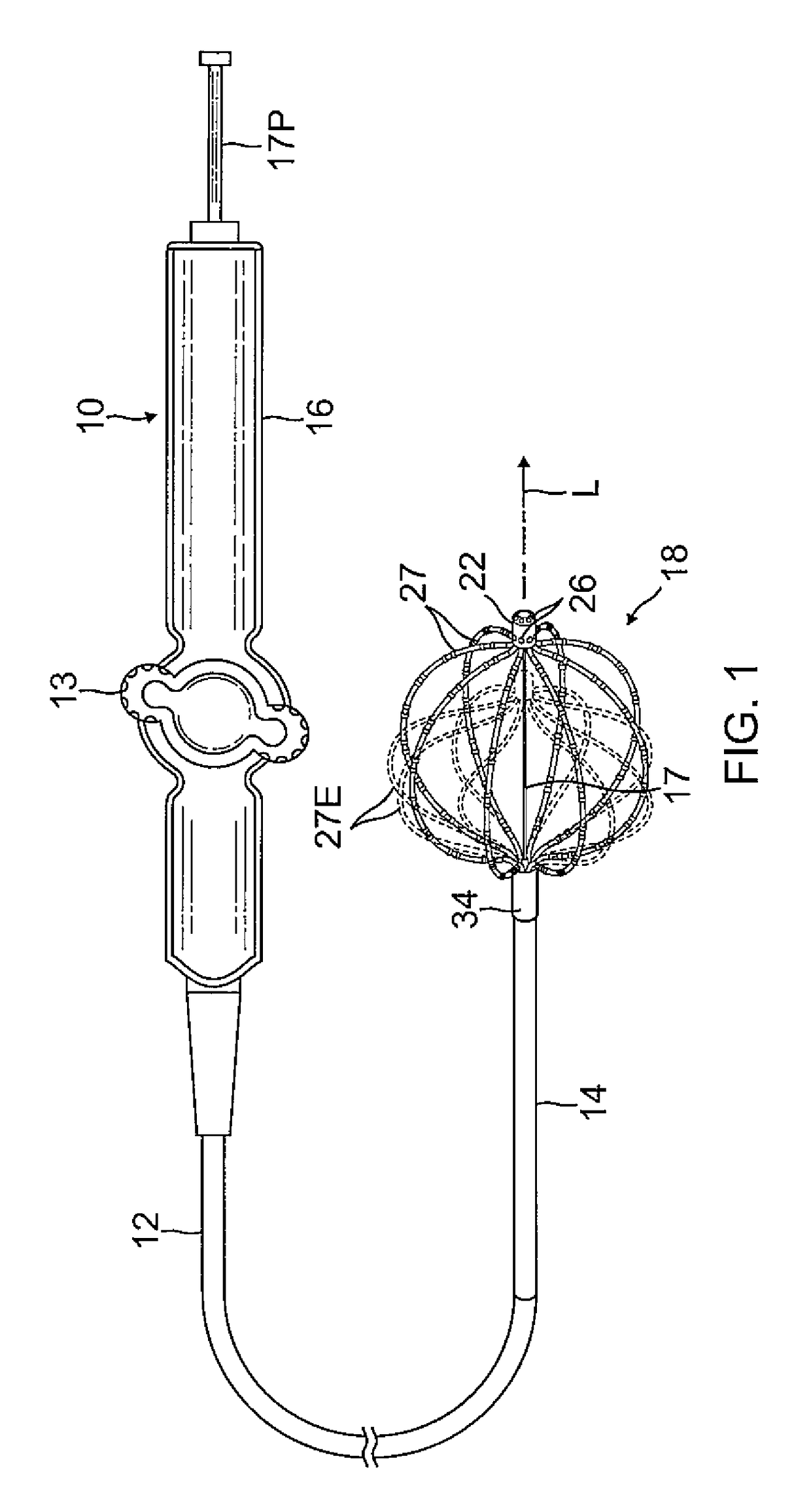
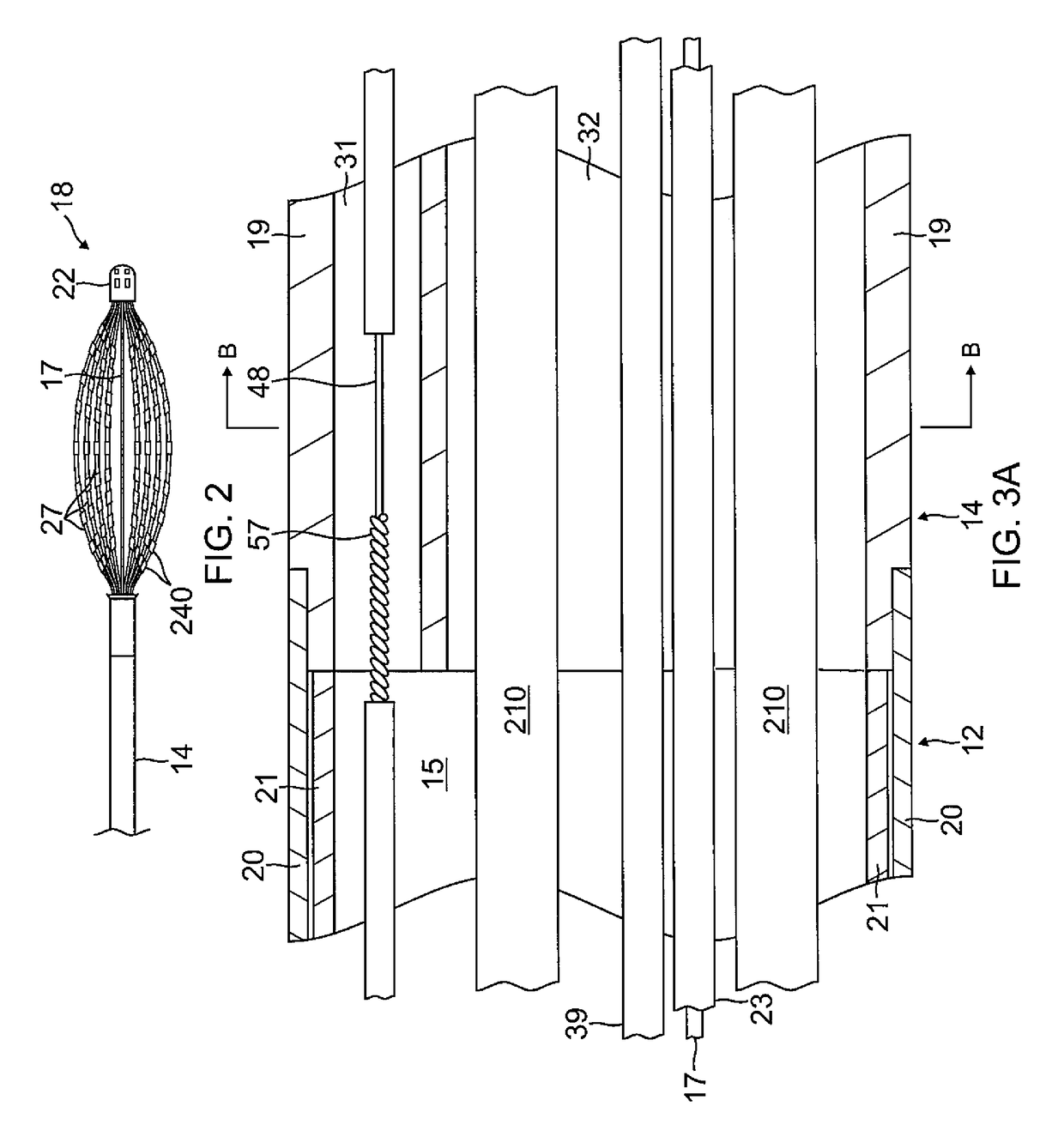
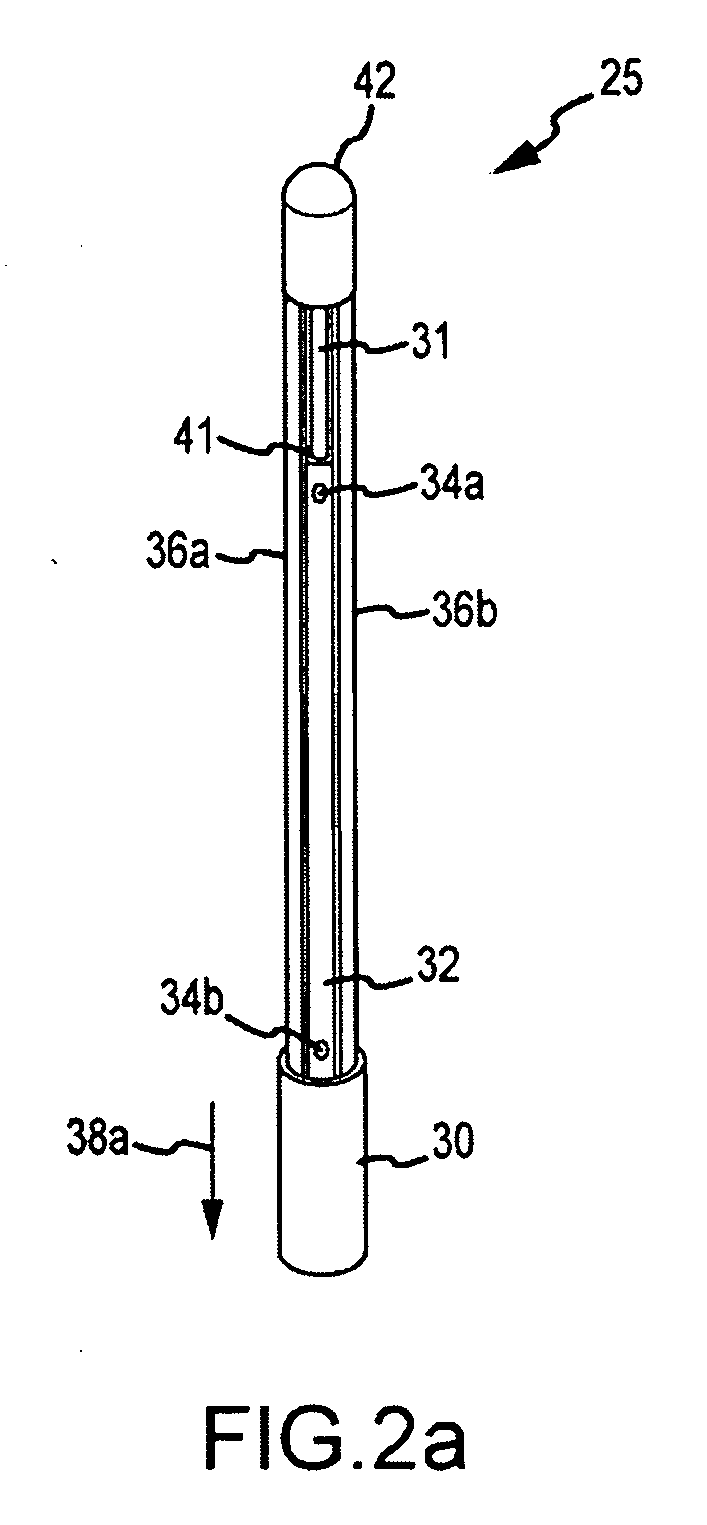
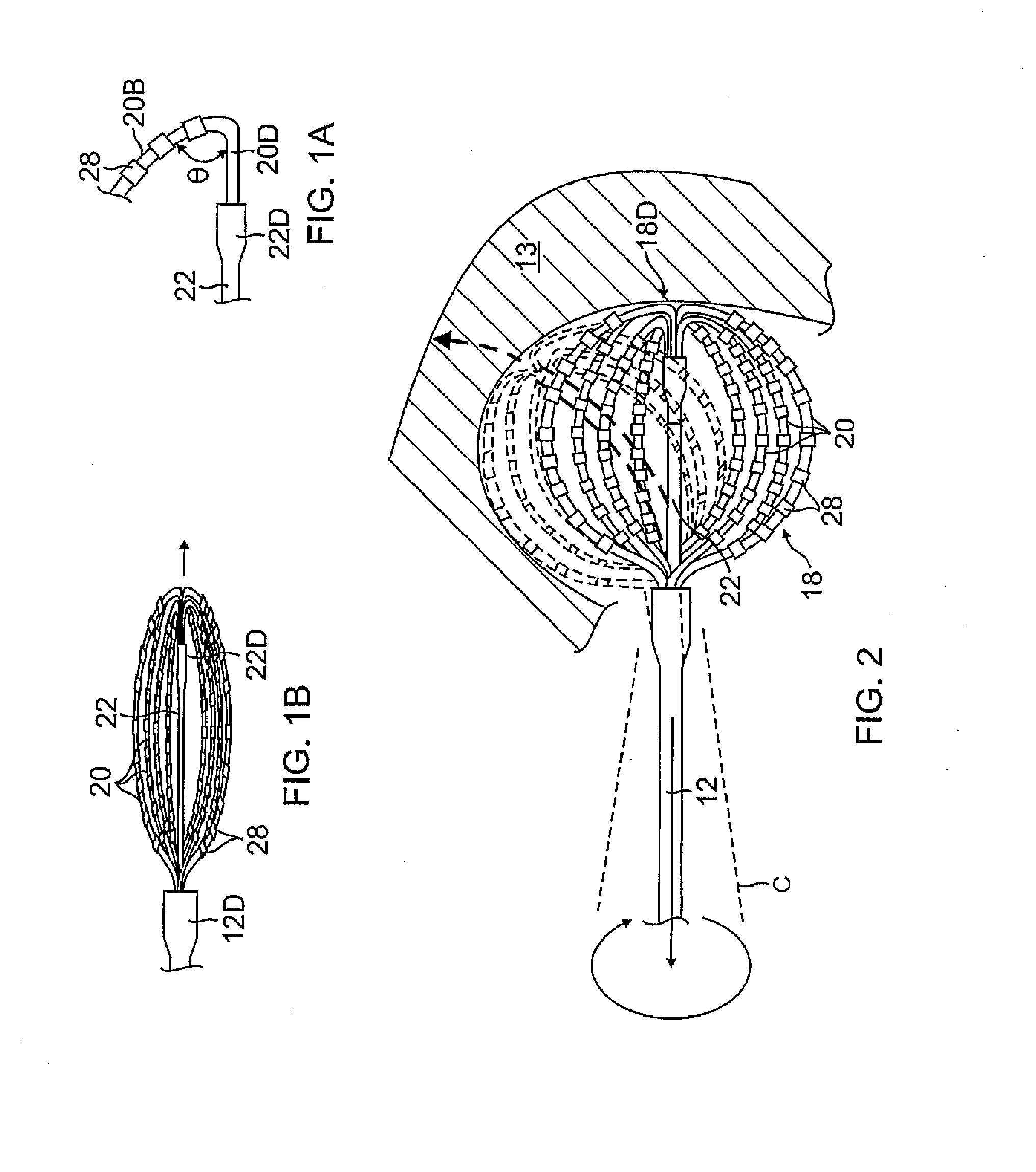
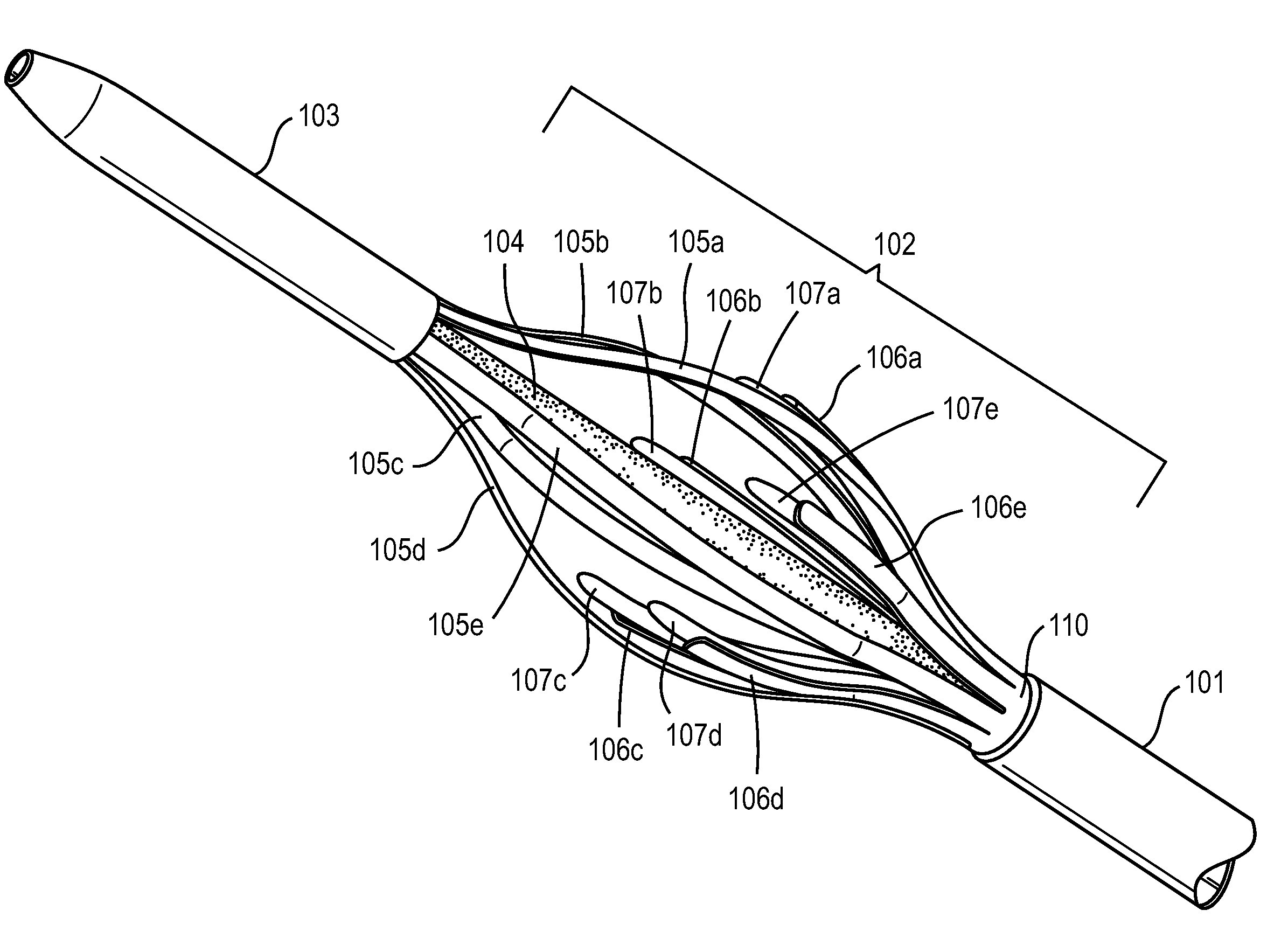
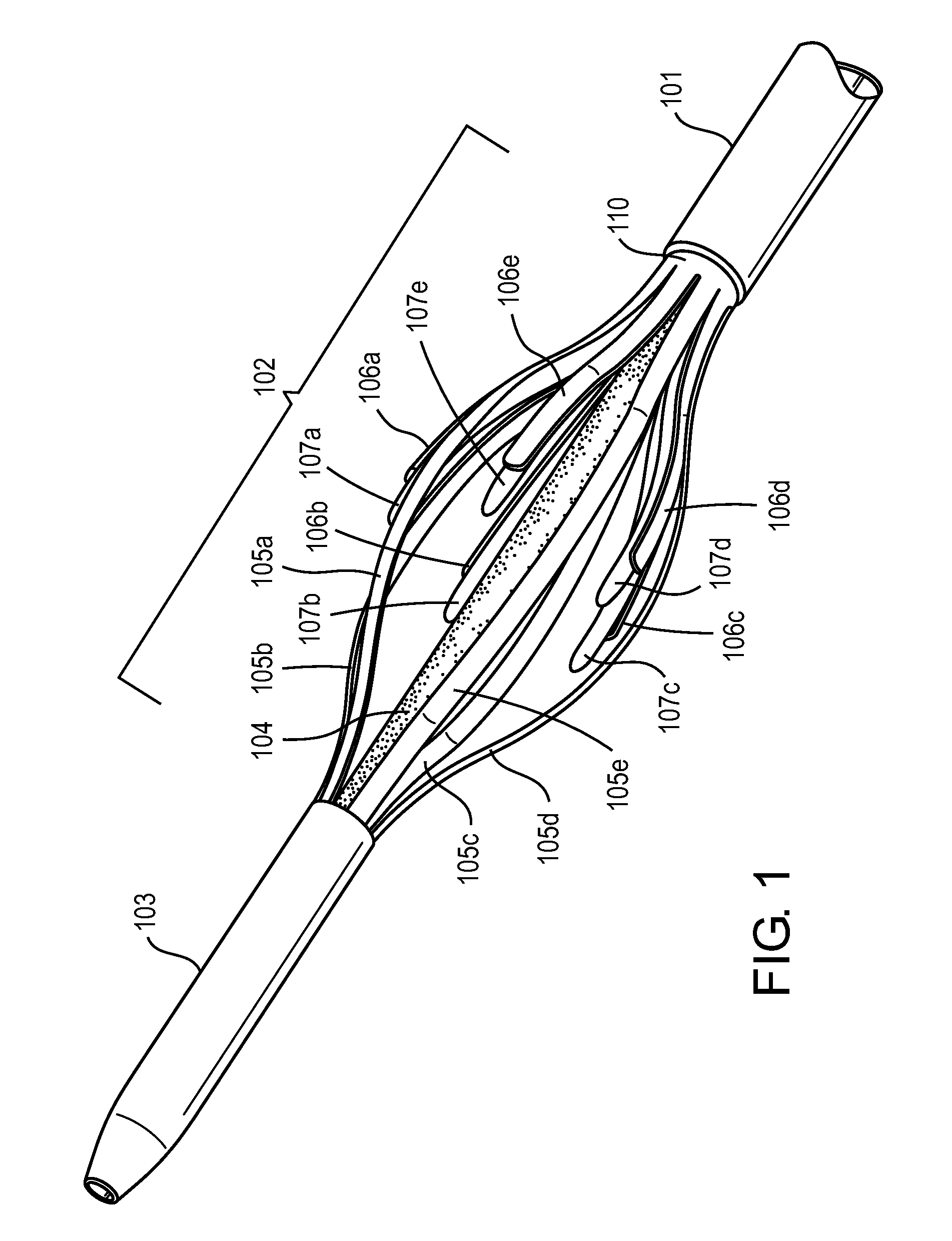
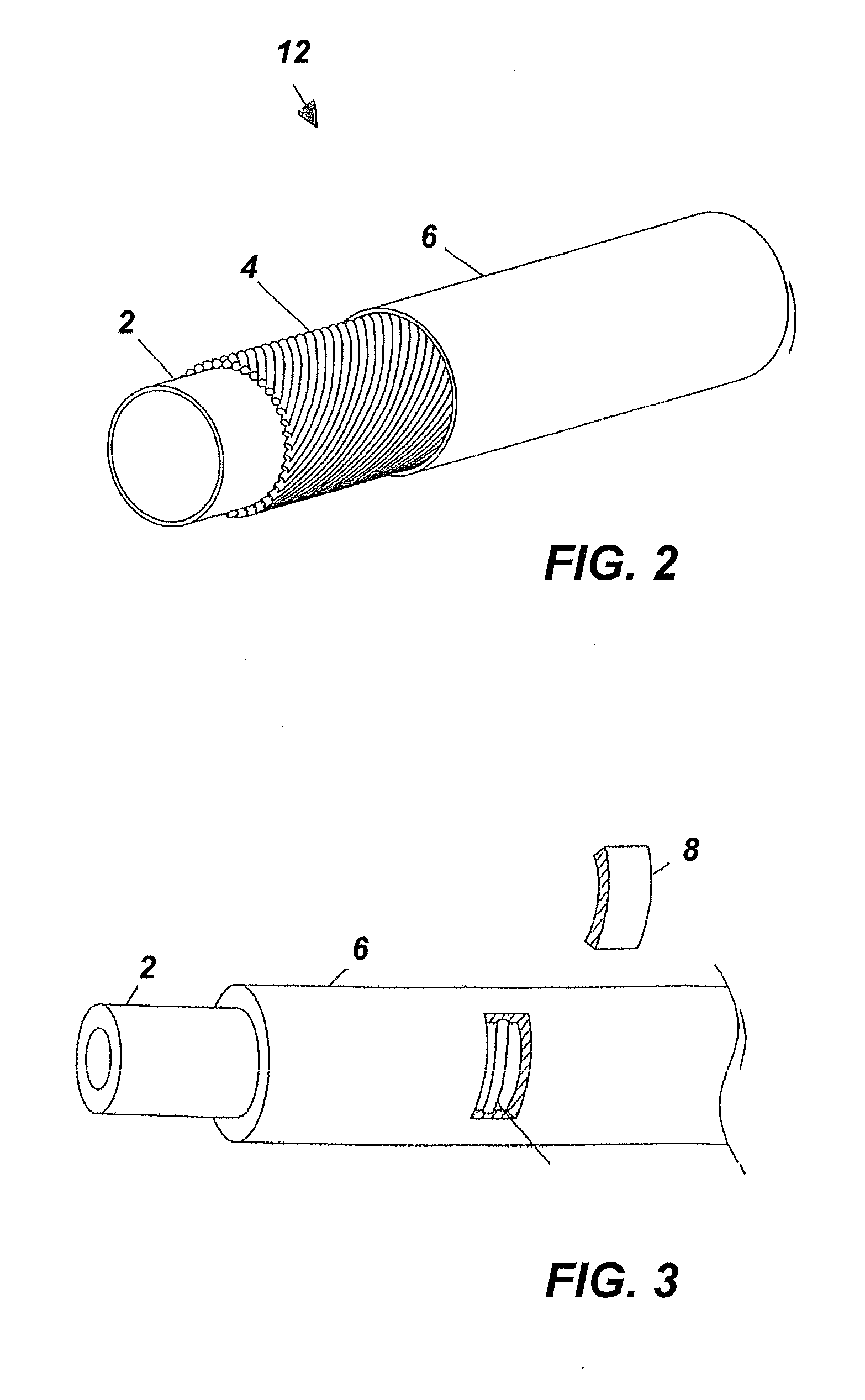
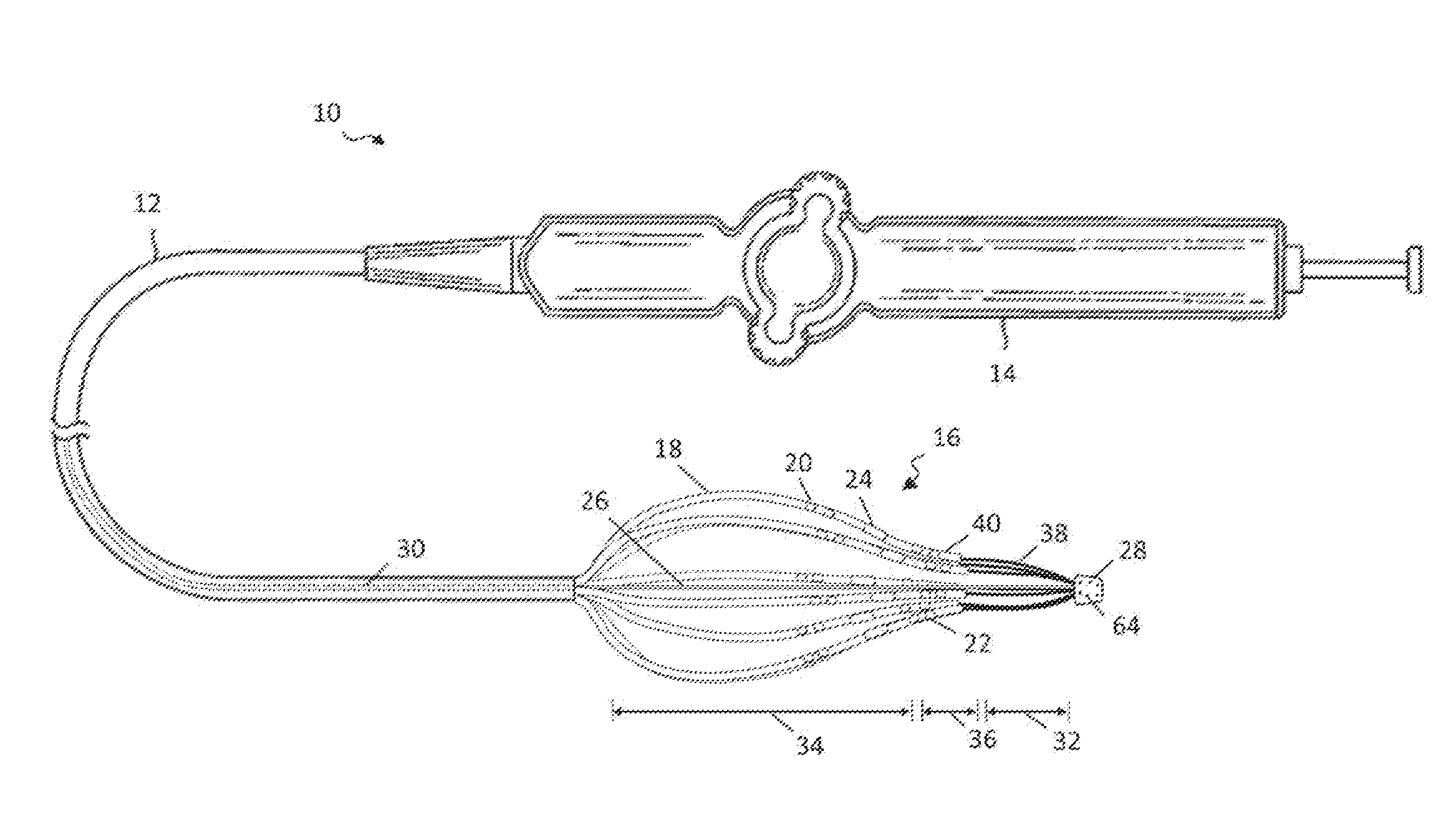
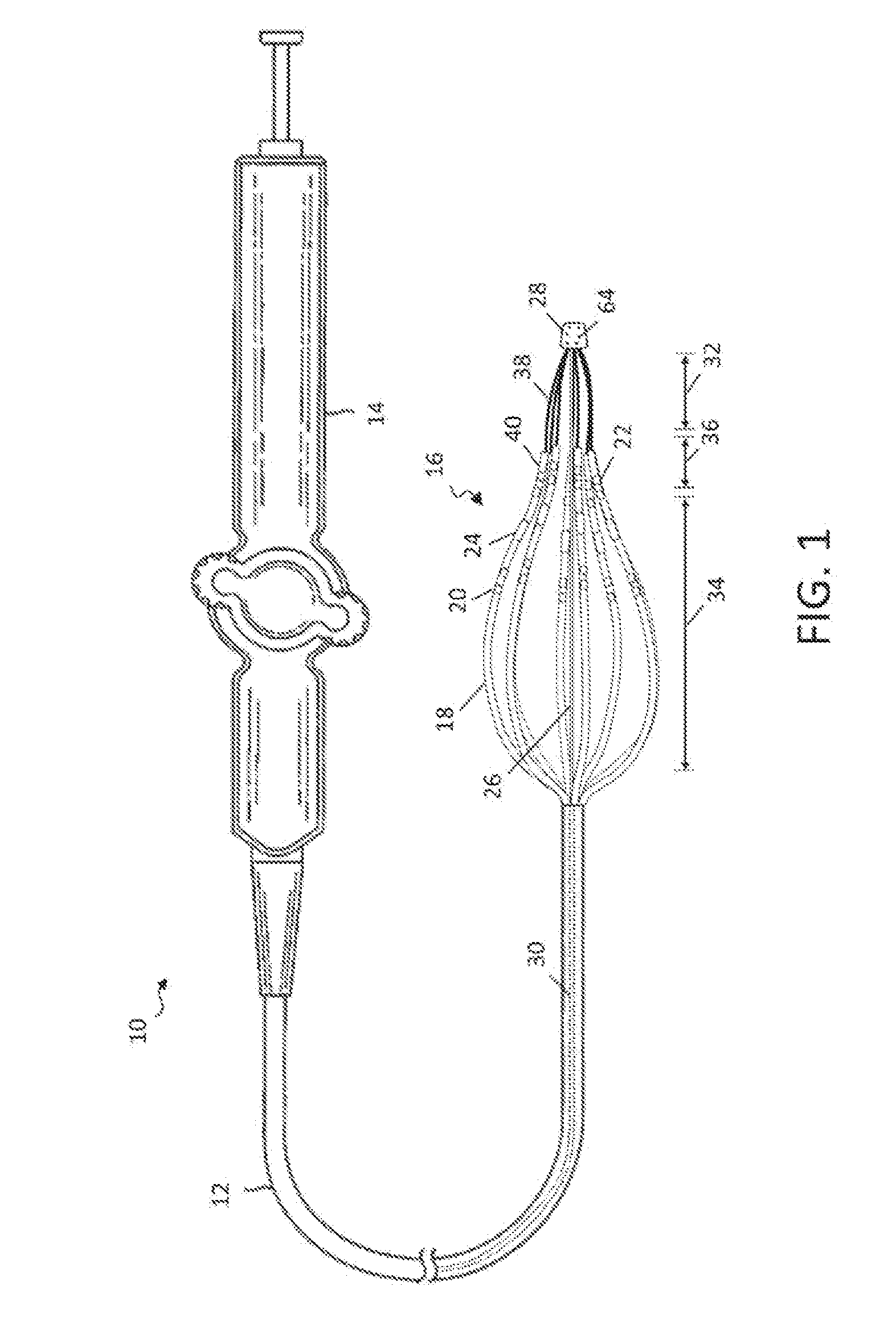
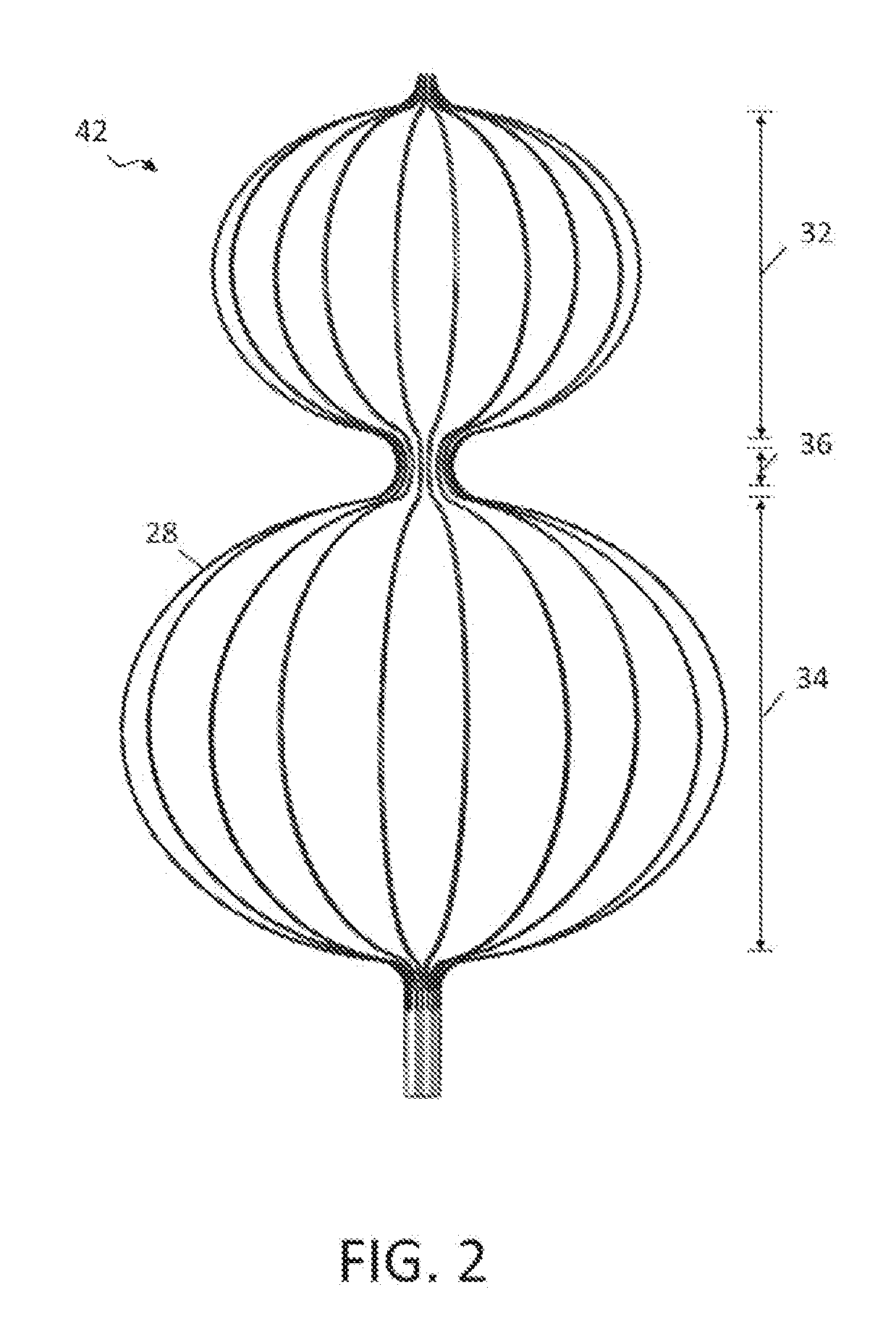
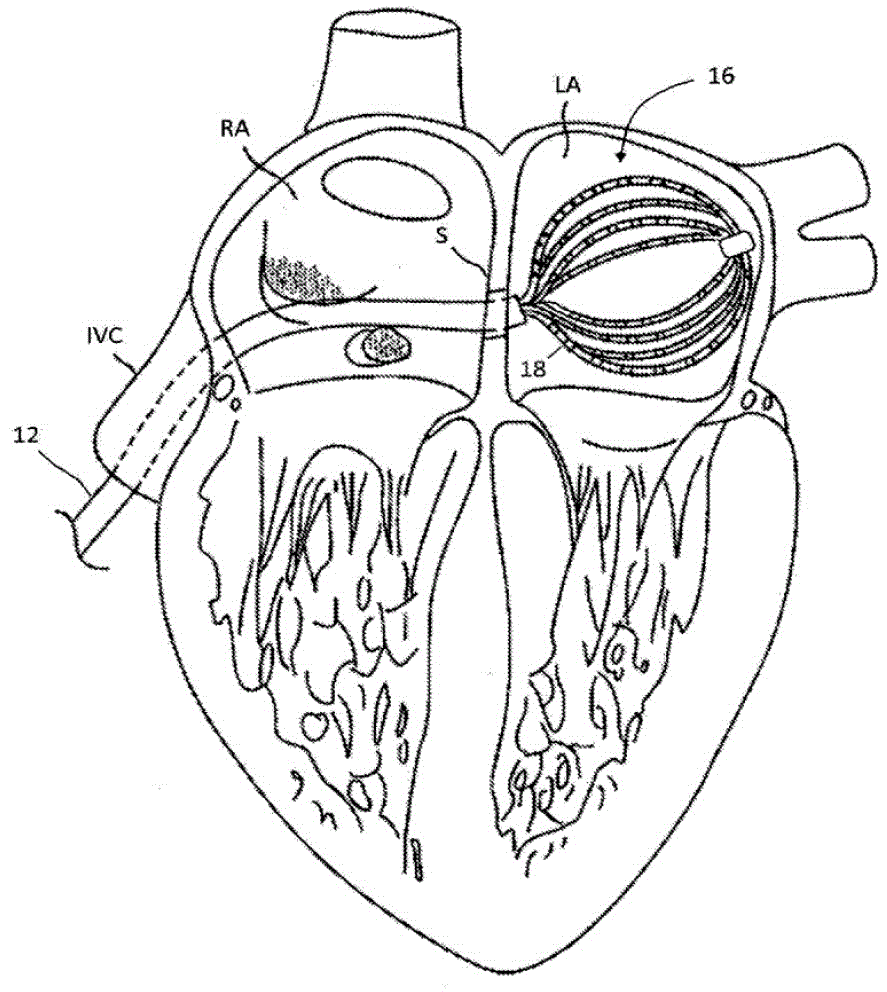
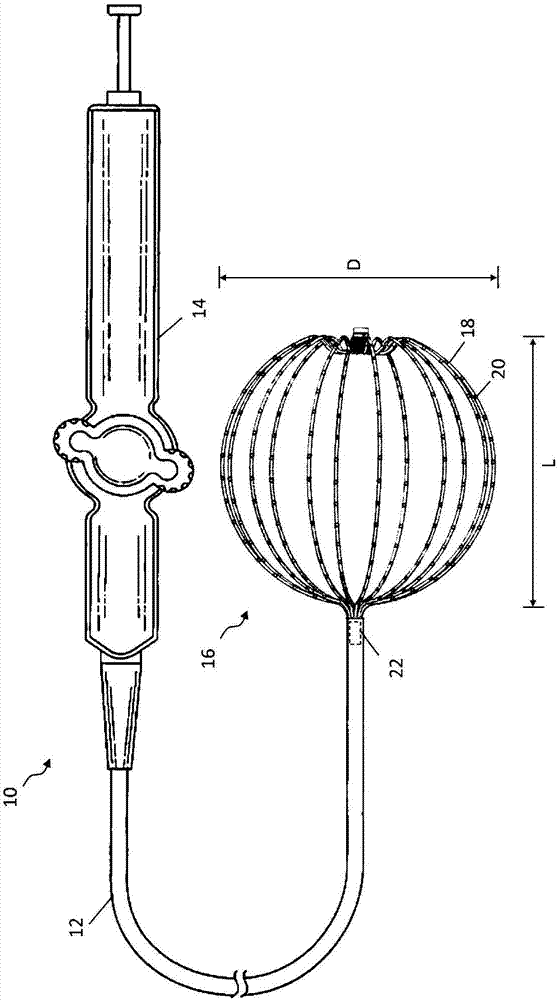
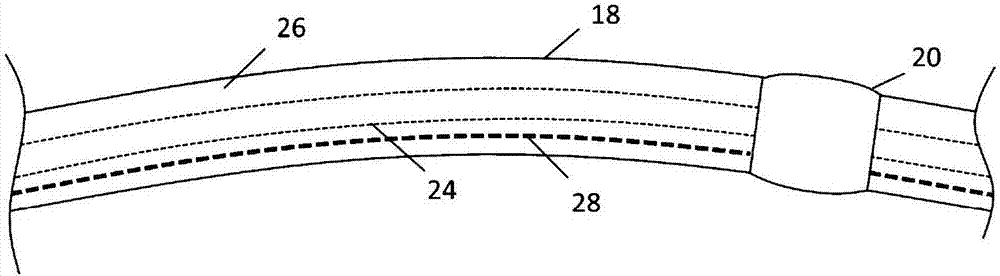
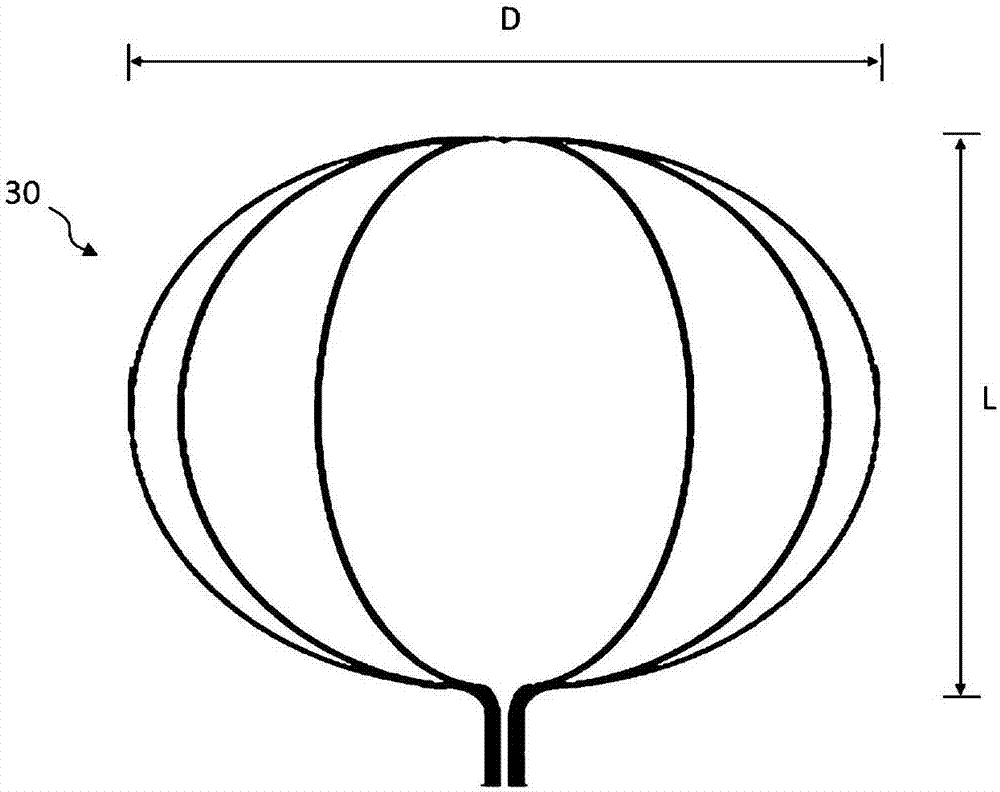
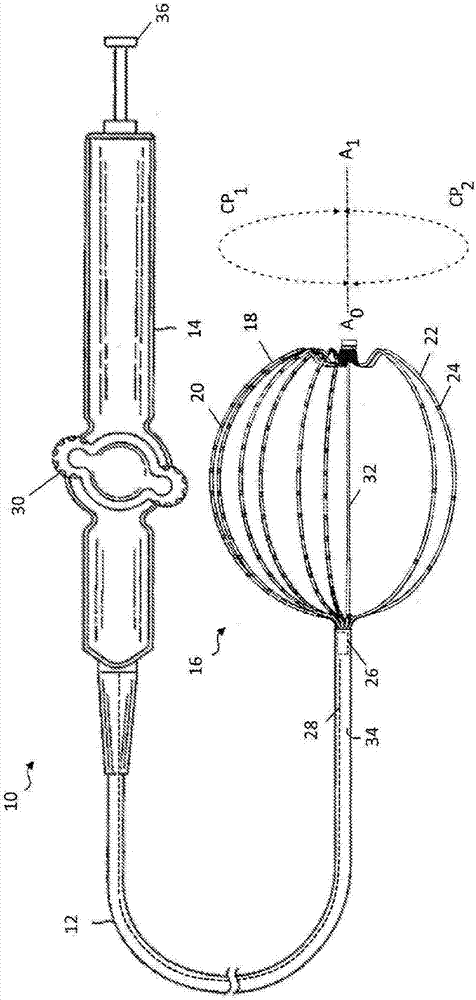
Intravascular foreign object retrieval catheter
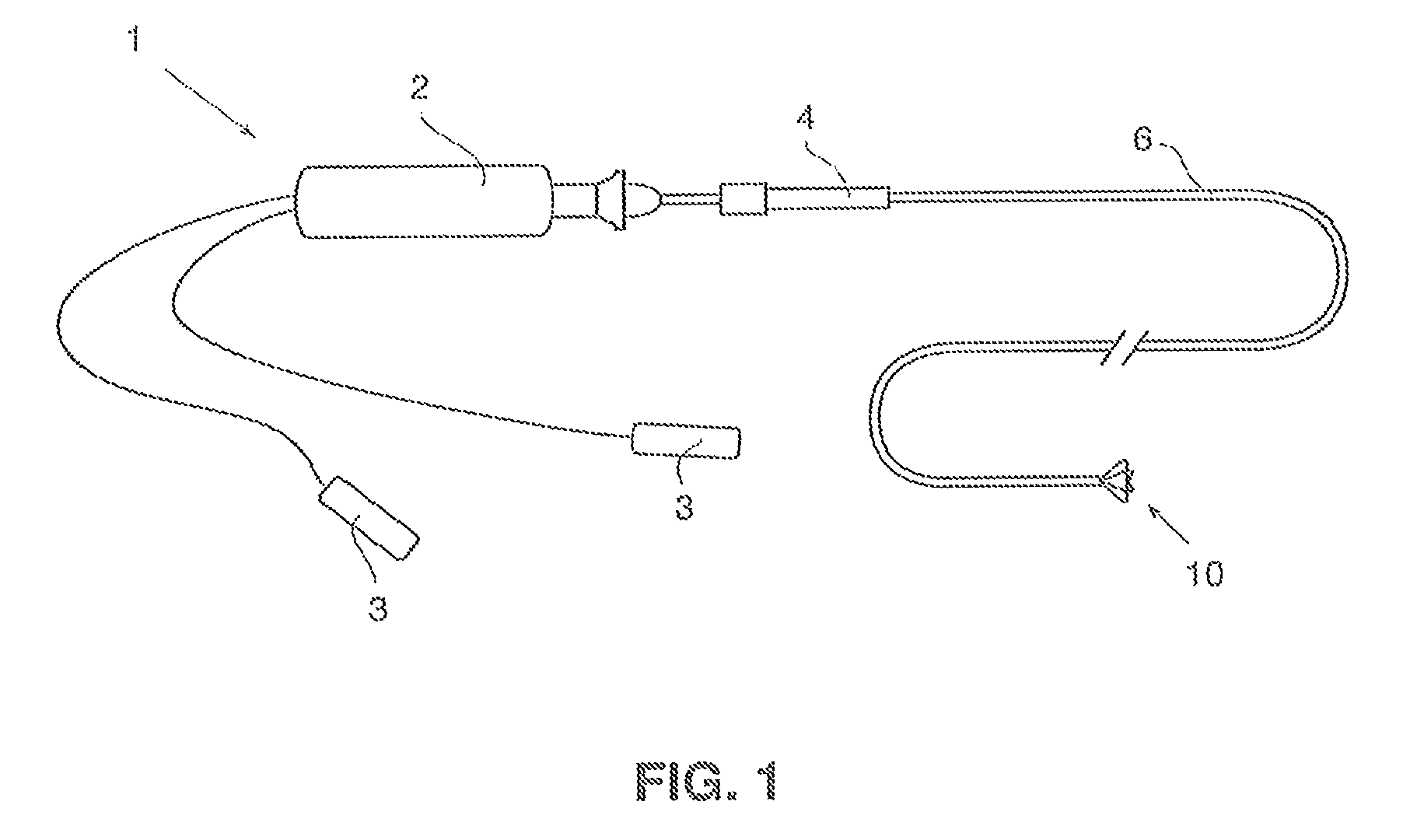
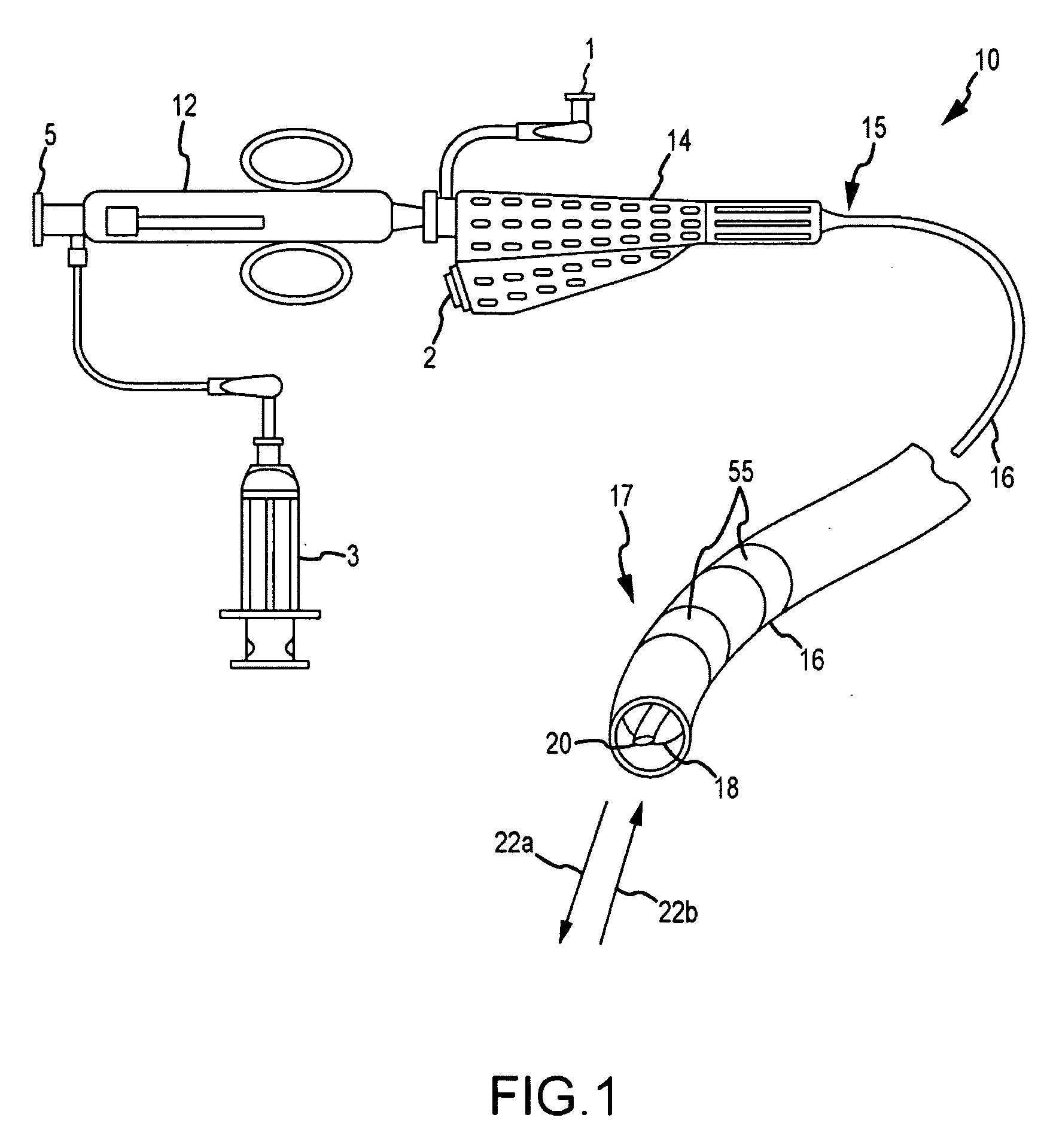
The present invention discloses an intravascular foreign object retrieval catheter having an elongated, flexible first outer containment catheter having a second basket catheter contained therein and having a third microcatheter contained therein and having a fourth snare wire contained therein having a loop on the end thereof. The containment catheter, the basket catheter and the microcatheter work together as coaxial tubes. The basket catheter is slidable within the containment catheter, the microcatheter is slidable within the basket catheter, and the wire is slidable within the microcatheter. The basket catheter has a containment basket on its distal end which is used to surround a foreign object whereupon the innermost wire having a loop on its end is then placed around the foreign object. Thereafter, the microcatheter is advanced along the innermost wire in order to tighten the loop around the foreign object. The microcatheter and the loop with the object contained therein are retrieved into the containment basket. The containment basket is retrieved into the containment catheter where the object may or may not be partially crushed and then the containment catheter is removed from the patient having the foreign object contained therein.
Owner:DRISKILL GEORGE MARK
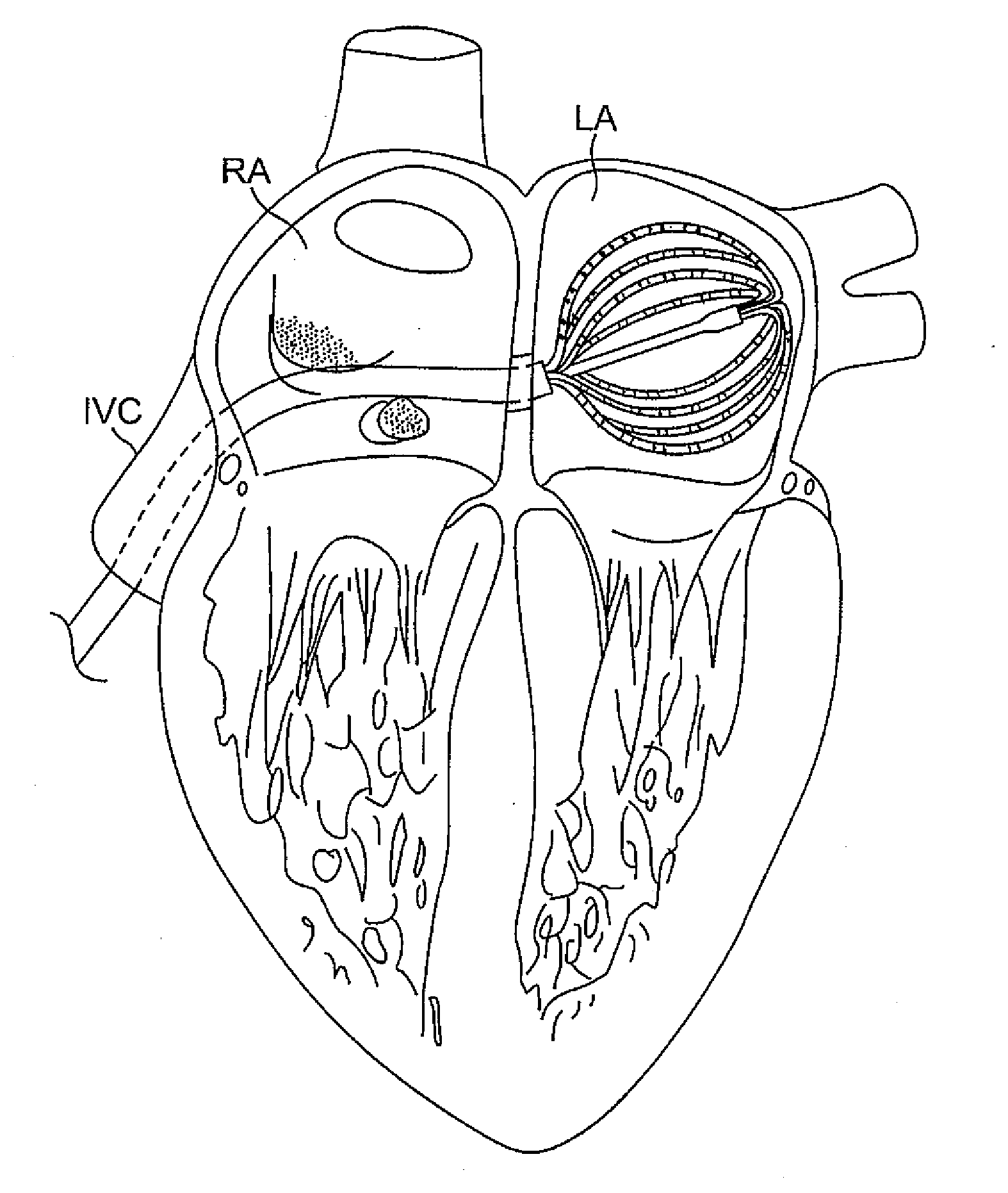
Method and apparatus for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque
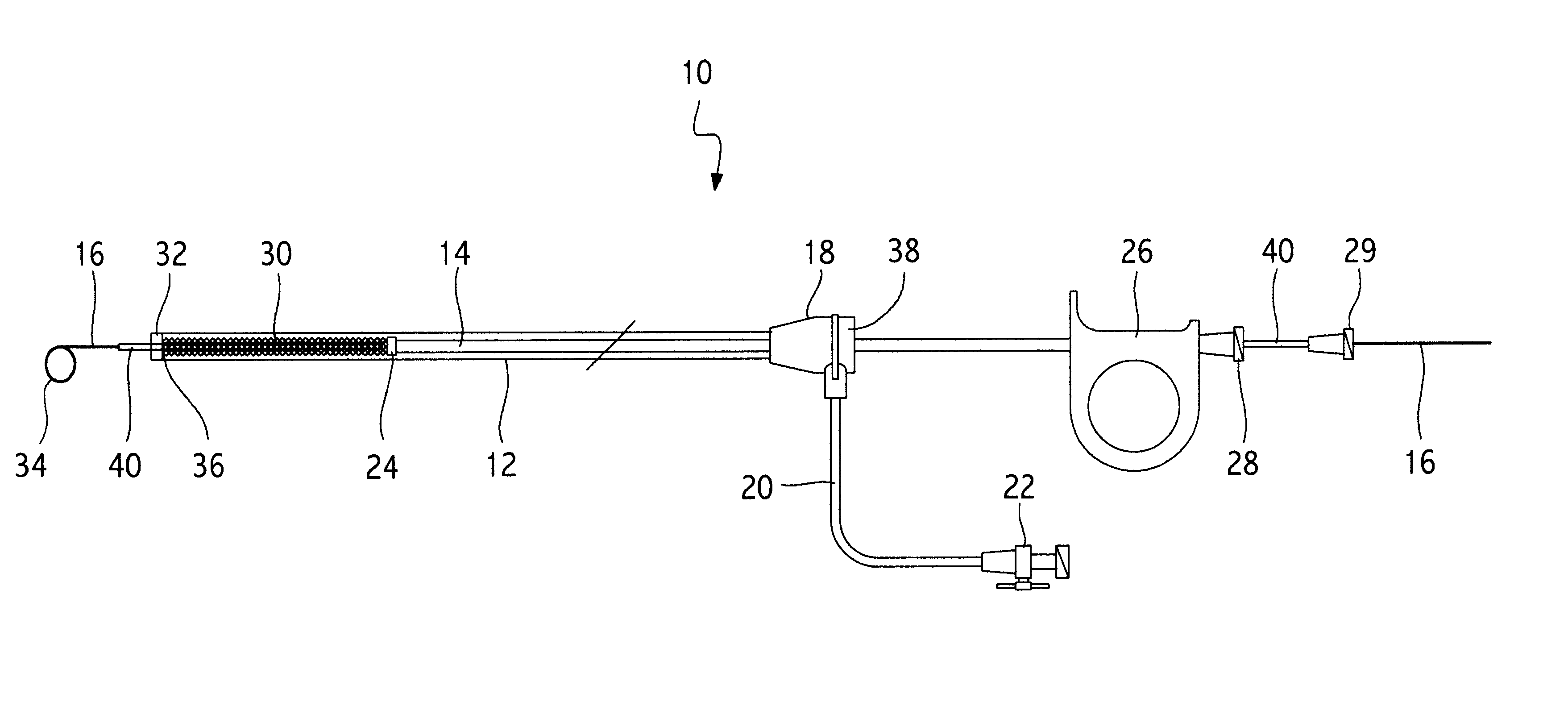
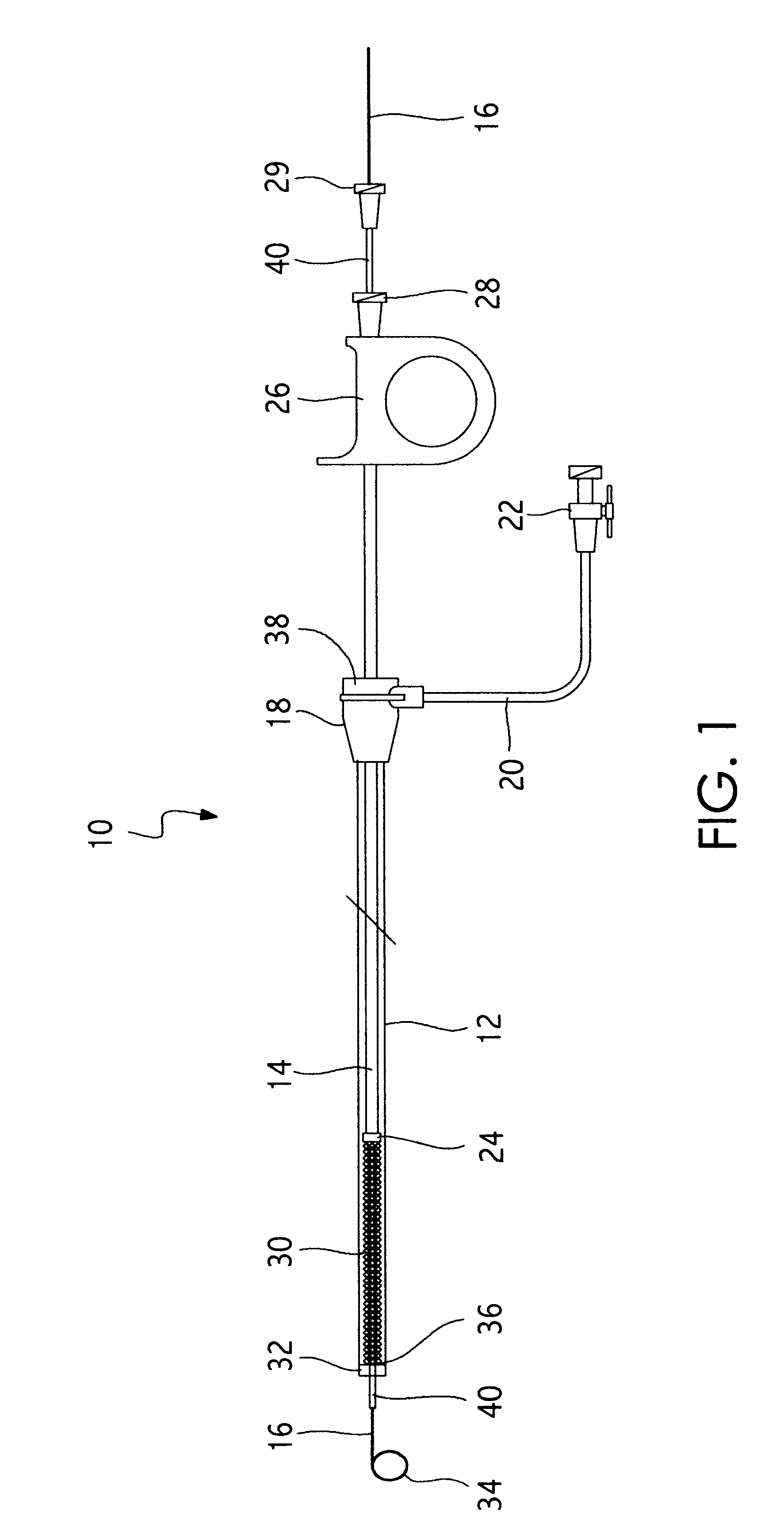
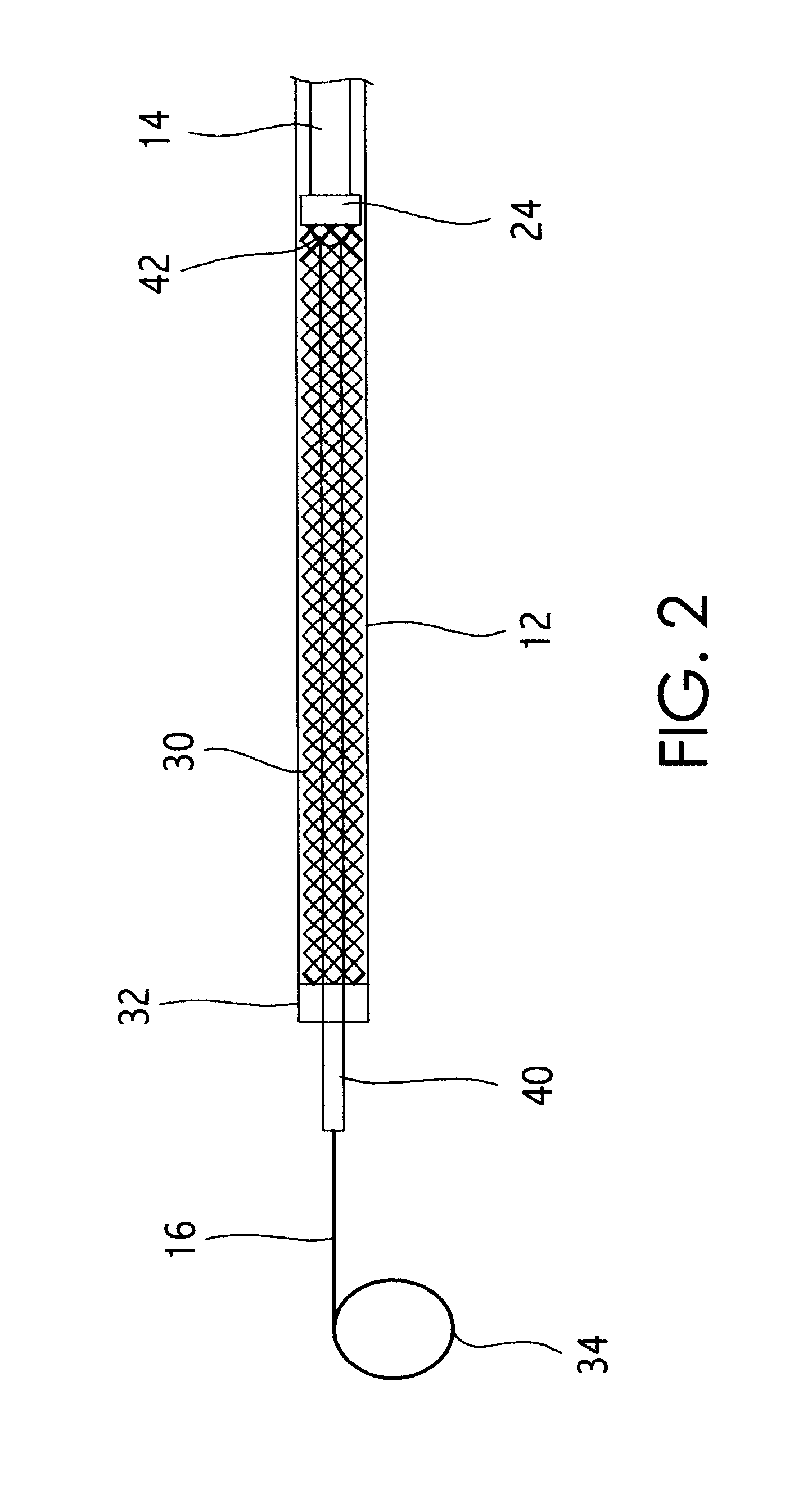
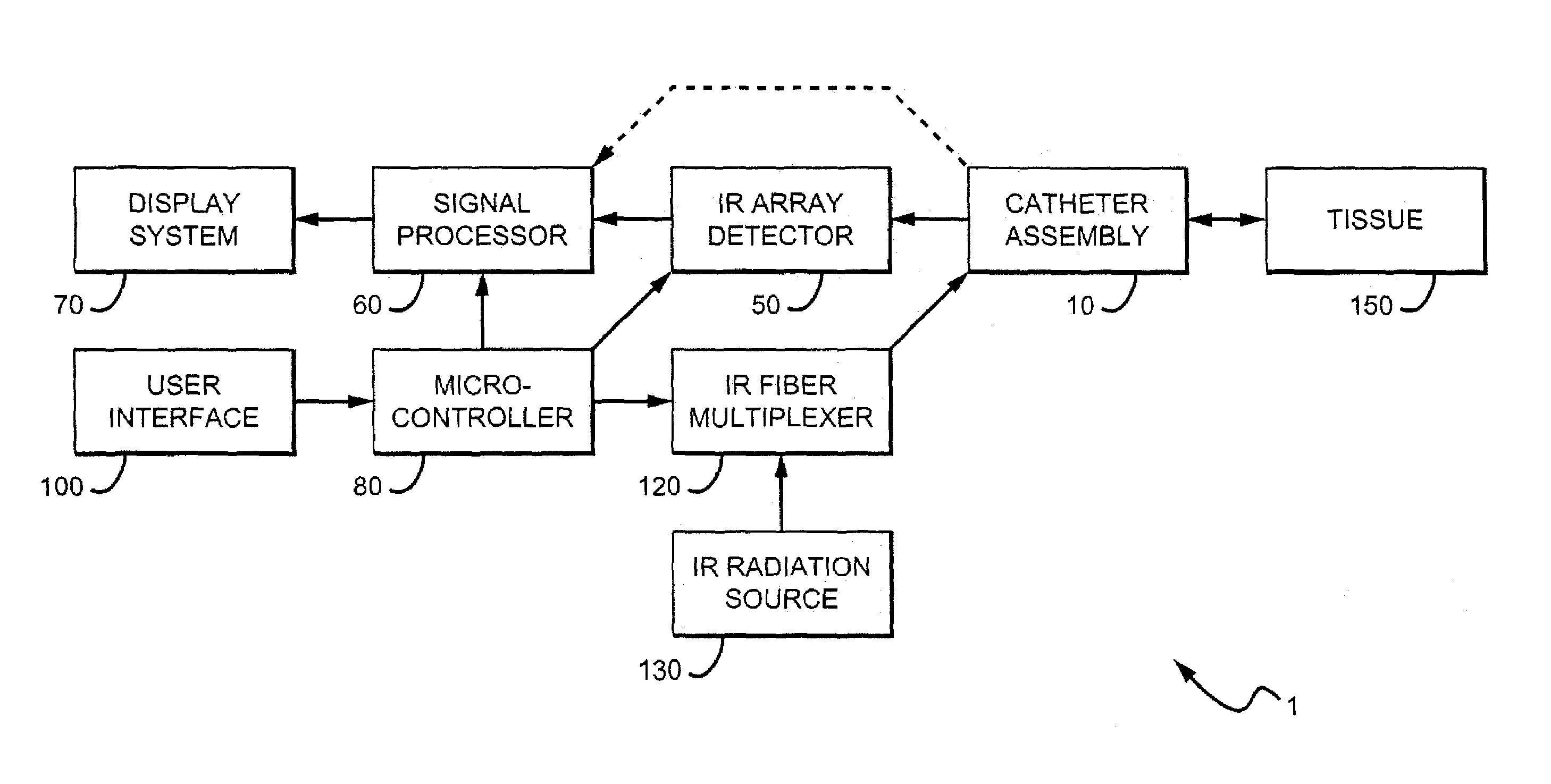
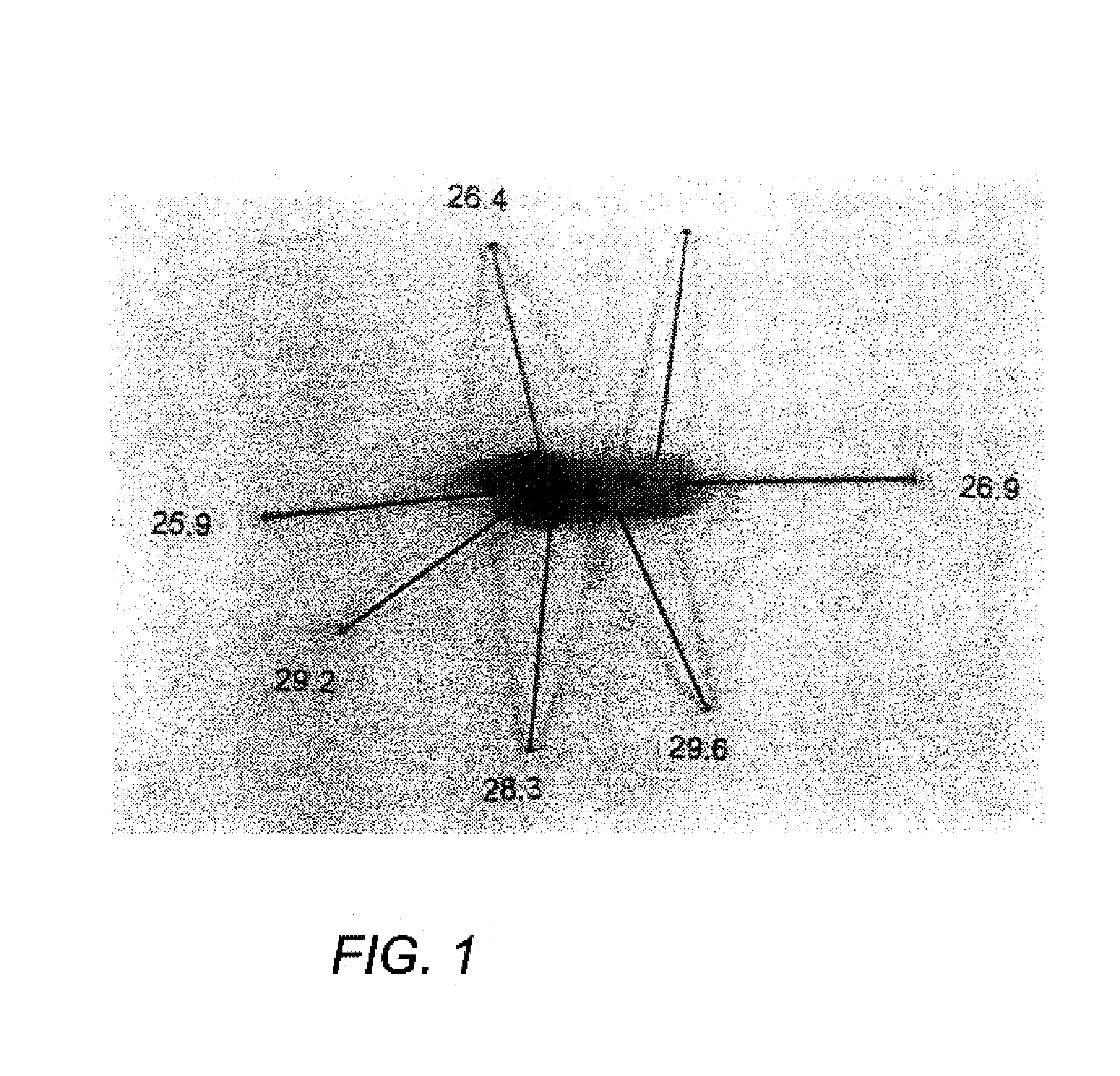
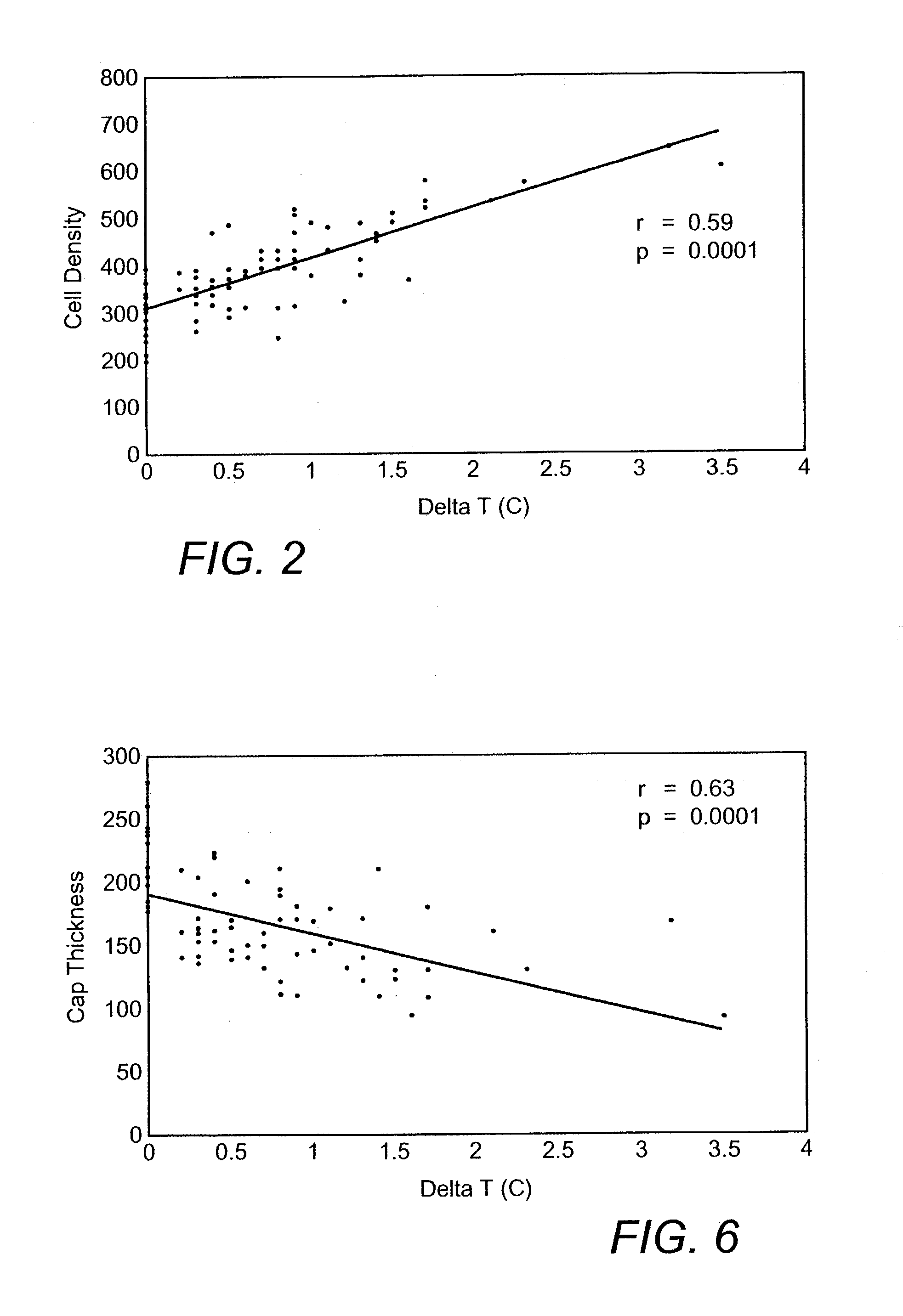
Methods and devices are disclosed for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque, or plaque at risk of reducing blood flow in a vessel, by identifying a region of elevated temperature along a living vessel wall. The disclosure that human atherosclerotic plaque with measurable temperature heterogeneity has the morphological characteristics of plaque that is likely to ulcerate provides a new and sensitive technique for detecting and treating these dangerous plaques before myocardial infarction and its consequences occur. The disclosed methods are advantageous over conventional plaque detection techniques because they are capable of differentiating between those plaques that are at great risk of rupture, fissure, or ulceration, and consequent thrombosis and occlusion of the artery, and those that are not presently at risk. Infrared heat-sensing catheters useful for identifying potentially fatal arterial plaques in patients with disease of the coronary or other arteries are also described. In some embodiments a coherent infrared fiber optic bundle is employed to radially and longitudinally explore a luminal wall to identify inflamed, heat-producing, atherosclerotic plaque. Certain other methods and devices are disclosed which are particularly suited for non-invasively identifying and then monitoring the progression or amelioration of an inflamed plaque in a patient, and for monitoring for onset of inflammation in an implanted arteriovenous graft. Also disclosed are thermocouple basket catheters and thermistor basket catheters which are also capable of detecting temperature heterogeneity along a vessel wall.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
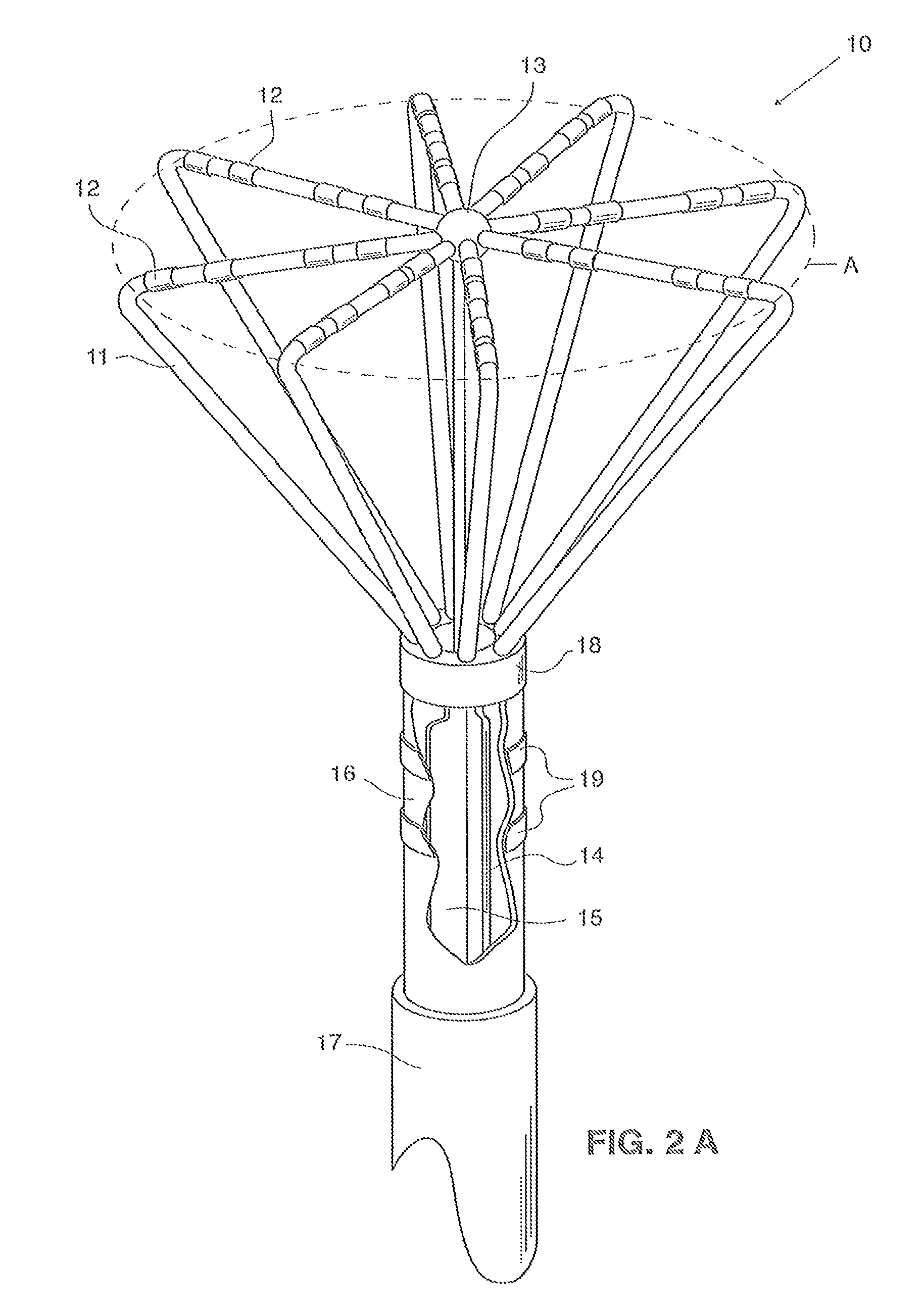
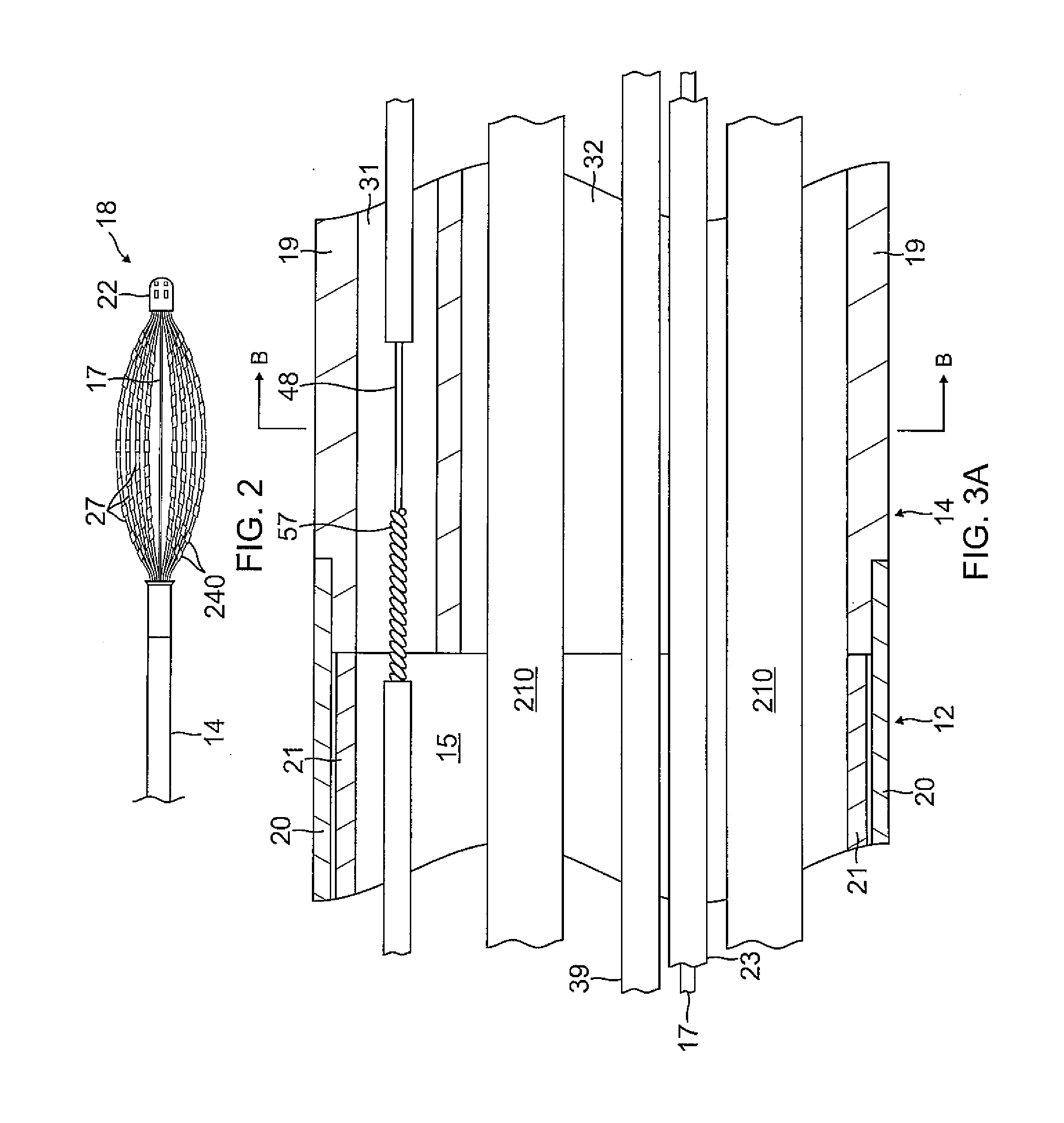
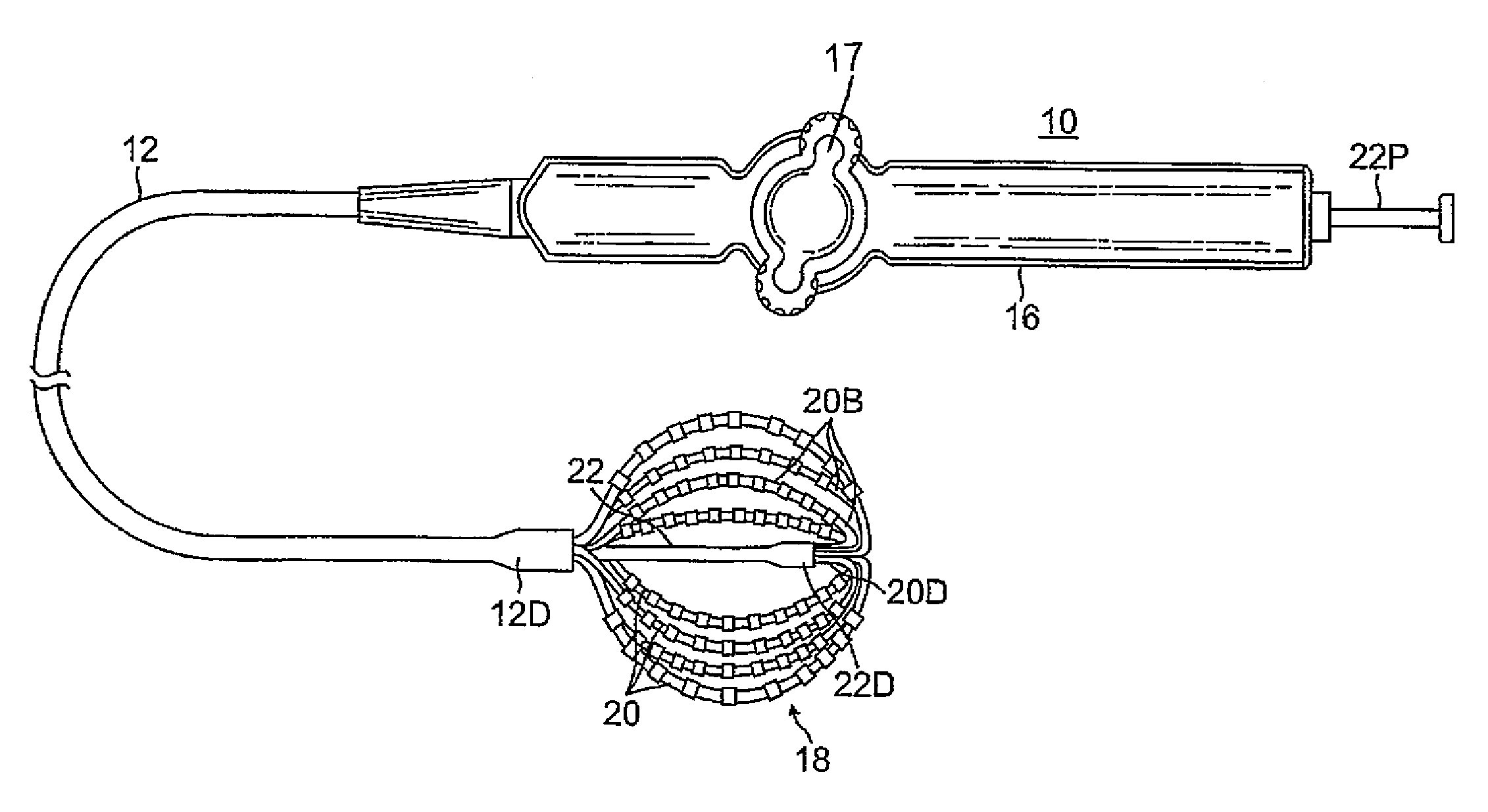
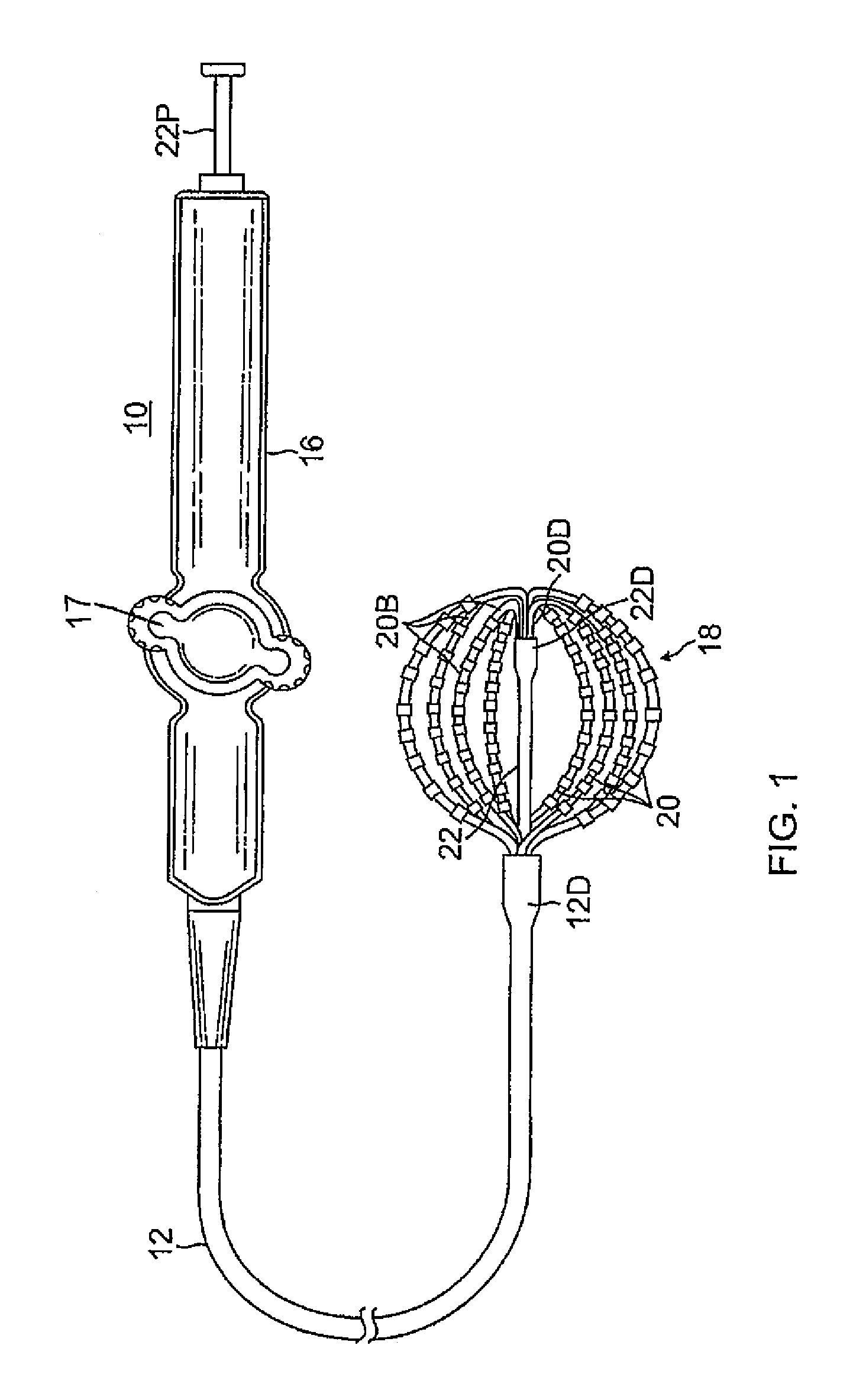
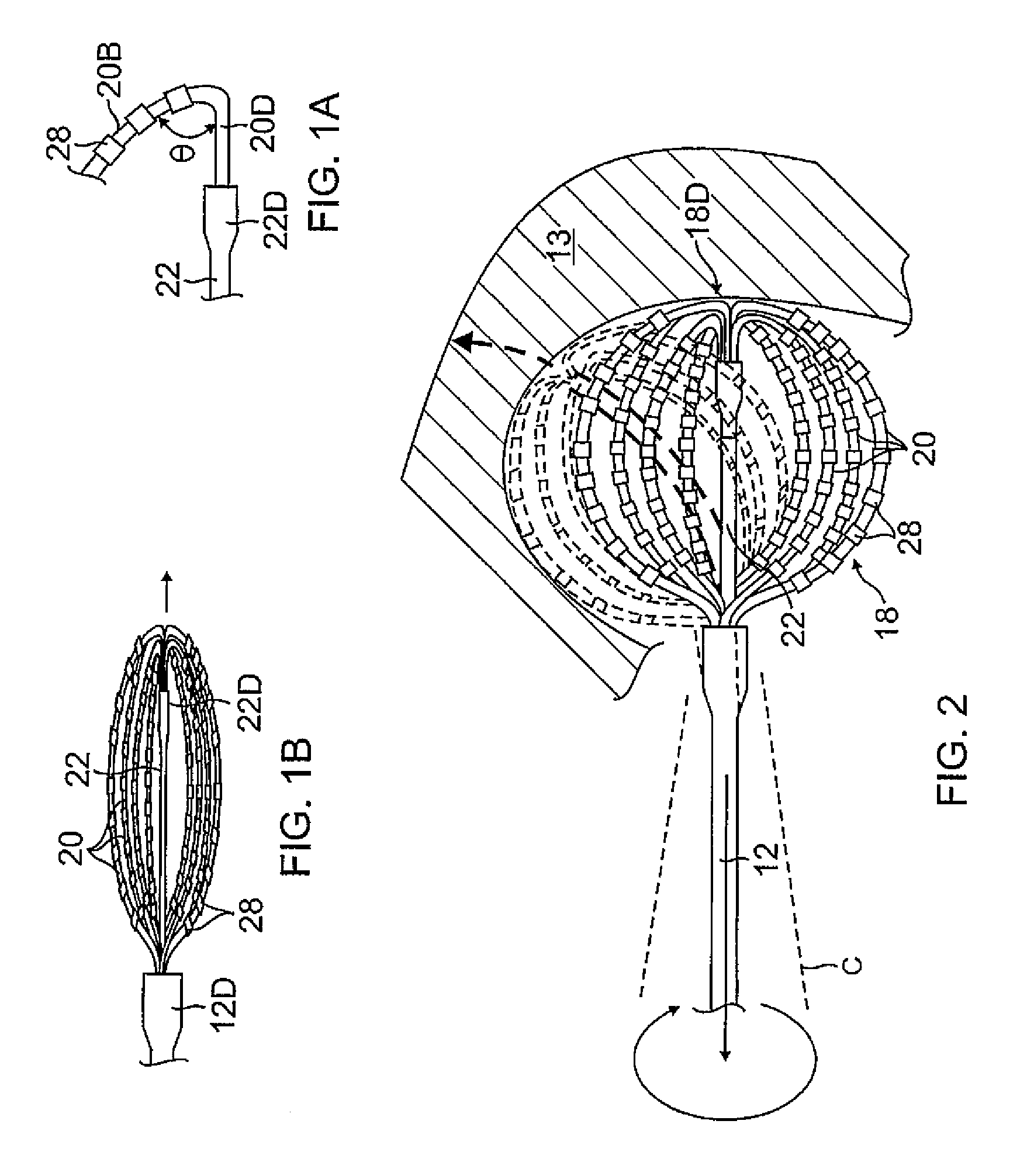
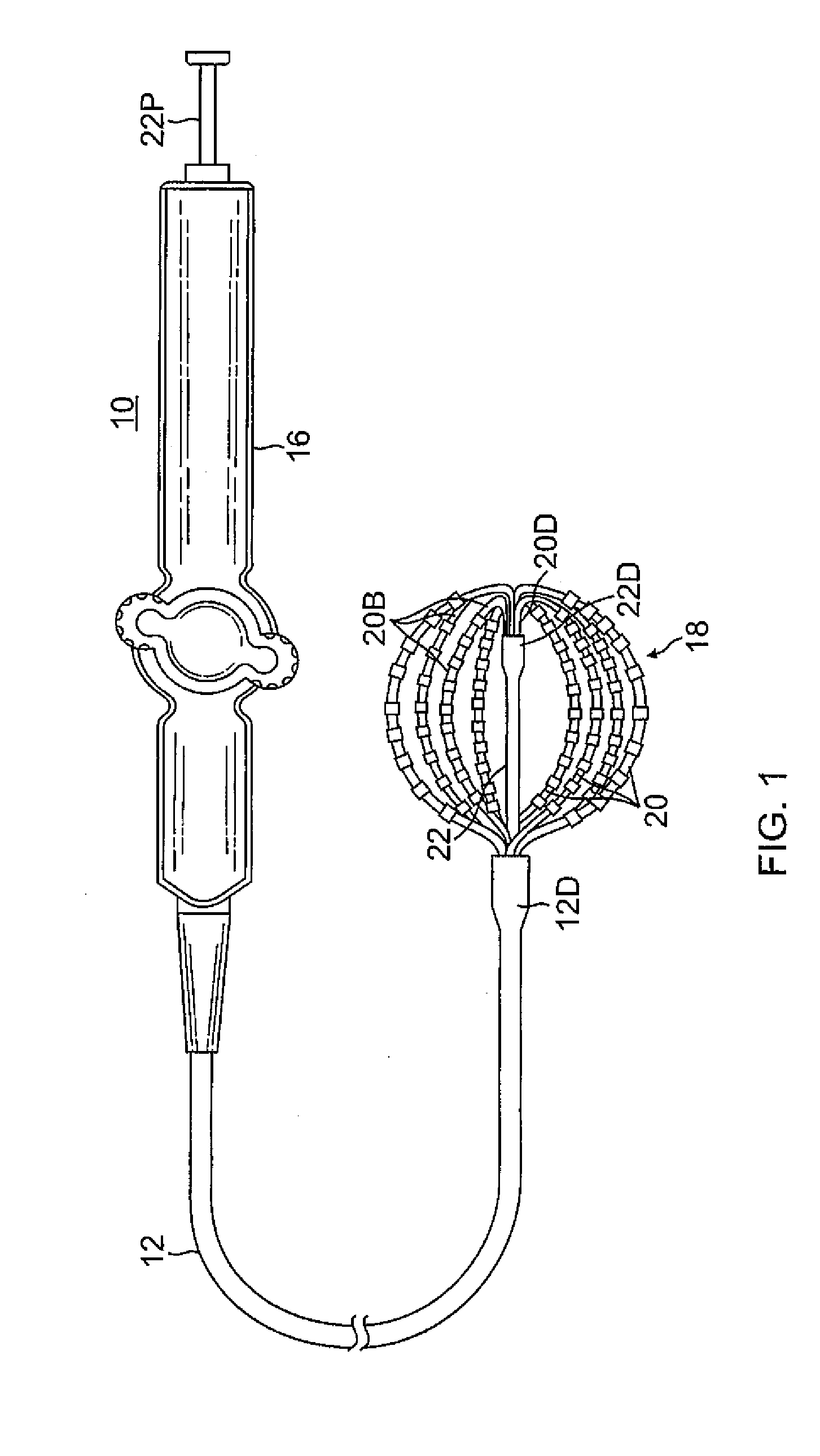
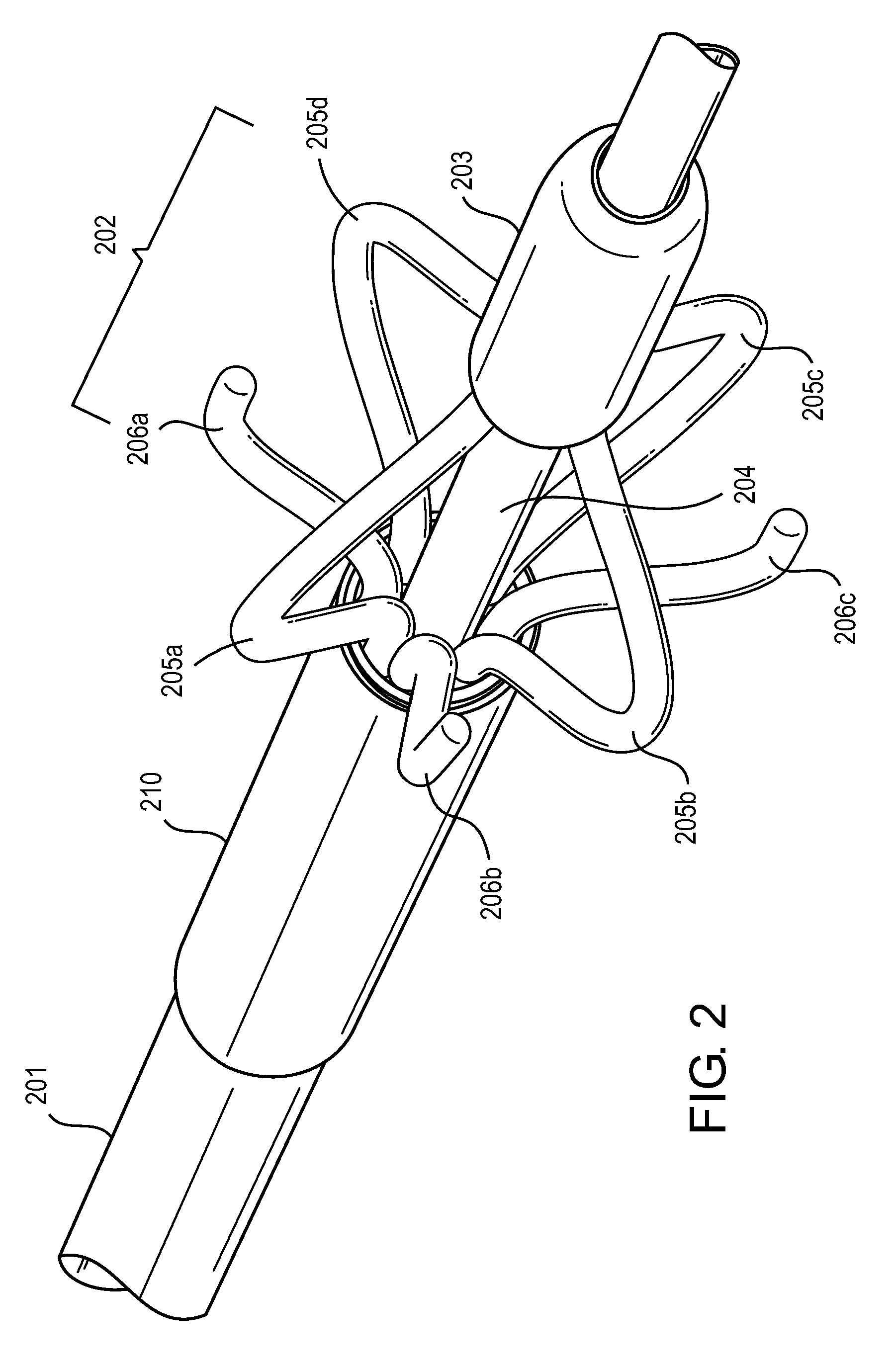
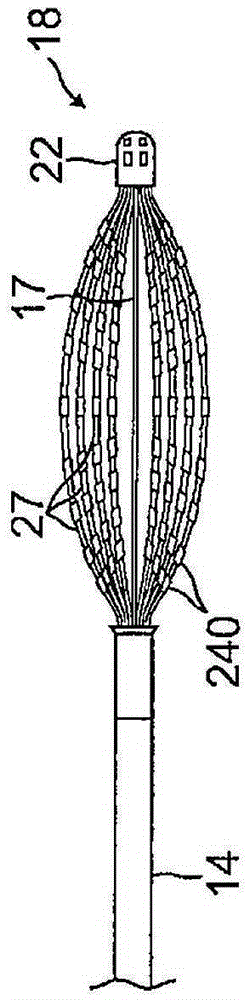
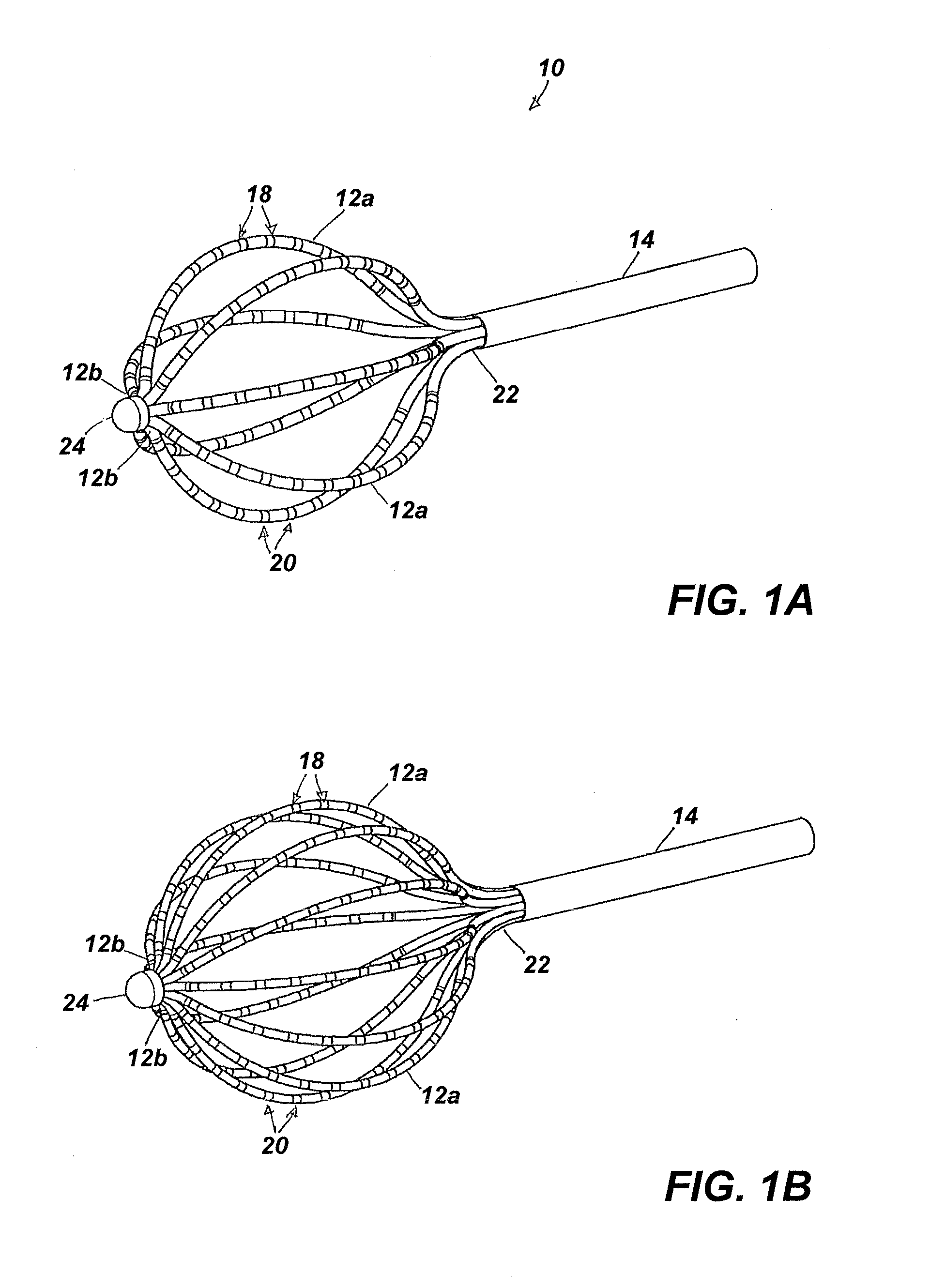
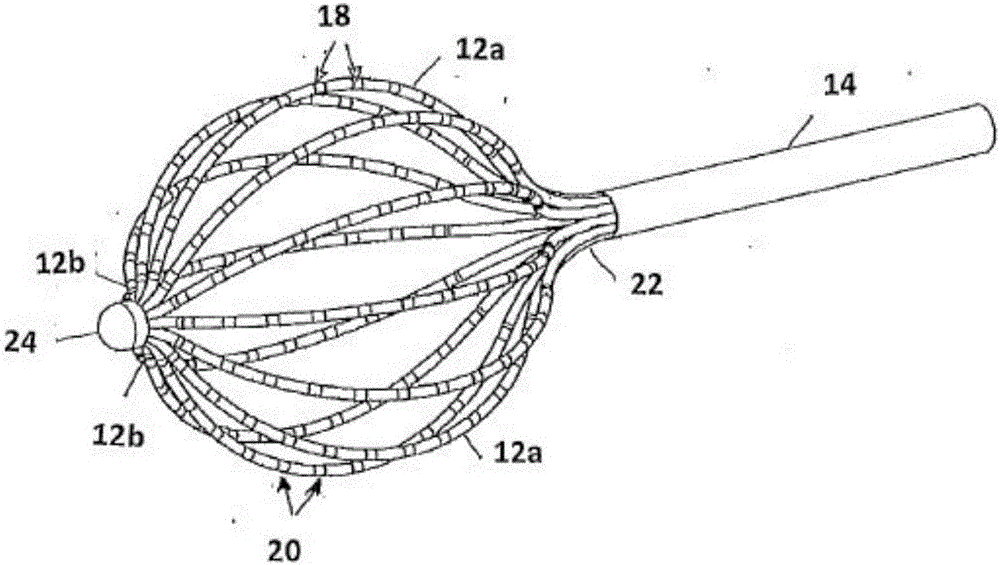
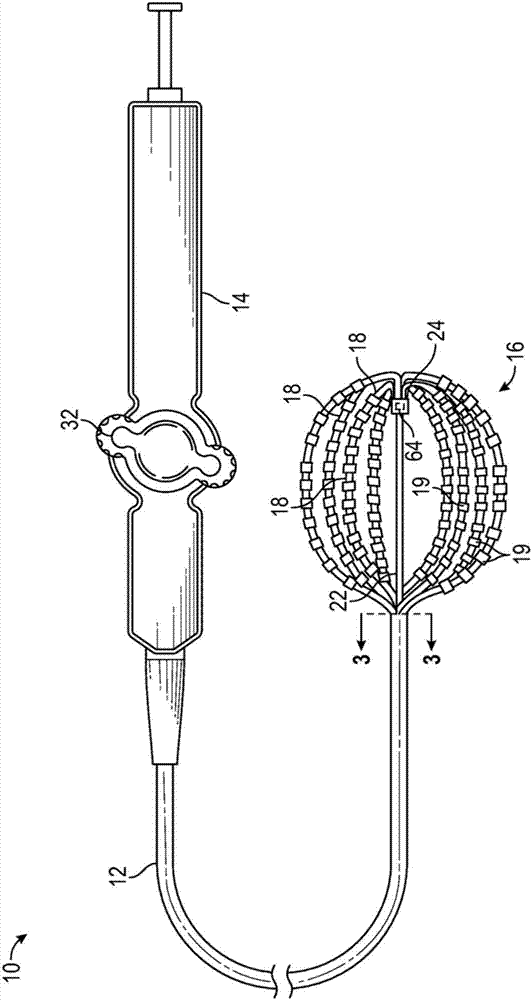
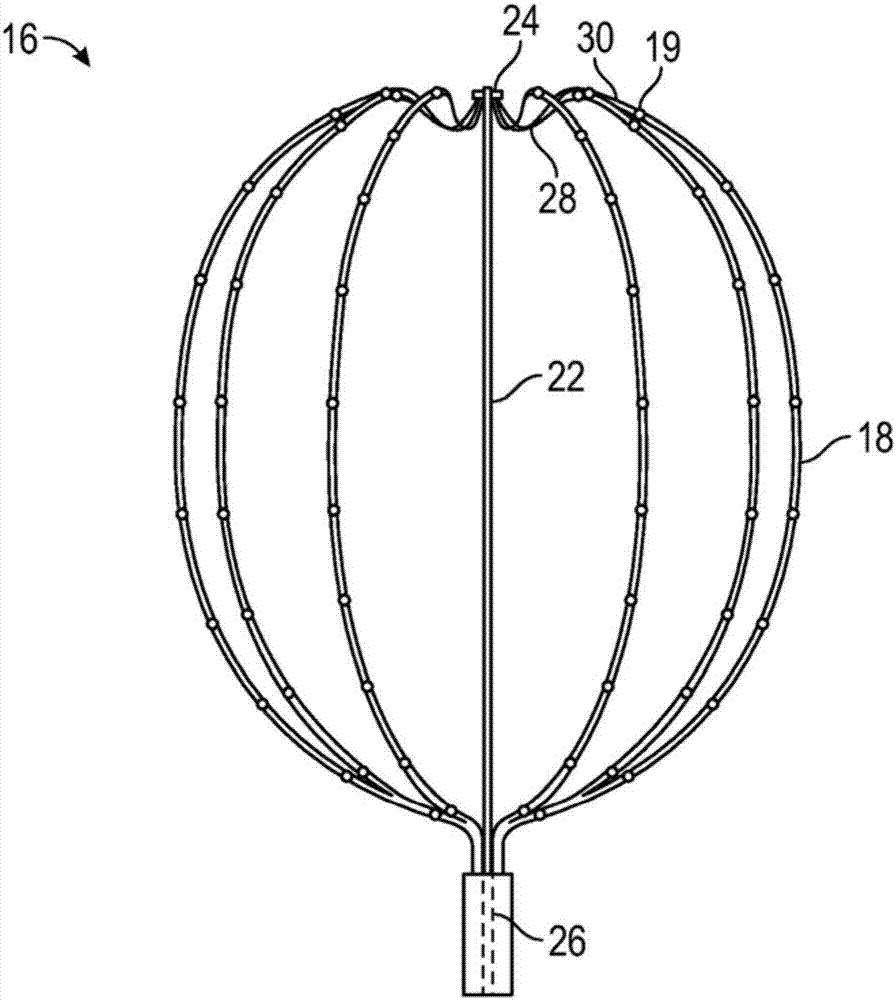
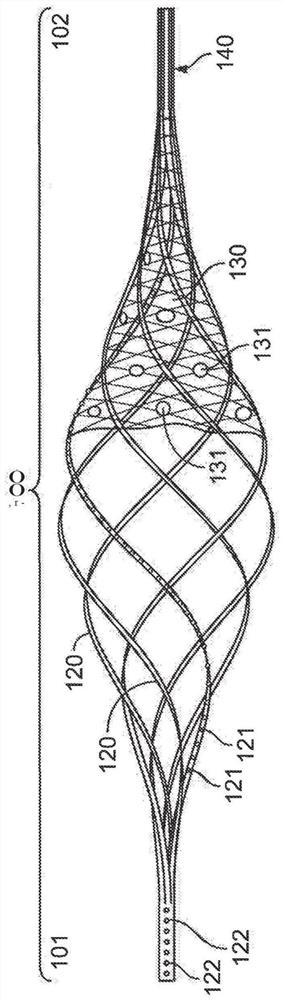
Basket catheter having multiple electrodes
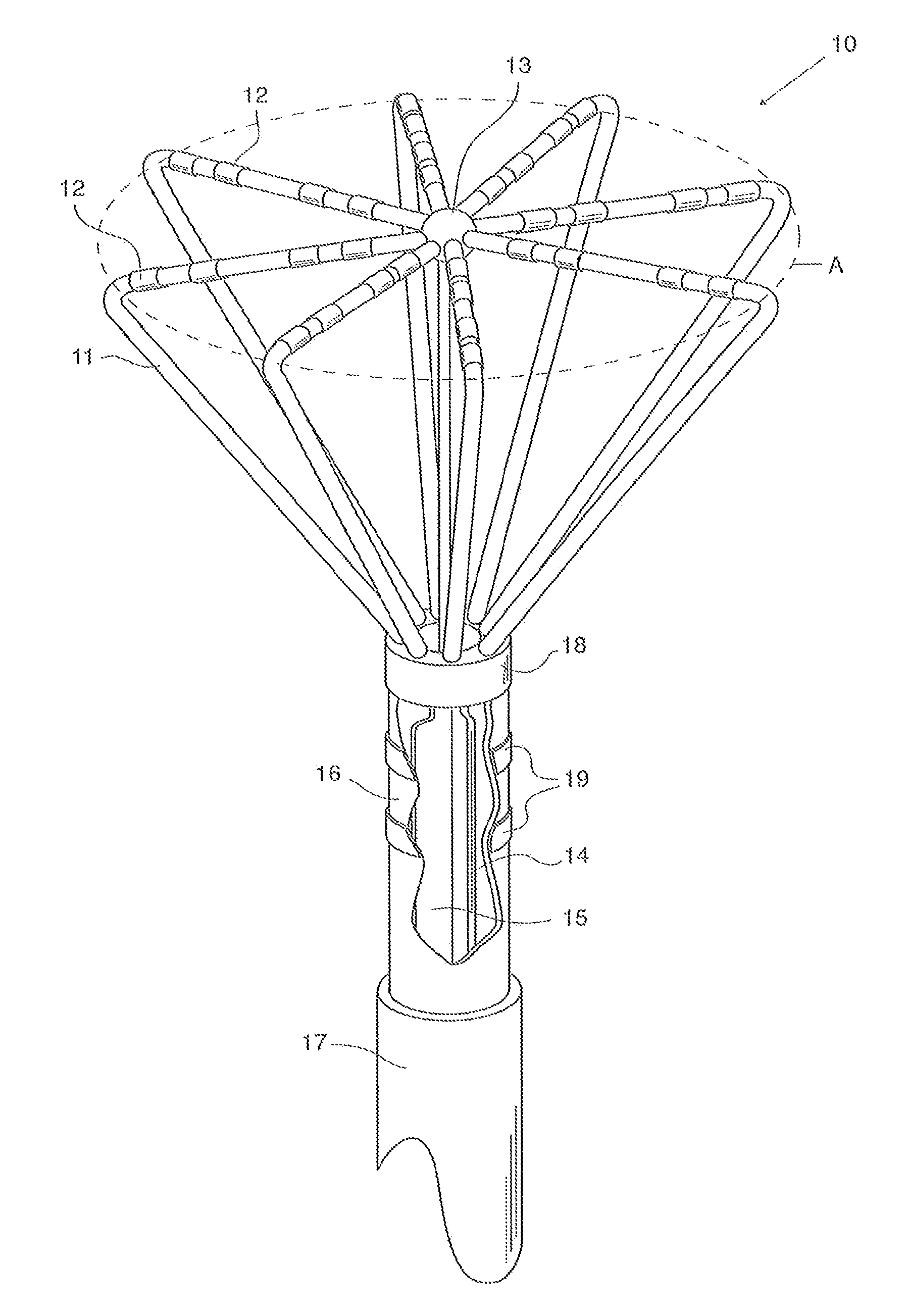
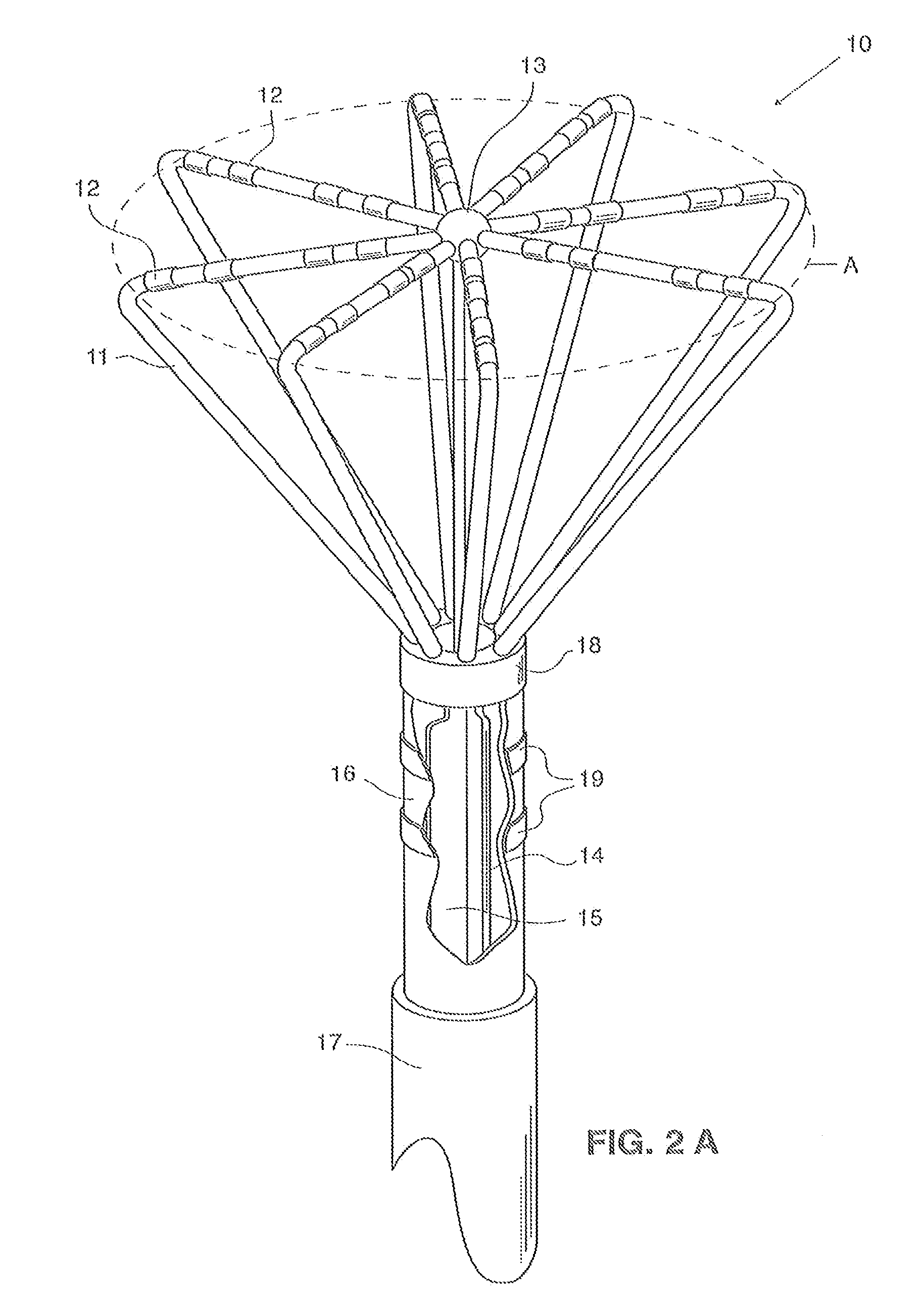
Embodiments of the present invention provide a catheter that comprises an elongated catheter body (16) and an electrode assembly (10) at the distal end of the catheter body. The electrode assembly comprises a plurality of spines (11), each of the spines having a proximal end connected to the distal end of the catheter and a distal end, the distal ends of the spines being connected at a spine tip junction (13). Each spine includes an elbow (20) having at least one discontinuity in stiffness at an intermediate position between the distal end and the proximal end thereof. The spines include a plurality of electrodes (12). The electrode assembly is collapsible to a collapsed arrangement to fit within a lumen of the elongated catheter body and expandable to an expanded arrangement with the elbows of the spines bending outwardly relative to the proximal and distal ends of the spines.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Steerable diagnostic catheters
InactiveUS7269453B2Small sizeOverall shapeElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyRest positionOhmic contact
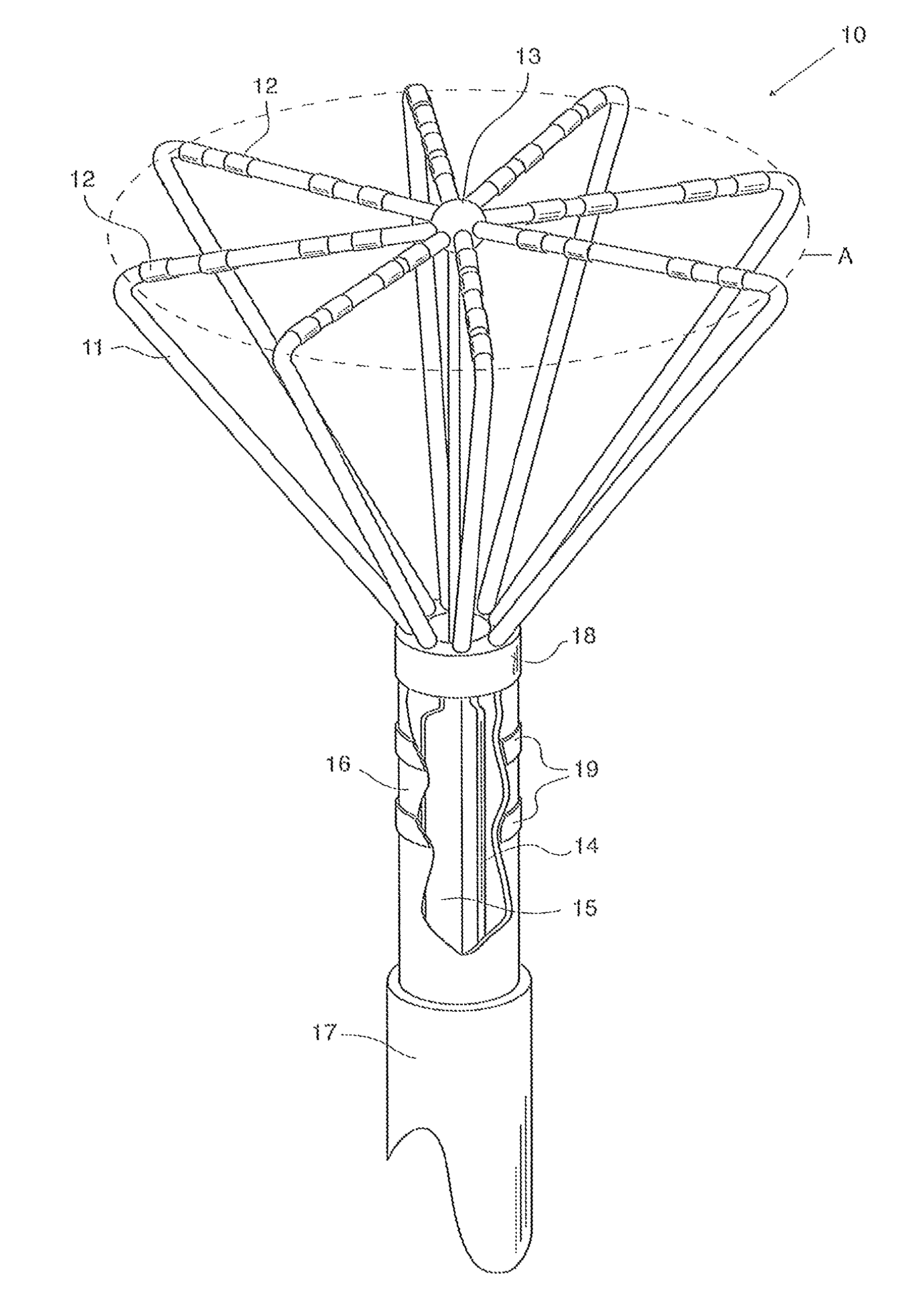
A diagnostic catheter with a steering device to direct the distal end of the catheter while it is inserted in a vessel. The catheter may include either a bi-directional steering mechanism, or a unidirectional steering mechanism. Pre-formed catheters with no steering means are also provided. The catheter bodies include a plurality of ring electrodes used for sensing the intracardial electrogram signal during operation of the catheter. The ring electrodes are placed in ohmic contact with their corresponding signal wires by a solderless connection. In addition, the catheter may be embodied as a basket catheter including a plurality of splines. After the catheter is inserted into the vessel or organ to be examined (typically the heart), the splines may be expanded from an at-rest position to form the basket. A central retractable and steerable member is included to provide the expansion force. The expansion force can also be provided by moving the proximal portion of the catheter relative to the central member. Each of the splines forming the basket includes a length of spring wire disposed therein to provide conformal forces causing the splines to conform to the surfaces being inspected.
Owner:MOGUL JAMIL
Basket catheter having multiple electrodes
Embodiments of the present invention provide a catheter that comprises an elongated catheter body (16) and an electrode assembly (10) at the distal end of the catheter body. The electrode assembly comprises a plurality of spines (11), each of the spines having a proximal end connected to the distal end of the catheter and a distal end, the distal ends of the spines being connected at a spine tip junction (13). Each spine includes an elbow (20) having at least one discontinuity in stiffness at an intermediate position between the distal end and the proximal end thereof. The spines include a plurality of electrodes (12). The electrode assembly is collapsible to a collapsed arrangement to fit within a lumen of the elongated catheter body and expandable to an expanded arrangement with the elbows of the spines bending outwardly relative to the proximal and distal ends of the spines.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
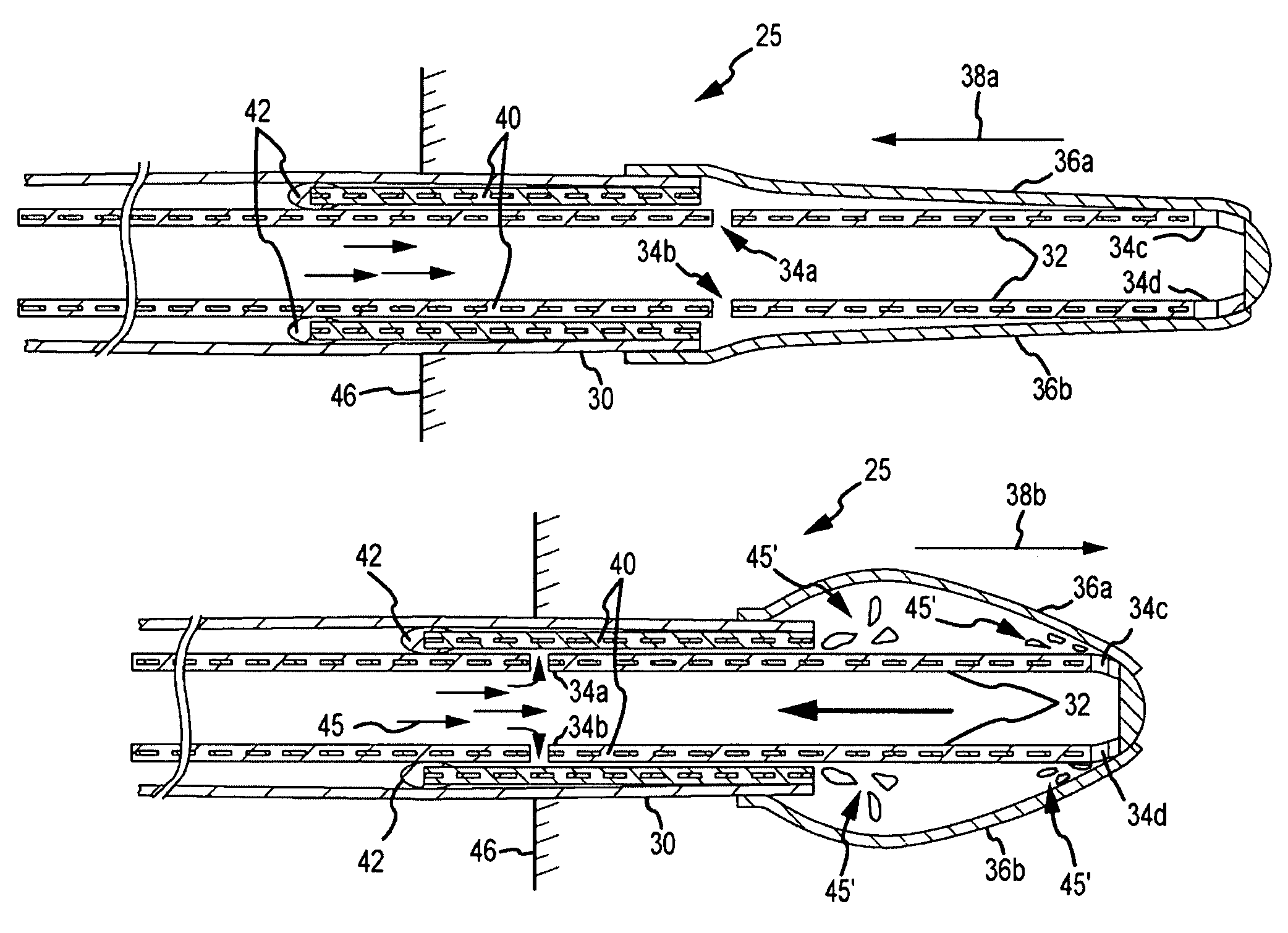
Basket catheter with improved spine flexibility
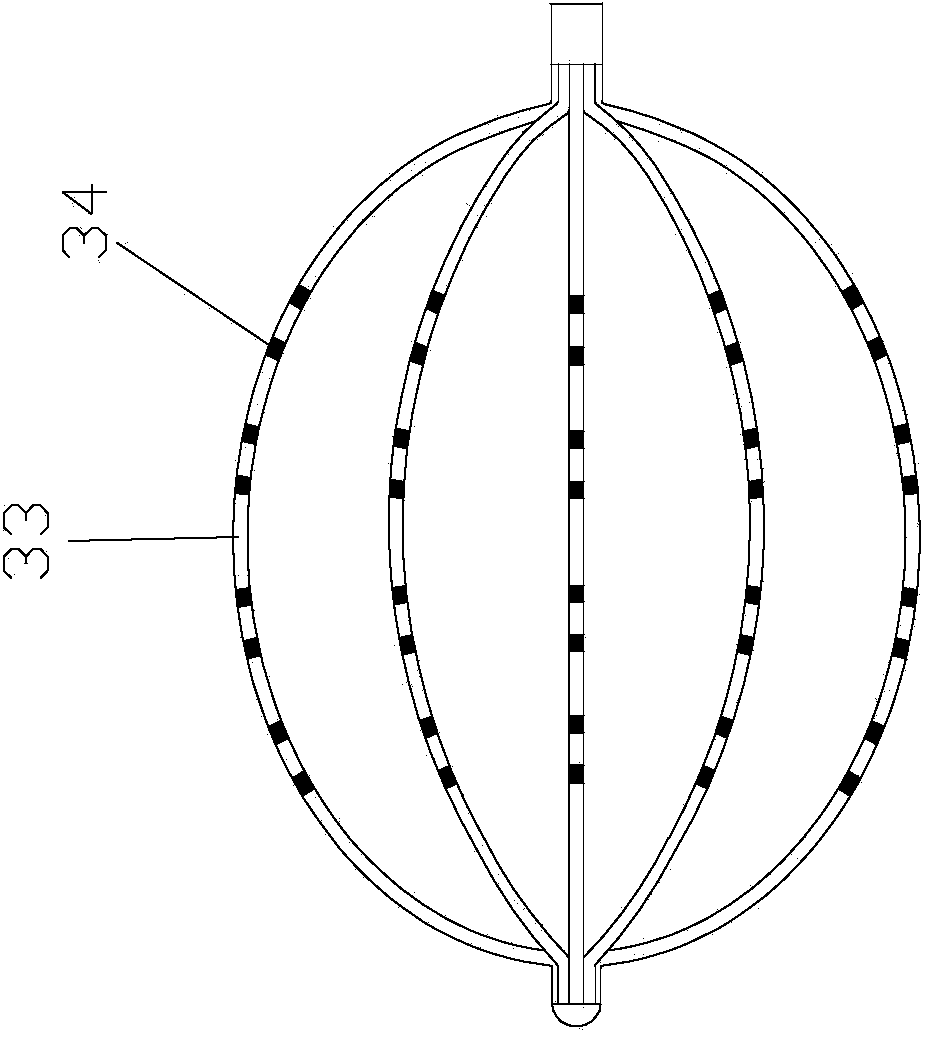
ActiveUS20160183877A1Reduce riskEasy to bendElectrocardiographyMedical devicesBasket catheterGuide tube
A catheter with basket-shaped electrode assembly with spines configured for hyper-flexing in a predetermined, predictable manner when a compressive force acts on the assembly from either its distal end or its proximal end. At least one spine has at least one region of greater (or hyper) flexibility that allows the electrode assembly to deform, for example, compress, for absorbing and dampening excessive force that may otherwise cause damage or injury to tissue wall in contact with the assembly, without compromising the structure and stiffness of the remaining regions of the spine, including its distal and proximal regions. The one or more regions of greater flexibility in the spine allow the spine to flex into a generally V-shape configuration or a generally U-shape configuration.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Basket catheter with improved spine flexibility
ActiveUS9782099B2Reduce riskEasy to bendElectrocardiographyMedical devicesProximal pointBasket catheter
A catheter with basket-shaped electrode assembly with spines configured for hyper-flexing in a predetermined, predictable manner when a compressive force acts on the assembly from either its distal end or its proximal end. At least one spine has at least one region of greater (or hyper) flexibility that allows the electrode assembly to deform, for example, compress, for absorbing and dampening excessive force that may otherwise cause damage or injury to tissue wall in contact with the assembly, without compromising the structure and stiffness of the remaining regions of the spine, including its distal and proximal regions. The one or more regions of greater flexibility in the spine allow the spine to flex into a generally V-shape configuration or a generally U-shape configuration.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Non-contact electrode basket catheters with irrigation
ActiveUS20100168647A1Reduce riskPrevent blood coagulationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineBasket catheter
Catheter systems and methods are disclosed. An exemplary catheter includes an outer tubing housing and an inner fluid delivery tubing, the inner fluid delivery tubing having at least one fluid delivery port. The catheter also includes a deployment member movable axially within the inner fluid delivery tubing. A plurality of splines are each connected at a proximal end to the outer tubing and at a distal end to deployment member. A seal is provided between the outer tubing and the inner fluid delivery tubing. A gasket is provided between the deployment member and the inner fluid delivery tubing. Both the seal and the gasket are configured to prevent blood or other fluid from ingressing into the outer tubing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
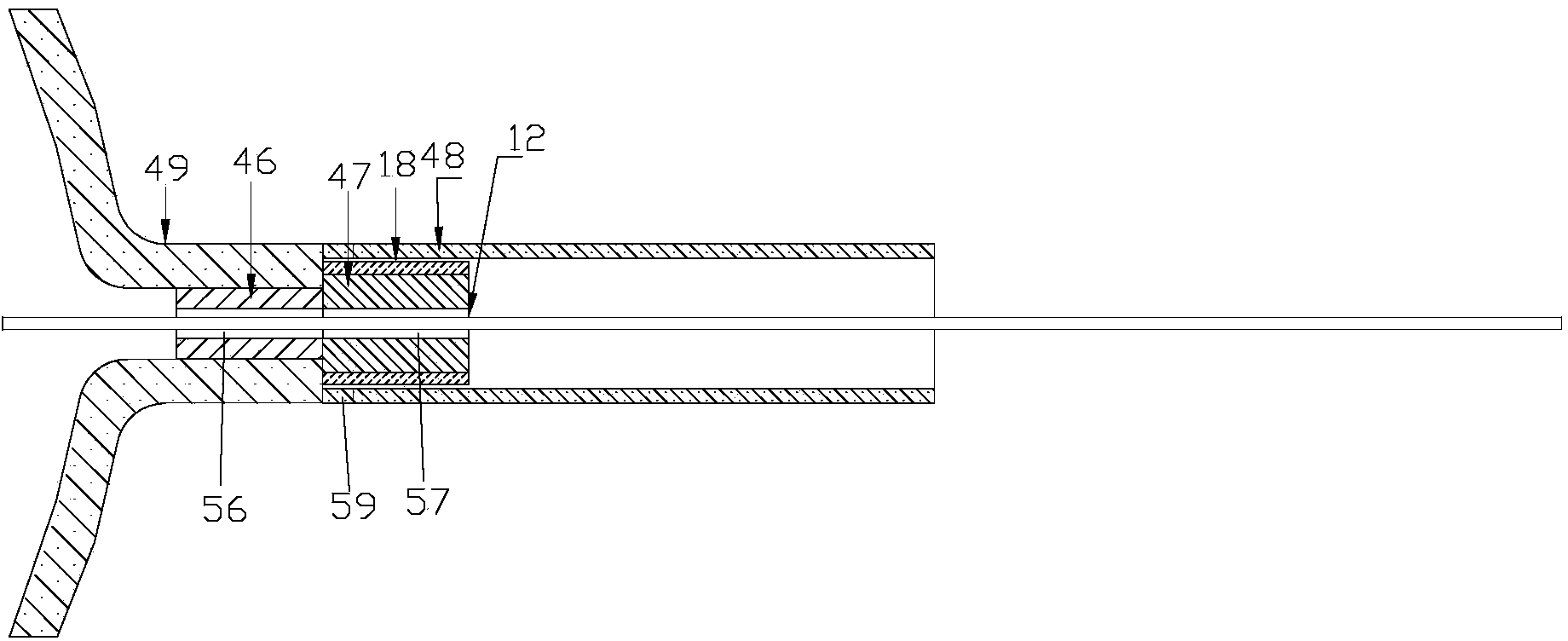
Basket catheter with deflectable spine
ActiveUS9204929B2Improved control and placementConstant precisionElectrocardiographyCatheterDilatorActuator
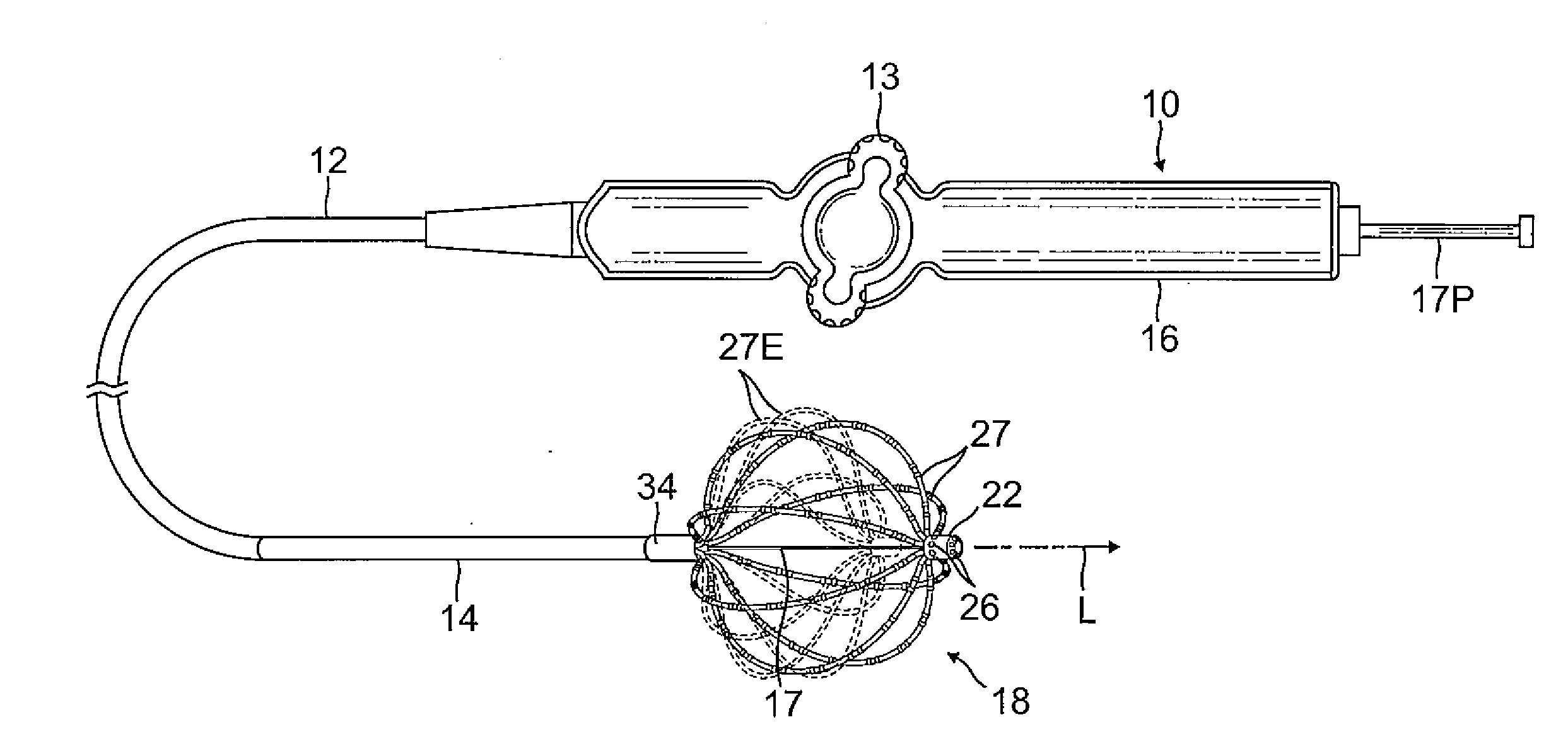
A catheter adapted for mapping and / or ablation in the atria has a basket-shaped electrode array with two or more location sensors with a deflectable expander. The catheter has comprises a catheter body, a basket electrode assembly at a distal end of the catheter body, and a control handle at a proximal end of the catheter body. The basket electrode assembly has a plurality of electrode-carrying spines and an expander that is adapted for longitudinal movement relative to the catheter body for expanding and collapsing the assembly via a proximal end portion extending past the control handle that can be pushed or pulled by a user. The expander is also adapted for deflection in responsive to an actuator on the control handle that allows a user to control at least one puller wire extending through the catheter body and the expander.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Multi-electrode basket catheter and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN103750899AEasy to take backFully contactedDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingSurgeryBasket catheter
The invention discloses a multi-electrode basket catheter and a manufacture method of the multi-electrode basket catheter to solve the technical problem of accurately and rapidly conducting mapping or radio frequency ablation treatment in the operation process. The multi-electrode basket catheter comprises a basket device. A basket of the basket device is composed of strip-shaped arms. The near end of each strip-shaped arm and the far end of the strip-shaped arm are connected to a near end connecting structure and a far end connecting structure. The strip-shaped arms are bent under the action of external force to form an arc shape or form a spatial curve so that the basket of an ellipsoid shape can be defined. The strip-shaped arms are stretched out or drawn back in the length direction of the strip-shaped arms under the action of external force to form a stranded wire. Annular electrodes are distributed on the outer surfaces of the strip-shaped electrodes. The manufacture method of the multi-electrode basket catheter includes the steps of manufacturing all parts and assembling the parts. Compared with the prior art, the multi-electrode basket catheter has the advantages that the size of the basket formed by the strip-shaped arms can be adjusted under the control of one handle, and therefore the electrodes distributed in the space on the strip-shaped arms make full and close contact with the tissue of the endocardium, mapping or radio frequency ablation treatment is accurately and rapidly conducted, and the basket is conveniently recycled.
Owner:APT MEDICAL INC
Basket catheter with deflectable spine
ActiveUS20150080693A1Improved control and placementConstant precisionElectrocardiographyCatheterSpinal columnDilator
A catheter adapted for mapping and / or ablation in the atria has a basket-shaped electrode array with two or more location sensors with a deflectable expander. The catheter has comprises a catheter body, a basket electrode assembly at a distal end of the catheter body, and a control handle at a proximal end of the catheter body. The basket electrode assembly has a plurality of electrode-carrying spines and an expander that is adapted for longitudinal movement relative to the catheter body for expanding and collapsing the assembly via a proximal end portion extending past the control handle that can be pushed or pulled by a user. The expander is also adapted for deflection in responsive to an actuator on the control handle that allows a user to control at least one puller wire extending through the catheter body and the expander.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
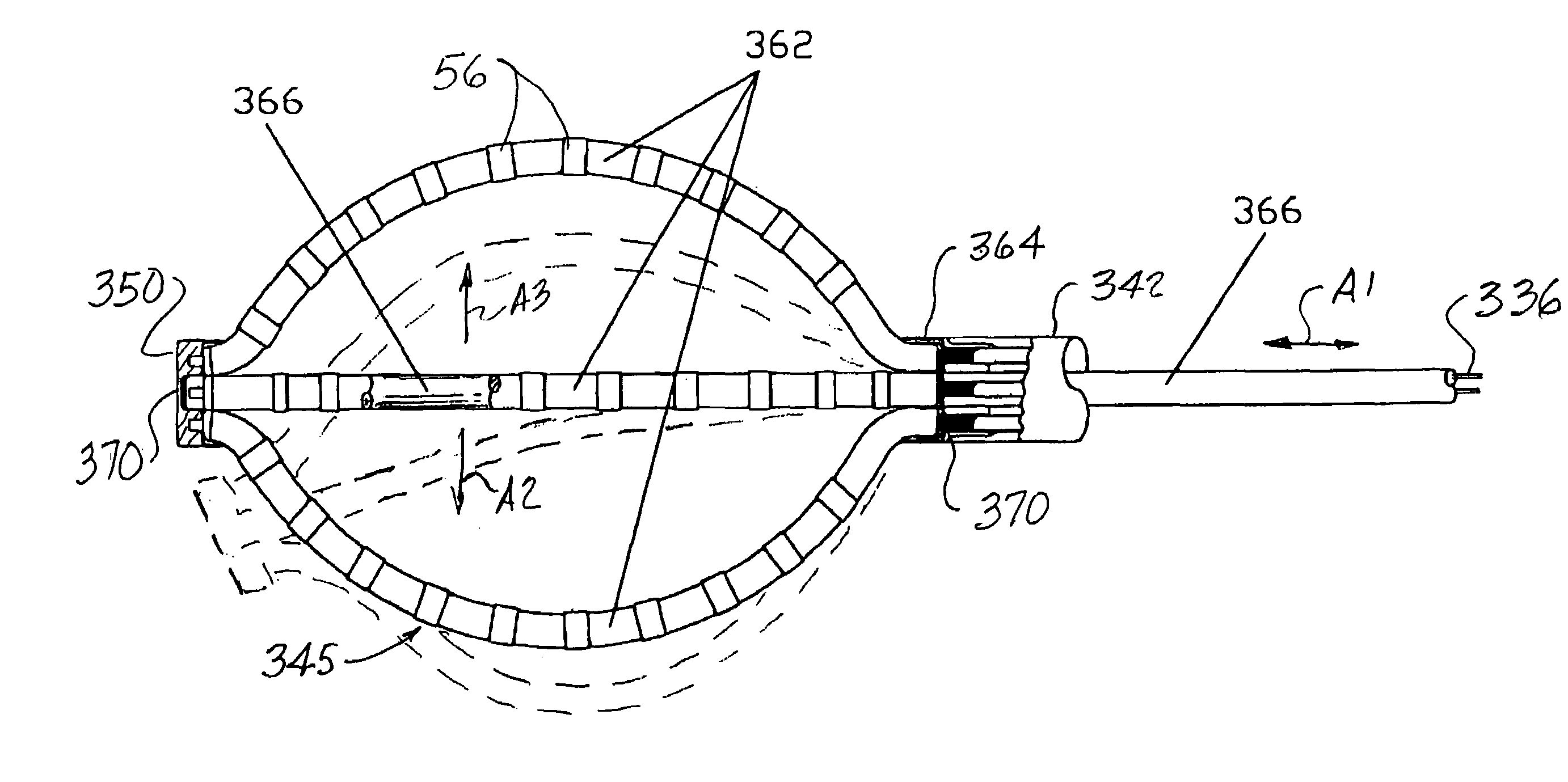
Non-contact electrode basket catheters with irrigation
ActiveUS9339331B2Reduce riskPrevent coagulationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringBasket catheterContact electrode
Catheter systems and methods are disclosed. An exemplary catheter includes an outer tubing housing and an inner fluid delivery tubing, the inner fluid delivery tubing having at least one fluid delivery port. The catheter also includes a deployment member movable axially within the inner fluid delivery tubing. A plurality of splines are each connected at a proximal end to the outer tubing and at a distal end to deployment member. A seal is provided between the outer tubing and the inner fluid delivery tubing. A gasket is provided between the deployment member and the inner fluid delivery tubing. Both the seal and the gasket are configured to prevent blood or other fluid from ingressing into the outer tubing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
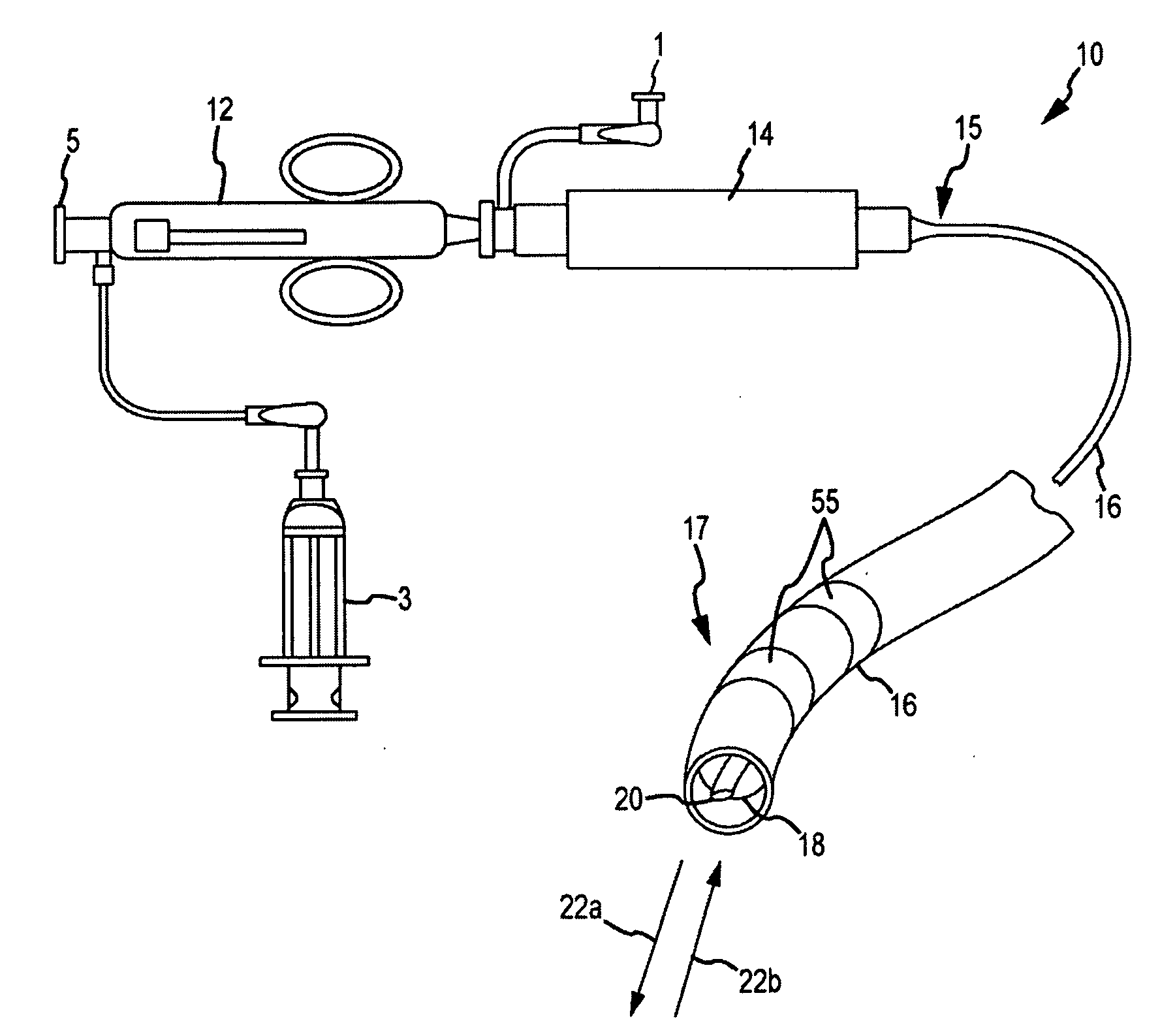
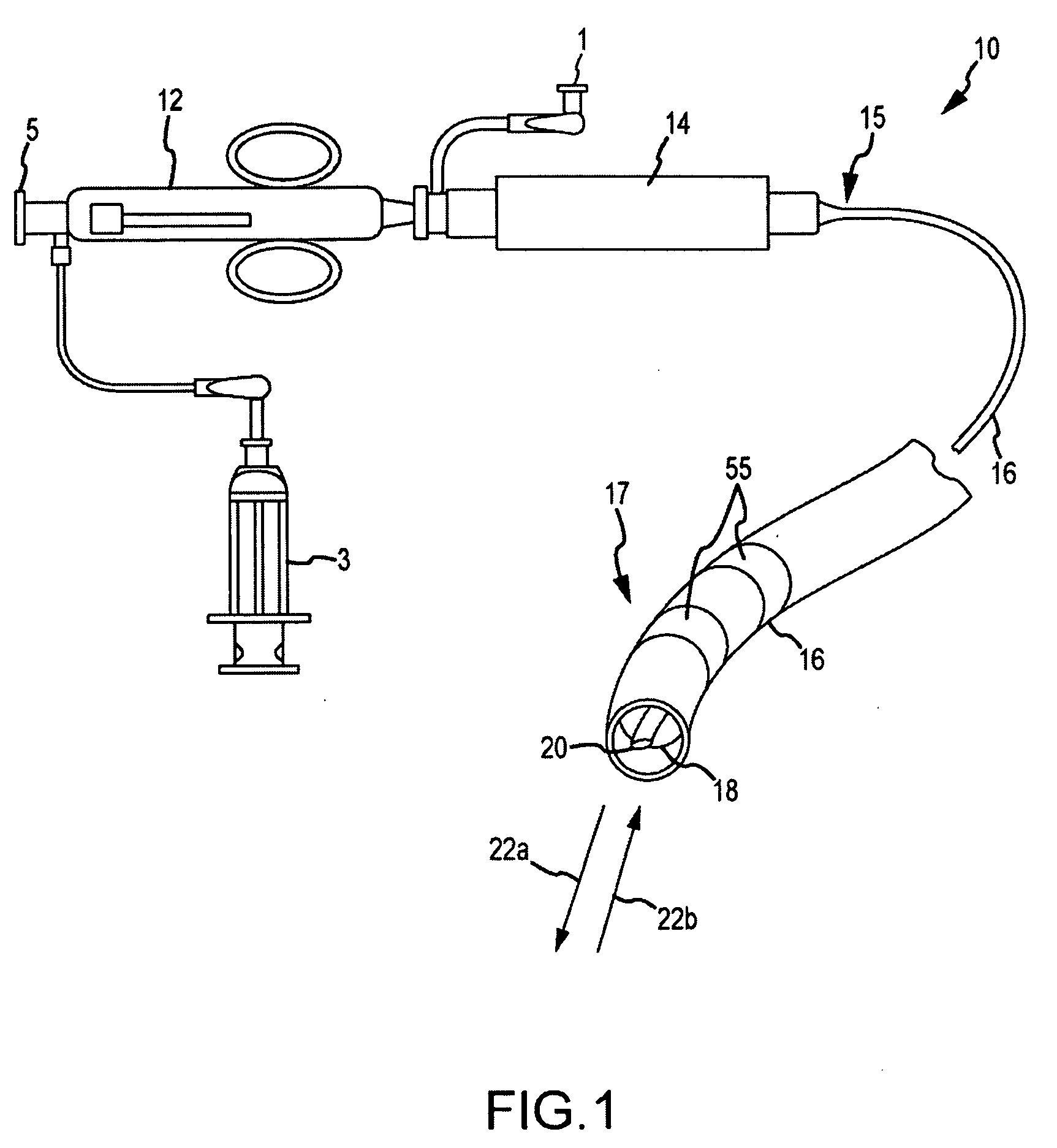
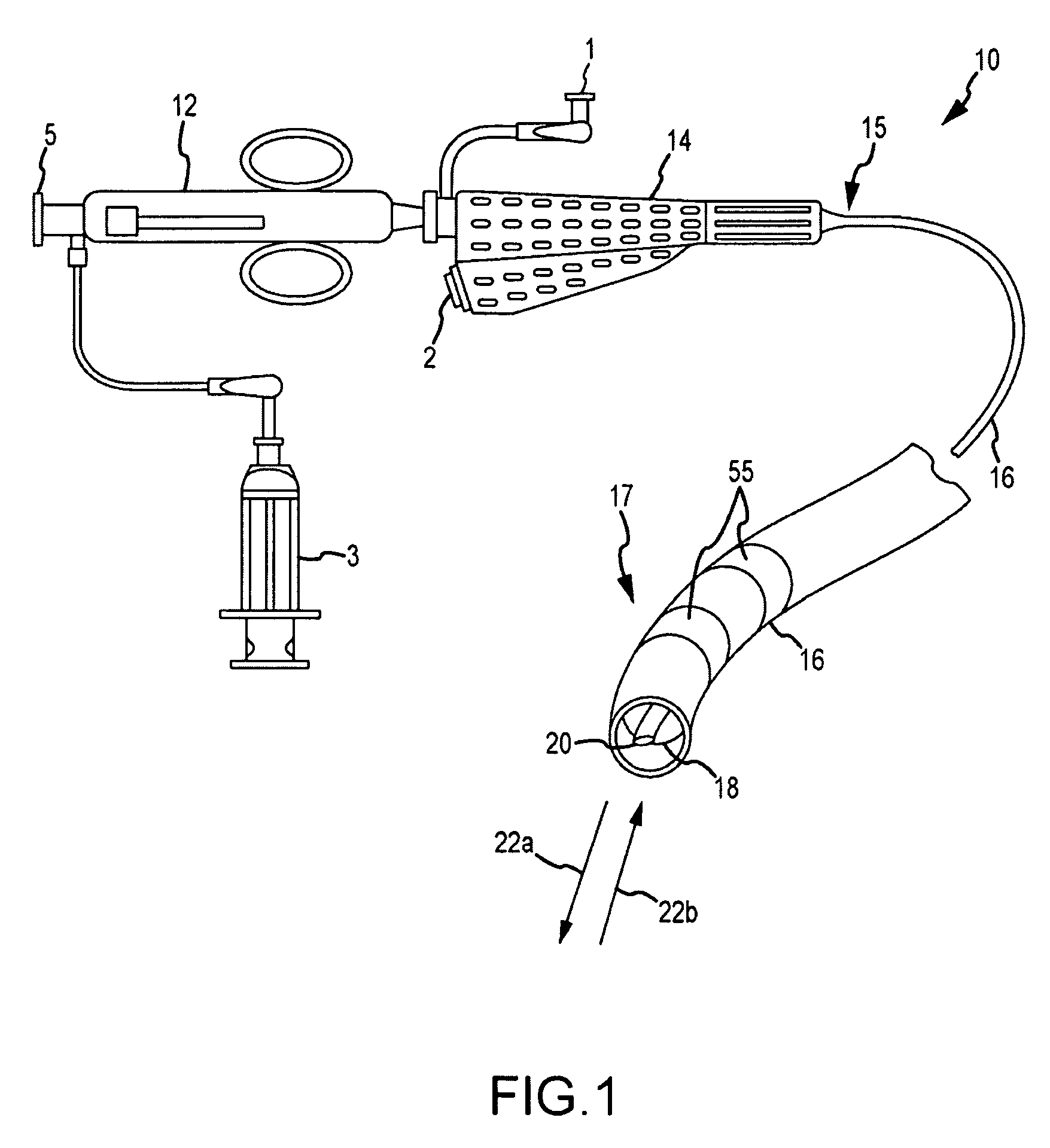
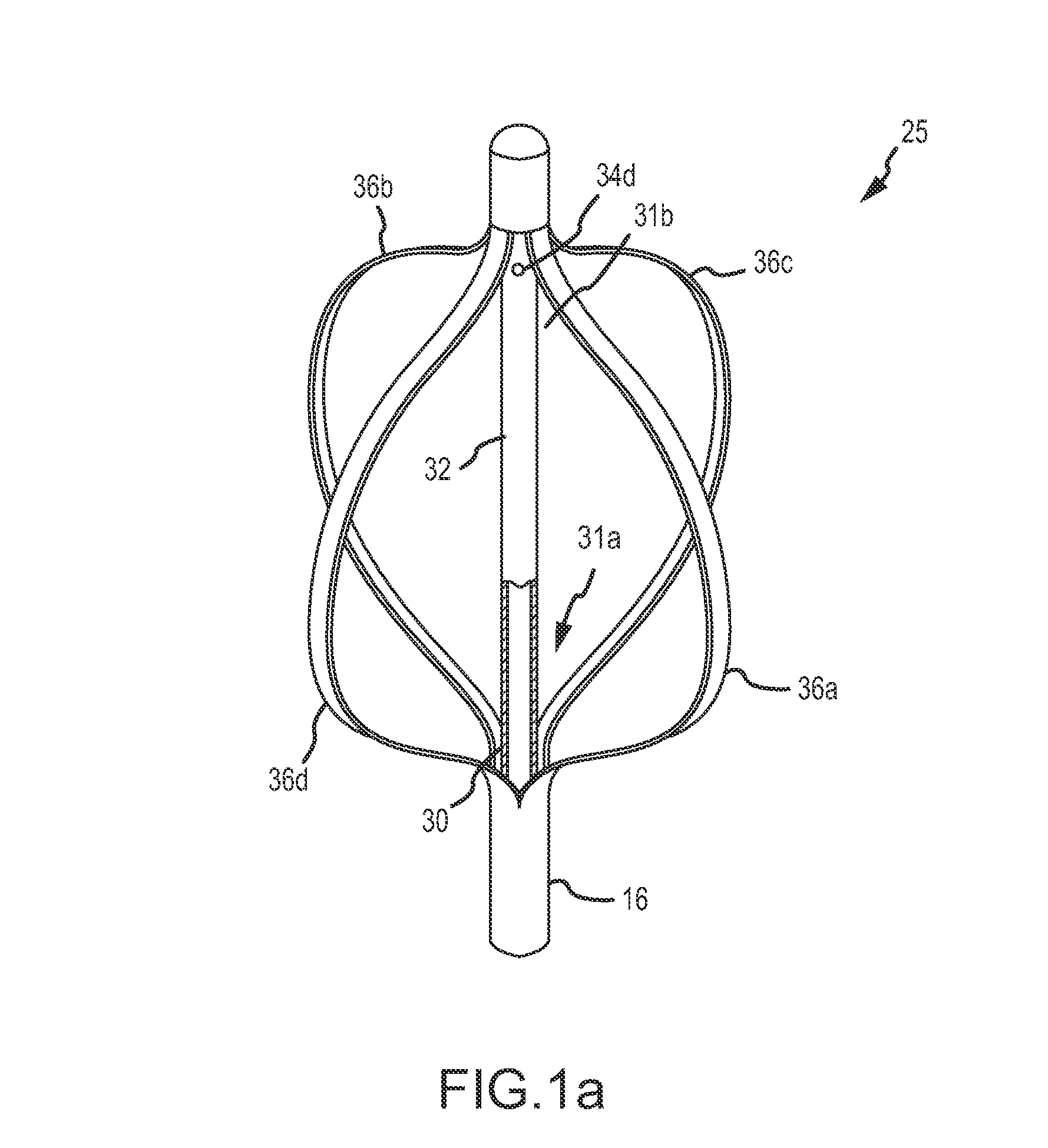
Hybrid basket catheters
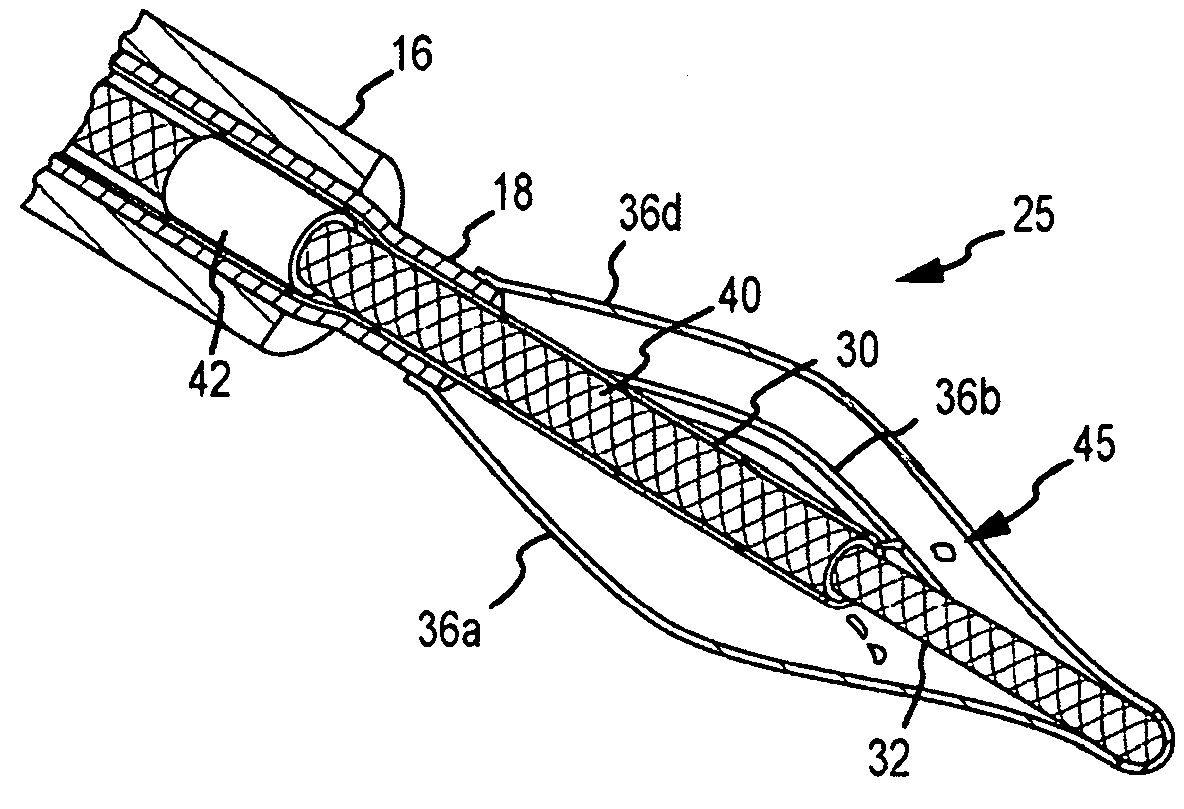
The invention provides hybrid basket-type intravascular catheter probes designed to optimize blood vessel wall contact or close proximity while traversing tortuous curves. Related diagnostic systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Basket catheter with microelectrode array distal tip
The invention relates to a basket catheter with a microelectrode array distal tip. A catheter adapted for greater mapping resolution and location precision has a basket-shaped, high density electrode assembly for large-area mapping, and an integrated distal tip providing an array of ultra-high density microelectrodes for acute focal mapping. The basket-shaped electrode assembly 18 has a plurality of electrode-carrying spines and the distal tip has a nonmetallic, electrically insulating substrate body with indentations in which microelectrodes are positioned in a manner that the outer surface is generally flush with the outer surface of the substrate body to present a generally smooth, atraumatic distal tip profile.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
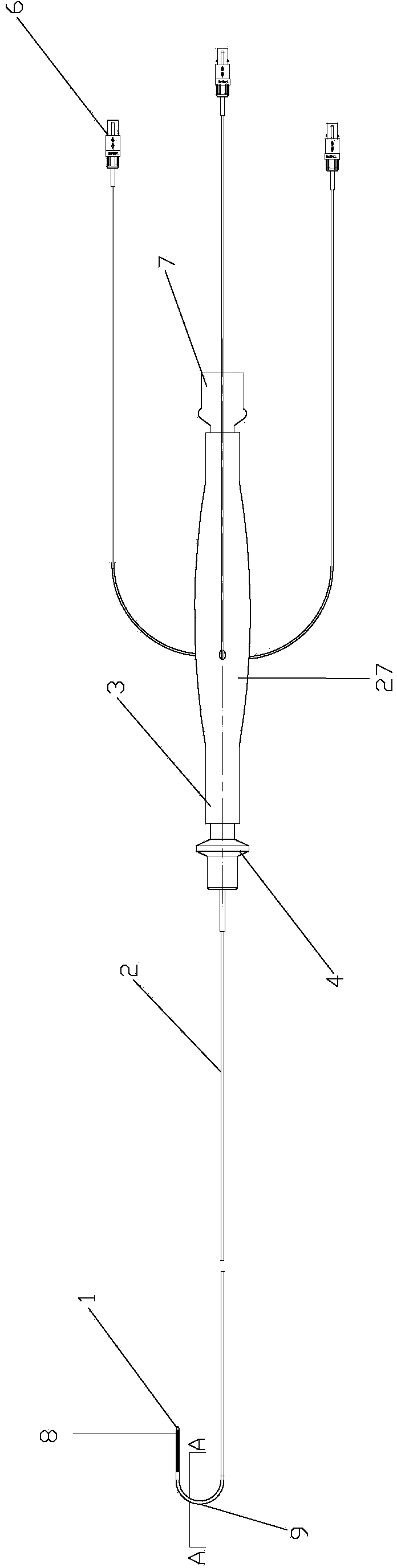
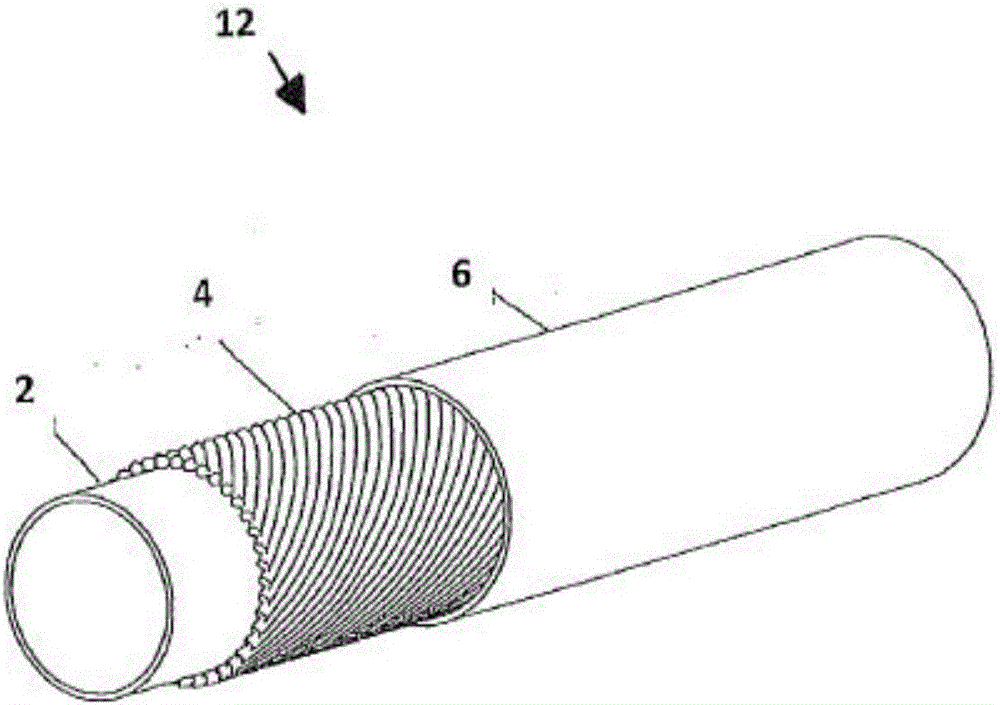
A basket catheter and method of manufacturing
A catheter sheath for a basket catheter that includes a plurality of electrical leads, each having a proximal end and a distal end and a lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. Each electrical lead includes a tubular member of non-conductive material, a plurality of electrical conductors extending from the proximal end to the distal end laid on the non-conductive tubular member, and an outer layer of non-conductive material applied over the electrical conductors to cover the conductors. The catheter sheath further includes one or more electrodes on a distal portion of each electrical lead in electrical communication with at least one of the plurality of electrical conductors through the outer layer. An elongate shape-forming member is received in the lumen of each of the plurality of electrical leads. The shape-forming member imparts an arched shape to the distal portion of each of the electrical leads so as to form a basket shape to a distal portion of the catheter sheath. The plurality of electrical leads are bundled together at their distal ends and proximal the distal arched portion of each electrical lead.
Owner:CATHRX LTD
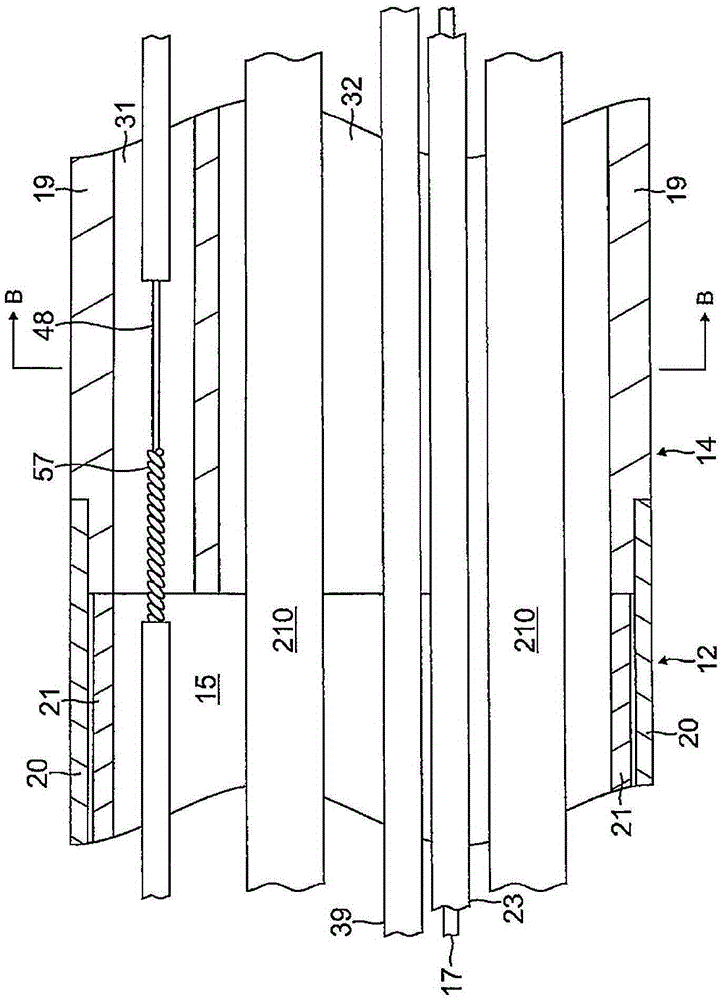
Seal for controlling irrigation in basket catheters
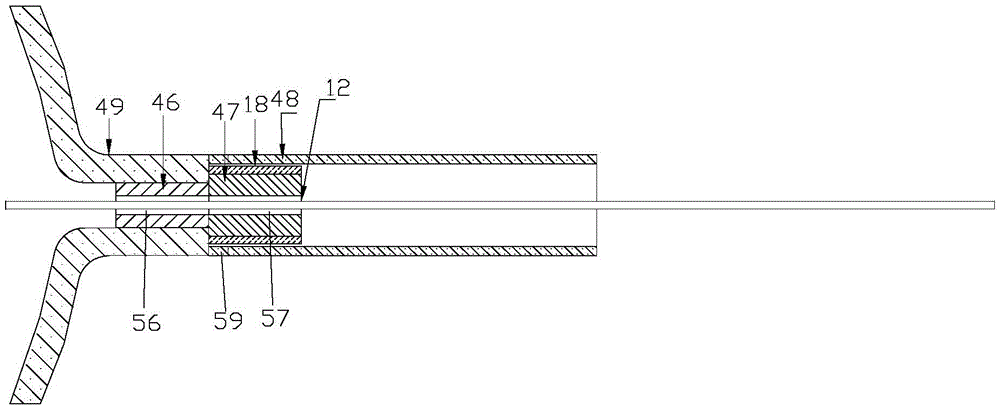
An exemplary basket catheter includes an outer tubing housing an inner fluid delivery tubing having at least one fluid delivery port. A plurality of splines are each connected at a proximal end of the splines to the outer tubing and at a distal end of the splines to the inner fluid delivery tubing. The inner fluid delivery tubing is operable to be moved in a first direction to expand the splines; and in a second direction to collapse the splines. A porous membrane is provided over at least a portion of the inner fluid delivery tubing. A seal is provided at a proximal end of the porous membrane between the porous membrane and the outer tubing and between the porous membrane and the inner fluid delivery tubing, the seal configured for irrigating between the plurality of splines of the basket catheter while preventing fluid ingress into the outer tubing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Balloon basket catheter device
PendingUS20210085931A1Reduce chancePrevent movementBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterThrombusBlood vessel
The present disclosure relates to catheter system comprising a balloon and an infusion basket designed to be deployed in complex vasculature to optimally treat vascular and arterial disease conditions such as blood clots, blood emboli, and deep vein thrombosis. The basket may comprise a shaft with a plurality of cuts along a portion of its length to form a plurality of tines that provide support for a plurality of porous tubes to form the limbs of the basket. The limbs of the basket expand radially away from the longitudinal axis of the basket when the longitudinal length of the basket is reduced. The limbs may also be connected to a drug delivery system, and in this manner, baskets of the present disclosure allow for the use of both mechanical and pharmaceutical means of thrombolysis and thrombectomy.
Owner:THROMBOLEX INC
A basket catheter and method of manufacturing
A catheter sheath for a basket catheter which includes a plurality of electrical leads each having a proximal end and a distal end and a lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. Each electrical lead includes a tubular member of non-conductive material, a plurality of electrical conductors extending from the proximal end to the distal end laid on the non-conductive tubular member, and an outer layer of non-conductive material applied over the electrical conductors to cover the conductors. The catheter sheath further includes one or more electrodes on a distal portion of each electrical lead in electrical communication with at least one of the plurality of electrical conductors through the outer layer. An elongate shape forming member is received in the lumen of each of the plurality of electrical leads. The shape forming member imparts an arched shape to the distal portion of each of the electrical leads so as to form a basket shape to a distal portion of the catheter sheath. The plurality of electrical leads are bundled together at their distal ends and proximal the distal arched portion of each electrical lead.
Owner:CATHRX LTD
Basket catheter with an improved seal
The invention relates to a basket catheter with an improved seal. Systems and methods are disclosed for providing and using an irrigated ablation catheter. The catheter includes a distal electrode assembly having a plurality of spines forming a basket shaped electrode assembly in communication with a system controller. The catheter also includes a pull-wire disposed within a lumen of a spine collar. The spine collar further includes a silicone seal for preventing encroachment of irrigation fluid and other bodily fluids into the pull-wire lumen.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
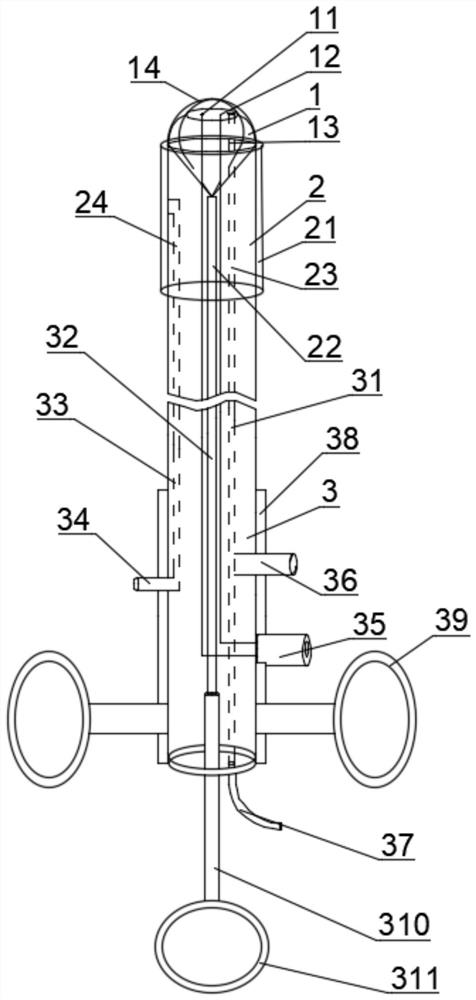
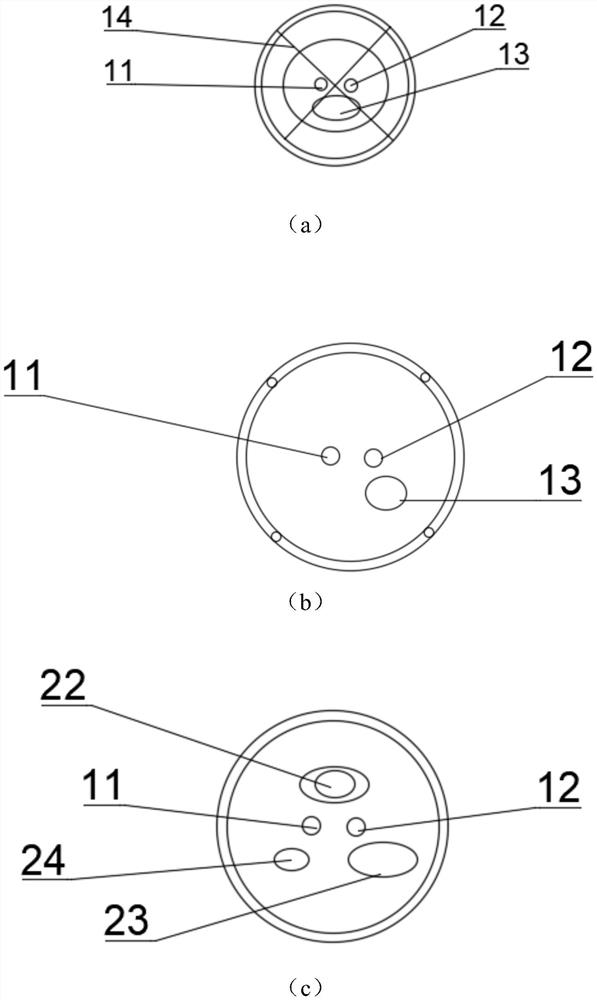
Lithotripsy basket catheter
PendingCN111839664AEasy accessAvoid deformationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsEngineeringBasket catheter
The invention provides a lithotripsy basket catheter, which comprises a catheter and a connecting rod type basket arranged in the catheter. A metal connecting rod channel and a contrast agent / guide wire channel are arranged in the catheter, and a first lithotripsy electrode and a second lithotripsy electrode are further arranged in the catheter. The first lithotripsy electrode, the second lithotripsy electrode, the metal connecting rod channel for displacement and the liquid injection channel body part are parallel to one another and do not make contact with one another. The basket comprises four metal wires, the metal connecting rod and a basket connecting rod connected to the tail end of the metal connecting rod, and a basket handle is connected to the tail of the basket connecting rod.The basket metal wires penetrate out of the side wall of the catheter, so that the distance between the basket metal wires is constant, basket deformation can be avoided, and calculi are easy to takeout. After calculi are taken out of the basket, the basket is tightened, and the calculi can be fixed and tightly attached to the lithotripsy electrodes at the head end of the catheter. And it is notnecessary to use a choledochoscope for assistance, and the lithotripsy basket catheter is more suitable for primary hospitals and is low in cost and convenient to popularize.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual basket catheter
This disclosure is directed to a catheter having a basket-shaped electrode assembly at the distal end of the catheter body formed from a plurality of spines with electrodes. Each spine is deflectable outwards into an expanded configuration, so that the basket-shaped electrode assembly has a proximal basket area and a distal basket area with different equatorial diameters.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Basket catheter with individual spine control
This disclosure is directed to a catheter having a basket-shaped electrode assembly formed from a plurality of spines, each with a plurality of electrodes. The spines are connected at their distal ends and extend through the catheter body to its proximal end. Each spine may be independently controlled, such as by adjusting its longitudinal position relative to the catheter body to causes it to bow outwards to a greater or lesser degree.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Balloon basket catheter device
The present disclosure relates to catheter systems including balloons and infusion baskets designed to be deployable in complex tubing systems for optimal treatment of blood and arterial diseases, such as blood clots, thrombus and deep vein thrombosis. The basket may include a rod having a plurality of cutouts along a portion of its length to form a plurality of bifurcations that provide support to a plurality of perforated tubes, thereby forming branches of the basket. When the longitudinal length of the basket decreases, the branches of the basket expand radially away from the longitudinal axis of the basket. The branches may also be connected to a drug delivery system such that the basket of the present disclosure allows for both mechanical and drug thrombolysis.
Owner:血栓莱斯公司
Lithotripsy basket catheter with lithotripsy balloon
PendingCN111839665AEasy accessConstant distanceSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMedicineLaser lithotripsy
The invention provides a lithotripsy basket catheter with a lithotripsy balloon. The lithotripsy basket catheter comprises a catheter e and a connecting rod type basket arranged in the catheter. The catheter comprises a first catheter section, a second catheter section and a third catheter section which are sequentially communicated; a balloon is arranged outside the second catheter section; and aballoon inflation channel and a basket connecting rod channel for displacement are arranged in the catheter. After calculi are taken by the basket, the basket is tightened, and the calculi can be fixed and tightly attached to the lithotripsy electrode at the head end of the catheter. After the balloon is filled, broken calculi can be prevented from entering an intrahepatic bile duct in the calculi breaking process. After the common bile duct calculi are crushed, the broken calculi can be dragged into the common bile duct by using the balloon, or after the common bile duct calculi are crushed,the broken calculi are dragged into the duodenum by using the balloon or the basket. By arranging the lithotripsy electrode, large common bile duct calculi can be subjected to plasma lithotripsy, microelectrode lithotripsy and laser lithotripsy under X-ray, choledochoscope assistance is not needed, and the lithotripsy basket catheter is more suitable for primary hospitals.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Double-layer basket catheter device
PendingCN114668482ASurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac arrhythmiaTreatment strategy
The invention discloses a double-layer basket catheter device which comprises a catheter assembly and a guide head. One end of the first mesh basket is connected to the far end of the catheter assembly, the other end of the first mesh basket is connected through a guide head, and multiple first electrodes are evenly distributed on the first mesh basket. One end of the second mesh basket is connected to the far end of the catheter assembly, the other end of the second mesh basket is connected through a guide head, and multiple second electrodes are evenly distributed on the second mesh basket; the first mesh basket and the second mesh basket can be synchronously expanded or contracted by operating the guide head; the second net basket is located in the first net basket. The first electrode can collect cardiac electrical signals when making contact with or not making contact with tissue, the second electrode collects the cardiac electrical signals in a non-contact mode, and collected information can be used for reflecting the spreading mode of cardiac electrical activity in different states. Clinical doctors are helped to judge an arrhythmia mechanism, and corresponding treatment strategies are formulated accordingly.
Owner:ENCHANNEL MEDICAL GUANGZHOU INC
Basket conduit with pre-strained frame
The invention is entitled "Basket Catheter with Prestrained Frame". The present invention discloses a catheter having a basket-shaped electrode assembly at the distal end of the catheter body, the basket-shaped electrode assembly being formed from a plurality of spines with electrodes. The plurality of ridges may be formed by a frame that is pre-strained to have a diameter greater than a diameter of the basket electrode assembly in an expanded arrangement and a length less than a length of the basket electrode assembly in an expanded arrangement.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Multi-electrode basket catheter and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103750899BEasy to take backFully contactedDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingTunica intimaBasket catheter
The invention discloses a multi-electrode basket catheter and a manufacture method of the multi-electrode basket catheter to solve the technical problem of accurately and rapidly conducting mapping or radio frequency ablation treatment in the operation process. The multi-electrode basket catheter comprises a basket device. A basket of the basket device is composed of strip-shaped arms. The near end of each strip-shaped arm and the far end of the strip-shaped arm are connected to a near end connecting structure and a far end connecting structure. The strip-shaped arms are bent under the action of external force to form an arc shape or form a spatial curve so that the basket of an ellipsoid shape can be defined. The strip-shaped arms are stretched out or drawn back in the length direction of the strip-shaped arms under the action of external force to form a stranded wire. Annular electrodes are distributed on the outer surfaces of the strip-shaped electrodes. The manufacture method of the multi-electrode basket catheter includes the steps of manufacturing all parts and assembling the parts. Compared with the prior art, the multi-electrode basket catheter has the advantages that the size of the basket formed by the strip-shaped arms can be adjusted under the control of one handle, and therefore the electrodes distributed in the space on the strip-shaped arms make full and close contact with the tissue of the endocardium, mapping or radio frequency ablation treatment is accurately and rapidly conducted, and the basket is conveniently recycled.
Owner:APT MEDICAL INC
Seal for controlling irrigation in basket catheters
InactiveUS20100168668A1Reduce riskImprove directionStentsBalloon catheterPorous membraneBasket catheter
Catheter systems and methods are disclosed including a seal for helping direct an anticoagulant or other fluid for proper irrigation in a basket catheter. An exemplary basket catheter includes an outer tubing housing an inner fluid delivery tubing having at least one fluid delivery port. A plurality of splines each connected at a proximal end of the splines to the outer tubing and at a distal end of the splines to the inner fluid delivery tubing. The inner fluid delivery tubing is operable to be moved in a first direction relative to the outer tubing to expand the splines to a deployed position. The inner fluid delivery tubing is also operable to be moved in a second direction relative to the outer tubing to collapse the splines to an undeployed position. A porous membrane is provided over at least a portion of the inner fluid delivery tubing having the at least one fluid delivery port. A seal is provided at a proximal end of the porous membrane between the porous membrane and the outer tubing and between the porous membrane and the inner fluid delivery tubing, the seal configured for irrigating between the plurality of splines of the basket catheter while preventing fluid ingress into the outer tubing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Basket Catheter With Prestrained Framework
A catheter having a basket-shaped electrode assembly at the distal end of the catheter body formed from a plurality of spines with electrodes. The plurality of spines are formed by a framework which is prestrained to have a diameter greater than the diameter of the expanded arrangement of the basket-shaped electrode assembly and a length less than the length of the expanded arrangement of the basket-shaped electrode assembly.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Asymmetric basket catheter
The invention is titled as asymmetric basket catheter. This disclosure is directed to a catheter having an asymmetric basket-shaped electrode assembly at the distal end of the catheter body formed from a plurality of spines with electrodes. The plurality of spines are radially distributed across a first circumferential portion. One or more counter spines are radially distributed across a remaining second circumferential portion. Diagnostic electrodes are arrayed across the spines, while the counter spines may have one or more reference electrodes.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com