High fluorescent intensity cross-linked allophycocyanin
a cross-linked, allophycocyanin technology, applied in the field of cross-linked allophycocyanin, can solve the problems of native apc dissociation into monomers and native apc incompatibility, and achieve the effect of improving time-resolved fluorescent energy transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of High Fluorescent Intensity, Stabilized Allophycocyanin Label
[0046]Native allophycocyanin (APC) may be extracted from red or blue-green algae and purified by standard methods. Brejc et al., 1995 J. Mol. Biol. 249, 424–440. The purified material is stored as an ammonium sulfate precipitate. Native APC is dialyzed from its ammonium sulfate precipitate form into 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) that contains no azide at 4° C. This should be done exhastively. The dialyzed APC is diluted to 1.5 mg / mL in 50 mM sodium phosphate. EDAC (1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride) is added as powder up to 35 mM, and allowed to react for 4 hours at room temperature. The reaction is quenched by mixing with 100 mM glycylglycine until it is dissolved, and the mixture is allowed to react at room temperature or in the cold for at least one hour. This is then qualitatively assayed to determine the degree of cross-linking achieved by diluting the cross-linked APC i...
example 2
Dissociation at Low Pigment Concentration
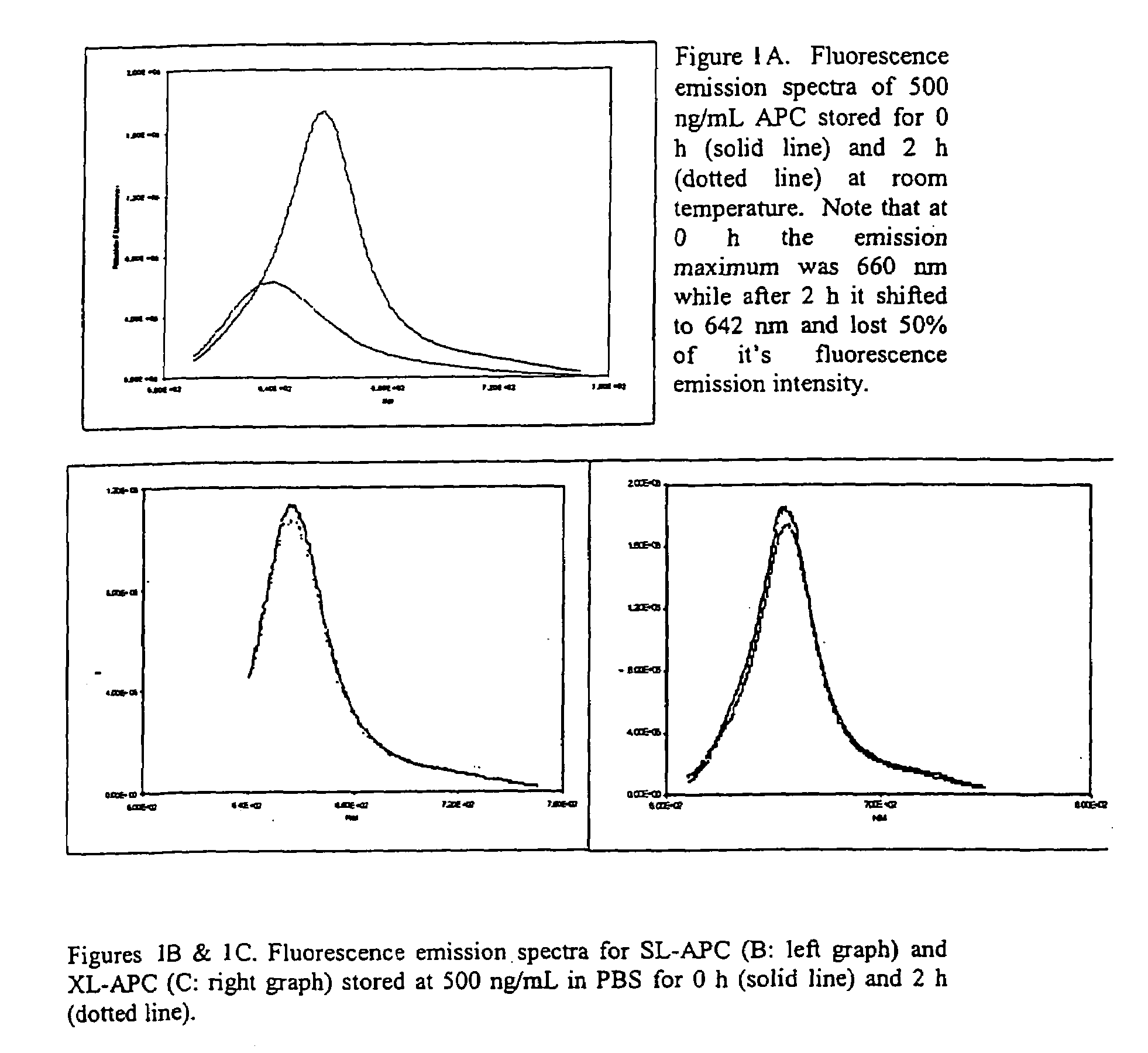
[0049]A major limitation to APC use in specific binding assays is its poor stability under pigment concentrations useful for these binding assays. Native APC broke down when stored at room temperature at a pigment concentration of 500 ng / mL (FIG. 1A). This decay occurred more rapidly than the two hour time point presented (data now shown). APC instability was manifested as a decrease in maximal fluorescence emission intensity and a shift in the fluorescence emission maximum by about 18 nm to the blue.
[0050]SL-APC and XL-APC were chemically stabilized to prevent dissociation at the low pigment concentrations normally encountered in a biological assay (Ong & Glazer, 1985). Storage at 500 ng / mL for 2 h at room temperature had little effect on their fluorescence emission spectra in either the absolute peak height or emission maximum (FIGS. 1B and 1C). This increased stability gives the cross-linked APCs the ability to be used in applications for ...
example 4
Fluorescense Stability in Sodium Perchlorate
[0052]One commonly used measure of the stability of cross-linked APC is its response to the application of a chaotrophic salt (Ong & Glazer, 1985; MacColl, et al., 1987 Phycobiliproteins, CRC Press, Inc. Boca Raton). Chaotropic salts dissociate native phycobiliproteins into their constituent subunits. Cross-linking of APC provides protection against such chaotrophic salt dissociation. As demonstrated in Table 1, when treated with sodium perchlorate, this chaotrophic salt causes native APC to loose 50% of its fluorescence emission intensity while undergoing about an 18 nm shift to the blue in fluorescence emission (to 642 nm). Both XL-APC and SL-APC maintain their original fluorescence emission maximum while maintaining 92 and 89% of their emission intensity, respectively.
[0053]
TABLE 1Effect of chaotropic salt treatment on fluorescence intensityof SL-APC, XL-APC and Native APC at 10 μg / mL. Treated with 1M Sodium Perchlorate, 50 mM Tris-HCl ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com