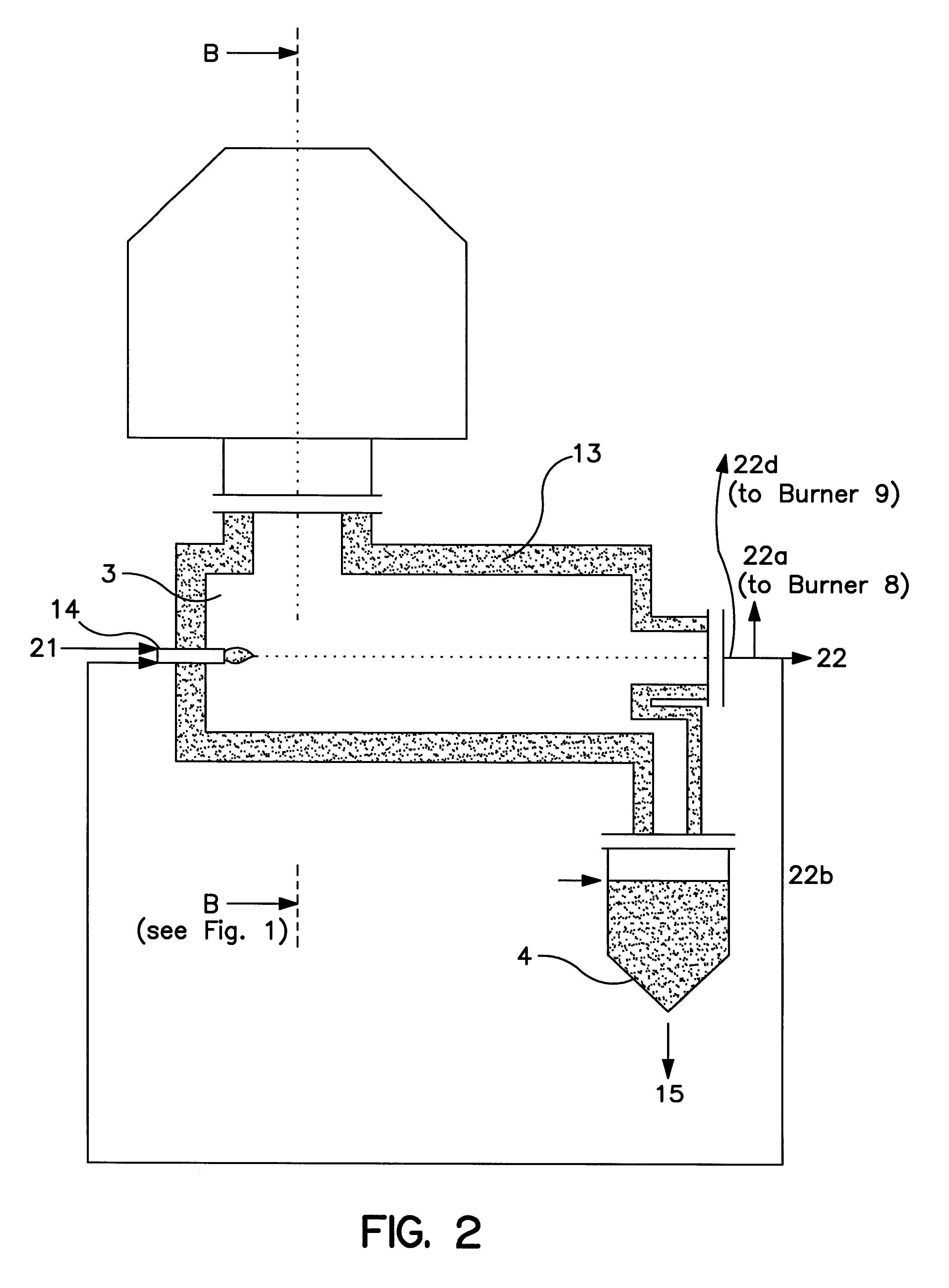
Process and device for gasification of waste
a gasification device and waste technology, applied in the direction of gasification of molten salts/metals, combustion types, manufacturing converters, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of environmental neutral incineration of waste products, the cost of shipping waste from the point of origin to the incineration facility to become a non-negligible part of the overall cost, and the effect of reducing the viscosity of slag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Refuse Incineration
Table 1 shows the composition of a standard refuse according to the Land Environmental Department of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The pre-treatment of the refuse is limited to the coarse crushing of the feed material to a grain size of less than 40 mm. Iron may also be removed by magnetic separation.
The 0-5 mm grain fraction is fed into the gasification space via the solids burners, while the 5-40 mm grain fraction is fed in via a nozzle by means of feed screws.
As Table 3 indicates, 357 m.sup.3.sub.i.N. [i.N.=in normal state] of oxygen (96 vol-% of O.sub.2) is used for the autothermal gasification of 1.0 ton of refuse.
Owing to the moisture content of the feed material, the cracked gas that is obtained has a large proportion of vapor. In addition, the cracked gas has large CO and H.sub.2 contents, so that sufficient energy reserves are available to cover any higher heat losses that may occur.
The ash from the refuse has high contents of SiO.sub.2 and Al.sub.2 O.sub.3, whi...
example 2
Gasification of Old PVC
An advantageous application of the slag bath gasifier according to the invention is the gasification of waste PVC since, in addition to refuse disposal, the HCl contained in the PVC can be recovered and used as HCl gas in oxychlorination and ultimately to produce PVC again.
Table 2 presents the composition of a PVC-containing waste mixture.
In addition to screening with corresponding crushing of the waste PVC to a grain size of d<40 mm and the magnetic separator for removing iron, an additional air separator (zigzag separator) should be provided for the pre-treatment process. In the latter separator, heavy non-ferrous metals are separated which, in the slag bath, are converted into metal chloride for the most part and thus would reduce the HCl yield. By contrast, the silicates and light metals (Al, Mg) are desired slag formers.
The option of using relatively coarse-grain feed material is especially economical in the case of PVC because this means that crushing in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com