Treatment of parasitic infections of fish surfaces
a technology for parasitic infections and fish surfaces, applied in the field of parasitic infection treatment, can solve the problems of high morbidity and mortality in wild and cultured fish, unsolved questions on their residual and toxic effects on the environment, and compounds, etc., and achieve the effect of strong in vitro antiparasitic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0075]In Vitro Effects Pseudomonas fluorescens Strain H6 Lipopeptide Biosurfactant on Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
Tomonts
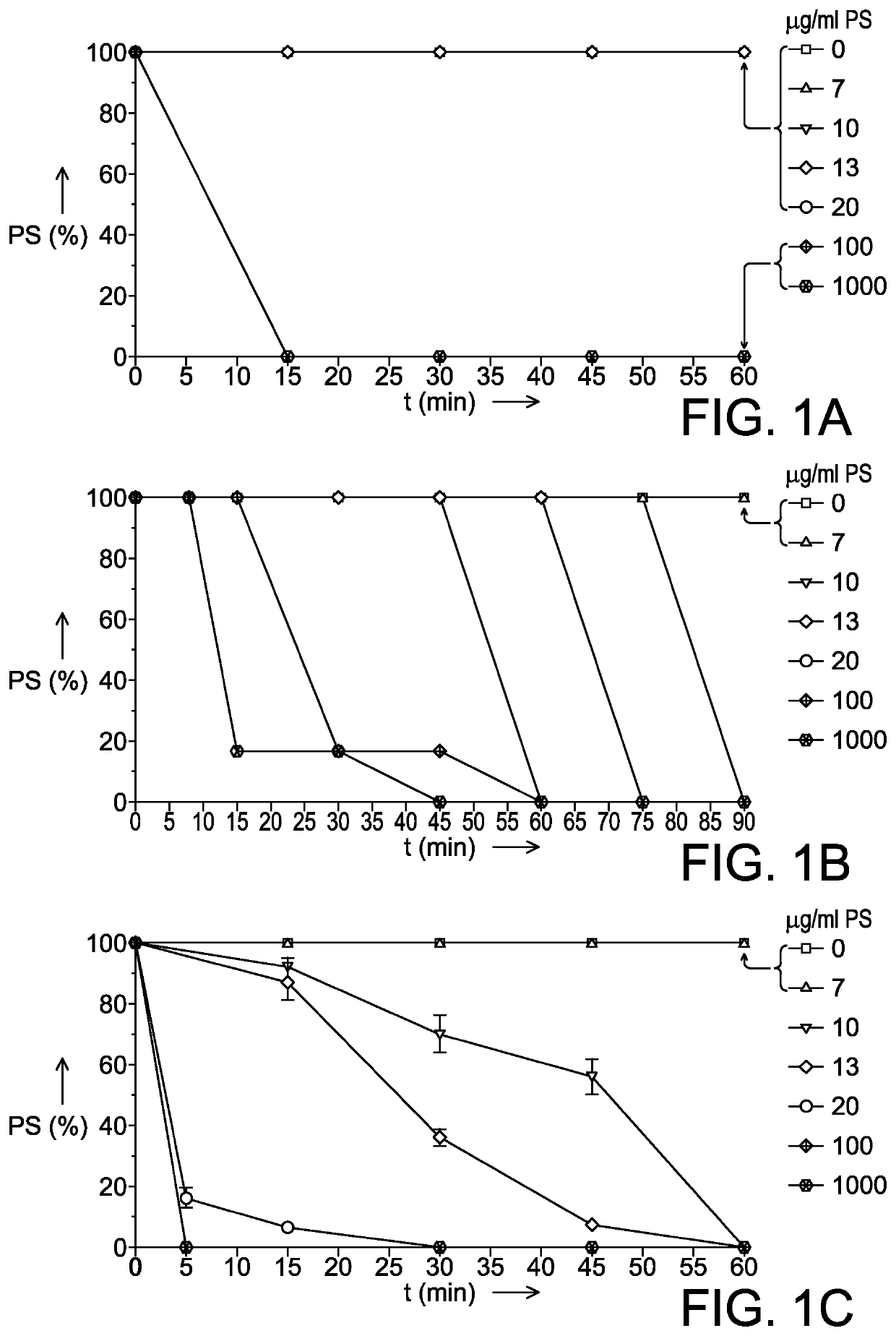
[0076]Ichthyophthirius multifiliis tomonts were only sensitive to the two highest concentrations (1000 and 100 μg / mL PS), which killed all parasites within 15 min (FIG. 1A).
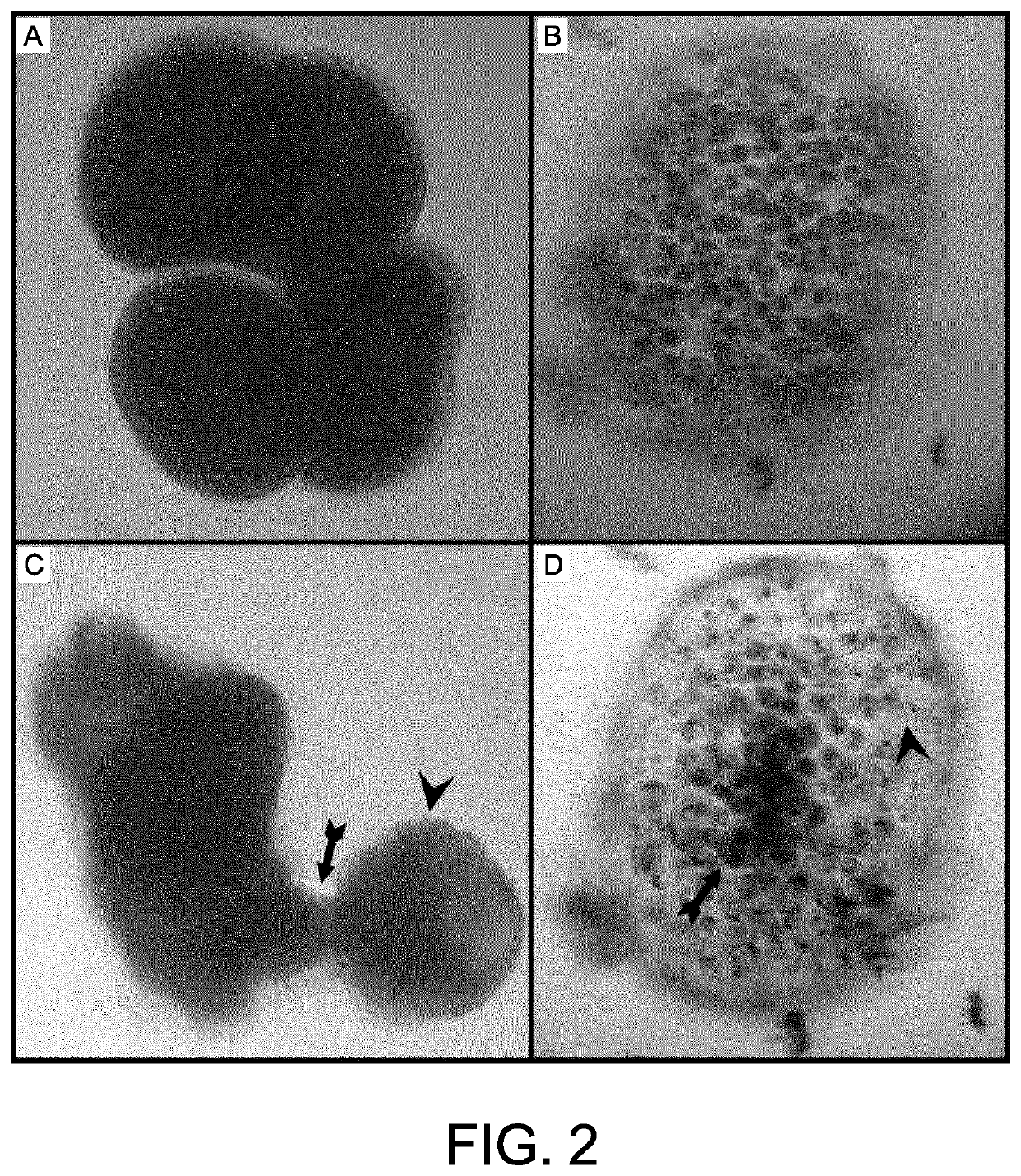
[0077]Cytoplasmic movements inside the tomonts (FIG. 2A) initially increased when exposed to the lipopeptide biosorfactant, whereafter a disruption of the membrane followed and finally cytoplasm was released into the surroundings of the tomonts (FIG. 2C).
[0078]A 10 μg / mL PS concentration had no effect on this parasite life stage within the observation period tested.
Tomocysts
[0079]Ichthyophthirius multifiliis tomocysts, with their enclosed tomites (FIG. 2B), showed a different sensitivity to the lipopeptide biosurfactant when compared to tomonts (FIG. 1B).
[0080]At the highest tested concentration of 1000 μg / mL PS, the majority of tomites in the tomocysts (83%) were immotile after 15 min of expo...
example 2
Sensitivity of Fish to Pseudomonas Lipopeptide Biosurfactant
[0086]Rainbow trout showed no immediate or late adverse reactions when exposed for 3 h to PS concentrations of 10 and 13 μg / mL. No toxic effects on fish could be detected.
example 3
Comparison of In Vitro Activity of Various Biosurfactants Against Tomonts and Theronts
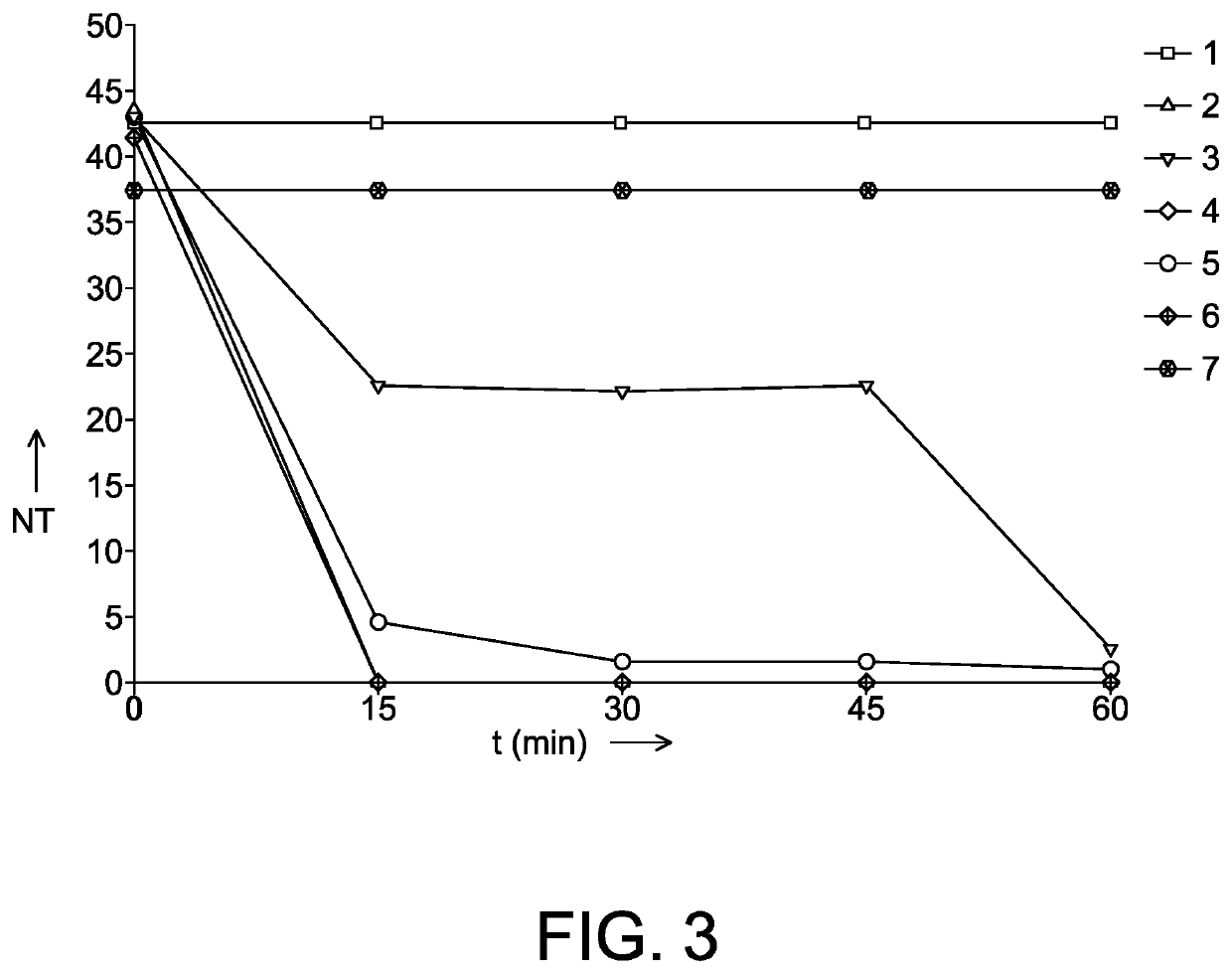
[0087]Collection of I. multifiliis was performed as described above. Extracts of the biosurfactant massetolide A was obtained from Pseudomonas fluorescens SS101 as described in De Bruijn et al (2008), the putisolvin-like biosurfactant from Pseudomonas putida 267 as described in Kruijt et al (2008) and the viscosin-like biosurfactant of Pseudomonas H6 as described above. A stock solution of 15 mg / mL was prepared for each surfactant by dissolving the product in sterile distilled water whereafter a dilution series was prepared for parasite exposures that was performed as described in above. Concentrations of 0.15 and 0.015 mg / ml were tested for all three biosurfactants against tomonts (one replicate) and theronts (in duplicate) and mortality recorded every 15 min up to 1 h of exposure. Significant differences were calculated for the theront mortality data by analysis of variance followed by Dunnet's p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com