Peptide having cancer selective translocation function and use thereof
a technology of selective translocation and peptide, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, instruments, etc., can solve and achieve the effect of reducing the problems of side effects and low image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Target-Selective Cell / Tissue-Penetrating Peptide
[0040]Peptides were prepared by the F-moc chemistry method using an automatic peptide synthesizer, and then the peptide moieties were cut by resin, washed, freeze-dried, followed by purification by liquid chromatography, thereby preparing a VPTD peptide represented as SEQ ID NO: 1 (VSRRRRRRGGRRRR) and an HPTD peptide represented as SEQ ID NO: 2 (CSSRKKNPNCRRH). The molecular weights of the purified peptides were analyzed by MALDI.
example 2
Preparation of Tumor-Targeting and Tumor-Penetrating Peptide-Drug Conjugates
[0041]The VPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the HPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 2, prepared in Example 1, contained the free-sulfhydryl group of a cysteine residue, and thus chemical linkage between the peptide and the anticancer protein RNase or doxorubicin was induced using the free-sulfhydryl group as a chemical crosslinking agent. The surfaces of RNase and doxorubicin (Dox) were modified to have a thiol group attached to the carboxyl group on the surfaces. 10 molecules of peptide-SH were added to 1 molecule of particle surface-SH and reacted at 4° C. for 12 hours, and then unreacted molecules were removed by ultrafiltration, followed by freeze drying, thereby obtaining a conjugate of the VPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 and RNase, a conjugate of the VPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 and Dox, a conjugate of the HPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 2 and RNase, and a conjugate of the HPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 2 and Dox.
example 3
Tumor Cell Penetration Abilities of Tumor-Targeting and Cell-Penetrating Peptides
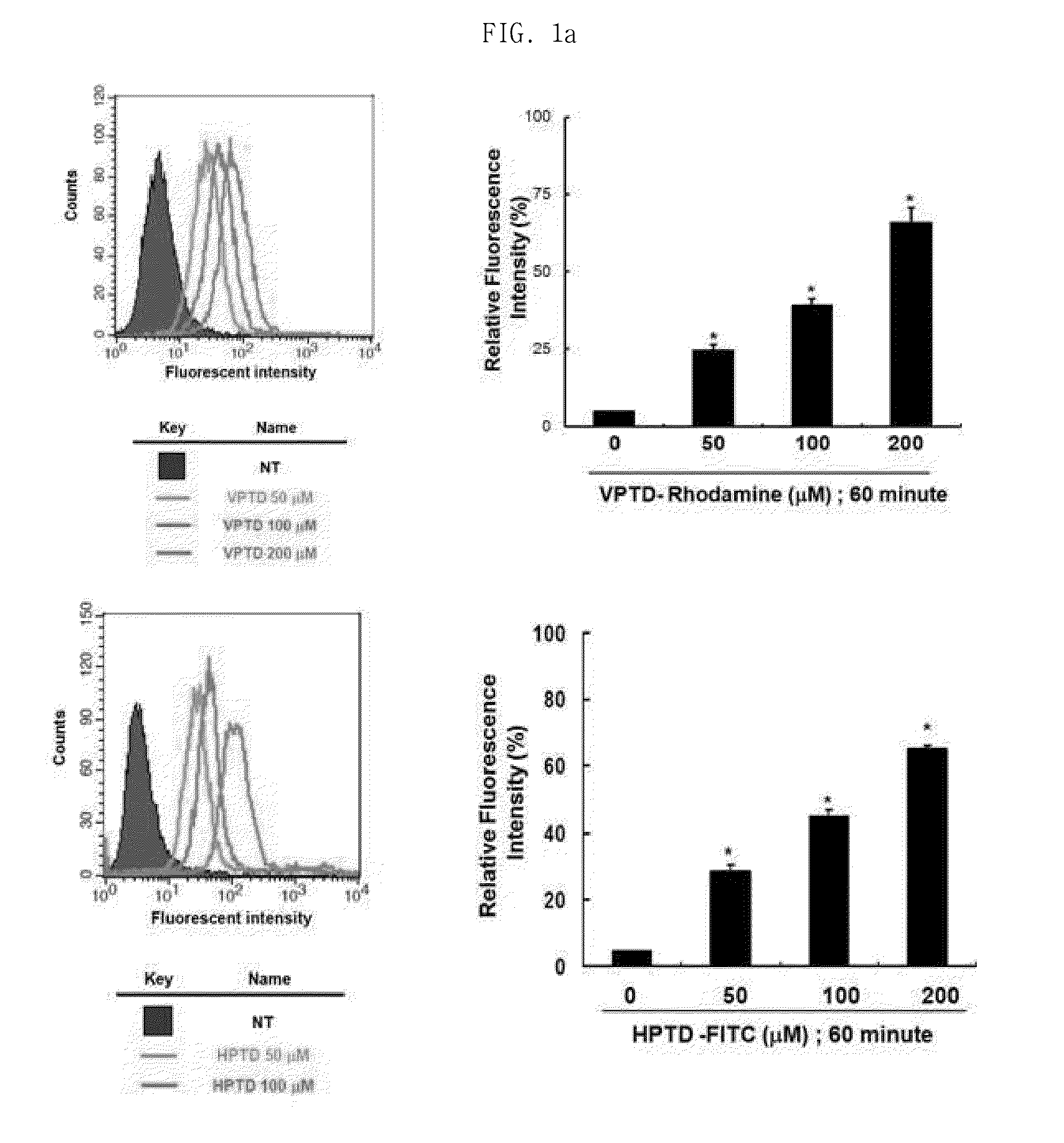
[0042]In order to test the tumor cell-targeting and tumor cell-penetrating abilities of the VPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the HPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1, prepared in Example 1, the termini of the prepared peptides were labeled with a fluorescent dye, and then each of the peptides was inoculated into a tumor cell line (MDA-MB-231, ATCC) at various concentrations.
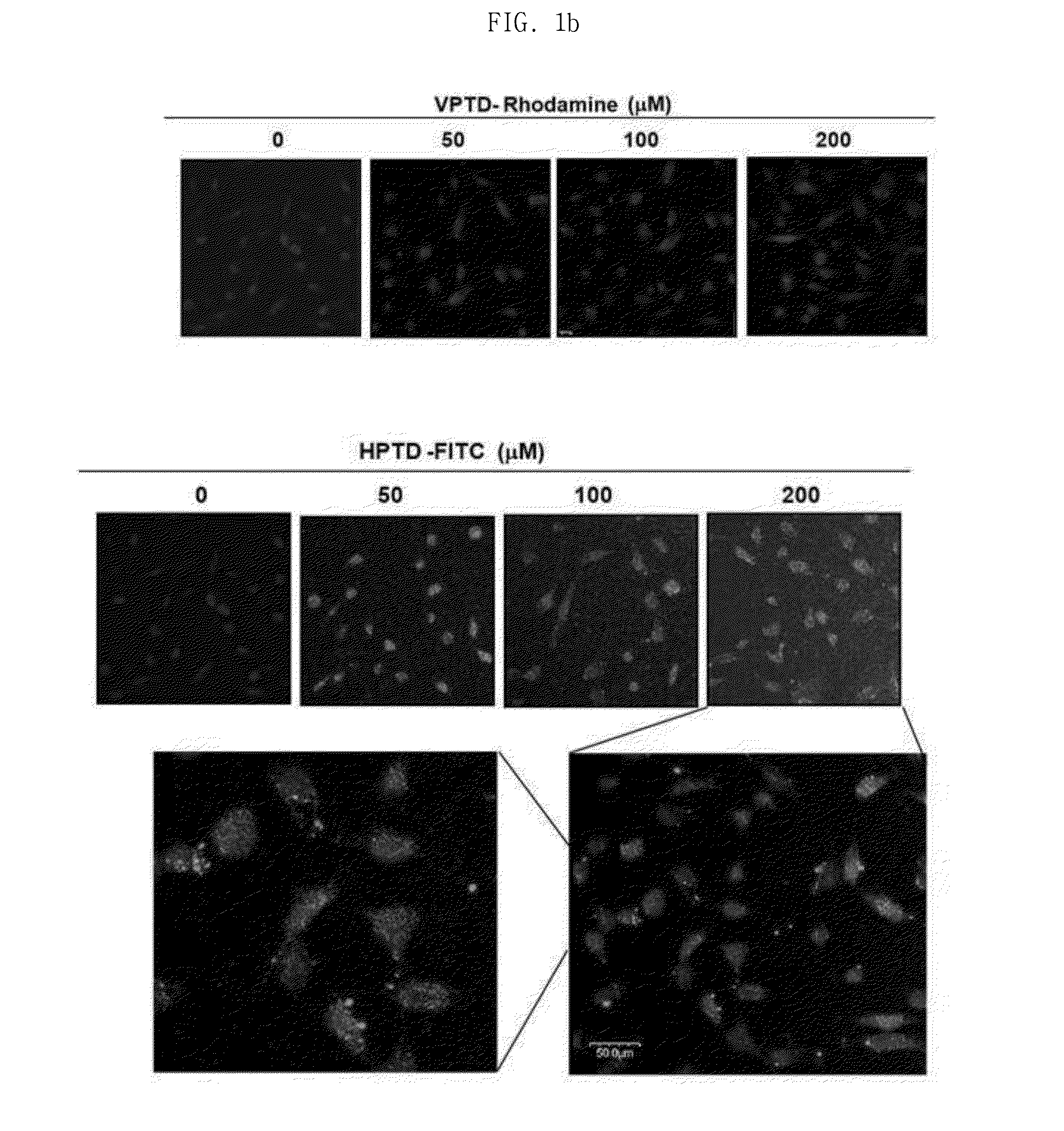
[0043]60 minutes after the inoculation, the fluorescence of the cells was measured by FACS, and the results of the measurement are shown in FIG. 1. As can be seen in FIG. 1(A), the fluorescence of the tumor cells increased in a manner dependent on the concentration of the peptide. FIG. 1(B) shows the results of observing the fluorescence of the tumor cells by a confocal laser scanning microscope in order to examine the tumor cell penetration abilities of the VPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the HPTD peptide of SEQ ID NO: 1. In FIG. 1(B), in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fluorescent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular-weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com