Multimeric antimicrobial peptide complex which is displayed on cell surface
a multi-meric, antimicrobial technology, applied in the direction of peptides, dna/rna fragmentation, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problem that conventional methods for producing antimicrobial peptides cannot provide large amounts of antimicrobial peptides in a cost-effective manner, and the number of usable antibiotics has been limited. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing cost, high antimicrobial activity, and widespread us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Determination of Sequence of Amino Acid Linker that is Digested by Pepsin and Measurement of Antimicrobial Activity of Monomeric Antimicrobial Peptide Comprising the Amino Acid Linker
1-1: Determination of Sequence of Amino Acid Linker that is Digested by Pepsin
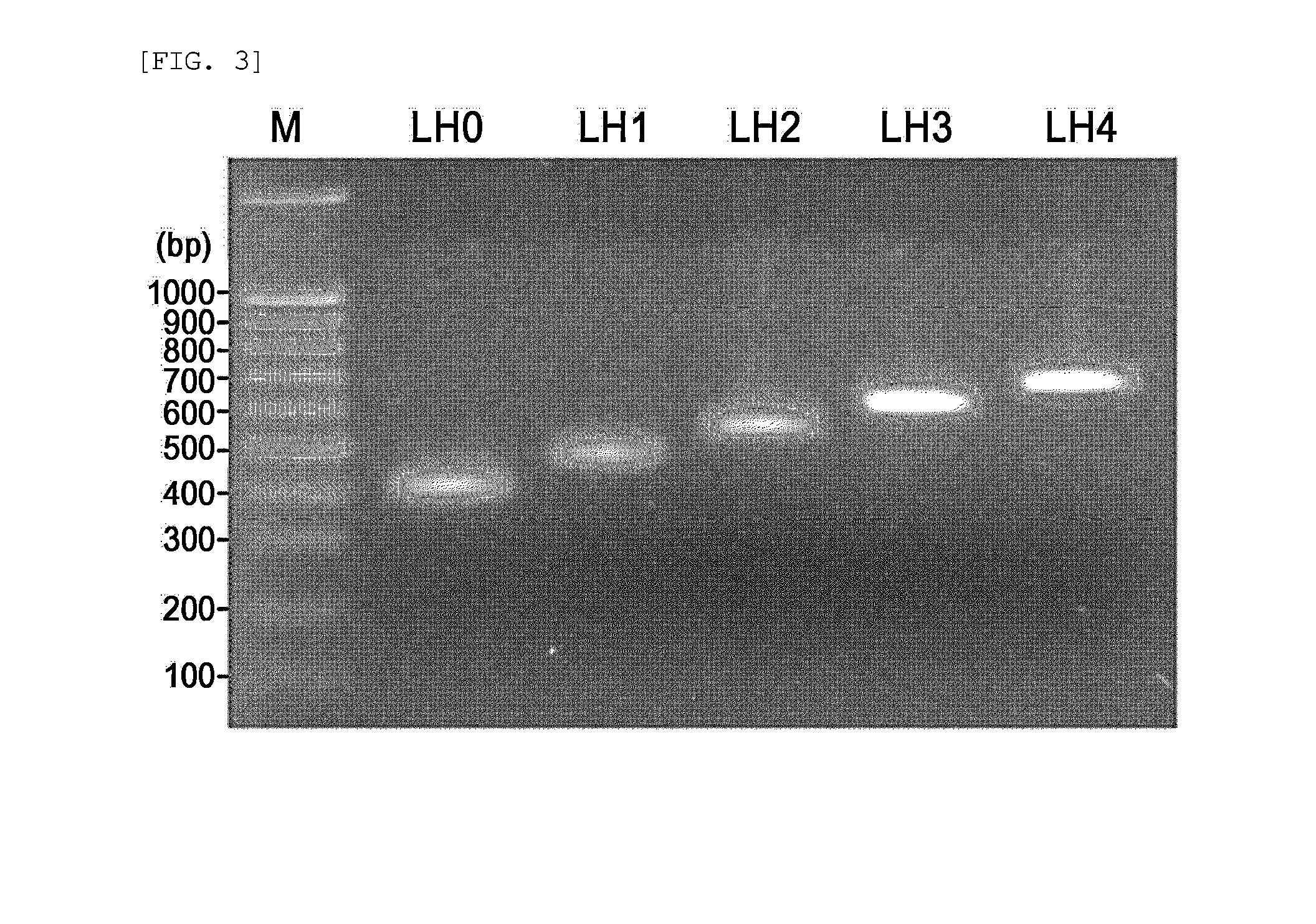
[0080]In order to prepare an antimicrobial peptide polymer which is separated into monomeric units by pepsin, antimicrobial peptide units (SEQ ID NO. 9: RVVRQWPIGRVVRRVVRRVVR) of SEQ ID NO: 1 disclosed in Korean Patent Registration No. 0441402 were linked to each other using any amino acid as a linker, thereby obtaining an antimicrobial peptide polymer. Then, the sequence of the amino acid linker that is digested by pepsin to separate the peptide polymer into monomeric forms was determined using the computer program tool ExPAsy (Expert protein analysis system, Swiss). As a result, a peptide linkage formed between the C-terminus of each of leucine, phenylalanine and tyrosine and the N-terminus of the antimicrobial peptide was d...
example 2
Preparation of Antimicrobial Peptide Polymer which is Digested by Pepsin
[0084]A DNA fragment was constructed, which encodes the monomeric antimicrobial peptide (Hinge2L) comprising the amino acid linker (leucine) that is digested by pepsin added to the C-terminus of the antimicrobial peptide as described in Example 1. The DNA vector was cloned into a vector. Specifically, PCR was performed using primers of SEQ ID NO: 1 (5′-GAAGACCCCGTGTTGTTCG TCAGTGGCCGATTGGTCGTGTCGTTCGCCGTGTTGTTCG-3′) and SEQ ID NO: 2 (5′-GGATGGATCCTAAGCACGCAGACGAACGACGCGACGAACAACACGGCGAACGACACG-3′), thereby obtaining a double-stranded DNA fragment encoding a monomeric antimicrobial peptide (consisting of 22 amino acids) comprising the amino acid linker that is digested by pepsin leucine added to the C-terminus of the antimicrobial peptide of SEQ ID NO: 9. The PCR reaction was performed for 30 cycles, each consisting of DNA denaturation at 94° C. for 30 sec, annealing at 56° C. for 30 sec and DNA synthesis at 72° C...
example 3
Construction and Cloning of DNA Fragment of Antimicrobial Peptide Polymer Linked to Cell Surface Anchoring Motif
3-1: Construction and Cloning of Antimicrobial Peptide Polymer DNA Linked to Lpp-OmpA
[0087]In order for the antimicrobial peptide polymer to be displayed on the host cell surface, a Lpp-OmpA DNA fragment serving as a cell surface anchoring motif was constructed, which has the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 7 comprising a portion of an E. coli outer membrane protein A (OmpA) attached to the leader sequence of E. coli lipoprotein and to the cell outer membrane. The Lpp-OmpA DNA fragment was cloned into a vector.
[0088]Specifically, in order to construct the Lpp-OmpA DNA fragment, primers of SEQ ID NO: 3 (5′-CGCCATATGAAAGCTACTAAACTGG TACTGGGCAACAACAATGGCCCGACC-3′), SEQ ID NO: 4 (5′-GCAAACACCGGAGAAAC GCCGGTG-3′), SEQ ID NO: 5 (5′-TTCTCCGGTGTTTGCTGGCGGTGTTG-3′) and SEQ ID NO: 6 (5′-CGGGATCCTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGAACACGCAGTCT TCCACGGGTAG-3′) were synthesized, recombinant PCR was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Antimicrobial properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com