Plants Having Enhanced Yield-Related Traits and a Method for Making the Same
a technology of yield-related traits and plants, which is applied in the field of plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same, can solve the problems of abnormal flowers, reduced flowering time, delayed flowering, etc., and achieves the effect of increasing yield and enhancing yield-related traits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of Sequences Related to the Nucleic Acid Sequence Used in the Methods of the Invention
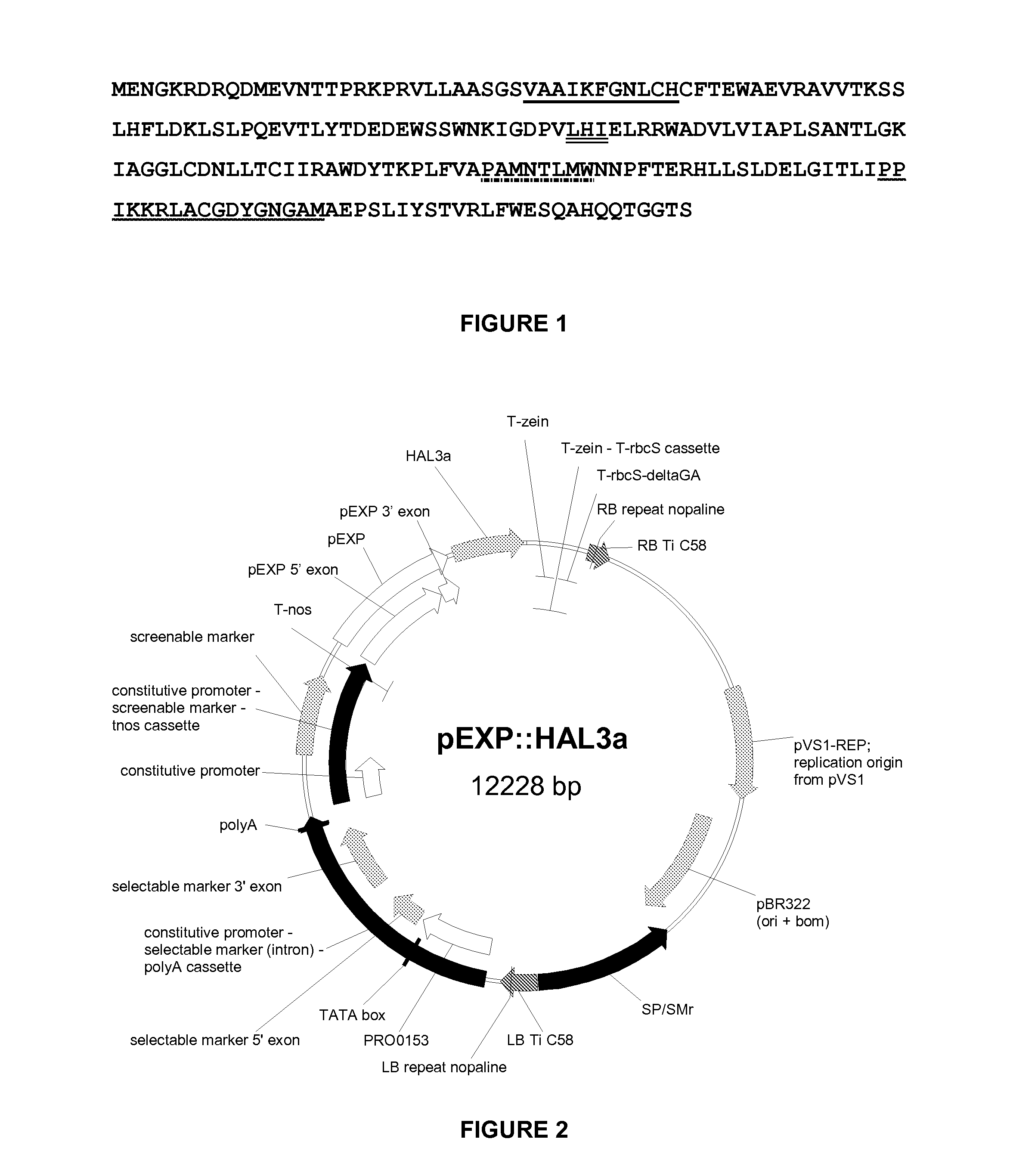
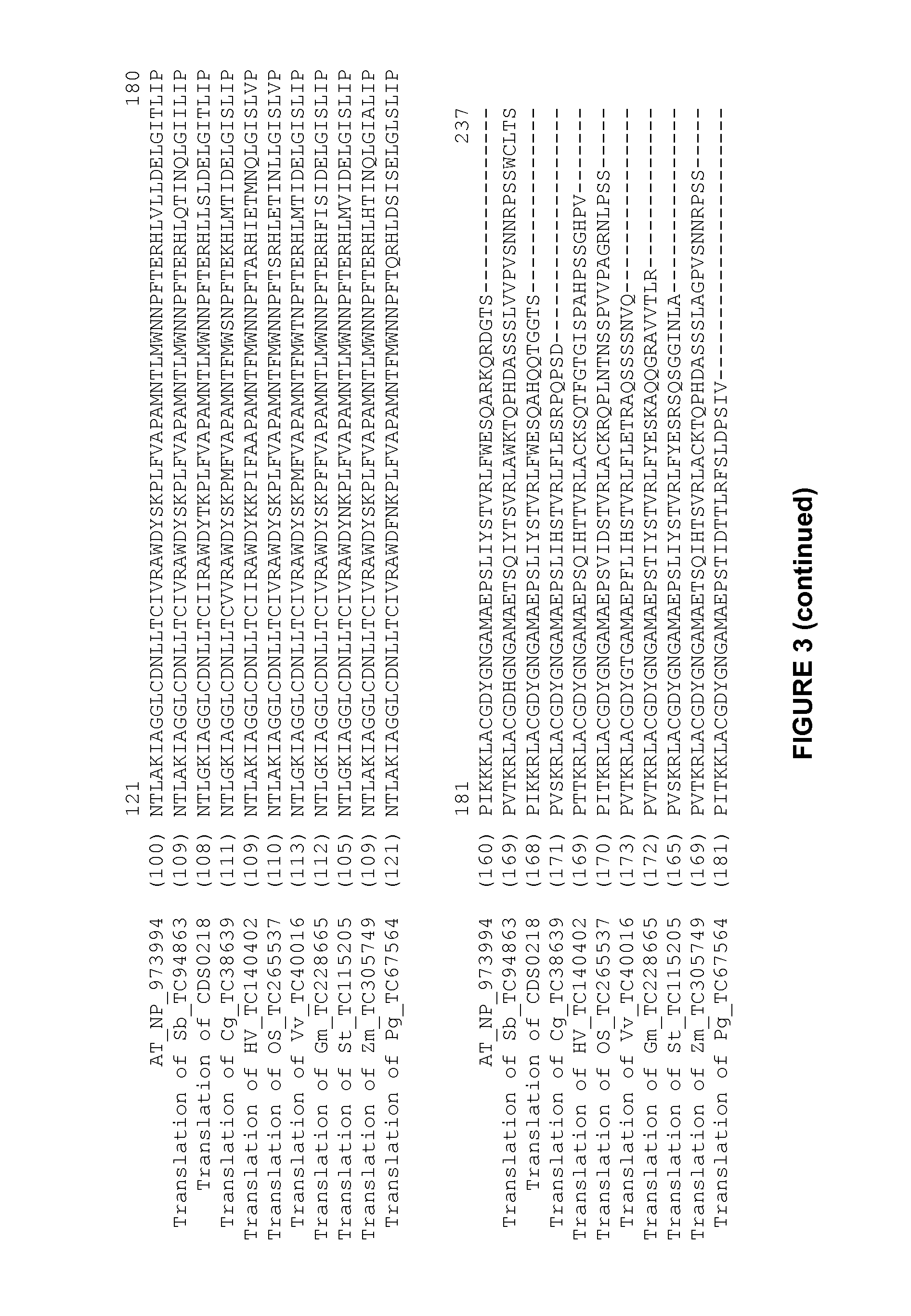
[0724]Sequences (full length cDNA, ESTs or genomic) related to the nucleic acid sequence used in the methods of the present invention were identified amongst those maintained in the Entrez Nucleotides database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) using database sequence search tools, such as the Basic Local Alignment Tool (BLAST) (Altschul et al. (1990) J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410; and Altschul et al. (1997) Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389-3402). The program is used to find regions of local similarity between sequences by comparing nucleic acid or polypeptide sequences to sequence databases and by calculating the statistical significance of matches. For example, the polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid of the present invention was used for the TBLASTN algorithm, with default settings and the filter to ignore low complexity sequences set off. The output of the analy...
example 2
Cloning of the Nucleic Acid Sequence Used in the Methods of the Invention
[0727]The nucleic acid sequence used in the methods of the invention was amplified by PCR using as template a custom-made Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings cDNA library (in pCMV Sport 6.0; Invitrogen, Paisley, UK). PCR was performed using Hifi Taq DNA polymerase in standard conditions, using 200 ng of template in a 50 μl PCR mix. The primers used were prm00957 (SEQ ID NO: 3; sense, start codon in bold:
5′ aaaaagcaggctcacaatggagaatgggaaaagagac 3′)
and prm00958 (SEQ ID NO: 4; reverse, complementary,:
5′ agaaagctgggttggttttaactagttccaccg 3′),
which include the AttB sites for Gateway recombination. The amplified PCR fragment was purified also using standard methods. The first step of the Gateway procedure, the BP reaction, was then performed, during which the PCR fragment recombines in vivo with the pDONR201 plasmid to produce, according to the Gateway terminology, an “entry clone”, pHAL3. Plasmid pDONR201 was purchased f...
example 3
Expression Vector Construction
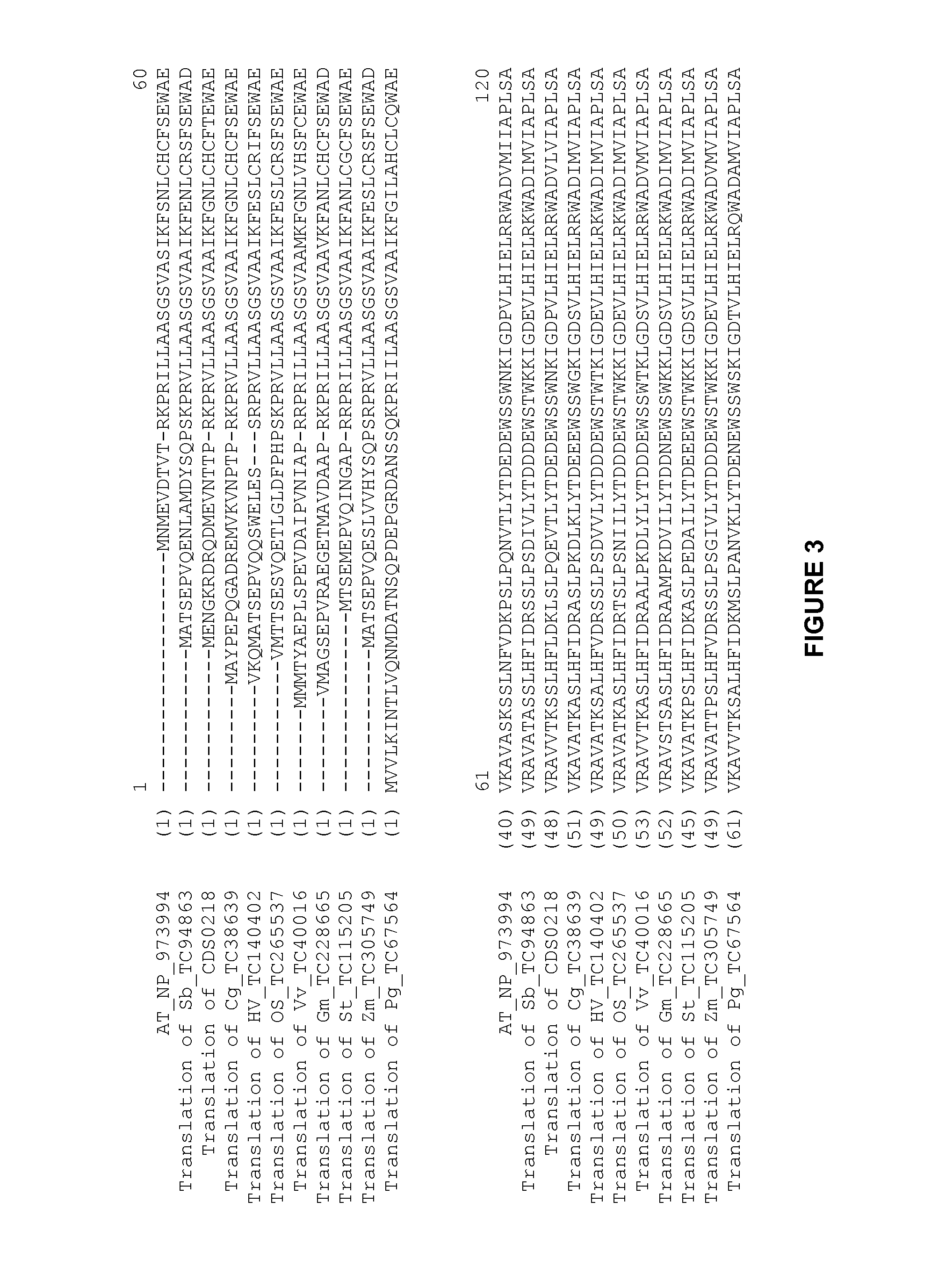
[0728]The entry clone pHAL3 was subsequently used in an LR reaction with pEXP, a destination vector used for Oryza sativa transformation. This vector contains as functional elements within the T-DNA borders: a plant selectable marker; a screenable marker expression cassette; and a Gateway cassette intended for LR in vivo recombination with the nucleic acid sequence of interest already cloned in the entry clone. A rice beta expansin promoter (SEQ ID NO: 5) for shoot-specific expression was located upstream of this Gateway cassette.
[0729]After the LR recombination step, the resulting expression vector pEXP::HAL3 (FIG. 2) was transformed into Agrobacterium strain LBA4044 and subsequently to Oryza sativa plants.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com