Functionalized nanoparticles and methods of use thereof
a technology of functionalized nanoparticles and nanoparticles, which is applied in the field of functionalized nanoparticles, can solve problems such as severe limitations in the therapeutic efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
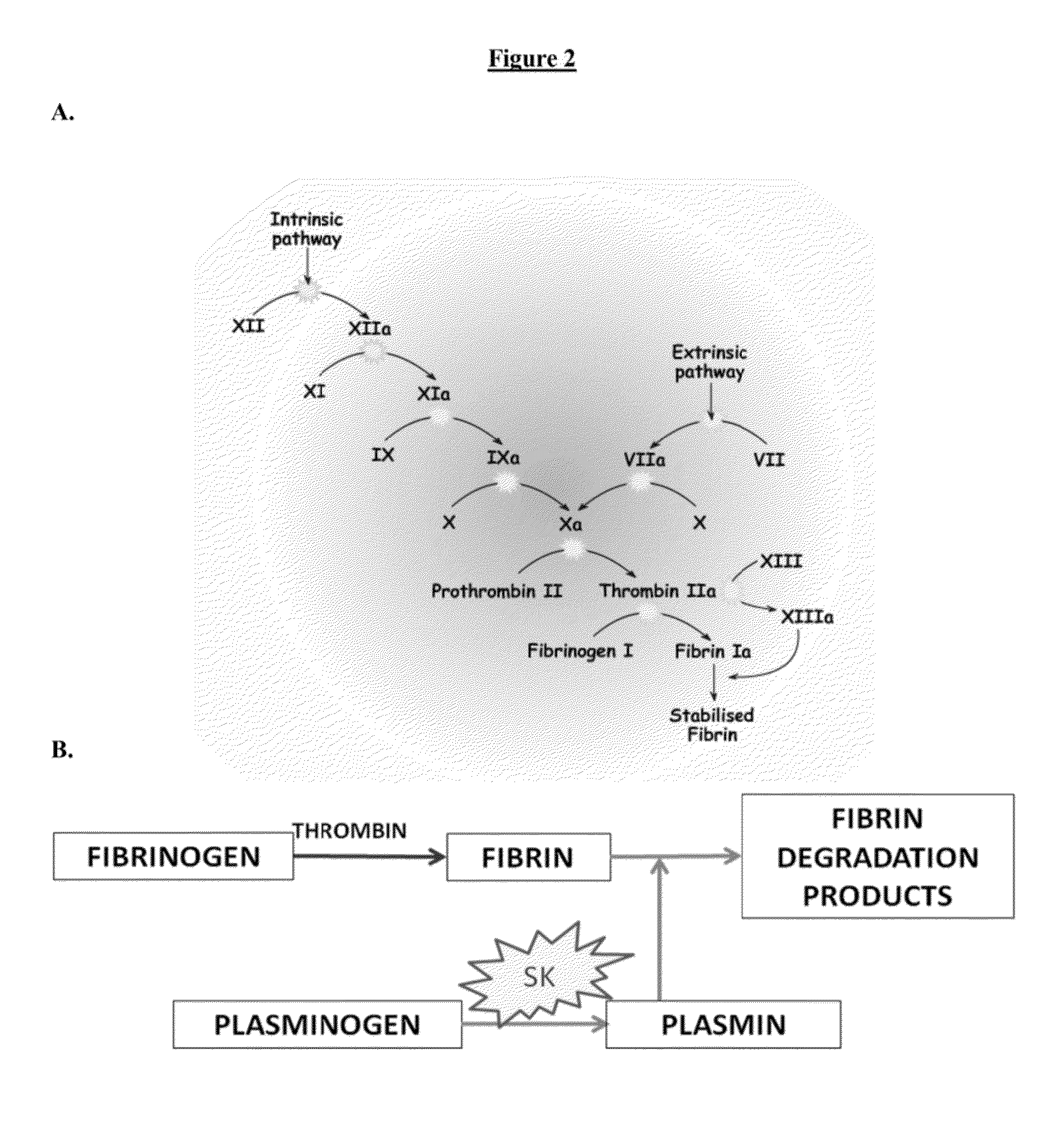
[0106]Inefficient transport of drug delivery systems through tumor extracellular matrix (ECM) severely limits therapeutic efficacy. Tumors are characterized by the presence of a neo-vasculature that is underdeveloped and leaky. This leads to deposition of fibrin, a key ingredient of blood clot, within the tumor matrix (M. Schafer, S. Werner, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9, 628 (2008)). The presence of fibrin is an important cause of elevated interstitial fluid pressure (IFP) in tumors (J. Ma, D. J. Waxman, Mol Cancer Ther 7, 3670 (2008)). Elevated IFP, in turn, results in increased resistance to convective transport of drug carriers in the tumor matrix and decreases the amount of drug reaching tumor cells (L. T. Baxter, R. K. Jain, Microvasc Res 37, 77 (1989)). This is especially true for central regions of the tumor, which are typically under-perfused. This is a critical problem because these poorly-perfused regions (which have low pH and low pO2) harbor the most aggressive and drug-resis...
example 2
[0116]Distribution of nutrients and drugs in most organs is governed by convective flow of blood to the organ and diffusion of the molecule in the organ. In solid tumors, this distribution is dictated by the tumor microenvironment and is highly irregular leading to regions lacking oxygen (hypoxia) and essential nutrients. These regions harbor cells that are most virulent and often responsible for tumor relapse and resistance; adequate drug levels are needed in these regions for complete remission.
[0117]Factors that affect intratumoral distribution include the tumor microenvironment (e.g., vascular architecture, ECM and IFP) and the physicochemical properties of drugs (e.g., size and charge). The rate of tumor cell growth is greater than the rate at which blood capillary cells proliferate. Accordingly, pro-angiogenic factors are not secreted uniformly throughout the tumor, which leads to abnormal vasculature that does not span the complete tumor volume. Additionally, the distribution...
example 3
Methods
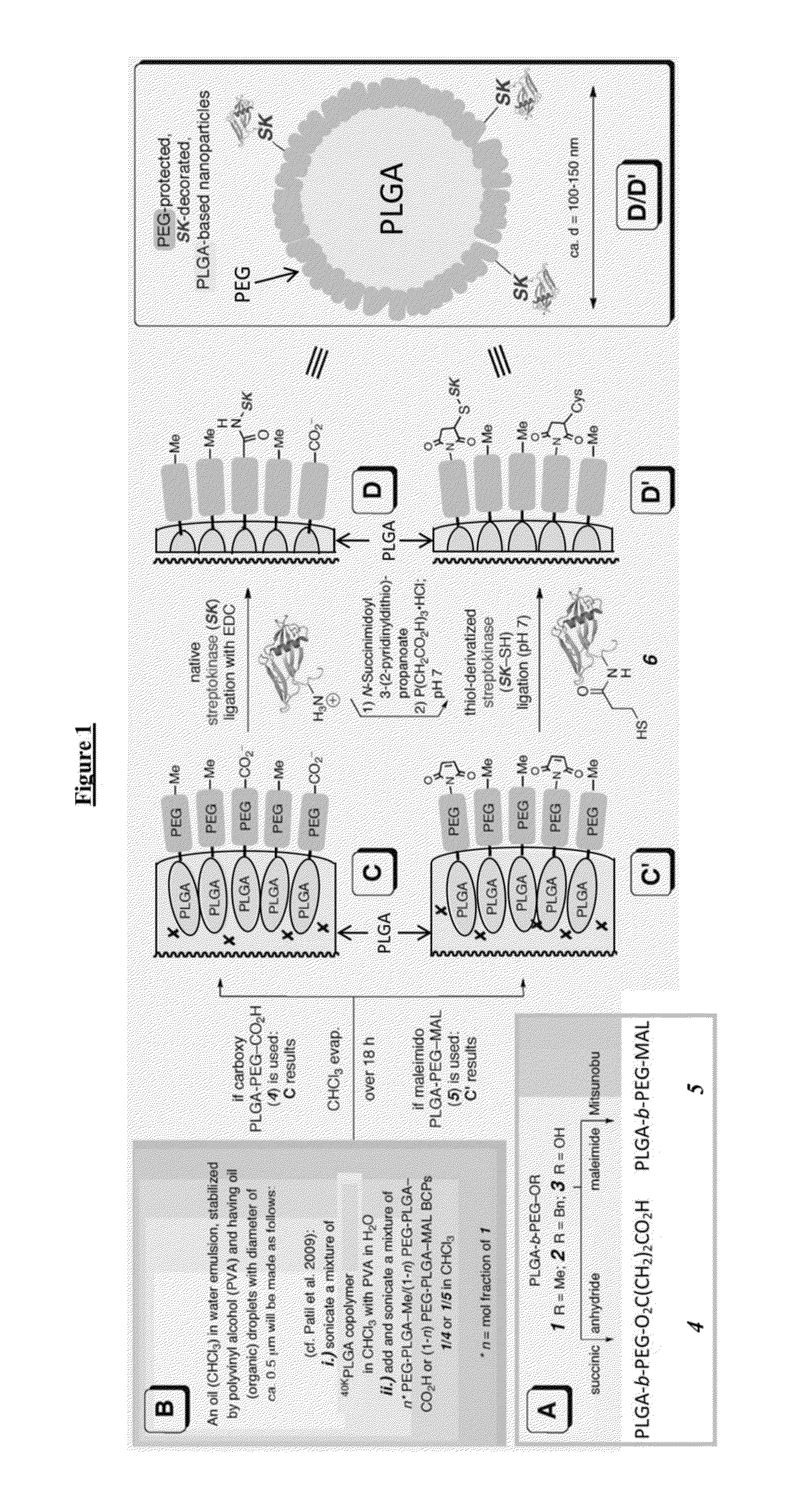
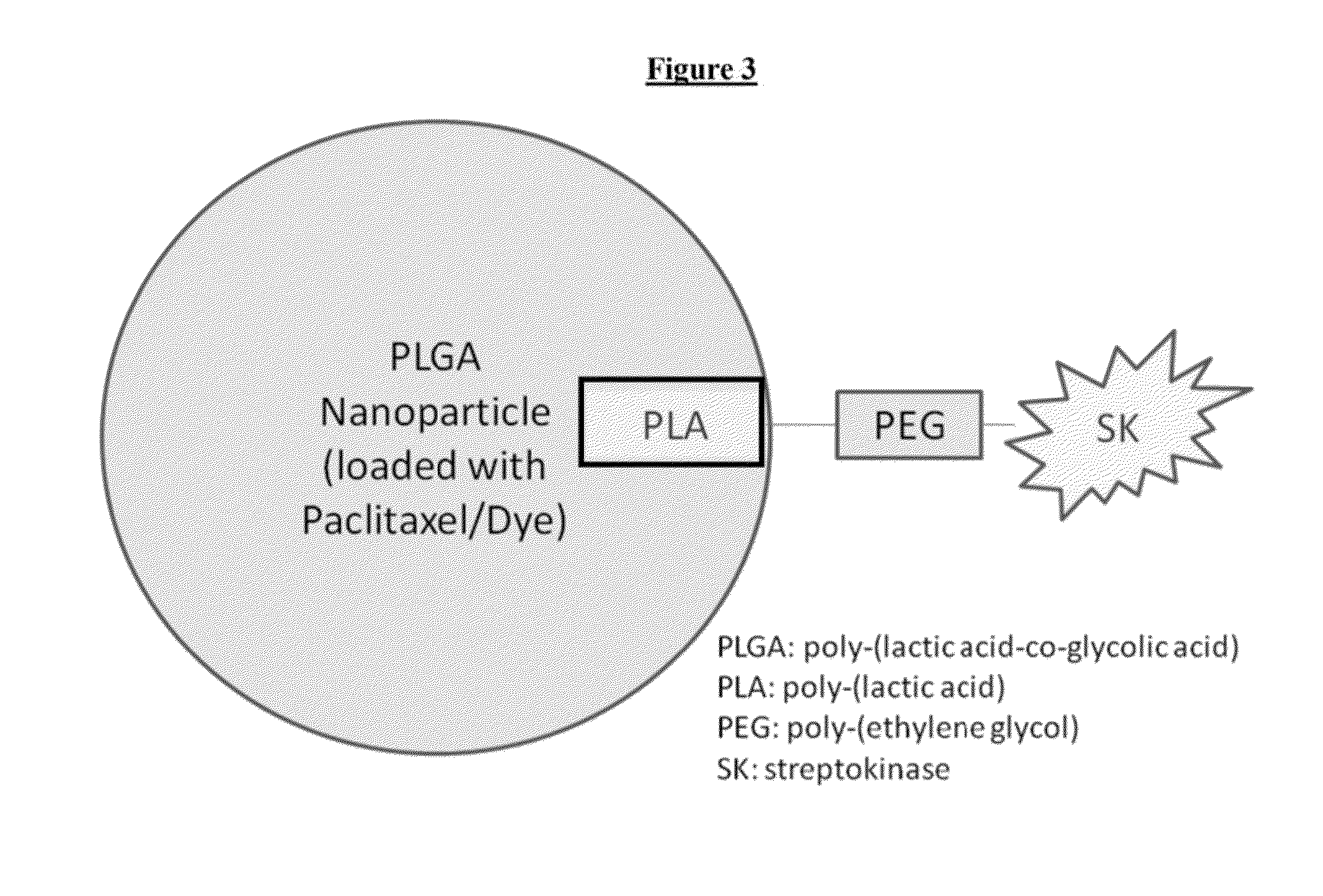
[0139]Synthesis of streptokinase functionalized nanoparticles (SK NP). Poly-(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) (Lactel Absorbable Polymers, USA) nanoparticles loaded with paclitaxel, coumarin-6 or SDB5491 were synthesized by a solvent evaporation technique. These nanoparticles were surface functionalized with a carboxyl terminated 10K-3.4K diblock co-polymer of poly-(lactide) (PLA) and poly-(ethylene glycol) (PEG) (Laysan Bio Inc. USA) and were synthesized as described by Patil, Y. B., et al., Single-step surface functionalization of polymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials, 2009. 30(5): p. 859-66.
[0140]For streptokinase conjugation, the nanoparticles were dispersed in deionized water (20 mg / mL). Catalysts, N-hydroxy sulfo-succinimide (sulfo-NHS) (Sigma Aldrich, USA) and 1-Ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) (Sigma Aldrich, USA) were added to this dispersion. A molar ratio of 10:1:: catalysts: block co-polymer was maintained. Af...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com