Kexin-Derived Vaccines to Prevent or Treat Fungal Infections
a technology of kexin and dna, applied in the field of kexin-derived vaccines to prevent or treat fungal infections, can solve the problems of delayed pcp rather than elimination, drug resistance is emerging, and not all aids patients respond to treatment, so as to improve the effectiveness of kexin dna vaccine, effective pcp vaccination, and greater protection from pc challenge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
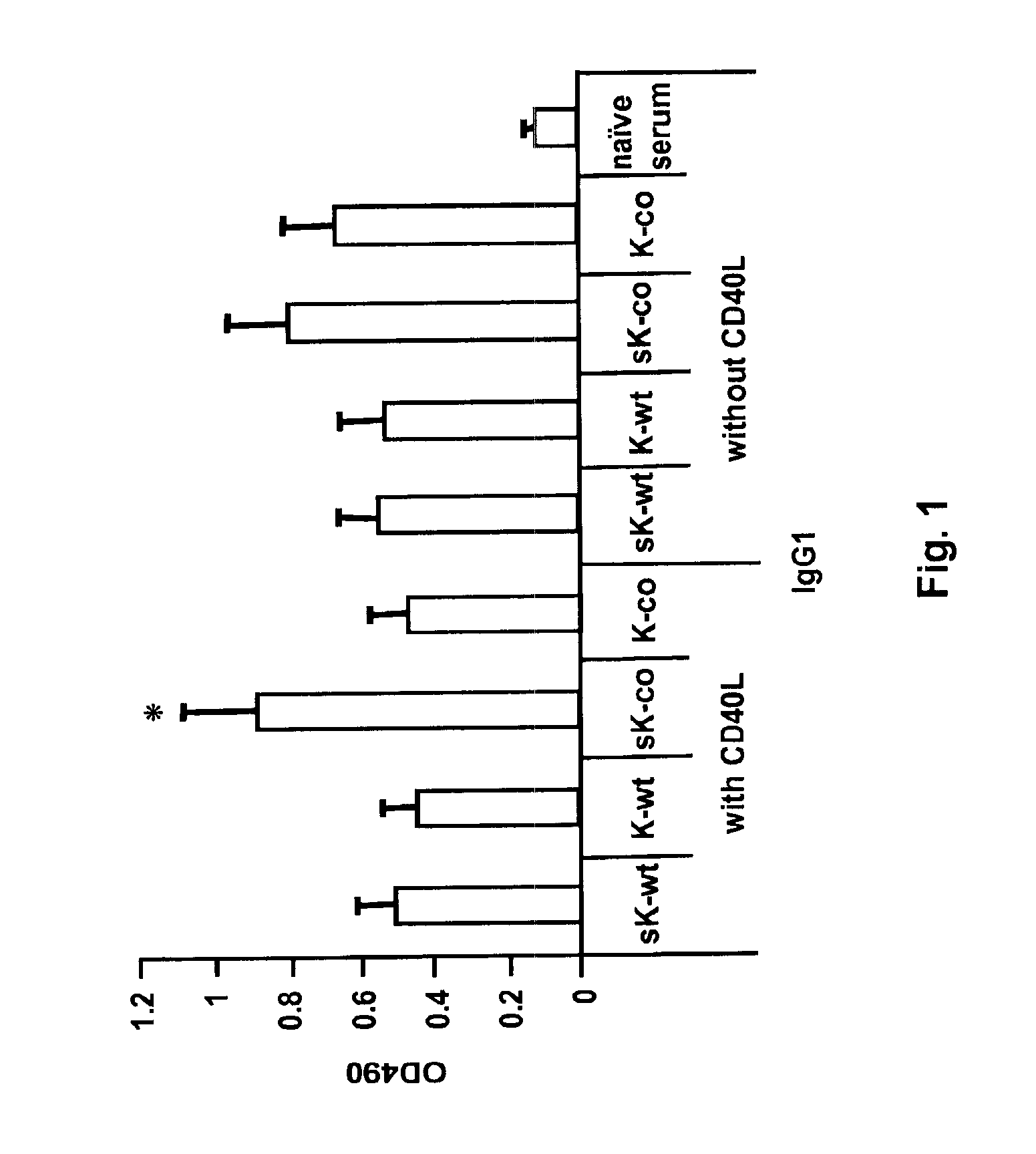
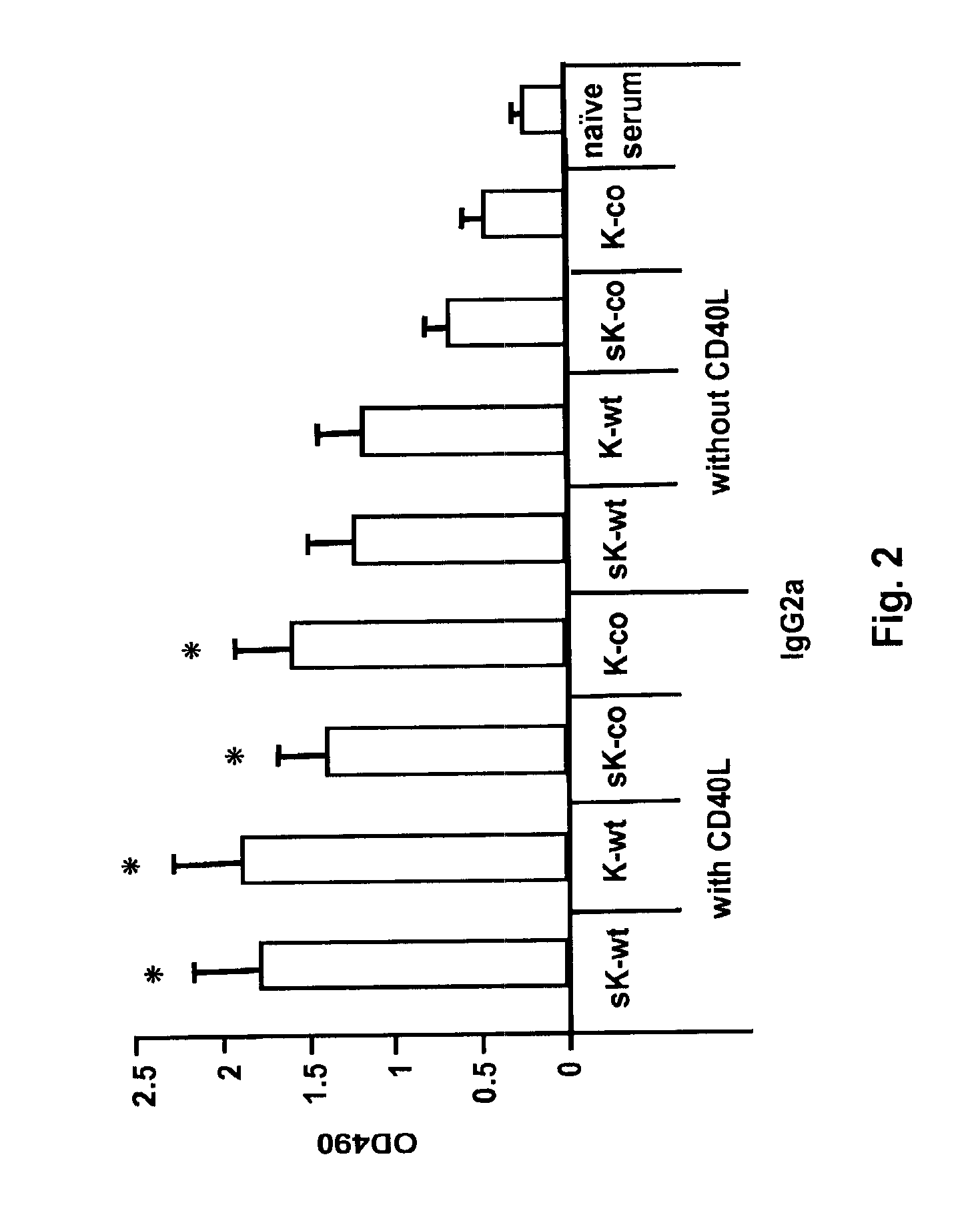
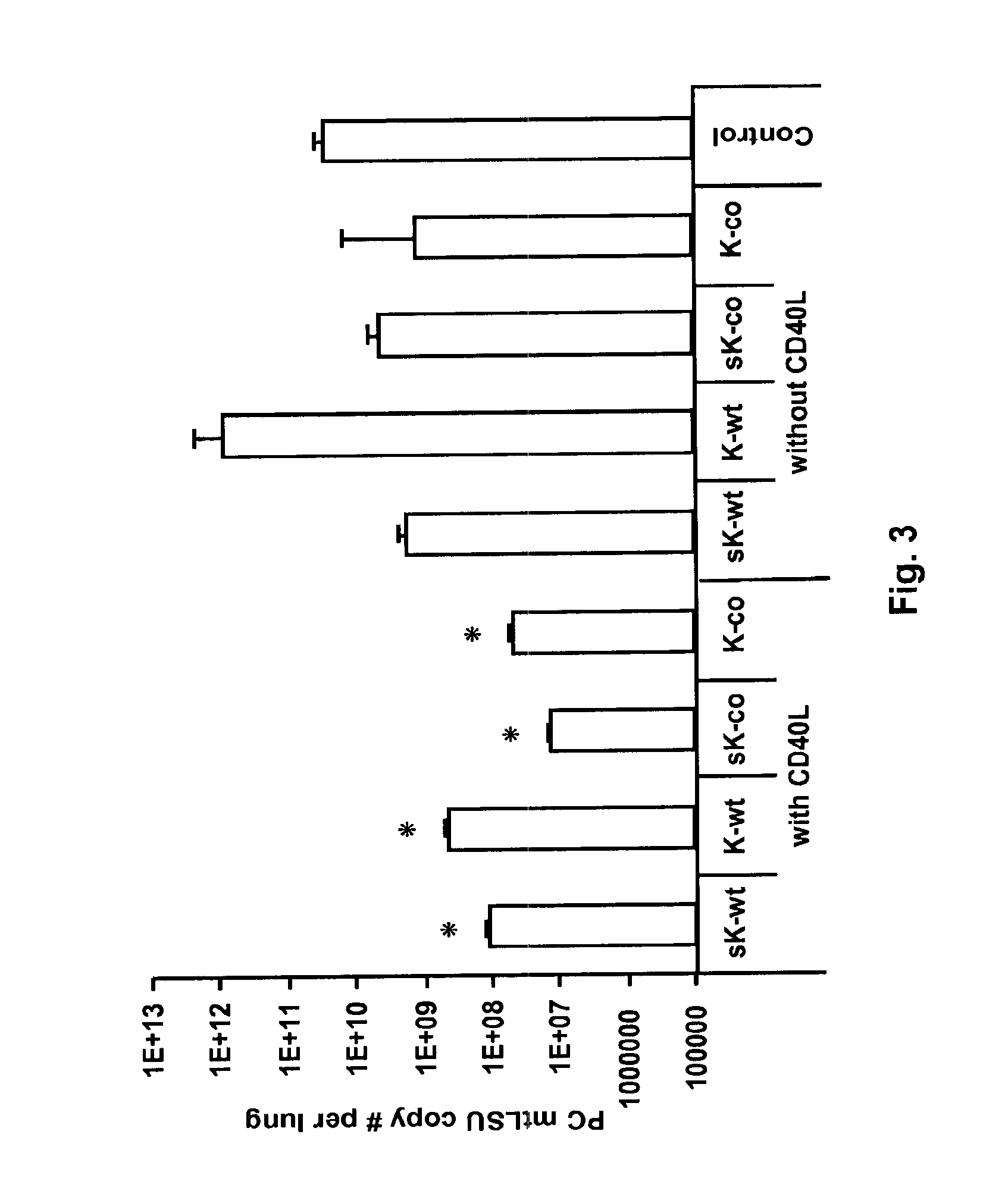
[0093]Co-administration of CD40L with mini-Kexin vaccination induces a CD4IND humoral response and protection against PC in vivo. Four forms of mini-Kexin DNA are used for vaccination: mini-Kexin-wild type (mKexin-WT); mini-Kexin that has been codon optimized for mammalian expression (mKexin-CO); miniKexin that has been engineered to be secreted with an IgGk leader sequence (smKexin); and smKexin that has been codon optimized (smKexin-CO). We compared these wild type and codon-optimized forms of the DNA vaccine. We also compare mucosal boosting with recombinant adenovirus and recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara strain (MVA) vectors. Outcome measures include anti-Kexin and anti-PC isotype-specific antibody responses, as well as anti-Kexin subclass determinations. Serum is tested in functional assays including opsonic phagocytosis, and passive transfer protection into scid mice. We also examine the efficacy of the vaccine against PC challenge performed at several times after vaccinat...
example 2
[0094]Our hypothesized mechanism predicts that endogenous IL-23 is required; and results in durable vaccine responses in both CD4+ T-cell deficient mice and CD40L knockout mice. Specifically we demonstrate the efficacy of CD40L co-transduction in CD40L knockout mice; and the requirement of IL-12 family members (including IL-12p35, IL-12p40, and IL-23), and critical activation molecules that are induced by CD40L-modified DCs to generate effective primary and memory B-cell responses. Preliminary studies have suggested that IL-23 production is critical to generate B-cell memory against PC antigen.
example 3
[0095]CD4IND pathogen-specific immune responses against Pneumocystis kexin are generated in an SIV model of immunodeficiency in macaques. We expect that the mini-kexin constructs will produce vaccine-induced immune responses in SIV-infected, CD4 deficient macaques. Control or SIV infected macaques will undergo DNA priming, followed by mucosal boosting 4 weeks after mock or live SIV infection. Outcome measures will include humoral responses to the vaccine, and the prevention of Pneumocystis colonization as determined by PCR of BAL fluid. Preliminary studies suggest that Pneumocystis colonization occurs in up to 80% of SIV infected macaques, compared to 0% in non-SIV infected monkeys. We will also challenge SIV-infected monkeys with live Pneumocystis, and demonstrate vaccine efficacy in the challenge model.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| real time PCR | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com