Accumulator tank with partition walls
a technology of accumulation tank and partition wall, which is applied in the field of accumulation tank, can solve the problems of reducing the maximum temperature, turbulence in the tank, and destroying stratification, and achieve the effect of efficient accumulation of heat in the tank
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
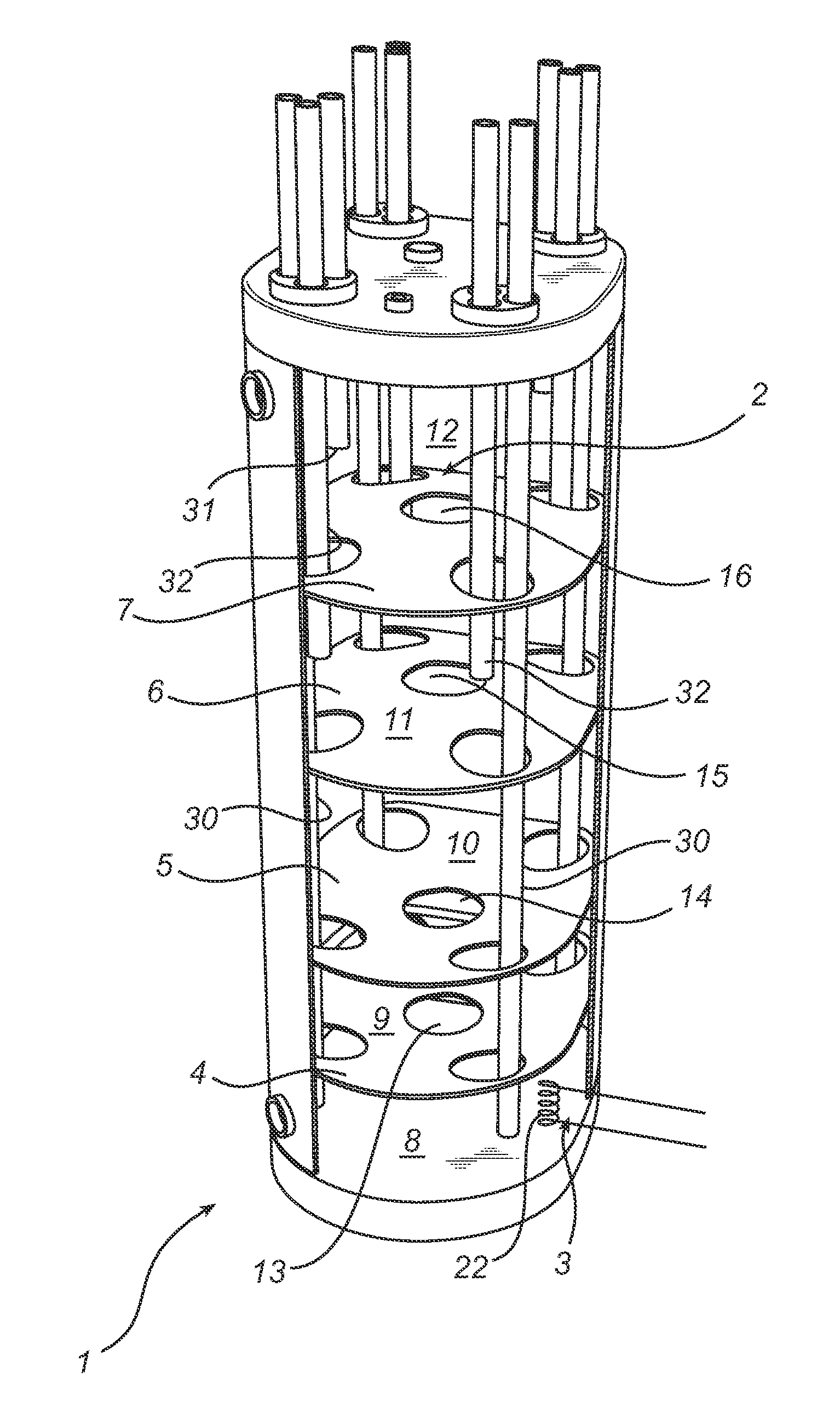
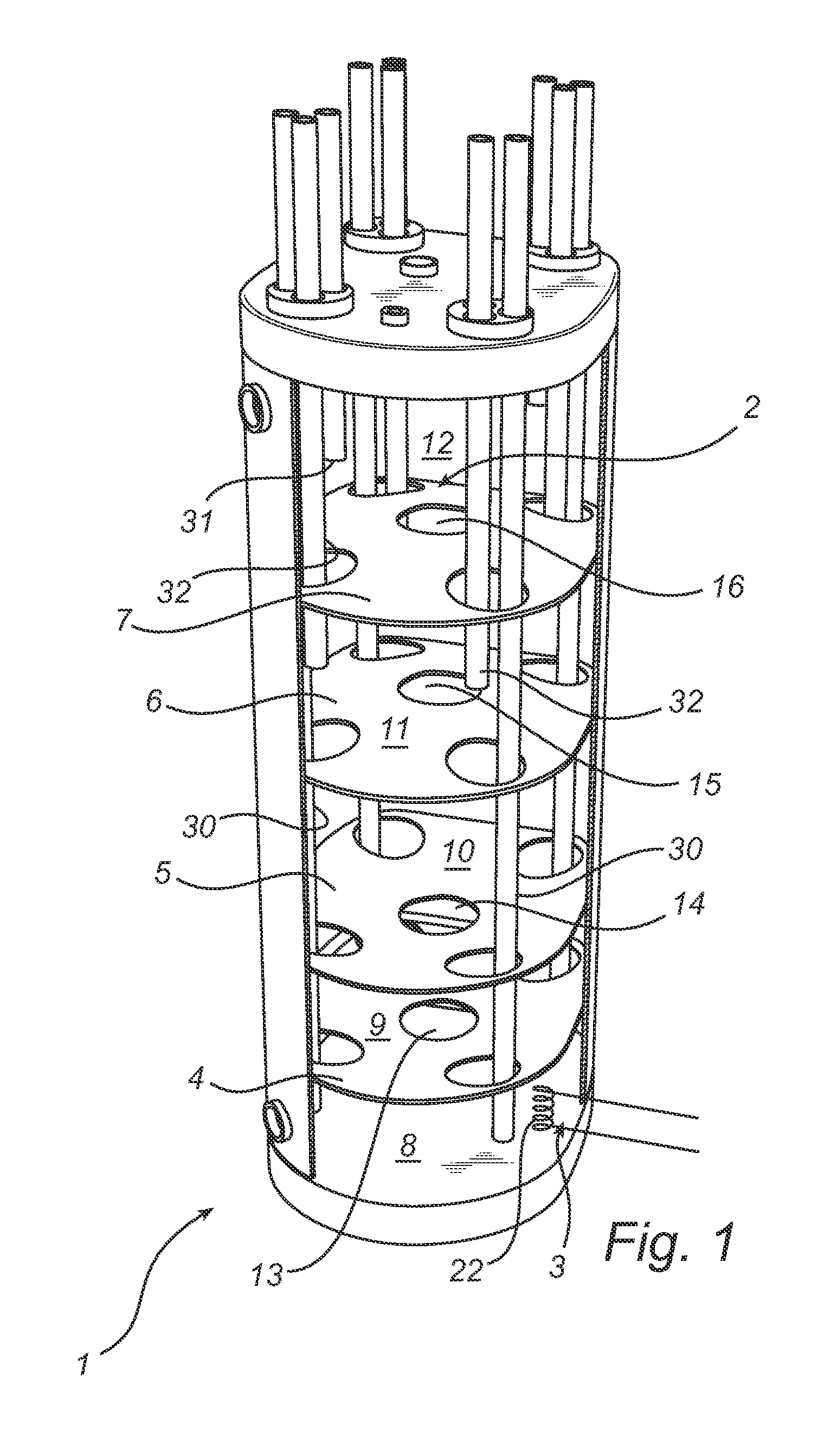
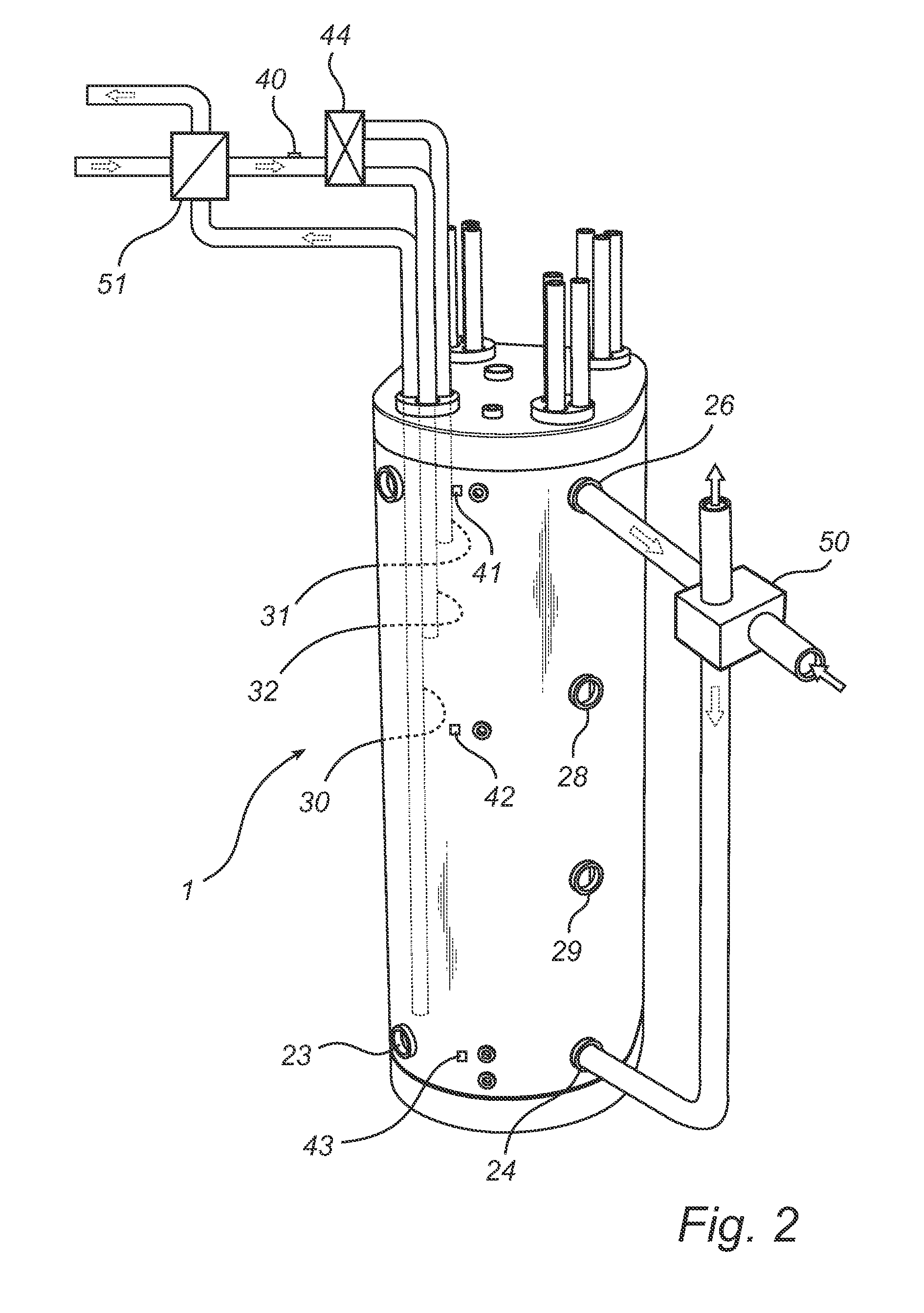
[0026]FIG. 1 shows a preferred embodiment of an accumulator tank 1 according to the present invention. The accumulator tank 1 is upright, shaped like a straight cylinder and has a top section 2 and a bottom section 3 as well as inner partition walls 4, 5, 6, 7 which divide the tank into a plurality of spaces 8, 9, 10, 11, 12. Each partition wall has holes 13, 14, 15, 16 for allowing communication of medium between the spaces 8, 9, 10, 11, 12. There is also provided in each partition wall and in the upper end surface of the accumulator tank 1 holes 17, 18, 19, 20 through which pipes or bundles of pipes 21 are adapted to extend. In the circumferential surface of the accumulator tank 1, two or more connecting means 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 29 are provided for communication with two or more spaces 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 of the accumulator tank 1.
[0027]A connection can be established with each of the spaces 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 according to the embodiment shown in FIG. 1 via the respective penetrating ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com