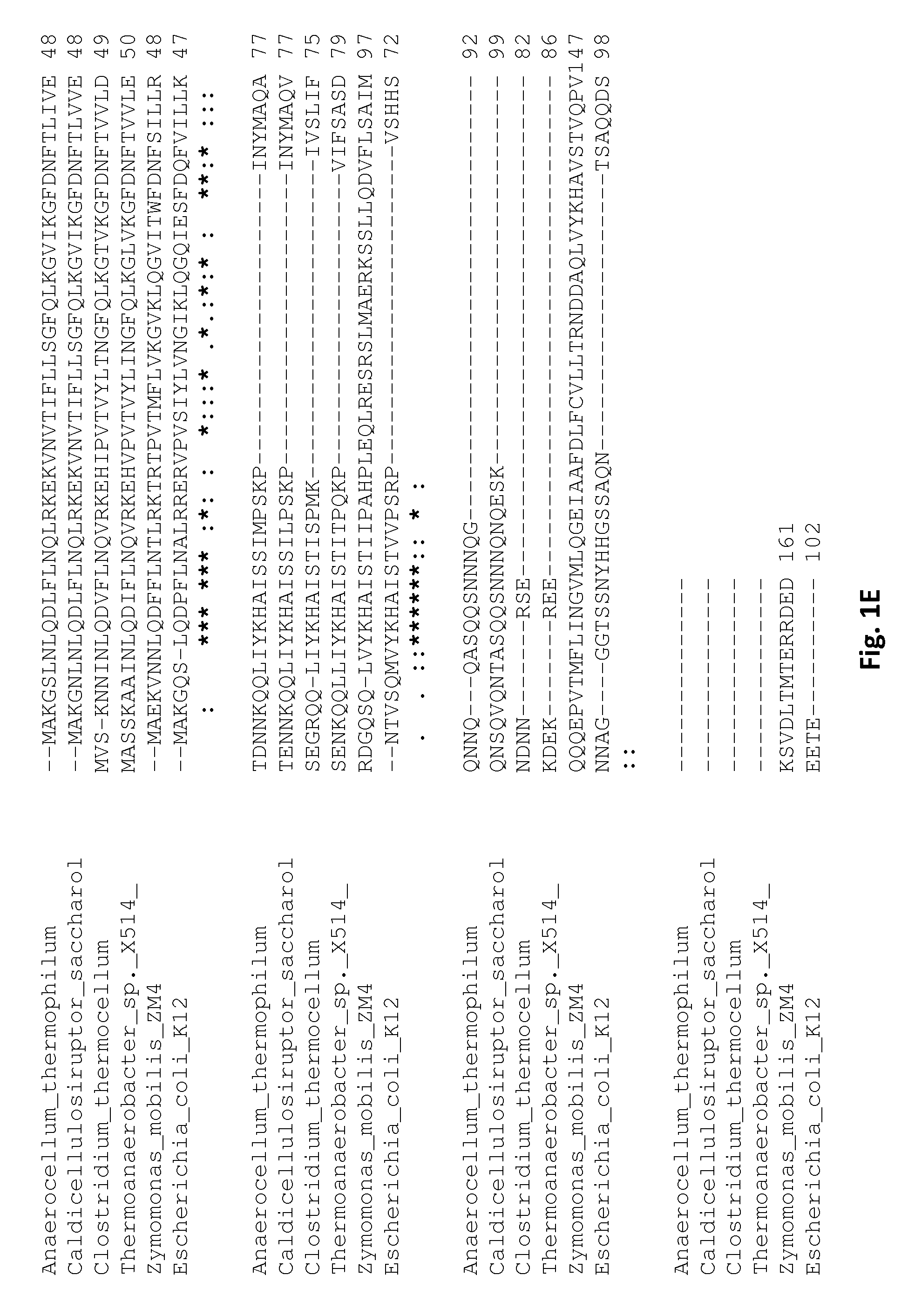
Microorganisms Having Enhanced Tolerance To Inhibitors and Stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0068]This example describes the materials and methods used in the experiments described in the subsequent examples.
Strains and Culture Conditions
[0069]Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 2. E. coli strains were cultured using Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or plates. E. coli WM3064 was supplemented with 100 μg / mL diaminopimelic acid (DAP). Z. mobilis ZM4 was obtained from the
[0070]American Type Culture Collection (ATCC31821) and the Z. mobilis acetate tolerant strain AcR has been described previously (Joachimsthal et al. 2000). ZM4 and AcR were cultured in RM medium at 30° C. S. cerevisiae wild-type, deletion mutant and GST-fusion ORF over-expression strains were obtained through Open Biosystems (Huntsville, Ala.). S. cerevisiae strains were cultured in rich YPD media. CM media with 2% glucose was used for S. cerevisiae wild-type and S. cerevisiae deletion mutants, CM media with 2% glucose minus uracil was used for S. cerevisiae GST-over expressing strai...
example 2
[0077]This example describes the results of the experiments showing that overexpression of the Zymomonas mobilis global regulator gene hfq confers enhanced tolerance to sodium acetate.
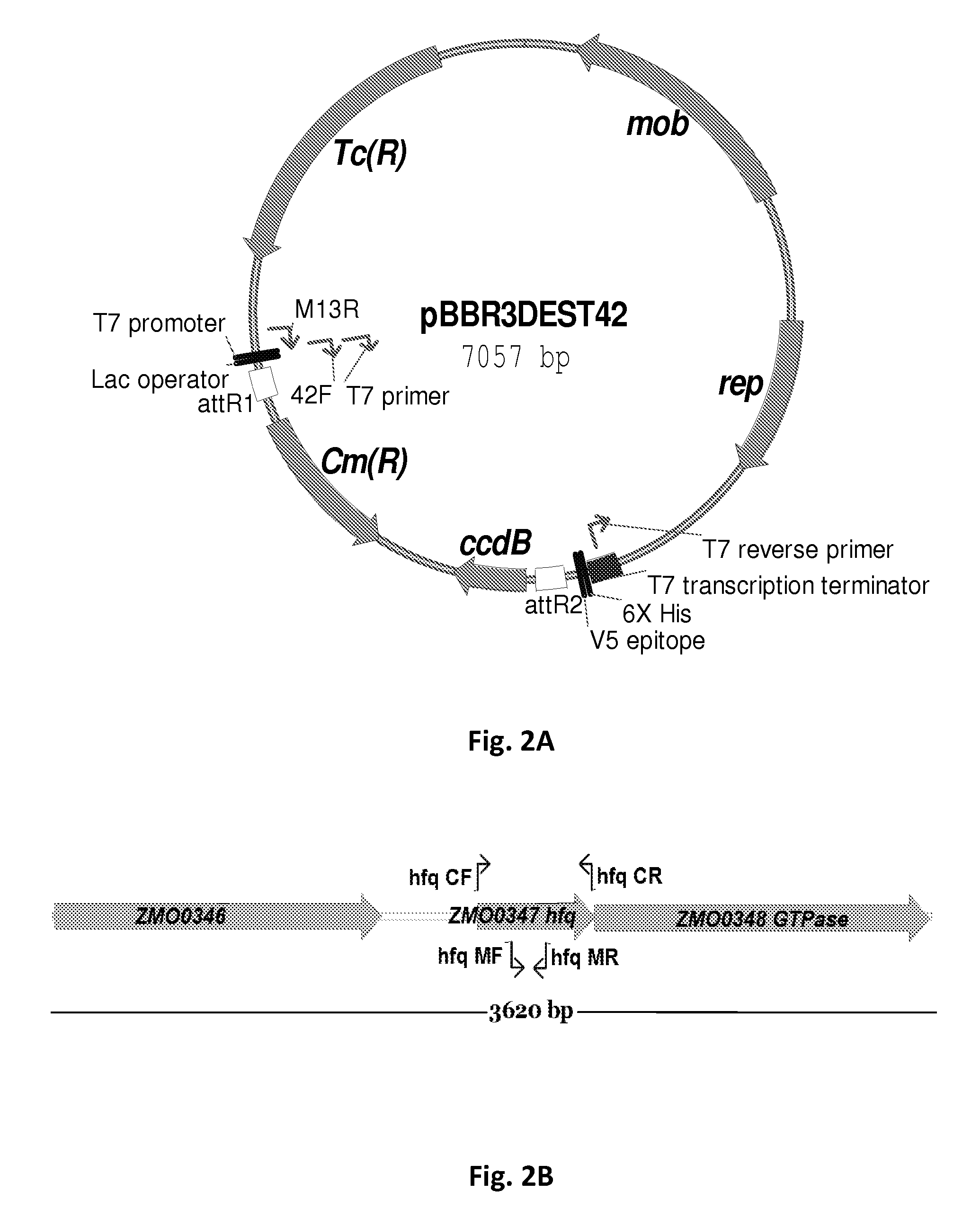
[0078]The Z. mobilis hfq gene (SEQ ID NO: 1) was cloned into the vector pBBR3-DEST42 (FIG. 2A) and the resulting plasmid construct p42-0347 was transformed into the wild-type strain ZM4 and acetate mutant AcR through conjugation. In addition, an insertional mutant of Z. mobilis strain AcR hfq gene (ZMO0347) was created using the pKNOCK system (Brown 2006; Alexeyev 1999) and complemented with plasmid p42-0347. The hfq gene and the primer positions used for mutant construction and hfq gene over-expression are shown in FIG. 2B. An insertional mutant of hfq (ZMO0347) was generated in the AcR background and designated as strain “AcRIM0347”. The hfq gene was over-expressed via plasmid p42-0347 in both wild-type ZM4 and the acetate mutant AcR backgrounds, their susceptibilities to sodium acetate and other str...
example 3
[0080]This example describes the experiments performed to compare the negative effects of pretreatment inhibitors on Z. mobilis growth, and to demonstrate that Hfq overexpression confers tolerance to pretreatment inhibitors.
[0081]Pretreatment Inhibitors had Negative Effects on Z. mobilis Growth
[0082]The growth of Z. mobilis strains was reduced in the presence of acetate, vanillin, furfural, or HMF with increased lag phases and / or slower growth rates and / or final bacterial cell densities depending on the respective condition and strain (Tables 3-4; FIGS. 4A-4E and 5A-5E). Among the different forms of acetate counter-ions tested, sodium acetate had the most significant inhibitory effect on wild-type Z. mobilis growth. This was followed by potassium acetate and ammonium acetate, and sodium chloride had the least negative influence on wild-type Z. mobilis growth (Table 3; FIGS. 4A-4E). Wild-type ZM4 growth was completely inhibited when RM medium was supplemented with 195 mM sodium aceta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com