System and method for reducing flicker noise from CMOS amplifiers
a technology of correlated low frequency noise and amplifier, which is applied in the direction of amplifiers with semiconductor devices only, amplifiers with semiconductor devices, amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of objectionable artifacts in acquired images, noise in the bias circuit to be correlated, and each of these techniques has one or more limitations, so as to reduce correlated low frequency noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
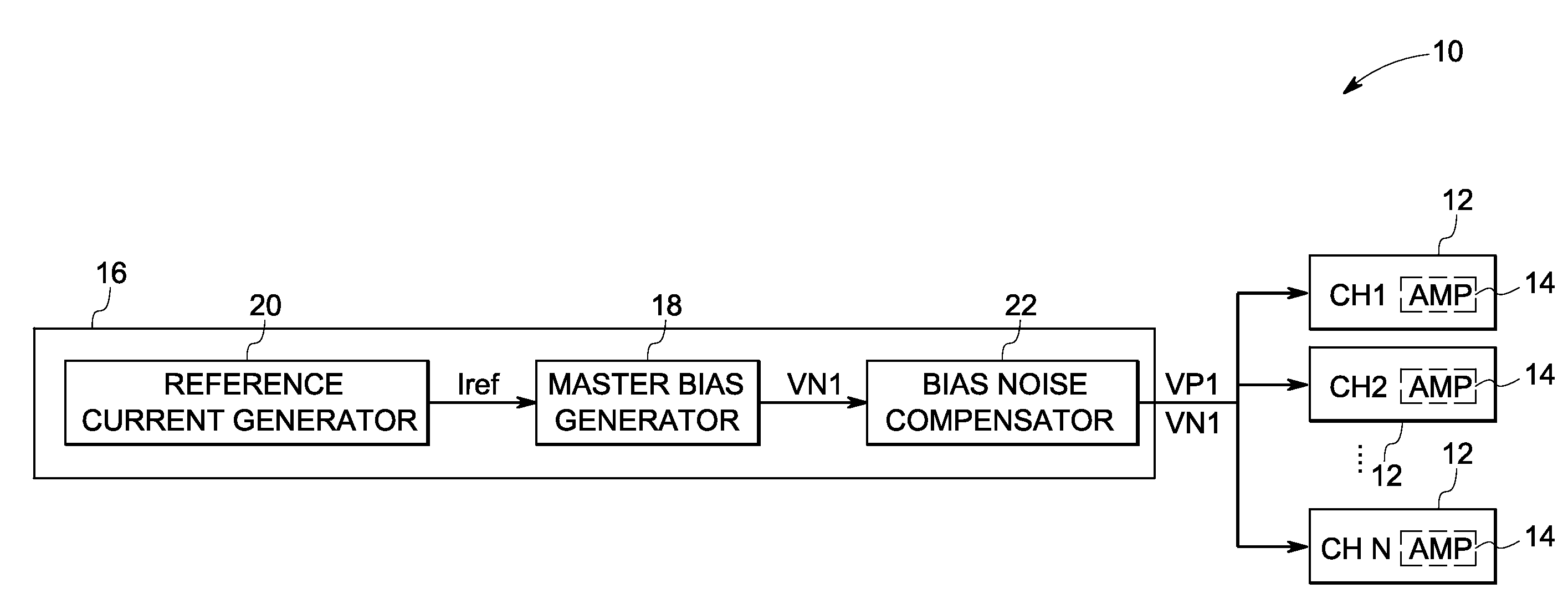
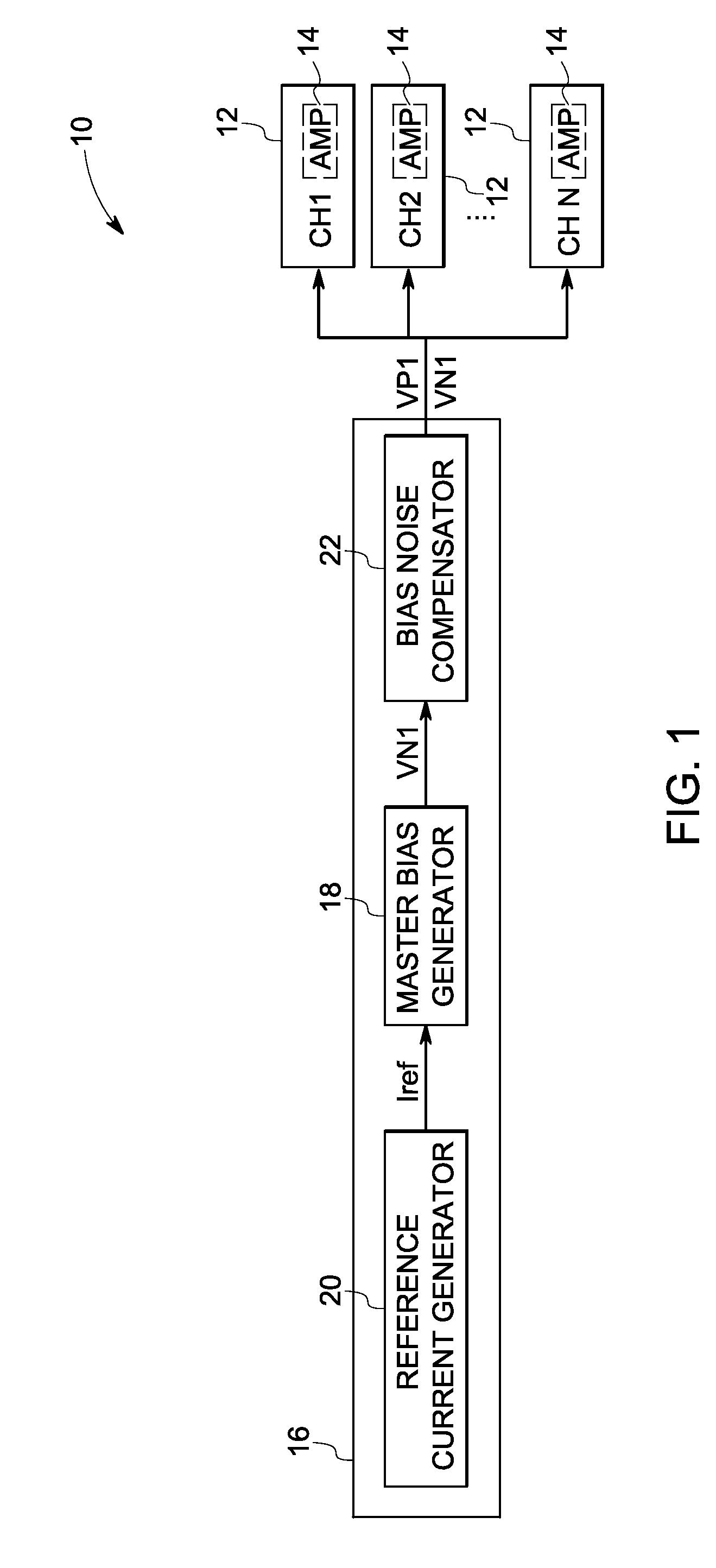
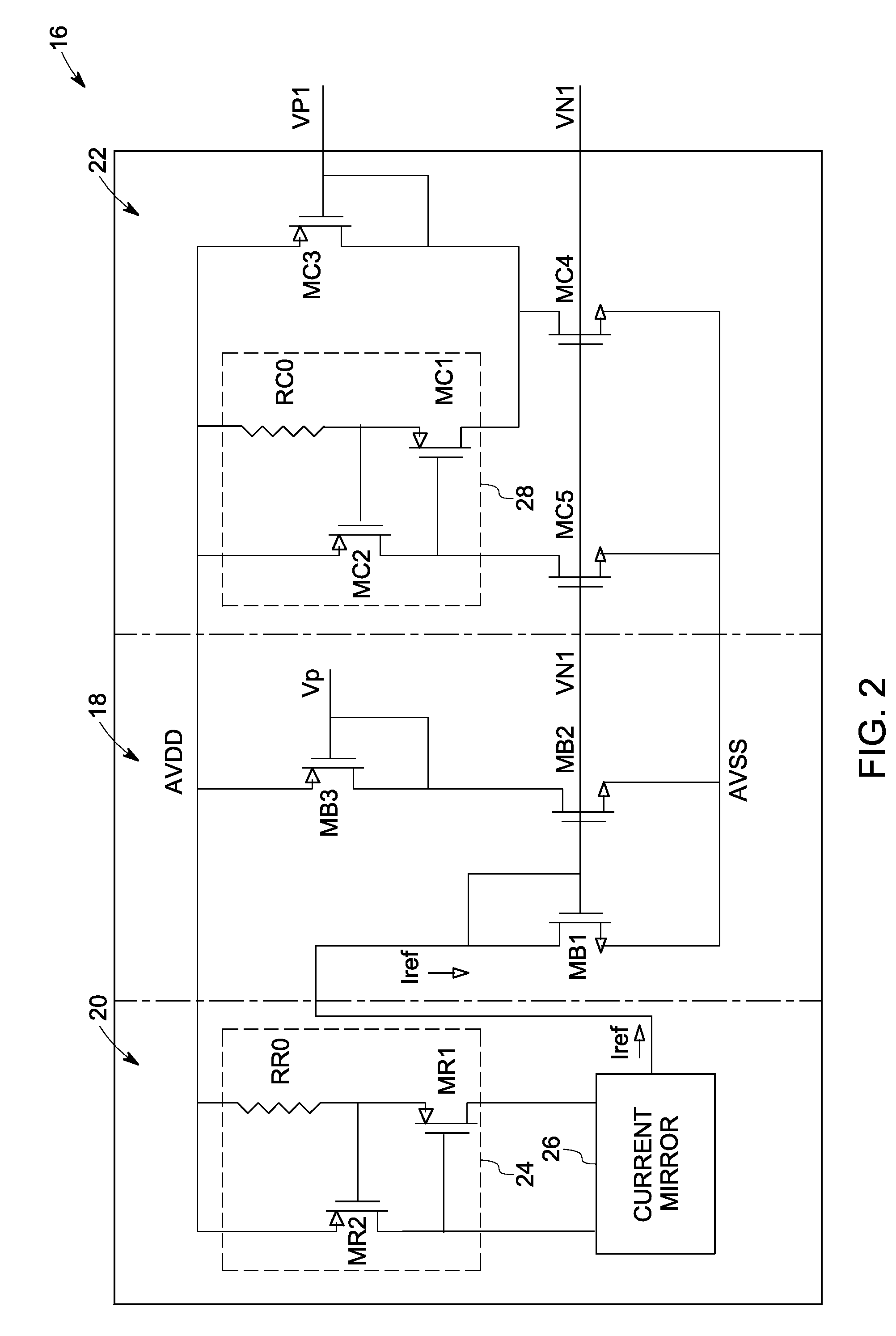
[0014]Embodiments of the present invention are generally directed to correlated low frequency noise reduction techniques in complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) amplifiers. Such embodiments may be used in a variety of semiconductor devices, such as for bipolar junction transistor (BJT) based devices, field effect transistor (FET) based devices, and so forth. Moreover, such embodiments may be used in a variety of applications, such as for data acquisitions, data reception and / or transmission, data conversion, data storage and so forth. Though the present discussion provides examples in a data acquisition context with respect to CMOS amplifiers, the application of these embodiments in other contexts and in other devices is well within the scope of the present invention.
[0015]Referring now to FIG. 1, a schematic of an exemplary data acquisition circuit 10 is illustrated in accordance with aspects of the present technique. The data acquisition circuit 10 includes multiple data...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com